Determination of Multi-components in Marine Sediments by Core Scanner Based on BP Neural Network of Genetic Algorithm
-
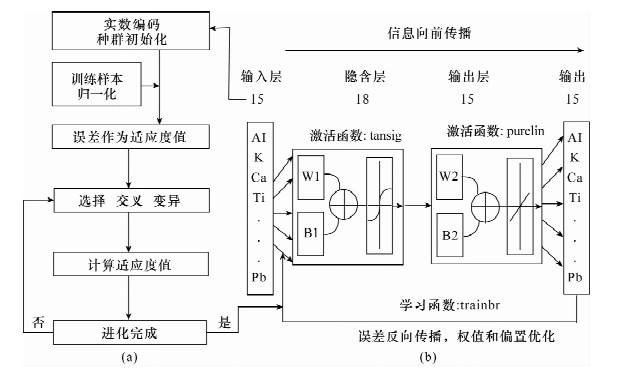
摘要: 海洋沉积物样品成分复杂,由于基体效应的影响,利用岩心扫描仪开展X射线荧光光谱分析只能得到目标元素的强度信息,不利于该方法在成矿机制和古环境等研究领域更好地发挥作用。本文采用岩心扫描仪测定海洋沉积物中的铝硅钾钙钛锰铁钒铬铜锌铷锶钇和铅15种元素,尝试引入BP神经网络模型利用其非线性拟合能力校正基体效应。实验表明,以水系沉积物、海洋沉积物和岩石国家标准物质以及定值海洋沉积物样品为训练样本,采用遗传算法优化BP神经网络的初始权值和偏置,可以有效校正除硅之外的14种元素基体效应的影响,实现了岩心扫描仪XRF测量结果由强度到浓度的转化。本方法的精密度为0.6%~6.8%(RSD, n=11),国家标准物质和海洋沉积物实际样品中15种组分的预测值与参考值的相对偏差在0.5%~17.5%之间,适合于海洋沉积物中多种主次量组分的快速分析,拓展了岩心扫描仪的功能。Abstract: Marine sediments have complex components. Due to the influence of the matrix effect, intensities of elements can only be acquired when using a Core Scanner to carry out X-ray Fluorescence Spectrum analysis, which restricts its application in the fields of paleoecology and mineralization. A method has been introduced for the fast determination of Al2O3, K2O, CaO, TiO2, MnO, Fe2O3, V, Cr, Cu, Zn, Rb, Sr, Y and Pb in marine sediments by Core Scanner, the effects of back-propagation neural network on correcting the nonlinear matrix effects have been investigated and are presented in this paper. Experimental results show that using national certified reference materials of stream sediments, marine sediments and rocks as training samples, a genetic algorithm is used to optimize the initial weight and bias of BP neural network. The matrix effect of 14 elements except Si was corrected by the GA-BP neural network method, which converts the Core Scanner X-ray Fluorescence Spectrum output results from intensities to concentrations. The relative standard deviations of this method are 0.6%-6.8% (n=11). The relative deviations between the predicted values and the reference values of the 15 components of the national standard materials and marine sediment samples range from 0.5% to 17.5%. This indicates that the proposed method is suitable for fast analysis of multi-components in marine sediments, extending the functions of the Core Scanner.
-
Key words:
- genetic algorithm /
- neural network /
- core scanner /
- marine sediments /
- matrix effect
-

-
表 1 方法精密度
Table 1. Precision tests of the method
组分 各组分含量分次测定值(%) 平均值
(%)RSD
(%)Al2O3 10.46 10.73 10.76 10.66 10.48 10.55 10.66 10.61 1.1 SiO2 65.47 64.50 64.42 65.11 65.35 65.18 65.05 65.01 0.6 K2O 2.01 1.97 1.98 1.97 2.03 2.01 1.98 1.99 1.2 CaO 5.31 5.38 5.43 5.37 5.31 5.30 5.32 5.35 0.9 TiO2 0.90 0.90 0.94 0.90 0.91 0.93 0.92 0.91 1.8 MnO 0.082 0.079 0.080 0.078 0.079 0.078 0.080 0.079 1.8 Fe2O3 4.81 4.90 4.93 4.89 4.87 4.85 4.84 4.87 0.8 组分 各组分含量分次测定值(μg/g) 平均值
(μg/g)RSD
(%)V 97.7 102 95.2 99.6 101 96.6 98.4 98.6 2.4 Cr 84.5 82.1 81.9 87.2 83.6 85.5 82.3 83.9 2.4 Cu 31.1 29.9 30.7 31.6 33.4 34.0 31.1 31.7 4.7 Zn 78.9 81.8 76.0 77.7 77.5 78.2 80.4 78.6 2.5 Rb 80.9 80.1 81.3 82.3 79.5 78.4 79.5 80.3 1.6 Sr 169 170 168 167 165 157 166 166 2.6 Y 28.4 27.2 26.5 24.3 27.5 24.0 27.1 26.4 6.3 Pb 20.6 22.5 23.3 23.6 20.9 25.0 23.1 22.7 6.8 表 2 标准物质的预测结果
Table 2. The explication results of elements in national standard materials
组分 GBW07301a GBW07304a GBW07305 GBW07314 预测值
(%)标准值
(%)相对误差
(%)预测值
(%)标准值
(%)相对误差
(%)预测值
(%)标准值
(%)相对误差
(%)预测值
(%)标准值
(%)相对误差
(%)Al2O3 15.50 15.36 0.9 10.82 10.94 -1.1 15.24 15.37 -0.8 12.93 13.07 -1.1 SiO2 58.10 59.07 -1.6 71.56 73.85 -3.1 54.76 56.44 -3.0 60.22 61.91 -2.7 K2O 2.75 2.80 -1.8 1.54 1.51 2.0 2.1 2.11 -0.5 2.5 2.48 0.8 CaO 4.06 4.00 1.5 0.84 0.82 2.4 5.39 5.34 0.9 4.37 4.31 1.4 TiO2 0.93 0.90 3.3 0.86 0.90 -4.4 0.87 0.90 -3.3 0.84 0.83 1.2 MnO 0.13 0.12 8.3 0.14 0.13 7.7 0.14 0.15 -6.7 0.093 0.096 -3.1 Fe2O3 6.60 6.50 1.5 4.63 4.55 1.8 5.88 5.84 0.7 5.43 5.36 1.3 组分 预测值
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)相对误差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)相对误差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)相对误差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)标准值
(μg/g)相对误差
(%)V 121 115 5.2 94.7 99.0 -4.3 115 109 5.5 101 103 -1.9 Cr 123 128 -3.9 77.4 70.0 10.6 79.2 70.0 13.1 82.4 86.0 -4.2 Cu 30.8 28.0 10.0 30.3 33.0 -8.2 131 137 -4.4 28.6 31.0 -7.7 Zn 86.1 90.0 -4.3 136 139 -2.2 252 243 3.7 82.7 87.0 -4.9 Rb 122 126 -3.2 91.4 89.0 2.7 114 118 -3.4 113 109 3.7 Sr 510 486 4.9 148 143 3.5 205 204 0.5 156 150 4.0 Y 25.2 22.0 14.5 25.5 29.0 -12.1 23.4 26.0 -10.0 24.2 27.0 -10.4 Pb 27.6 31.0 -11.0 72.8 68.0 7.1 117 112 4.5 21.4 25.0 -14.4 表 3 海洋沉积物实际样品的预测结果
Table 3. The explication results of elements in marine sediment samples
组分 样品ZJ-1 样品ZJ-2 样品ZJ-3 样品ZJ-4 预测值
(%)参考值
(%)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(%)参考值
(%)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(%)参考值
(%)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(%)参考值
(%)相对偏差
(%)Al2O3 13.75 13.92 -1.2 8.40 8.29 1.3 15.40 15.18 1.4 9.79 10.02 -2.3 SiO2 46.13 45.11 2.3 55.32 56.80 -2.6 50.74 52.07 -2.6 38.24 37.54 1.9 K2O 3.32 3.37 -1.6 1.05 1.11 -5.4 3.42 3.39 1.0 1.59 1.57 1.5 CaO 2.56 2.51 2.0 4.97 5.00 -0.6 3.37 3.42 -1.4 18.85 19.07 -1.2 TiO2 0.75 0.70 7.0 0.38 0.35 7.4 1.48 1.57 -5.7 0.40 0.44 -9.9 MnO 1.30 1.34 -2.8 1.07 1.01 5.7 0.76 0.73 4.1 0.13 0.12 10.2 Fe2O3 8.20 8.09 1.3 4.14 4.19 -1.2 9.61 9.84 -2.4 3.88 3.71 4.5 组分 预测值
(μg/g)参考值
(μg/g)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)参考值
(μg/g)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)参考值
(μg/g)相对偏差
(%)预测值
(μg/g)参考值
(μg/g)相对偏差
(%)V 132 123 7.3 64 68 -5.9 193 200 -3.5 92.4 98.6 -6.3 Cr 48.6 54.4 -10.7 96.2 99.7 -3.5 38.2 32.5 17.5 68.4 76.6 -10.7 Cu 313 316 -1.0 281 287 -2.1 413 402 2.7 64.0 57.7 10.9 Zn 121 125 -3.2 160 154 3.9 231 228 1.3 95.0 90.6 4.9 Rb 103 111 -7.2 68.3 76.5 -10.7 90.4 94.6 -4.4 64.0 60.2 6.3 Sr 366 382 -4.2 428 409 4.6 319 303 5.3 622 640 -2.8 Y 333 340 -2.1 231 246 -6.1 181 169 7.1 39.0 34.7 12.4 Pb 46.2 52.1 -11.3 61.7 56.4 9.4 37.4 32.6 14.7 23.20 26.6 -12.8 -
[1] Rodríguez-Germade I, Rubio B, Rey D.XRF Scanners as a Quick Screening Tool for Detecting Toxic Pollutant Elements in Sediments from Marín Harbour in the Ría De Pontevedra[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 86(1):458-467. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25044038
[2] Liang L J, Sun Y B, Yao Z Q, et al.Evaluation of High-resolution Elemental Analyses of Chinese Loess Deposits Measured by X-ray Fluorescence Core Scanner[J].Catena, 2012, 92:75-82. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.010
[3] 谢永清, 龙江平, 乔吉果, 等.运用岩芯扫描仪划分沉积相的可行性分析[J].热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(4):30-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY201304005.htm
Xie Y Q, Long J P, Qiao J G, et al.Feasibility of Sedimentary Facies Discrimination by Core Scanner[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(4):30-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY201304005.htm
[4] 陈宇亮, 郑洪波.XRF岩扫描在第四纪沉积物研究中的应用[J].海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(4):51-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-hydt201404009.htm
Chen Y L, Zheng H B.The Application of XRF Core Scanning to Quatermaty Sediments[J].Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(4):51-59. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-hydt201404009.htm
[5] 马雪洋, 陈豆, 阳亚平, 等.哈拉湖岩芯XRF扫描元素统计分析及其环境意义[J].盐湖研究, 2014, 22(4):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ201404002.htm
Ma X Y, Chen D, Yang Y P, et al.Statistical Analysis of XRF Scanned Elements and Their Environmental Significance in Hala Lake[J].Journal of Saltlake Research, 2014, 22(4):1-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ201404002.htm
[6] 张晓楠, 张灿, 吴铎, 等.基于XRF岩心扫描的中国西部湖泊沉积物元素地球化学特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(1):163-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201501025.htm
Zhang X N, Zhang C, Wu D, et al.Element Geochemistry of Lake Deposits Measured by X-ray Fluorescence Core Scanner in Northwest China[J].Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(1):163-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201501025.htm
[7] Wang X Q, Jin Z D, Chen L M, et al.High-resolution X-ray Fluorescence Core Scanning of Landslide-dammed Reservoir Sediment Sequences on the Chinese Loess Plateau:New Insights into the Formation and Geochemical Processes of Annual Freeze-Thaw Layers[J].Geoderma, 2016, 279:122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.06.008
[8] Flood R P, Bloemsma M R, Weltje G J, et al.Compositional Data Analysis of Holocene Sediments from the West Bengal Sundarbans, India:Geochemical Proxies for Grain-size Variability in a Delta Environment[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2016(in press). https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rory_Flood/publication/304362969_Compositional_data_analysis_of_Holocene_sediments_from_the_West_Bengal_Sundarbans_India_Geochemical_proxies_for_grain-size_variability_in_a_delta_environment/links/576d639108ae62194742438e.pdf?origin=publication_list
[9] 张喜林, 范德江, 王亮, 等.X射线岩心扫描系统对海洋沉积物成分测定质量的综合评价和校正[J].海洋学报, 2013, 35(6):86-95. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/seac201306009.htm
Zhang X L, Fan D J, Wang L, et al.The Calibration and Quality Evaluation of Elemental Analysis Results of Marine Sediment Measured by an X-ray Fluorescence Core Scanner[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(6):86-95. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/article/seac201306009.htm
[10] 陈钢花, 胡琮, 曾亚丽, 等.基于BP神经网络的碳酸盐岩储层缝洞充填物测井识别方法[J].石油物探, 2015, 54(1):99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201501015.htm
Chen G H, Hu Z, Zeng Y L, et al.Logging Identification Method of Fillings in Fractures and Cavers in Carbonate Reservoir Based BP Neural Network[J].Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2015, 54(1):99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201501015.htm
[11] 叶咸, 许模, 廖晓超, 等.遗传算法优化BP神经网络在求解水文地质参数中的应用[J].水电能源科学, 2013, 31(12):55-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201312014.htm
Ye X, Xu M, Liao X C, et al.Application of Optimized BP Neural Network Based Genetic Algorithm in Solving Hydrogeologic Parameters[J].Water Resources and Power, 2013, 31(12):55-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201312014.htm
[12] 陈文景, 郭常升, 王景强, 等.基于遗传BP神经网络的海底沉积物声速预报[J].海洋学报, 2016, 38(1):116-123. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201601011.htm
Chen W J, Guo C S, Wang J Q, et al.A Study on Forecasting Sound Velocity of Sea-floor Sediments Based on GA-BP Method[J].Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(1):116-123. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201601011.htm
[13] Ariza-Avidad M, Cuellar M P, Salinas-Castillo A, et al.Feasibility of the Use of Disposable Optical Tongue Based on Neural Networks for Heavy Metal Identification and Determination[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 783:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.035
[14] 胡昊, 许冬, 龙江平, 等.北部湾海底沉积物稀土元素与影响因子关系的BP神经网络定量分析[J].海洋学研究, 2016, 34(1):18-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DHHY201601003.htm
Hu H, Xu D, Long J P, et al.Quantitative Analysis of BP Neural Network on the Relationships between REE Content and Impact Factors in Beibu Gulf[J].Journal of Marine Sciences, 2016, 34(1):18-26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DHHY201601003.htm
[15] 沈沁梅, 周卫东, 李科学.激光诱导击穿光谱结合神经网络测定土壤中的Cr和Ba[J].光子学报, 2010, 39(12):2134-2138. doi: 10.3788/gzxb
Shen Q M, Zhou W D, Li K X.Determination of Cr and Ba in Soil Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy with Artificial Neural Networks[J].Acta Photonica Sinica, 2010, 39(12):2134-2138. doi: 10.3788/gzxb
[16] 陈国松, 黄招霞, 唐美华, 等.人工神经网络及模拟退火算法应用于原子吸收光谱法同时测定钙、磷[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2008, 44(7):597-599. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH200807005.htm
Chen G S, Huang Z X, Tang M H, et al.Application of Algorithms of Artificial Neural Network and Simulated Annealing to Simultaneous AAS Determination of Calcium and Phosphorus[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2008, 44(7):597-599. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH200807005.htm
[17] 邱萍.人工神经网络-微分脉冲伏安法同时测定尿液中的多巴胺、尿酸及抗坏血酸[J].分析测试学报, 2011, 30(8):933-936. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-test201108021.htm
Qiu P.Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine, Uric Acid and Ascorbic Acid in Urine Sample by Differential Pulse Voltammetry and Artificial Neural Networks[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2011, 30(8):933-936. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-test201108021.htm
[18] 曹家兴, 陆建平.遗传算法-贝叶斯正则化BP神经网络拟合滴定糖蜜中有机酸[J].分析化学, 2011, 39(5):743-747. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-fxhx201105032.htm
Cao J X, Lu J P.Titration Analysis of Multi-organic Acids in Sugarcane Molasses by Back-propagation Neural Network Integrated with Bayesian Regularization and Genetic Algorithm[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(5):743-747. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-fxhx201105032.htm
[19] Agatonovic-Kustrin S, Loescher C M.Qualitative and Quantitative High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Analysis of Calendula Officinalis Using High Resolution Plate Imaging and Artificial Neural Network Data Modelling[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2013, 798:103-108. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.08.048
[20] 王书涛, 陈东营, 魏蒙, 等.荧光光谱法和PSO-BP神经网络在山梨酸钾浓度检测中的应用[J].中国激光, 2015, 42(5):1-7. http://www.opticsjournal.net/Abstract.htm?id=OJ150506000064UqXtZw
Wang S T, Chen D Y, Wei M, et al.Application of Fluorescence Spectroscopy and PSO-BP Neural Network in the Detection of Potassium Sorbate Concentration[J].Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(5):1-7. http://www.opticsjournal.net/Abstract.htm?id=OJ150506000064UqXtZw
[21] 王菊香, 邢志娜, 李伟, 等.BP神经网络法结合红外光谱快速测定在用润滑油胺类抗氧剂含量[J].计算机与应用化学, 2016, 33(2):197-199. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYH201602014.htm
Wang J X, Xing Z N, Li W, et al.Rapid Determination of Amino Antioxidant Content in in-service Lubricating Oil Based on BP-ANN Combined with FTIR[J].Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2016, 33(2):197-199. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYH201602014.htm
[22] 石睿, 庹先国, 李哲, 等.SDD探测X射线中BP网络全谱定量分析技术研究[J].分析试验室, 2013, 32(1):121-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201301031.htm
Shi R, Tuo X G, Li Z, et al.The Research of BP Network Quantitative Analysis Technology of the Full X-ray Spectrum Detected by SDD[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2013, 32(1):121-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201301031.htm
[23] 徐立鹏, 葛良全, 谷懿, 等.基于PCA-BP神经网络的EDXRF分析测定地质样品中铁、钛元素含量的应用研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(5):1392-1396. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GUAN201305058.htm
Xu L P, Ge L Q, Gu Y, et al.Research on the Application of Principal Component Analysis and Improved BP Neural Network to the Determination of Fe and Ti Contents in Geological Samples[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(5):1392-1396. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GUAN201305058.htm
[24] 李芳, 陆安祥, 王纪华.基于列文伯格-马夸尔特-反向传播人工神经网络的X射线荧光光谱定量分析方法[J].食品安全质量检测学报, 2016, 7(3):1152-1158. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPAJ201603053.htm
Li F, Lu A X, Wang J H.Quantitative Analysis Method Based on Levenberg-Marquardt Back-propagation Artificial Neural Network for X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry[J].Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2016, 7(3):1152-1158. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPAJ201603053.htm
[25] 王俊, 刘明哲, 庹先国, 等.遗传算法优化的BP神经网络在EDXRF中对钛铁元素含量的预测[J].原子能科学技术, 2015, 49(6):1143-1148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201506031.htm
Wang J, Liu M Z, Tuo X G, et al.BP Neural Network Optimized by Genetic Algorithm Approach for Titanium and Iron Content Prediction in EDXRF[J].Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2015, 49(6):1143-1148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201506031.htm
[26] 阴江宁, 肖克炎, 李楠, 等.BP神经网络在化探数据分类中的应用[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(10):1564-1571.
Yin J N, Xiao K Y, Li N, et al.Application of BP Neural Network in the Classification of Geo-chemical Survey Data[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(10):1564-1571.
[27] 施彦编著.神经网络设计方法与实例分析[M].北京:北京邮电大学出版社, 2009:35.
Shi Y.Design Method and Example Analysis of Neural Network[M].Beijing:Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2009:35.
[28] 夏祥华, 孙汉文.基于遗传算法的曲线拟合方法用于重叠荧光光谱的定量解析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(8):2157-2161.
Xia X H, Sun H W.Curve Fitting Based on Cenetic Algorithms for Quantitative Resolution in Overlapped Fluorescence Spectra[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(8):2157-2161.
[29] 邹孝恒, 郝中骐, 易荣兴, 等.基于遗传算法和偏最小二乘法的土壤激光诱导击穿光谱定量分析研究[J].分析化学, 2015, 43(2):181-186.
Zou X H, Hao Z Q, Yi R X, et al.Quantitative Analysis of Soil by Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Using Genetic Algorithm-partial Least Squares[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(2):181-186.
-




 下载:
下载: