Application of ICP-MS to Study REEs Geochemistry of Structure Alteration Rocks in Southwestern Guizhou Province, China
-
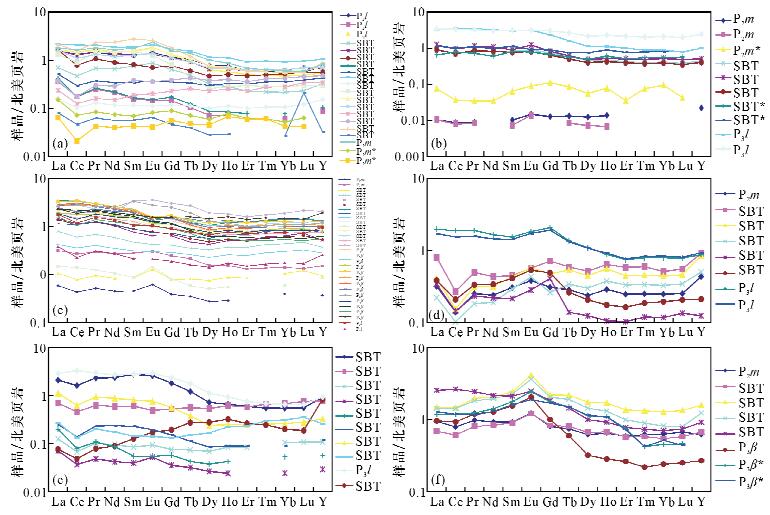
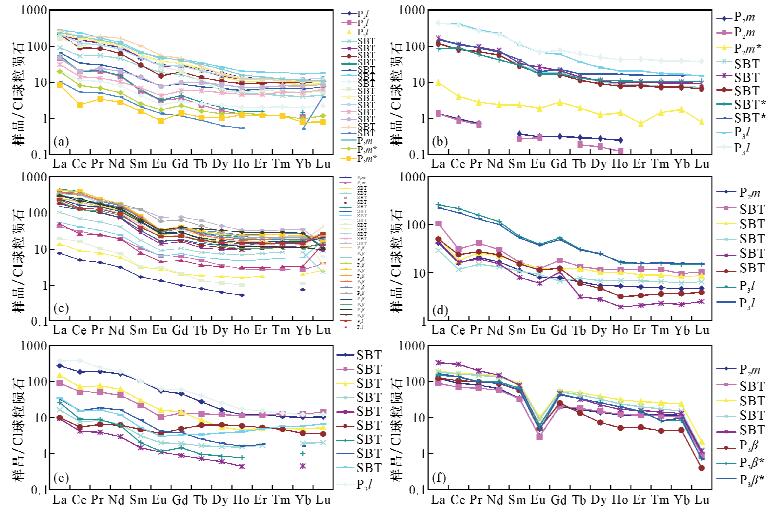
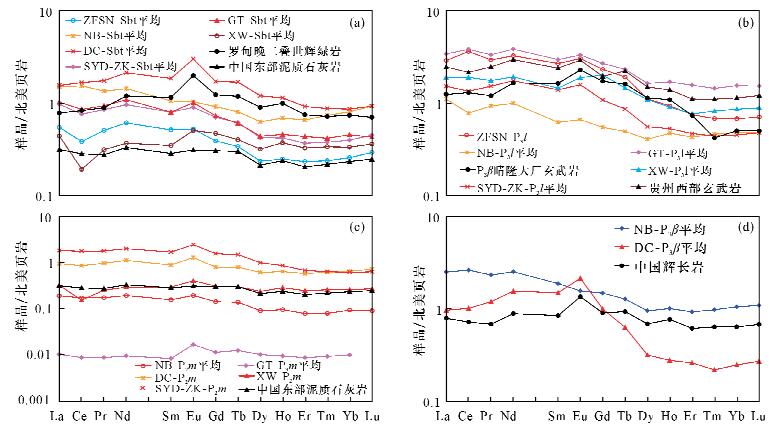
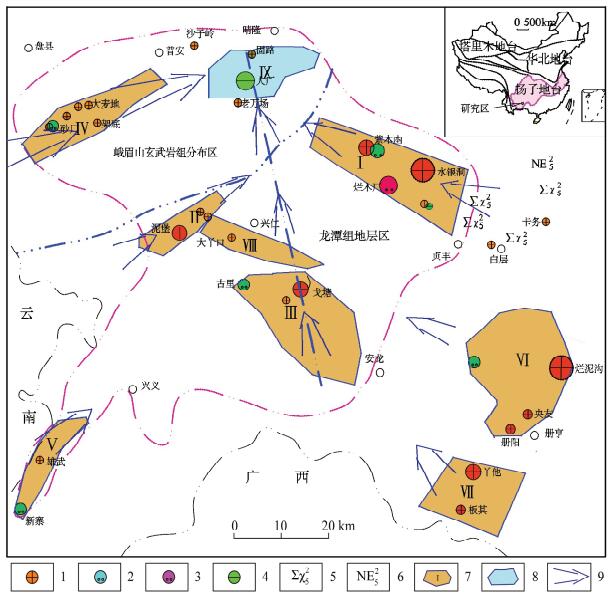
摘要: 构造蚀变体(SBT)是沉积作用、构造作用和热液蚀变的综合产物。SBT作为黔西南地区金、锑、萤石等矿产的重要就位空间,金锑矿成矿与其密切相关。近年在黔西南地区发现了丰富的金资源量,关键在于SBT体系的提出及与之为核心的成矿模式的建立和应用。本文应用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)分析了黔西南台地相区典型矿床的SBT样品,揭示稀土元素的地球化学特征。结果表明,不同矿区SBT的ΣREEs=49.55×10-6~271.72×10-6,含量变化较大,LREEs/HREEs=5.62~13.59,轻重稀土分馏明显,轻稀土富集;SBT对北美页岩和CI球粒陨石标准化配分模式图均表现为轻稀土富集的右倾型、“四分组”效应明显、强烈热液作用,为同一体系的产物;大厂至戈塘一线显示高的正铕异常,推测有两个方向含矿热液在此汇聚。本文系统对比了黔西南地区SBT稀土元素地球化学特征,反映该区成矿流体来源及演化,为本区微细浸染型金矿的成矿预测提供了依据。
-
关键词:
- 黔西南金矿 /
- 构造蚀变体 (SBT) /
- 金矿成矿作用 /
- 稀土元素 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract: The structure alteration rocks (named as SBT) is the product of sedimentation, tectonization, and hydrothermal alteration. It is the major body hosting many ore deposits such as gold, antimony, and fluorite in Southwest Guizhou. Recently establishment and application of a metallogenic model based on the SBT made a significant breakthrough in gold prospecting in Southwest Guizhou. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to determine REEs concentrations of SBT samples from several typical ore deposits in Southwest Guizhou. The results show that: (1) ΣREEs concentrations of SBT from different locations are variable, ranging from 49.55×10-6 to 271.72×10-6 (in Table 1). (2) The SBT is enriched in LREEs, with LREEs/HREEs ranging from 5.62 to 13.59 (in Table 1). The REEs patterns normalized to North American shale and chondrite display enrichment of LREEs and distinct 'Four grouping' effect, indicating that they are the products of the same hydrothermal process (in Fig.2-Fig.4). The strongly positive europium anomalies in the Getang—Dachang area suggest the convergence of two hydrothermal ore fluid systems with different directions in this region. This study characterized the REEs content and its distribution in SBT from Southwest Guizhou Province, which is crucial for understanding the origin and evolution of ore-forming fluids, and provides guidance for gold prospecting in Southwest Guizhou Province. -

-
表 1 黔西南地区SBT稀土元素组成 (×10-6) 及特征参数
Table 1. REEs compositions and characteristic parameters of SBT in Southwestern Guizhou Province
样品编号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ΣREEs LREEs HREEs LREEs
/HREEsLaN/YbN δEu δCe ZFSN-P3l 90.49 239.10 23.02 87.50 15.72 3.56 12.00 1.51 6.43 0.97 2.54 0.34 2.01 0.31 485.50 459.39 26.11 17.60 4.24 1.21 1.24 NB-P2m平均 6.03 11.49 1.38 5.24 0.93 0.23 0.74 0.11 0.53 0.10 0.27 0.04 0.28 0.04 27.41 25.30 2.11 12.01 2.04 1.28 0.95 NB-SBT平均 47.24 102.86 10.69 38.85 6.26 1.23 4.79 0.64 3.66 0.72 2.24 0.37 2.41 0.41 222.36 207.13 15.24 13.59 1.85 1.05 1.08 NB-P3β平均 79.04 174.69 18.40 68.06 11.09 1.85 7.72 1.01 5.54 1.05 3.16 0.49 3.13 0.48 375.70 353.12 22.58 15.64 2.38 0.93 1.09 NB-P3l平均 34.71 51.71 7.35 26.81 3.65 0.78 2.84 0.39 2.36 0.49 1.46 0.23 1.44 0.21 134.42 125.00 9.42 13.27 2.28 1.14 0.77 DC-P2m 29.99 57.36 7.70 30.32 5.24 1.52 4.16 0.63 3.57 0.67 1.98 0.31 1.94 0.32 145.71 132.12 13.58 9.73 1.46 1.53 0.90 DC-SBT平均 49.09 111.56 13.85 57.70 10.95 3.55 8.93 1.34 6.99 1.19 3.14 0.44 2.58 0.41 271.72 246.69 25.03 9.86 1.80 1.68 1.01 DC-P3β 30.52 67.39 9.44 42.19 8.82 2.53 5.19 0.50 1.85 0.29 0.89 0.11 0.74 0.12 170.59 160.88 9.70 16.58 3.87 1.72 0.94 SYD-ZK-P3l平均 47.78 89.32 12.00 46.98 8.19 1.86 5.60 0.68 3.22 0.55 1.59 0.22 1.34 0.21 219.56 206.14 13.42 15.36 3.36 1.28 0.88 SYD-ZK-P2m 57.90 117.80 14.19 54.13 10.04 2.89 8.18 1.18 5.79 0.90 2.31 0.32 1.84 0.28 277.74 256.95 20.80 12.35 2.96 1.49 0.97 SYD-ZK-SBT平均 30.73 50.79 6.77 26.18 4.74 1.07 3.67 0.49 2.47 0.44 1.26 0.19 1.19 0.20 130.19 120.28 9.91 12.14 2.44 1.20 0.83 GT-P3m平均 0.33 0.59 0.07 0.26 0.05 0.02 0.06 0.01 0.06 0.01 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.00 1.52 1.31 0.21 6.41 1.10 1.46 0.94 GT-SBT平均 32.47 57.17 7.44 29.51 4.73 1.20 3.80 0.48 2.56 0.48 1.49 0.21 1.36 0.19 143.10 132.52 10.58 12.53 2.26 1.33 0.87 GT-P3l平均 106.70 252.65 26.17 102.81 17.34 3.89 13.90 1.82 9.46 1.76 5.30 0.72 4.58 0.67 547.75 509.55 38.20 13.34 2.20 1.17 1.13 XW-P2m 10.27 10.24 2.01 7.99 1.76 0.48 1.62 0.24 1.39 0.30 0.85 0.13 0.78 0.12 38.18 32.75 5.43 6.03 1.25 1.32 0.53 XW-SBT平均 13.95 12.95 2.49 10.01 2.07 0.60 2.46 0.32 1.86 0.39 1.12 0.17 1.00 0.16 49.55 42.07 7.48 5.62 1.32 1.23 0.51 XW-P3l平均 59.49 125.80 13.80 51.65 8.53 2.22 10.43 1.15 6.32 0.94 2.59 0.41 2.55 0.39 286.25 261.48 24.77 10.56 2.20 1.09 1.04 罗甸晚二叠世辉绿岩 24.73 55.53 7.09 32.43 6.82 2.35 6.43 0.94 5.26 1.04 2.56 0.36 2.21 0.31 148.05 128.95 19.10 6.75 1.05 1.66 0.99 贵州西部玄武岩 77.10 142.40 19.40 79.40 14.03 3.41 10.09 1.75 8.65 1.44 3.76 0.55 3.38 0.53 365.89 335.74 30.15 11.14 2.15 1.34 0.87 P3β晴隆大厂玄武岩 39.05 86.25 9.47 44.54 9.61 2.68 8.93 1.27 6.58 1.13 2.49 0.21 1.49 0.22 213.89 191.58 22.31 8.59 2.47 1.35 1.06 中国辉长岩 25.00 48.00 5.40 24.00 5.00 1.60 4.70 0.74 4.00 0.80 2.10 0.32 1.90 0.30 123.86 109.00 14.86 7.34 1.24 1.55 0.98 中国东部泥质石灰岩 10.00 19.00 2.20 9.00 1.70 0.37 1.60 0.24 1.25 0.25 0.70 0.11 0.70 0.11 47.23 42.27 4.96 8.52 1.35 1.05 0.96 注:ZFBX—贞丰背斜金矿;NB—泥堡金矿;DC—大厂锑矿;SYD—水银洞金矿;GT—戈塘金矿;XW—雄武金矿。 -
[1] 刘建中, 刘川勤.贵州水银洞金矿床成因探讨及成矿模式[J].贵州地质, 2005, 22(1):9-13. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GZKX200400002046.htm
Liu J Z, Liu C Q.Origin and metallogenic model for Shuiyingdong gold deposit of Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2005, 22(1):9-13. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GZKX200400002046.htm
[2] 刘建中, 夏勇, 张兴春, 等.层控卡林型金矿床矿床模型——贵州水银洞超大型金矿[J].黄金科学技术, 2008, 16(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ200803000.htm
Liu J Z, Xia Y, Zhang X C, et al.Model of strata karlin-type gold deposit:The Shuiyingdong super-scale gold deposit[J].Gold Science and Technology, 2008, 16(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ200803000.htm
[3] 刘建中, 夏勇, 邓一明, 等.贵州水银洞SBT研究及区域找矿意义探讨[J].黄金科学技术, 2009, 17(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ200903002.htm
Liu J Z, Xia Y, Deng Y M, et al.Researches on the Sbt of Shuiyindong gold deposit and significance for regional prospecting[J].Gold Science and Technology, 2009, 17(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ200903002.htm
[4] 贾双琳, 赵平, 杨刚, 等.混合酸敞开或高压密闭溶样ICP-MS测定地质样品中的稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):186-191. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140206&flag=1
Jia S L, Zhao P, Yang G, et al.Quick determination of rare earth elements in geological samples with open acid digestion or high-pressure closed digestion by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):186-191. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140206&flag=1
[5] 赵平, 金会心, 毛小浩, 等.含稀土磷精矿酸解过程稀土的分布规律[J].有色金属 (冶炼部分), 2015(11):33-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201511010.htm
Zhao P, Jin H X, Mao X H, et al.Distribution of Re during acid leaching of REE-bearing phosphorus concentrates[J].Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2015(11):33-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201511010.htm
[6] Qi L, Hu J, Conrad G D.Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2000, 51(3):507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
[7] Su W C, Zhang H T, Hu R Z, et al.Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite from the Shuiyindong carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China:Implications for gold depositional processes[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6):653-662. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0328-9
[8] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts:Implication for the Mantle Composition and Process[M]//Saunder A D, Norry M J.Magmatism in the Ocean Basins.London:Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1989:313-345.
[9] 迟清华, 鄢明才编著.应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:27-51.
Chi H Q, Yan M C.Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2007:27-51.
[10] 韩伟, 罗金海, 樊俊雷, 等.贵州罗甸晚二叠世辉绿岩及其区域构造意义[J].地质论评, 2009, 55(6):795-803. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200906006.htm
Han W, Luo J H, Fan J L, et al.Late permian diabase in Luodian, Southeastern Guizhou, and its tectonic significances[J].Geological Review, 2009, 55(6):795-803. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200906006.htm
[11] 成杭新, 庄广民, 赵传冬, 等.贵州西部Pt、Pd异常源稀土元素地球化学示踪的初步研究[J].地质与勘探, 2003, 39(2):46-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200302010.htm
Cheng H X, Zhuang G M, Zhao C D.A preliminary study on REE geochemical trace for anomaly source of Pt and Pd in Western Guizhou Province[J].Geology and Prospecting, 2003, 39(2):46-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200302010.htm
[12] 陈代演.滇东黔西区层控锑、汞矿床的元素组合及其产生原因初析[J].矿产与地质, 1993, 7(4):247-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD199304002.htm
Chen D Y.Element assosiations and their genesis in strata-bound Sb-Hg ore deposit in Eastern Yuanan and Western Guizhou[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 1993, 7(4):247-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD199304002.htm
[13] 韩吟文, 马振东编著.地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003.
Han Y W, Ma Z D.Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2003.
[14] 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华编著.稀土元素地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989.
Wang Z G, Yu X Y, Zhao Z H.Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1989.
[15] 张瑜, 夏勇, 王泽鹏, 等.贵州簸箕田金矿单矿物稀土元素和同位素地球化学特征[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(2):385-395. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002041.htm
Zhang Y, Xia Y, Wang Z P, et al.REE and stable isotope geochemical characteristics of Bojitian gold deposit, Guizhou Province[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2):385-395. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002041.htm
[16] 夏勇.贵州贞丰县水银洞金矿床成矿特征和金的超常富集机制研究[D].贵阳:中国科学院地球化学研究所, 2005.
Xia Y.Characteristics and model for shuiyindong gold deposit in Southwestern Guizhou, China[D].Guiyang:Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005.
[17] Wang Z P, Xia Y, Song X Y, et al.Study on the evolution of ore-formation fluids for Au-Sb ore deposits and the mechanism of Au-Sb paragenesis and differentiation in the Southwestern part of Guizhou Province, China[J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2013, 32:56-68. doi: 10.1007/s11631-013-0607-5
-



 下载:
下载: