Determination of 11 Major and Minor Elements in Geothermal Water of the Riduo Hotsprings from Tibet by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry
-
摘要:
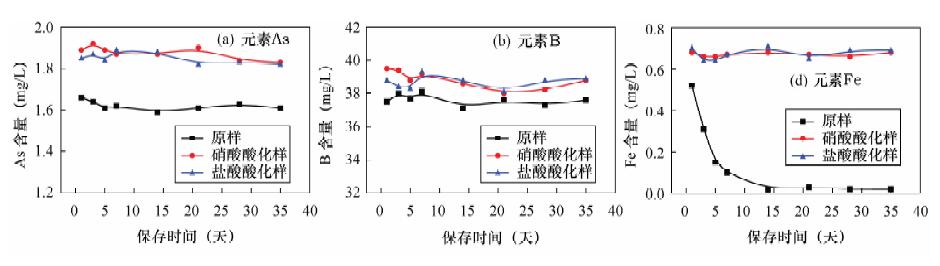
西藏地热水的矿化度普遍较高, 矿物质种类丰富, 本文建立了采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱(ICP-OES)同时测定西藏日多温泉地热水中11种主次量元素(钾钠钙镁硅硼锂锶砷铁和硫酸根)的分析方法。使用双向观测模式可确保不同浓度元素的同时检出, 且地热水采用1%硝酸介质保存, 在5周时间内11种元素含量的测定值基本稳定。方法检出限为0.0006~0.0162 mg/L, 加标回收率为95.5%~105.8%, 精密度(RSD, n=10) 均小于6%, 实际水样的测试结果与传统方法基本吻合。本方法为西藏温泉的水文地球化学研究提供了大量可靠的数据。
Abstract:Geothermal water in Tibet has a high degree of mineralization with abundant mineral substances. Simultaneous determination of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, silicon, boron, lithium, strontium, arsenic, iron and sulfate radical in geothermal water of Riduo Hotspring by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) was developed in this study. Analytical conditions were optimized by application of two-way observation mode to ensure simultaneous determination of the multi-elements in geothermal water. In addition, geothermal water was preserved in 1% nitric acid and the results of 11 elements after five weeks are stable. This method has a detection limit of 0.0006-0.0162 mg/L, recoveries of 95.5%-105.8% by standard addition, and relative standard deviation (RSD, n=10) of less than 6%. The analytical results were in good agreement with those obtained by traditional methods. This method provides a number of reliable data for hydrogeochemical research on geothermal water in Tibet.
-

-
表 1 方法检出限及检测范围
Table 1. Detection limit and measured range of the elements
测定元素 标准系列浓度
(mg/L)相关系数 方法检出限
(mg/L)测定范围
(mg/L)As 0, 1, 5, 50 1.0000 0.0102 0.031~50 B 0, 1, 5, 50 1.0000 0.0057 0.018~50 Ca 0, 5, 50, 100, 500 0.9992 0.0054 0.017~500 Fe 0, 1, 5, 50 0.9999 0.0006 0.002~50 K 0, 5, 50, 100, 500 0.9994 0.0252 0.076~500 Li 0, 1, 5, 50 0.9999 0.0012 0.004~50 Mg 0, 5, 50, 100, 500 0.9996 0.0162 0.049~500 Na 0, 5, 50, 100, 500 0.9995 0.0162 0.049~500 S(SO42-) 0, 50, 200, 500 0.9999 0.078 0.24~500 Si(SiO2) 0, 10, 20, 100 0.9998 0.0036 0.011~100 Sr 0, 1, 5, 50 0.9999 0.0012 0.0036~50 表 2 方法加标回收率和精密度
Table 2. Recovery and precision tests of the method
元素 原样 回收率
(%)硝酸酸化样 回收率
(%)测定低值
(mg/L)测定高值
(mg/L)测定平均值
(mg/L)RSD
(%)加标前量
(μg)加标量
(μg)加标后量
(μg)加标前量
(μg)加标量
(μg)加标后量
(μg)As 33.4 20 52.1 93.5 37.4 20 56.5 95.5 1.80 1.92 1.86 2.0 B 744 100 851 107.0 764 100 864 100.0 35.2 40.6 38.2 4.5 Ca 1516 2000 3452 96.8 1496 2000 3612 105.8 69.3 77.0 73.9 3.4 Fe - - - - 13.2 20 34.3 105.5 0.59 0.71 0.66 5.4 K 552 200 744 96.0 544 200 736 96.0 25.7 29.1 26.9 3.5 Li 45.6 20 67.2 108.0 44.8 20 65.8 105.0 2.14 2.35 2.24 3.0 Mg 77 200 287 105.0 75.6 200 285 104.8 3.59 4.03 3.73 5.4 Na 6600 2000 8546 97.3 6540 2000 8502 98.1 307.5 348 324 4.2 S(SO42-) 5320 4000 9339 100.5 5460 4000 9421 99.0 260.4 281 272 2.7 Si(SiO2) 1570 800 2422 106.5 1572 800 2410 104.8 73.6 79.7 77.5 2.7 Sr 44.2 20 63.6 97.0 43.6 20 63.7 100.5 2.05 2.29 2.16 3.3 表 3 ICP-OES与传统方法测定结果比较
Table 3. A comparison of analytical results with ICP-OES and traditional methods
测定方法 元素含量(mg/L) As B Ca Fe K Li Mg Na S(SO42-) Si(SiO2) Sr 本方法 1.87 37.3 74.8 0.65 26.8 2.21 3.89 348 269 79.5 2.22 传统方法 1.83 36.8 72.0 0.61 25.9 2.33 3.84 367 284 83.4 2.35 注:B、Ca、Mg、SO42-、SiO2对比测定采用原样,其他元素测定采用硝酸酸化样。 表 4 西藏部分温泉水中硫含量分布
Table 4. Sulfur distribution in some geothermal springs of Tibet
温泉名称 所属地区 水化学类型 硫酸根(SO42-)
含量(mg/L)硫化物(S2-)
含量(mg/L)测定误差
(%)羊八井温泉 拉萨地区 Na-HCO3-Cl 70 0.48 1.9 日多温泉 拉萨地区 Na-SO4-Cl-HCO3 279 0.57 0.6 德仲温泉 拉萨地区 Ca-Na-HCO3 48.5 0.21 1.2 邱桑温泉 拉萨地区 Na-Ca-HCO3 12.6 < 0.02 0 色温泉 山南地区 Na-HCO3 33.6 0.06 0.5 拉普温泉 山南地区 Na-Cl-HCO3 40.4 0.72 5.0 邛多江温泉 山南地区 Na-HCO3 10.6 0.18 4.8 曲普温泉 阿里地区 Na-HCO3 87.8 4.18 13.4 塔格架温泉 日喀则地区 Na-HCO3 79.1 0.84 3.0 康布温泉 日喀则地区 Na-Cl-HCO3 19.3 < 0.02 0 曲卓木温泉 日喀则地区 Na-Ca-HCO3-Cl-SO4 333 < 0.02 0 曲孜卡温泉 昌都地区 Na-HCO3 44.9 0.03 0.2 注:本表中数据来源于国土资源部公益性基金项目——西藏典型地热田地热水资源科学利用研究(201211035)。 -
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] -



 下载:
下载: