Review on the Analytical Methods of Typical Emerging Organic Pollutants in the Environment
-
摘要: 环境中持久性有机污染物(POPs)、药物及个人护理品(PPCPs)和消毒水副产物(DBPs)等新型有机污染物对生态环境和人体健康具有潜在威胁,研究其来源、检测方法、环境分布和迁移转化已经成为热点。新型有机污染物组成复杂,如短链氯化石蜡有7000多种同类物,采用传统分析手段无法实现分离,对这些物质的准确定性和定量面临挑战。近年来在新型有机污染物检测技术开发方面已取得较大进展:根据待测样品的性质可使用快速溶剂萃取、固相微萃取等多种提取方法,凝胶渗透色谱、多层复合层析柱和固相萃取柱是有效的净化手段,采用气相色谱-质谱或液相色谱-质谱实现了对指示性单体准确定性定量,检出限可达ng/g级。但对于环境影响较大的新型有机污染物如手性多氯联苯(PCBs),由于各手性PCBs单体之间在分离过程中发生峰共溢现象,需要应用专门的手性色谱柱进行分析,尚未建立可靠的检测方法。本文认为,一方面需要探索磁性固相基质分散萃取技术等高效的前处理技术对干扰物质进行有效分离;另一方面需要提高全二维气相/液相色谱、傅里叶变换质谱等色谱/质谱检测技术的识别性和灵敏度,开发出简便、标准化的定量方法。
-
关键词:
- 持久性有机污染物 /
- 药物及个人护理品 /
- 消毒水副产物 /
- 气相色谱-高分辨质谱 /
- 液相色谱-质谱
Abstract:BACKGROUND Persistent organic pollutants (POPs), pharmaceuticals, personal care products (PPCPs) and disinfection by products (DBPs) have raised significant concerns for their potential ecological threat to the environment and human health. Research on their source, detection method, environmental distribution, migration and transformation has become the hot topic. OBJECTIVES To introduce recent analytical techniques and applications for the determination of POPs, PPCPs and DBPs in environmental and biota samples, and summarize the extraction, separation and instrumental analyses of the halogenated emerging organic pollutants. To discuss future trends for improving the POPs, PPCPs and DBPs analyses and potential emerging organic pollutants. METHODS In recent years the analytical techniques for emerging organic pollutants have made great progress. According to the nature of samples, a variety of extraction methods have been used, such as accelerated solvent extraction and solid phase microextraction. Effective clean-up steps include GPC, multi-layer column and SPE. Conventional analytical methods of emerging organic pollutants have been based mainly on GC-ECD. With the fast development of chromatography and mass spectrometry, congener-specific analysis has become a mainstream method. The analysis of certain emerging organic pollutants at trace levels is now a routine due to the advancement of HRGC-HRMS. RESULTS Methods for the analysis of emerging organic pollutants in a variety of environmental, biota and food matrices have been well developed during the past several decades. However, the analytical challenge still remains for a direct analysis of emerging pollutants. For example, short chain chlorinated paraffin has more than 7000 kinds of congeners. The traditional analytical methods cannot achieve their separation, and accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis of these pollutants is challenging. CONCLUSIONS The analytical technique for emerging organic pollutants still has a long way to go. On the one hand, it is necessary to explore effective pretreatment techniques such as magnetic solid-phase matrix dispersion extraction technology to reduce the possible interference. On the other hand, it is necessary to improve the recognition, sensitivity, accuracy and practicability of chromatographic mass spectrometry techniques such as comprehensive Two-dimensional Gas Chromatography and Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry and develop a simple and standard quantitative method. -

-
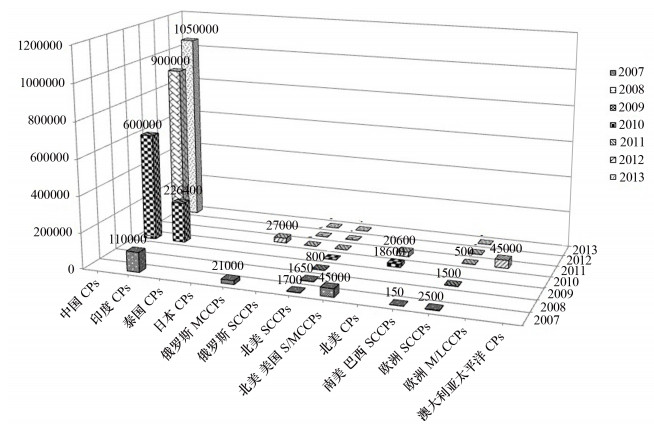
图 1 一些国家2007—2013年氯化石蜡产量[56]
Figure 1.
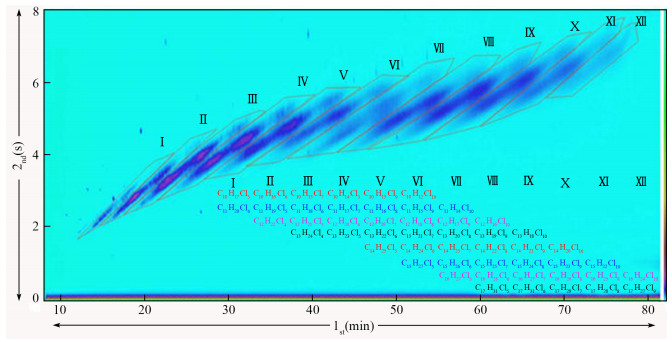
图 2 氯含量51.5%的SCCPs与氯含量52%的MCCPs混合物在GC×GC-ECNI-HRTOF-MS上的总离子流图[31]
Figure 2.
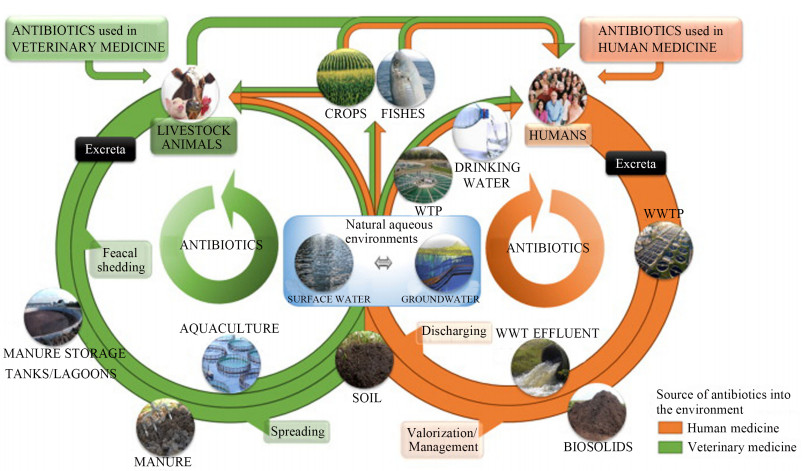
图 3 抗生素在环境中迁移转化途径[70]
Figure 3.
表 1 环境介质中新型POPs分析技术与方法
Table 1. Analytical methods for the determination of POPs in environmental samples
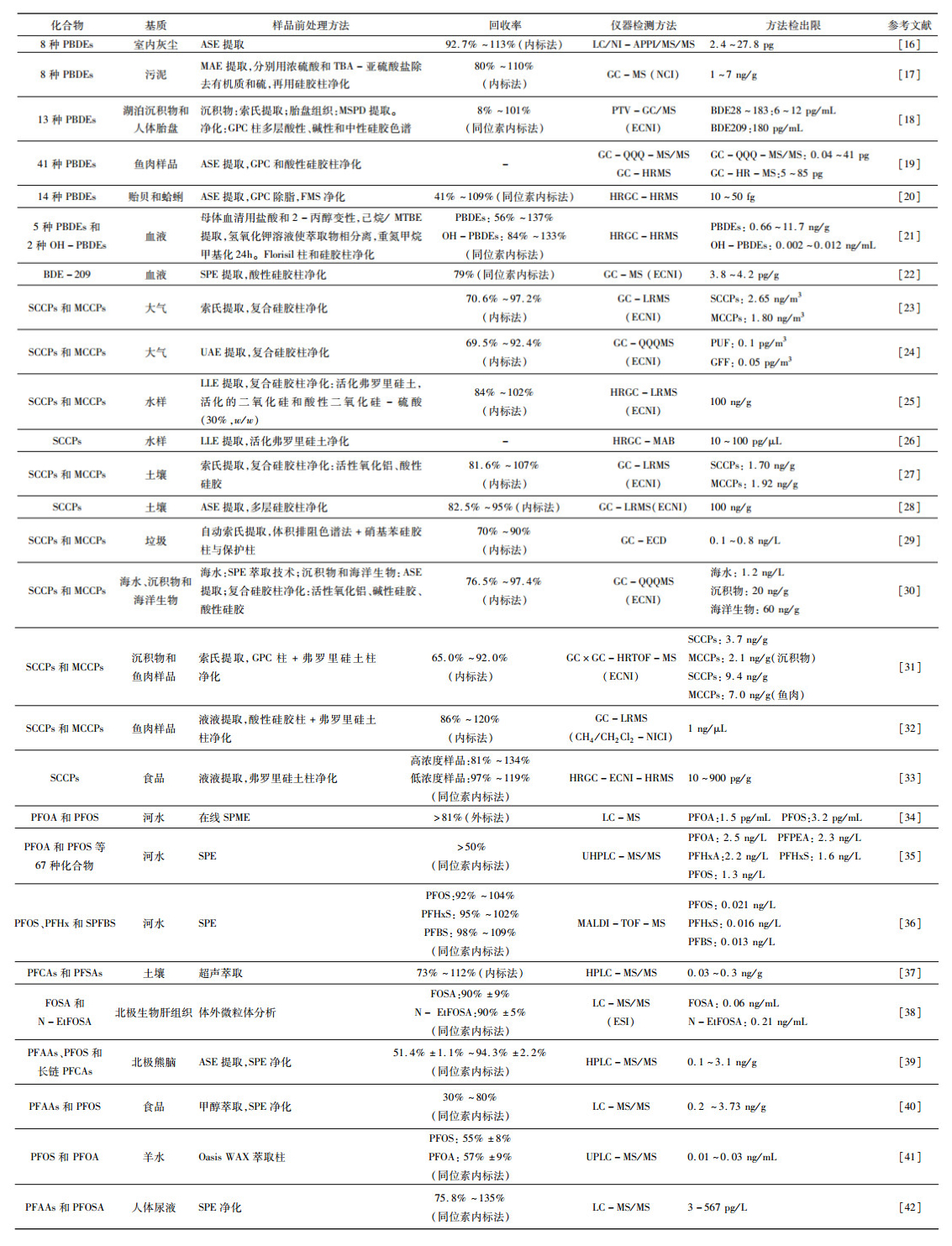
表 2 环境介质中PPCPs分析技术与方法
Table 2. Analytical methods for the determination of PPCPs in environmental samples
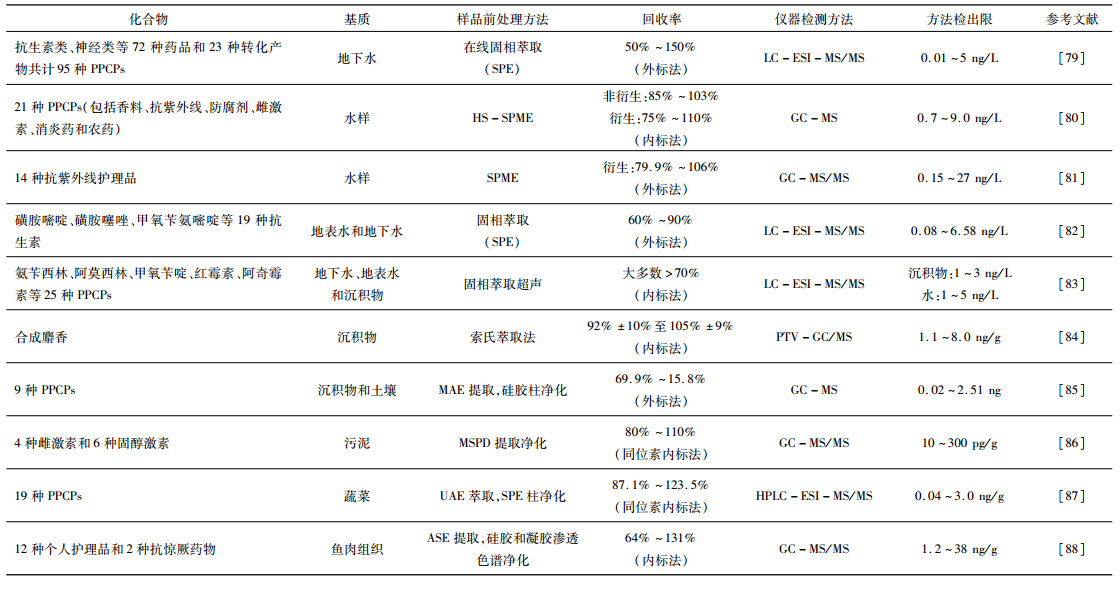
表 3 水样中DBPs分析技术与方法
Table 3. Analytical methods for the determination of DBPs in water samples
-
[1] Sharma B M, Bharat G K, Tayal S, et al.Environment and human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in India:A systematic review of recent and historical data[J].Environment International, 2014, 66:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.01.022
[2] Liu J L, Wong M H.Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs):A review on environmental contamination in China[J].Environment International, 2013, 59:208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2013.06.012
[3] Liu J, Zhang X.Comparative toxicity of new halophenolic DBPs in chlorinated saline wastewater effluents against a Marine Alga:Halophenolic DBPs are generally more toxic than haloaliphatic ones[J].Water Research, 2014, 65:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.024
[4] Harmens H, Foan L, Simon V, et al.Terrestrial mosses as biomonitors of atmospheric POPs pollution:A review[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 173:245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.005
[5] Grellier J, Rushton L, Briggs D J, et al.Assessing the human health impacts of exposure to disinfection by-products-A critical review of concepts and methods[J].Environment International, 2015, 78:61-81. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.02.003
[6] Zhu Z C, Chen S J, Zheng J, et al.Occurrence of bro-minated flame retardants (BFRs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in agricultural soils in a BFR-manufacturing region of North China[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2014, 481:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.023
[7] Zhi H, Zhao Z, Zhang L.The fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water from Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China[J].Chemosphere, 2015, 119:1134-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.054
[8] Zhao H, Wang Y, Wang R.In situ formation of well-dispersed palladium nanoparticles immobilized in imidazolium-based organic ionic polymers[J].Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(74):10871-10874. doi: 10.1039/C4CC04662E
[9] Tian Z, Li H, Xie H, et al.Concentration and distribution of PCNs in ambient soil of a municipal solid waste incinerator[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 491-492:75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.130
[10] Noguera O K, Aga D S.Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 316:242-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.058
[11] Wu Q Y, Tang X, Huang H, et al.Antiestrogenic activity and related disinfection by-product formation induced by bromide during chlorine disinfection of sewage secondary effluent[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 273:280-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.028
[12] Sun Q, Lü M, Hu A, et al.Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a wastewater treatment plant in Xiamen, China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 277:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.056
[13] Salihovic S, Nilsson H, Hagberg J, et al.Trends in the analysis of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in human blood[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 46:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.06.009
[14] Barghi M, Shin E S, Choi S D, et al.HBCD and TBBPA in human scalp hair:Evidence of internal exposure[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 207:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.032
[15] Mannetje A, Coakley J, Mueller J F, et al.Partitioning of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) between human serum and breast milk:A literature review[J].Chemosphere, 2012, 89(8):911-918. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.06.049
[16] Lagalante A F, Oswald T D.Analysis of Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by liquid chromatography with negative-ion atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/NI-APPI/MS/MS):Application to house dust[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2008, 391(6):2249-2256. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2156-z
[17] Shin M, Svoboda M L, Falletta P.Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) for the determination of polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) in sewage sludge[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(8):2923-2929. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1168-4
[18] Wei H, Dassanayake P S, Li A.Parametric evaluation for programmable temperaturevaporisation large volume injection in gas chromatographic determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 90(7):535-547. doi: 10.1080/03067310902871299
[19] Mackintosh S A, Pérez-Fuentetaja A, Zimmerman L R, et al.Analytical performance of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer compared to a high resolution mass spectrometer for the analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2012, 747:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.021
[20] Pizzini S, Marchiori E, Piazza R, et al.Determination by HRGC/HRMS of PBDE levels in edible mediterranean bivalves collected from North-Western Adriatic Coasts[J].Microchemical Journal, 2015, 121:184-191. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2015.03.010
[21] Parry E, Zota A R, Park J S, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hydroxylated PBDE metabolites (OH-PBDEs):A six-year temporal trend in Northern California pregnant women[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 195:777-783. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.065
[22] van den Berg M, Houba R, Leslie H A, et al.Serum levels of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in women from different European countries and possible relationships with lifestyle and diet[J].Environment International, 2017, 107:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.06.014
[23] Chaemfa C, Xu Y, Li J, et al.Screening of atmospheric short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in India and Pakistan using polyurethane foam based passive air sampler[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9):4799-4808.
[24] Ma X, Zhang H, Zhou H, et al.Occurrence and gas/particle partitioning of short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in the atmosphere of Fildes Peninsula of Antarctica[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 90:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.03.021
[25] Zeng L, Wang T, Wang P, et al.Distribution and trophic transfer of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in an aquatic ecosystem receiving effluents from a sewage treatment plant[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(13):5529-5535.
[26] Moore S, Vromet L, Rondeau B.Comparison of metasta-ble atom bombardment and electron capture negative ionization for the analysis of polychloroalkanes[J].Chemosphere, 2004, 54(4):453-459. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00709-4
[27] Wang X T, Wang X K, Zhang Y, et al.Short-and medi-um chain chlorinated paraffins in urban soils of Shanghai:Spatial distribution, homologue group patterns and ecological risk assessment[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 490:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.121
[28] Zeng L, Wang T, Han W, et al.Spatial and vertical dis-tribution of short chain chlorinatedparaffins in soils from wastewater irrigated farmlands[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(6):2100-2106.
[29] Nilsson M L, Bengtsson S, Kylin H.Identification and determination of chlorinated paraffins using multivariate evaluation of gas chromatographic data[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 163:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.010
[30] Ma X, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al.Bioaccumulation and tro-phic transfer of short chain chlorinated paraffins in a marine food web from Liaodong Bay, North China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(10):5964-5971.
[31] Xia D, Gao L, Zheng M, et al.A novel method for pro-filing and quantifying short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in environmental samples using GC×GC-ECNI-HRTOF-MS[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50:7601-7609.
[32] Zencak Z, Borgen A, Reth M, et al.Evaluation of four mass spectrometric methods for the gas chromatographic analysis of polychlorinated N-alkanes[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2005, 1067(1):295-301.
[33] Harada K H, Takasuga T, Hitomi T, et al.Dietary expo-sure to short-chain chlorinated paraffins has increased in Beijing, China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(16):7019-7027.
[34] Saito K, Uemura E, Ishizaki A, et al.Determination of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate by automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 658(2):141-146. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.11.004
[35] Loos R, Tavazzi S, Paracchini B, et al.Analysis of polar organic contaminants in surface water of the Northern Adriatic Sea by solid-phase extraction followed by ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography-Qtrap® MS using a hybrid triple-quadrupole linear ion trap instrument[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 405(18):5875-5885. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-6944-8
[36] Cao D, Hu M, Han C, et al.Proton sponge-functionalized silica as high performance adsorbents for solid-phase extraction of trace perfluoroalkyl sulfonates in the environmental water samples and their direct analysis by MALDI-TOF-MS[J].Analyst, 2012, 137(9):2218-2225. doi: 10.1039/c2an16190g
[37] Li F, Zhang C, Qu Y, et al.Quantitative characterization of short-and long-chain perfluorinated acids in solid matrices in Shanghai, China[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2010, 408(3):617-623. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.032
[38] Letcher R J, Chu S, McKinney M A, et al.Comparative hepatic in vitro depletion and metabolite formation of major perfluorooctane sulfonate precursors in Arctic Polar Bear, Beluga Whale, and Ringed Seal[J].Chemosphere, 2014, 112:225-231. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.022
[39] Greaves A K, Letcher R J, Sonne C, et al.Brain region distribution and patterns of bioaccumulative perfluoroalkyl carboxylates and sulfonates in East Greenland Polar Bears (Ursus Maritimus)[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2013, 32(3):713-722. doi: 10.1002/etc.2107
[40] Rivière G, Sirot V, Tard A, et al.Food risk assessment for perfluoroalkyl acids and brominated flame retardants in the french population:Results from the second french total diet study[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2014, 491-492:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.104
[41] Zhang T, Qin X.Assessment of fetal exposure and mater-nal elimination of perfluoroalkyl substances[J].Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(8):1878-1881.
[42] Zhang Y, Beesoon S, Zhu L, et al.Biomonitoring of perfluoroalkyl acids in human urine and estimates of biological half-life[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(18):10619-10627.
[43] Muñoz A J, Roscales J L, Ros M, et al.Towards the implementation of the stockholm convention in Spain:Five-year monitoring (2008-2013) of POPs in air based on passive sampling[J].Environmental Pollution, 2016, 217:107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.052
[44] Gao Q, Budarin V L, Cieplik M, et al.PCDDs, PCDFs and PCNs in products of microwave-assisted pyrolysis of woody biomass-distribution among solid, liquid and gaseous phases and effects of material composition[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 145:193-199. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.110
[45] Fournier A, Rychen G, Marchand P, et al.Polychlorina-ted biphenyl (PCB) decontamination kinetics in lactating goats (Capra Hircus) following a contaminated corn silage exposure[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(29):7156-7164. doi: 10.1021/jf401048j
[46] Muir D, Lohmann R.Water as a new matrix for global assessment of hydrophilic POPs[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 46:162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.12.019
[47] Król S, Zabiegała B, Namies'nik J.Human hair as a biomarker of human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs)[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 47:84-98. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.02.010
[48] Wang X, Wang J, Jiao C, et al.Retracted:Preparation of magnetic mesoporous poly-melamine-formaldehyde composite for efficient extraction of chlorophenols[J].Talanta, 2018, 179:676-684. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.002
[49] Diao C, Li C, Yang X, et al.Magnetic matrix solid phase dispersion assisted dispersive liquid liquid microextraction of ultra trace polychlorinated biphenyls in water prior to GC-ECD determination[J].Microchimica Acta, 2016, 183(3):1261-1268. doi: 10.1007/s00604-016-1761-3
[50] Abhilash P C, Singh B, Srivastava P, et al.Remediation of lindane by Jatropha curcas L:Utilization of multipurpose species for rhizoremediation[J].Biomass and Bioenergy, 2013, 51:189-193. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.01.028
[51] McManus S L, Coxon C E, Richards K G, et al.Quanti-tative solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis of the pesticides lindane, heptachlor and two heptachlor transformation products in groundwater[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1284:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.099
[52] Marek R F, Thorne P S, Wang K, et al.PCBs and OH-PCBs in serum from children and mothers in urban and rural U.S.communities[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(7):3353-3361. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3798030
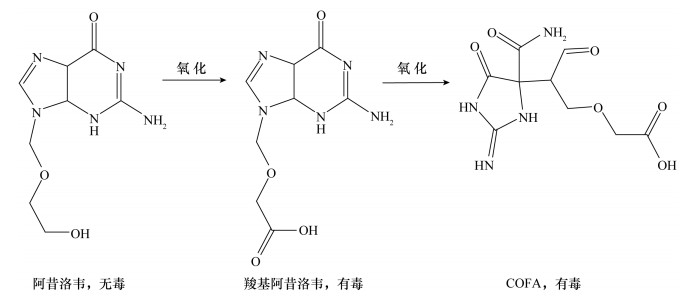
[53] Besis A, Samara C.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the indoor and outdoor environments-A review on occurrence and human exposure[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 169:217-229. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.009
[54] Berton P, Lana N B, Ríos J M, et al.State of the art of environmentally friendly sample preparation approaches for determination of PBDEs and metabolites in environmental and biological samples:A critical review[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 905:24-41. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.009
[55] Giandomenico S, Spada L, Annicchiarico C, et al.Chlorinated compounds and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in mussels (mytilus galloprovincialis) collected from Apulia Region Coasts[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 73(1):243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.013
[56] van Mourik L M, Gaus C, Leonards P E G, et al.Chlori-nated paraffins in the environment:A review on their production, fate, levels and trends between 2010 and 2015[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 155:415-428. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.037
[57] Geng N, Zhang H, Zhang B, et al.Effects of short-chain chlorinated paraffins exposure on the viability and metabolism of human Hepatoma Hepg2 cells[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(5):3076-3083.
[58] Gao W, Cao D, Wang Y, et al.External exposure to short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins for the general population in Beijing, China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(1):32-39.
[59] Wang T, Wang Y, Jiang G.On the environmental health effects and socio-economic considerations of the potential listing of short-chain chlorinated paraffins into the stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(21):11924-11925.
[60] Gjoes N, Gustavsen K O.Determination of chlorinated paraffins by negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1982, 54(8):1316-1318. doi: 10.1021/ac00245a014
[61] Schinkel L, Lehner S, Knobloch M, et al.Transformation of chlorinated paraffins to olefins during metal work and thermal exposure-Deconvolution of mass spectra and kinetics[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 194:803-811. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.168
[62] Zafeiraki E, Costopoulou D, Vassiliadou I, et al.Deter-mination of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in various foodstuff packaging materials used in the greek market[J].Chemosphere, 2014, 94:169-176. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.092
[63] Kowalczyk J, Ehlers S, Oberhausen A, et al.Absorption, distribution, and milk secretion of the perfluoroalkyl acids PFBS, PFHXS, PFOS, and PFOA by dairy cows fed naturally contaminated feed[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(12):2903-2912. doi: 10.1021/jf304680j
[64] Zhu P, Ling X, Liu W, et al.Simple and fast determi-nation of perfluorinated compounds in Taihu Lake by SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS[J].Journal of Chromatography B, 2016, 1031:61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.07.031
[65] Urtiaga A, Soriano A, Carrillo-Abad J.Bdd anodic treat-ment of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA).Evaluation of operating variables and by-product formation[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 201:571-577. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.027
[66] Xie S, Paau M C, Li C F, et al.Separation and precon-centration of persistent organic pollutants by cloud point extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(16):2306-2317. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.075
[67] Zhu S, Gao L, Zheng M, et al.Determining indicator toxa-phene congeners in soil using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2014, 118:210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.09.044
[68] Xia D, Gao L, Zhu S, et al.Separation and screening of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in environmental samples using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with micro electron capture detection[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 406(29):7561-7570. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8209-6
[69] 王丹, 隋倩, 赵文涛, 等.中国地表水环境中药物和个人护理品的研究进展[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(9):743-751.
[70] Carvalho I T, Santos L.Antibiotics in the aquatic en-vironments:A review of the European Scenario[J].Environment International, 2016, 94:736-757. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025
[71] Munro K, Miller T H, Martins C P B, et al.Artificial neural network modelling of pharmaceutical residue retention times in wastewater extracts using gradient liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry data[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1396:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.063
[72] McEachran A D, Shea D, Bodnar W, et al.Pharma-ceutical occurrence in groundwater and surface waters in forests land-applied with municipal wastewater[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2016, 35(4):898-905. doi: 10.1002/etc.3216
[73] Kleywegt S, Pileggi V, Yang P, et al.Pharmaceuticals, hormones and bisphenol a in untreated source and finished drinking water in Ontario, Canad-Occurrence and treatment efficiency[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(8):1481-1488. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.010
[74] Sui Q, Cao X, Lu S, et al.Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater:A review[J].Emerging Contaminants, 2015, 1(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.emcon.2015.07.001
[75] Fridman O, Goldberg A, Ronin I, et al.Optimization of lag time underlies antibiotic tolerance in evolved bacterial populations[J].Nature, 2014, 513(7518):418-421. doi: 10.1038/nature13469
[76] Li X, Zheng W, Kelly W R.Occurrence and removal of pharmaceutical and hormone contaminants in rural wastewater treatment Lagoons[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 445-446:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.035
[77] Schlüter-Vorberg L, Prasse C, Ternes T A, et al.Toxification by transformation in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment:The antiviral drug acyclovir[J].Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2015, 2(12):342-346.
[78] Prasse C, Wagner M, Schulz R, et al.Biotransformation of the antiviral drugs acyclovir and penciclovir in activated sludge treatment[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(7):2761-2769. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0222199050
[79] López S R, Jurado A, Vázquez-Suñé E, et al.Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban groundwaters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 174:305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.022
[80] Basaglia G, Pietrogrande M.Optimization of a SPME/GC/MS method for the simultaneous determination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waters[J].Chromatographia, 2012, 75(7-8):361-370. doi: 10.1007/s10337-012-2207-7
[81] Vila M, Celeiro M, Lamas J P, et al., Simultaneous in-vial acetylation solid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of multiclass organic UV filters in water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 323:45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.056
[82] Tong L, Huang S, Wang Y, et al.Occurrence of an-tibiotics in the aquatic environment of Jianghan Plain, Central China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 497-498:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.068
[83] Radović T, Grujić S, Petković A, et al.Determination of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in river sediments and corresponding surface and ground water in the Danube River and tributaries in Serbia[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 187(1):1-17.
[84] Sumner N R, Guitart C, Fuentes G, et al.Inputs and distributions of synthetic musk fragrances in an estuarine and coastal environment:A case study[J].Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(1):215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.018
[85] Rice S L, Mitra S.Microwave-assisted solvent extraction of solid matrices and subsequent detection of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2007, 589(1):125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.02.051
[86] Albero B, Sánchez B C, Miguel E, et al.Analysis of natural-occurring and synthetic sexual hormones in sludge-amended soils by matrix solid-phase dispersion and isotope dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1283:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.113
[87] Wu X, Conkle J L, Gan J.Multi-residue determination of pharmaceutical and personal care products in vegetables[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1254:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.041
[88] Subedi B, Mottaleb M A, Chambliss C K, et al.Simultaneous analysis of select pharmaceuticals and personal care products in fish tissue using pressurized liquid extraction combined with silica gel cleanup[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(37):6278-6284. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.07.031
[89] Augusto F, Hantao L W, Mogollón N G S, et al.New materials and trends in sorbents for solid-phase extraction[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 43:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.08.012
[90] Spietelun A, Marcinkowski Ł, Guardia M, et al.Recent developments and future trends in solid phase microextraction techniques towards green analytical chemistry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1321:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.030
[91] Bobeldijk I, Vissers J P C, Kearney G, et al.Screening and identification of unknown contaminants in water with liquid chromatography and quadrupole-orthogonal acceleration-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2001, 929(1-2):63-74. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01156-6
[92] Regli S, Chen J, Messner M, et al.Estimating potential increased bladder cancer risk due to increased bromide concentrations in sources of disinfected drinking waters[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(22):13094-13102.
[93] Richardson S D, Fasano F, Ellington J J, et al.Occu-rrence and mammalian cell toxicity of iodinated disinfection byproducts in drinking water[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(22):8330-8338.
[94] Dad A, Jeong C H, Pals J A, et al.Pyruvate remediation of cell stress and genotoxicity induced by haloacetic acid drinking water disinfection by-products[J].Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 2013, 54(8):629-637. doi: 10.1002/em.v54.8
[95] Stalter D, O'Malley E, Gunten U, et al.Fingerprinting the reactive toxicity pathways of 50 drinking water disinfection by-products[J].Water Research, 2016, 91:19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.047
[96] Cortés C, Marcos R.Genotoxicity of Disinfection Bypro-ducts and Disinfected Waters:A Review of Recent Literature[J].Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 2018, 831:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.04.005
[97] Cancho B, Ventura F, Galceran M, et al.Determination, synthesis and survey of iodinated trihalomethanes in water treatment processes[J].Water Research, 2000, 34(13):3380-3390. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00079-8
[98] Calderón P D, Bayona J M.Development of an analytical procedure for the determination of trihalomethanes in leafy vegetable by headspace-spme followed by GC-ECD determination[J].Food Analytical Methods, 2015, 8(5):1093-1100. doi: 10.1007/s12161-014-9965-9
[99] Kubáň P, Makarõtševa N, Kiplagat I K, et al.Deter-mination of five priority haloacetic acids by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection and solid phase extraction preconcentration[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2012, 35(5-6):666-673. Wang D, Sui Q, Zhao W T, et al.Pharmaceutical and personal care products in the surface water of China:A review[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(9):743-751. doi: 10.1002/jssc.v35.5/6
[100] Teh H B, Li S F Y.Simultaneous determination of bromate, chlorite and haloacetic acids by two-dimensional matrix elimination ion chromatography with coupled conventional and capillary columns[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1383:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.01.037
[101] Nsubuga H, Basheer C.Determination of haloacetic acids in swimming pool waters by membrane-protected micro-solid phase extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1315:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.09.050
[102] Alhooshani K, Basheer C, Kaur J, et al.Electromem-brane extraction and HPLC analysis of haloacetic acids and aromatic acetic acids in wastewater[J].Talanta, 2011, 86:109-113. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.08.026
[103] Prieto-Blanco M C, Alpendurada M F, López-Mahía P, et al.Improving methodological aspects of the analysis of five regulated haloacetic acids in water samples by solid-phase extraction, ion-pair liquid chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2012, 94:90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.02.061
[104] Kubwabo C, Stewart B, Gauthier S A, et al.Improved derivatization technique for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5h)-furanone in drinking water[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2009, 649(2):222-229. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.07.035
[105] Planas C, Ventura F, Caixach J, et al.Analysis of 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5h) -furanone (MX) and its brominated analogues in chlorine-treated water by gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (GC-QQQ-MS/MS)[J].Talanta, 2015, 144:145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.033
[106] Luo Q, Chen X, Wei Z, et al.Simultaneous and high-throughput analysis of iodo-trihalomethanes, haloacetonitriles, and halonitromethanes in drinking water using solid-phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry:An optimization of sample preparation[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2014, 1365:45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.003
[107] Gilchrist E S, Healy D A, Morris V N, et al.A review of oxyhalide disinfection by-products determina-tion in water by ion chromatography and ion chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 942:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.09.006
[108] Subedi B, Usenko S.Enhanced pressurized liquid extraction technique capable of analyzing polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorodibenzofurans, and polychlorobiphenyls in fish tissue[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1238:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.037
-



 下载:
下载: