Determination of Sulfur in High-sulfur Bauxite by Alkali Fusion-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry
-
摘要: 应用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)测定高硫铝土矿(硫含量≤8%)中的硫时,由于硫存在-2、+4和+6等多种价态,常用的酸溶法和碱熔法处理高硫铝土矿时往往无法完全氧化硫而导致硫测定结果偏低。本文用过氧化钠熔融、热水浸取和盐酸酸化提取高硫铝土矿中的硫,使用基体匹配法绘制校准曲线补偿铝和钠对硫测定的光谱干扰,以S182.034 nm(184 nm)作为分析谱线,采用ICP-OES对硫进行测定。结果表明:3 g过氧化钠在700℃下熔融10 min,可以较好地氧化高硫铝土矿中的硫;校准曲线的线性相关系数为0.9999,方法检出限为0.025 μg/mL,相对标准偏差(RSD,n=6)小于5%;与碳硫仪的测定结果相比较,两种方法无显著性差异。本方法溶样彻底,无样品损失,为今后实现应用ICP-OES同时测定高硫铝土矿中的硫和其他元素奠定了基础。
-
关键词:
- 铝土矿 /
- 硫 /
- 过氧化钠碱熔 /
- 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法
Abstract: When Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) is used to analyze the sulfur content of high-sulfur (S≤8%) bauxite, commonly used acid dissolving and alkali fusion methods cannot oxidize sulfur completely, leading to a false (lower) result of sulfur due to multiple valences of sulfur (-2, +4, +6). In this study, high-sulfur bauxite samples were fused with sodium hydroxide and leached out by hot water and hydrochloric acid, and the calibration curve was plotted through a matrix matching method to compensate for the spectral interferences of aluminum and sodium on sulfur. S182.034 nm (184 nm) was selected as the analytical line, and sulfur was analyzed by ICP-OES. Results show that sulfur in high-sulfur bauxite samples is completely oxidized with 3 g sodium peroxide at 700℃ for 10 min. The linear correlation coefficient of the calibration curve was 0.9999, the detection limit was 0.025 μg/mL, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=6) was less than 5%. Compared with the results of carbon sulfur analysis, there are no significant differences between the two methods. This method has the advantage of completely decomposing the samples without any loss, which will lay the foundations for the simultaneous determination of sulfur and other elements in high-sulfur bauxite by ICP-OES. -

-
表 1 不同溶样方法的比较
Table 1. Comparison of analytical results of sulfur with different dissolution methods
溶样方法 溶解状况 硫含量ICP-OES测定结果 样品1 样品2 样品3 平均值 (%) 绝对误差 (%) 平均值 (%) 绝对误差 (%) 平均值 (%) 绝对误差 (%) 盐酸+硝酸+氢氟酸+高氯酸 未溶清 0.50 -0.07 1.48 -0.20 2.00 -0.28 氢氧化钠 溶清 0.49 -0.08 1.46 -0.22 1.98 -0.30 氢氧化钠+过氧化钠 溶清 0.52 -0.05 1.55 -0.13 2.10 -0.18 过氧化钠 溶清 0.55 -0.02 1.64 -0.04 2.22 0.06 碳硫仪测定结果 0.57 - 1.68 - 2.28 - 注:绝对误差=ICP-OES测定值-碳硫仪测定值。 -
[1] 杨权平, 吕鲜翠.高硫铝土矿生产冶金级氧化铝的工业实践[J].轻金属, 2012(7):10-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS201207004.htm
Yang Q P, Lü X C.The industrial practice of producing metallurgical grade alumina from high sulfur bauxite[J].Light Metals, 2012(7):10-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS201207004.htm
[2] Hu X L, Chen W M, Xie Q L.Sulfur phase and sulfur removal in high sulfur-containing bauxite[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(7):1641-1647. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60908-4
[3] 付世伟.贵州高硫铝土矿开发利用前景分析[J].矿产勘查, 2011, 2(2):159-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201102013.htm
Fu S W.Prospection analysis of development of high-sulfur bauxite of Guizhou[J].Mineral Exploration, 2011, 2(2):159-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201102013.htm
[4] Yin J G, Han M R, Yang W Q, et al.Roasting pretreatment of high-sulfur bauxite with low-median grade in Chongqing, China[M].Light Metals, 2015:11-14.DOI:10.1002/9781119093435.ch2.
[5] Ge L, Gong X Z, Wang Z, et al.Sulfur removal from bauxite water slurry (BWS) electrolysis intensified by ultrasonic[J].Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2015, 26(9):142-148.
[6] Liu Z W, Li W X, Ma W H, et al.Research on digestion behavior of sulfur in high-sulfur bauxite[M].Light Metals, 2015:39-43.DOI: 10.1002/9781119093435.ch7.
[7] 胡小莲. 高硫铝土矿中硫在溶出过程中的行为及除硫工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011: 16-20.
Hu X L.Study on the behavior of sulfur during the digestion process of high sulfur-containing bauxite and on the process of sulfur removal[D].Changsha:Central South University, 2011:16-20.
[8] 唐华应, 方艳, 刘惠丽.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定钒铁中硫含量[J].冶金分析, 2013, 33(9):70-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201309021.htm
Tang H Y, Fang Y, Liu H L.Determination of sulfur in ferrovanadium by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(9):70-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201309021.htm
[9] 苏凌云.低温逆王水溶样-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定铁矿中硫和磷[J].冶金分析, 2014, 34(11):69-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201411014.htm
Su L Y.Determination of sulfur and phosphorus in iron ore by inductively coupled plasma atomic spectrometry after sample dissolution with inverse aqua reqia in low temperature[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(11):69-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201411014.htm
[10] 薛静, 李清昌.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定矿物中的常量硫[J].有色矿冶, 2013, 29(3):95-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKY201303033.htm
Xue J, Li Q C.Determination of constant sulfur in mineral by ICP-AES[J].Non-ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2013, 29(3):95-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKY201303033.htm
[11] 杜米芳, 任红灿, 岑治宝, 等.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法同时测定白云石中铁铝钙镁钾钠硫[J].岩矿测试, 2006, 25(3):276-278. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060388&flag=1
Du M F, Ren H C, Cen Z B, et al.Simultaneous determination of Fe, Al, Ca, Mg, K, Na, S in dolomite samples by ICP-AES with microwave digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2006, 25(3):276-278. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060388&flag=1
[12] 陈广志, 苏明跃, 王昊云.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定煤中磷[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(4):477-480. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110417&flag=1
Chen G Z, Su M Y, Wang H Y.Determination of phosphorus in coal samples by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry with microwave digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(4):477-480. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110417&flag=1
[13] 年季强, 顾锋, 朱春要, 等.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定萤石中硅铁镁钾钠磷硫[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(4):39-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201504009.htm
Nian J Q, Gu F, Zhu C Y, et al.Determination of silicon, ferric, magnesium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus and sulphur in fluorite by microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(4):39-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201504009.htm
[14] 王琰, 孙洛新, 张帆, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定含刚玉的铝土矿中硅铝铁钛[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(5):719-723. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130509&flag=1
Wang Y, Sun L X, Zhang F, et al.Determination of Si, Al, Fe and Ti in bauxite by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):719-723. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130509&flag=1
[15] 金献忠, 谢健梅, 梁帆, 等.碱熔融-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定铬矿石中铬铝铁镁硅[J].冶金分析, 2010, 30(1):29-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201001006.htm
Jin X Z, Xie J M, Liang F, et al.Determination of chromium, aluminum, iron, magnesium and silicon in chromium ore by alkali fusion-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2010, 30(1):29-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201001006.htm
[16] 高小飞, 倪文山, 姚明星, 等.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定黑钨精矿中痕量硫磷[J].冶金分析, 2012, 32(6):30-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201206009.htm
Gao X F, Ni W S, Yao M X, et al.Determination of trace sulfur and phosphorus in wolframite concentrate by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2012, 32(6):30-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201206009.htm
-



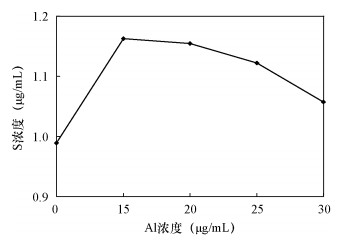
 下载:
下载: