Assessment of Accuracy and Error Sources of the Rietveld Quantitative Phase Analysis Method in Mineral Contents of Evaporites
-
摘要: Rietveld物相定量分析(RQPA)方法在地质学中已有大量应用,在蒸发岩定量分析中,对精确度的评价和误差控制是提高分析质量的重要因素。本文对人工配制和野外采集的样品(石膏和钾盐)进行RQPA分析,并与化学分析结果对比,评价其精确度并分析其主要的误差来源。结果表明:人工配制的氯化钠-氯化钾二元物相的绝对误差为0.4%~0.9%;氯化钠-氯化钾-碳酸钙三元物相的绝对误差为0.1%~1.2%;二元物相样品10次分析的标准偏差为0.702%,相对标准偏差为1.74%(氯化钾)和1.17%(氯化钠);野外采集的石膏和钾盐样品的RQPA分析结果与化学分析结果具有很好的一致性。表明RQPA方法在蒸发岩矿物组分定量分析中具有较高的精确度,其误差主要来源于样品性质、样品制备、测试条件和精修过程等。RQPA方法具有减弱择优取向效应、无需纯样以及提高数据利用率等优点,与化学分析技术联用在蒸发岩矿产勘探、储量评价以及工业应用中具有广泛的前景。
-
关键词:
- 蒸发岩 /
- Rietveld物相定量分析 /
- 结构精修 /
- 钾盐
Abstract: The Rietveld phase quantitative analysis (RQPA) method has been widely applied in geology. In the analysis of evaporite, the evaluation and error control of precision are important factors to improve the quality. The RQPA method was applied to simulated binary mixtures (halite and sylvite), ternary mixtures (halite, sylvite, and calcite), and geological samples (i.e., gypsum and sylvite samples). The contents of each mineral calculated by RQPA were compared with the results of chemical analytical data to evaluate the RQPA's accuracy and the main error sources were analyzed. The results show that the absolute errors between theoretical and calculated values are in the range of 0.4%-0.9% and 0.1%-1.2% for the binary and ternary mixtures, respectively. The mineral contents of geological samples matched very well with the results of the chemical analysis. The standard deviation of binary mixtures is 0.702 for 10 calculated results. The relative standard deviation of the same samples are 1.74%(KCl) and 1.17%(NaCl), respectively. The study indicates that the RQPA method is accurate in the quantitative analysis of mineral contents of evaporite rocks. The error sources arose mainly from the nature of the samples, sample preparation, measuring conditions, and refinement process. Due to the advantages of reducing the preferred orientation, not requiring pure samples, and high utilization of data, the RQPA method has a potentially extensive application in mineral exploration analysis, reserve evaluation, and industries of evaporites, when coupled with the chemical analysis method.-
Key words:
- evaporite /
- Rietveld quantitative phase analysis /
- Rietveld refinement /
- sylvite
-

-
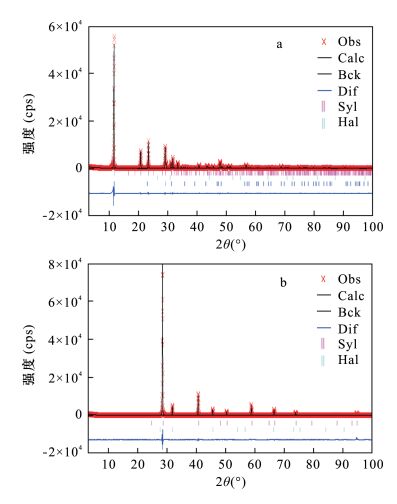
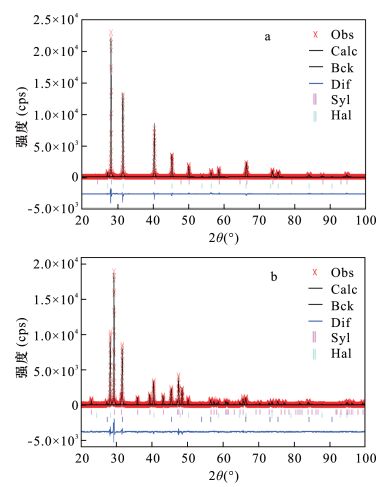
表 1 二元物相和三元物相RQPA分析结果
Table 1. RQPA results of binary mixture and ternary mixture
二元物相RQPA分析结果 三元物相RQPA分析结果 样品
编号化合物 理论含量
(%)计算含量
(%)Rwp
(%)Rp
(%)χ2 样品
编号化合物 理论含量
(%)计算含量
(%)Rwp
(%)Rp
(%)χ2 SH28 氯化钠
氯化钾20.0
80.020.7
79.39.39 6.76 2.02 SHC226 氯化钠
氯化钾
碳酸钙20.0
20.0
60.019.1
20.1
60.811.98 9.30 3.75 SH46 氯化钠
氯化钾40.0
60.040.9
59.19.82 7.56 2.21 SHC622 氯化钠
氯化钾
碳酸钙60.0
20.0
20.059.3
21.2
19.511.67 8.96 3.57 SH64 氯化钠
氯化钾60.0
40.059.6
40.49.76 7.37 2.18 SHC172 氯化钠
氯化钾
碳酸钙10.0
70.0
20.010.7
70.2
19.111.92 9.16 3.73 SH82 氯化钠
氯化钾80.0
20.079.5
20.59.34 6.97 2.01 SHC712 氯化钠
氯化钾
碳酸钙70.0
10.0
20.070.7
9.2
20.111.66 8.99 3.55 表 2 SH46样品10次RQPA结果
Table 2. RQPA results of SH46 sample analyzed for ten times
参数 10次测量结果 平均值
(%)标准偏差
(%)RSD
(%)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 氯化钾含量(%)
氯化钠含量(%)40.2
59.841.3
58.740.4
59.641.0
59.039.7
60.340.6
59.441.1
58.940.3
59.739.5
60.539.2
60.840.33
59.670.702
0.7021.74
1.17Rwp(%) 10.13 10.11 9.94 9.56 9.73 9.64 9.51 9.68 10.39 9.48 - - - Rp(%) 7.46 7.59 7.46 6.99 7.29 6.92 6.86 7.12 0.80 6.77 - - - χ2 2.36 2.35 2.28 2.12 2.19 2.15 2.09 2.17 2.50 2.08 - - - 表 3 样品化学分析结果及其计算的矿物含量
Table 3. The chemical compositions and calculated mineral contents of samples
化学分析结果 化学分析结果计算的矿物含量 元素 石膏样品
含量(%)钾盐样品
含量(%)矿物
组成石膏样品
含量(%)钾盐样品
含量(%)CaO 32.56 0.13 石膏 91.8 - Na2O 1.40 4.60 方解石 4.74 - K2O 0.04 56.50 石盐 2.64 8.67 MgO 0.04 0.014 钾盐 - 89.42 S 17.10 - 总计 99.18 98.09 -
[1] 李勇, 钟建华, 温志峰, 等.蒸发岩与油气生成、保存的关系[J].沉积学报, 2006, 24(4):596-606. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200604018.htm
Li Y, Zhong J H, Wen Z F, et al.Study on the relationship between evaporate and hydrocarbon generation[J].Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(4):596-606. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200604018.htm
[2] Last W M.Mineralogical Analysis of Lake Sediments[M].Dordrecht:Springer Netherlands, 2001.
[3] Guinebretiere R.X-ray Diffraction by Polycrystalline Mat-erials[M].London, Newport Beach, CA:Iste, 2007.
[4] Bish D L, Howard S A.Quantitative phase-analysis using the Rietveld method[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1988, 21:86-91. doi: 10.1107/S0021889887009415
[5] Will G.Powder Diffraction:The Rietveld Method and the Two-stage Method to Determine and Refine Crystal Structures from Powder Diffraction Data[M].New York:Springer, 2006.
[6] Rietveld H M.The Rietveld method[J].Physica Scripta, 2014, 89(9):1-6. http://digilib.batan.go.id/atom-indonesia/fulltex/v19-n2-7-93/InawatiTanto.pdf
[7] Dollase W A.Correction of intensities for preferred orientation in powder diffractometry-application of the march model[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1986, 19:267-272. doi: 10.1107/S0021889886089458
[8] Munson E O, Chalmers G R L, Bustin R M, et al.Utilizing smear mounts for X-ray diffraction as a fully quantitative approach in rapidly characterizing the mineralogy of shale gas reservoirs[J].Journal of Unconventional Oil & Gas Resources, 2016, 14:22-31. https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-unconventional-oil-and-gas-resources/recent-articles/
[9] Buatier M D, Chauvet A, Kanitpanyacharoen W, et al.Origin and behavior of clay minerals in the Bogd fault gouge, Mongolia[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2012, 34:77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2011.10.006
[10] Bish D, Blake D, Vaniman D, et al.The first X-ray diffraction measurements on Mars[J].IUCrJ, 2014, 1:514-522. doi: 10.1107/S2052252514021150
[11] Martin J, Beauparlant M, Lesage J, et al.Development of a quantification method for quartz in various bulk materials by X-ray diffraction and the Rietveld method[J].Powder Diffraction, 2012, 27(1):12-19. doi: 10.1017/S0885715612000036
[12] Santini T C.Application of the Rietveld refinement method for quantification of mineral concentrations in bauxite residues (alumina refining tailings)[J].International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 139:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.04.004
[13] Prandel L V, Saab S C, Brinatti A M, et al.Mineralogical analysis of clays in hardsetting soil horizons by X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction using Rietveld method[J].Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2014, 95:65-68. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2012.12.017
[14] Hestnes K H, Sorensen B E.Evaluation of quanti-tative X-ray diffraction for possible use in the quality control of granitic pegmatite in mineral production[J].Minerals Engineering, 2012, 39:239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2012.06.006
[15] Tammishetti V, Rai B, Ravikumar B, et al. Quan-titative estimation of mineral phases from chemical assays and powder X-ray diffraction Rietveld analysis:A case study on selective flocculation of iron ore slimes[J].Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2016, 69(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s12666-015-0820-5
[16] Kemp S J, Smith F W, Wagner D, et al.An improved approach to characterize potash-bearing evaporite deposits, evidenced in North Yorkshire, United Kingdom[J].Economic Geology, 2016, 111(3):719-742. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.111.3.719
[17] 王春连, 刘成林, 刘宝坤, 等.江陵凹陷古新统光卤石的发现及其钾盐找矿意义[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(1):129-136. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201501010.htm
Wang C L, Liu C L, Liu B K, et al.The discovery of carnallite in paleocene Jiangling Depression and its potash searching significance[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(1):129-136. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201501010.htm
[18] Toby B H.EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2001, 34(2):210-213. doi: 10.1107/S0021889801002242
[19] Young R A.The Rietveld Method[M].United Kingdom:Oxford University Press, 1995.
[20] Toby B H.R factors in Rietveld analysis:How good is good enough?[J].Powder Diffraction, 2006, 21(1):67-70. doi: 10.1154/1.2179804
[21] Mccusker L B, Dreele R B V, Cox D E, et al.Rietveld refinement guidelines[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1999, 32(1):36-50. doi: 10.1107/S0021889898009856
[22] 马礼敦.X射线粉末衍射的新起点——Rietveld全谱拟合[J].物理学进展, 1996, 16(2):251-271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXJ602.004.htm
Ma L D.The new start of X-ray diffraction-Rietveld whole pattern fitting[J].Progress in Physics, 1996, 16(2):251-271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXJ602.004.htm
[23] Bish D, Post J E.Quantitative mineralogical analysis using the Rietvetd full-pattern fitting method[J].American Mineralogist, 1993, 78(9):932-940. http://www.minsocam.org/ammin/AM78/AM78_932.pdf
[24] Moore D M, Reynolds R C.X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals[M].New York:Oxford University Press, 1989.
[25] Klug H P, Alexander L E.X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials (the 2nd edition)[M].New York:Wiley, 1974.
[26] Dewolff P M, Taylor J M, Parrish W.Experimental study of effect of crystallite size statistics on X-ray diffractometer intensities[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 1959, 30(1):63-69. doi: 10.1063/1.1734976
[27] De la Torre A G, Lopez-Olmo M G, Alvarez-Rua C, et al.Structure and microstructure of gypsum and its relevance to Rietveld quantitative phase analyses[J].Powder Diffraction, 2004, 19(3):240-246. doi: 10.1154/1.1725254
[28] 张晶晶, 齐砚勇, 邓磊.Rietveld全谱拟合法计算石灰石中碳酸钙和结晶硅含量[J].中国测试, 2014, 40(3):53-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYCS201403015.htm
Zhang J J, Qi Y Y, Deng L.Rietveld full spectrum fitting quantitative analysis of calcium carbonate and crystalline silicon content in limestone[J].China Measurment & Test, 2014, 40(3):53-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYCS201403015.htm
[29] Wang X B, Sanei H, Dai S F, et al.A novel method to estimate mineral compositions of mudrocks:A case study for the Canadian unconventional petroleum systems[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 73:322-332. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.03.013
[30] Subramanian S, Tammishetti V, Rai B, et al.Concurrent reconciliation of chemical and mineral assays for mineral processing circuits[J].International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 146:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.11.005
[31] Pawloski G A.Quantitative determination of mineral content of geological samples by X-ray diffraction:Reply[J].American Mineralogist, 1987, 72(3):441-443. http://ammin.geoscienceworld.org/content/72/3-4/438
-



 下载:
下载: