Hydrochemistry Characteristics in front of the Wulixia Reservoir Dam Associated with Feedback from Aerobic Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria
-
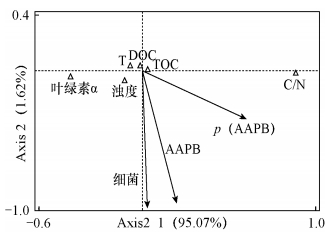
摘要: 微生物是水体生物地球化学循环的主要驱动者,也是能量代谢的主要参与者,在水体生态系统多样性与稳定性方面发挥着举足轻重的作用。好氧不产氧光合细菌(AAPB)是水体中一类分布广泛的重要功能类群,它们可利用光能补充自身能量代谢,并影响水体化学组分,其重要性被人们广泛认可并深入研究。为探讨岩溶区AAPB反馈作用下的五里峡水库坝前水体化学特征,本文对坝前不同层位水体进行实地监测,在获得不同层位水体溶解有机碳和颗粒有机碳稳定碳同位素特征的基础上,采用荧光定量PCR技术检测、研究了坝前水体不同层位AAPB分布规律。结果表明:取样期五里峡水库坝前水体为HCO3--Ca2+-Mg2+贫-中营养型;通过水体溶解氧、δ13CPOC、δ13CDOC和碳氮比综合分析得出,坝前水体有机碳主要由微型生物产生;AAPB占总浮游细菌的相对丰度范围在1.33%~1.60%,且AAPB在不同层位的丰度变化强度要高于总浮游细菌的丰度变化强度,表明相较于总浮游细菌,AAPB对水化学特征的反馈作用更加敏感;使用典范对应分析可揭示水体理化性质与AAPB的内在联系,结果显示AAPB和总浮游细菌均受浊度的影响较大,故基于颗粒沉降的海洋微生物泵作用也适用于陆地岩溶水库。因而,AAPB反馈作用下的水化学特征对揭示CO2-水-碳酸盐岩-微生物代谢体系具有重要的启示意义。Abstract: Micro-organisms are the main drivers of the water biogeochemical cycle and the major player in energy metabolism, which are pivotal processes for maintaining diversity and stability in ecological water systems. Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria (AAPB), the important functional groups widespread in the water, can acquire energy from light and further affect the hydrochemical composition. The importance of AAPB is well recognized and has been studied extensively. In order to study the relationship between the hydrochemical characteristics and the AAPB feedback effect in front of the Wulixia Reservoir dam, water samples from different layers were collected. Based on the stable carbon isotope of dissolved organic carbon and particulate organic carbon isotope composition, the distribution pattern of AAPB was measured by real-time PCR technology. Results show that the hydrochemical type in the front of the reservoir dam water system was HCO3--Ca2+-Mg2+ type and had a poor-moderate eutrophication state during the sampling period. The results of dissolved oxygen, stable carbon isotope and the C/N showed that the main source of organic carbon was produced by micro-organisms. The ratio of AAPB to total planktonic bacteria in the Wulixia Reservoir water was 1.33%-1.60%, and the variation degree of AAPB abundance was greater than that of the total planktonic bacteria abundance, which means that the AAPB feedback is more sensitive to the hydrochemical characteristics compared with that of total planktonic bacteria. The canonical correspondence analysis reveals the relationship between hydrochemical composition and AAPB. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) results show that AAPB and total planktonic bacteria are strongly influenced by turbidity, which makes it possible to apply marine microbiological pump theory in karst reservoirs. Hydrochemical characteristic feedback on AAPB will improve understanding of the metabolic system of CO2-H2O-carbonate and micro-organisms.
-

-
表 1 五里峡水库坝前水体的物理化学特征
Table 1. The physicochemical characterisitics of water sample in front of Wulixia Reservoir dam
环境因子 层位 (m) 0 2 4 6 8 水温 (℃) 13.36 13.34 13.38 13.39 13.39 Chla (μg/L) 0.87 3.02 2.66 3.20 4.59 pH 7.97 7.88 7.83 7.82 7.79 电导率 (μS/cm) 90.70 90.70 90.70 90.65 90.68 DO (mg/L) 9.45 9.36 9.34 9.31 9.28 浊度 (FNU) 4.58 4.34 4.65 4.30 6.23 ORP (mV) 139.40 141.75 150.03 160.55 166.76 TSI 23.08 36.64 35.29 37.29 41.22 TDS (mg/L) 36.64 36.64 36.64 36.64 36.64 硬度 (mg/L) 35.29 35.29 35.29 35.29 35.29 DOC (mg/L) 1.22 1.13 1.16 0.98 0.98 TOC (mg/L) 1.40 1.08 1.24 1.05 1.05 TN (mg/L) 1.21 1.11 1.03 0.98 0.93 K+ (mg/L) 0.63 0.65 0.62 0.67 0.65 Na+(mg/L) 0.45 0.46 0.49 0.46 0.44 Ca2+(mg/L) 14.78 15.80 14.60 12.89 12.58 Mg2+(mg/L) 2.74 2.73 2.75 2.77 2.76 Cl-(mg/L) 1.31 1.31 1.34 1.30 1.31 SO4-(mg/L) 3.01 2.99 3.00 2.98 2.97 HCO3-(mg/L) 51.55 51.55 51.55 44.68 44.68 SIc -0.70 -0.73 -0.82 -0.93 -0.98 SId -1.97 -2.07 -2.20 -2.38 -2.46 pCO2(×10-6 Pa) 3.29 3.22 3.17 3.22 3.19 注:pH、TSI、SIc和SId均为无量纲指标。 表 2 五里峡水库坝前水体碳同位素和C/N值
Table 2. Carbon isotope and C/N values of water sample in front of the Wulixia Reservoir dam
层位 (m) δ13CPOC(‰) δ13CDOC(‰) C/N 0 -29.65 -25.41 1.16 2 -27.77 -24.08 0.97 4 -29.09 -24.41 1.21 6 -29.19 -25.48 1.08 8 -29.79 -25.20 1.14 表 3 五里峡水库坝前水体16S rRNA与pufM基因归一化拷贝数
Table 3. The CNV of 16S rRNA and pufM genefrom water sample in front of the Wulixia Reservoir dam
层位 (m) 16S rRNA总拷贝数×1010(拷贝/mL) 16S rRNA归一化拷贝数 pufM基因总拷贝数×108(拷贝/mL) pufM基因归一化拷贝数 p(AAPB)(%) 0 6.50 0.20 10.40 0.22 1.60 2 4.76 0.15 6.32 0.13 1.33 4 7.55 0.24 11.30 0.24 1.50 6 5.28 0.17 8.16 0.17 1.54 8 7.69 0.24 11.50 0.24 1.49 注:16S rRNA归一化拷贝数、pufM基因归一化拷贝数均为无量纲指标。 -
[1] Fei Z, Hua L J, Qiang L I, et al.The research of typical microbial functional group reveals a new oceanic carbon sequestration mechanism—A case of innovative method promoting scientific discovery[J].Science China-Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(3):456-463. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5202-7
[2] Hall K, Arocena J M, Boelhouwers J, et al.The influence of aspect on the biological weathering of granites:Observations from the Kunlun mountains, China[J].Geomorphology, 2005, 67(1-2):171-188. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.09.027
[3] Kolber Z S, Falkowski P G.Contribution of aerobic photoheterotrophic bacteria to the carbon cycle in the ocean[J].Science, 2001, 292(5526):2492-2495. doi: 10.1126/science.1059707
[4] Rawat M, Moroney J V.The regulation of carbonic anhydrase and ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase by light and CO2 in chlamydomonas reinhardtii[J].Plant Physiology, 1995, 109(3):937-944. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.3.937
[5] Shi L M, Cai Y F, Chen Z T, et al.Diversity and abundance of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in two cyanobacterial bloom-forming lakes in China[J].Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 2010, 46(4):233-239. doi: 10.1051/limn/2010024
[6] Yurkov V, Csotonyi J T.New light on aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs[J].Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration, 2009, 28:31-55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-8815-5
[7] Jiao N Z, Zhang F, Hong N.Significant roles of bacterio chlorophylla supplemental to chlorophylla in the ocean[J].The ISME Journal, 2010, 4(4):595-597. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.135
[8] 焦念志.海洋微型生物生态学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2006:580.
Jiao N Z.Marine Microbial Ecology[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2006:580.
[9] Sieracki M E, Gilg I C, Thier E C, et al.Distribution of planktonic aerobic anoxygenic photoheterotrophic bacteria in the Northwest Atlantic[J].Limnology and Oceanography, 2006, 51(1):38-46. doi: 10.4319/lo.2006.51.1.0038
[10] Koblížek M.Ecology of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs in aquatic environments[J].FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2015, 39(6):854-870. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv032
[11] Lew S, Koblížek M, Lew M, et al.Seasonal changes of microbial communities in two shallow peat bog lakes[J].Folia Microbiologica, 2015, 60(2):165-175. doi: 10.1007/s12223-014-0352-0
[12] Hojerová E, Mašín M, Brunet C, et al.Distribution and growth of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs in the mediterranean sea[J].Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 13(10):2717-2725. doi: 10.1111/emi.2011.13.issue-10
[13] Mašín M, Ĉuperová Z, Hojerová E, et al.Distribution of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs in glacial lakes of Northern Europe[J].Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2012, 66(1):77-86. doi: 10.3354/ame01558
[14] Caliz J, Casamayor E O.Environmental controls and composition of anoxygenic photoheterotrophs in ultraoligotrophic high-altitude lakes (Central Pyrenees)[J].Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2014, 6(2):145-151. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12142
[15] Fauteux L, Cottrell M T, Kirchman D L, et al.Patterns in abundance, cell size and pigment content of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria along environmental gradients in Northern Lakes[J].PLoS One, 2015, 10(4):e0124035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124035
[16] Lew S, Lew M, Koblížek M.Influence of selected environmental factors on the abundance of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs in peat-bog lakes[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(14):13853-13863. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6521-8
[17] Jonsson A, Meili M, Bergström A K, et al.Whole-lake mineralization of allochthonous and autochthonous organic carbon in a large humiclake (Örträsket N, Sweden)[J].Limnology and Oceanography, 2001, 46(7):1691-1700. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.7.1691
[18] 曹建华, 袁道先, 潘根兴, 等.岩溶动力系统中的生物作用机理初探[J].地学前缘, 2001, 8(1):203-209. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200101042.htm
Cao J H, Yuan D X, Pan G X, et al.Preliminary study on biological action in karst dynamic system[J].Earth Science Frontier, 2001, 8(1):203-209. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200101042.htm
[19] 周玉婵, 曹建华, 李小方.水化学对水体着生微型生物群落组成与丰度的影响——以桂林毛村表层岩溶泉、砂页岩裂隙泉为例[J].中国岩溶, 2008, 27(3):261-265. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200803013.htm
Zhou Y C, Cao J H, Li X F.Comparison of periphyton community composition and abundance under different hydro-chemical influences between epikarst spring and sand-shale fissure spring in Maocun, Guilin[J].Carsologica Sinica, 2008, 27(3):261-265. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200803013.htm
[20] 李强, 靳振江.岩溶生物地球化学研究的进展与问题[J].中国岩溶, 2016, 35(4):349-356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201604001.htm
Li Q, Jin Z J.Perspectives on karst biogeochemistry[J].Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(4):349-356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201604001.htm
[21] Muyzer G, Waal E C D, Uitterlinden A G.Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(3):695-700. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gerard_Muyzer/publication/237569474_Profiling_ofComplexMicrobial_Populations_byDenaturing_Gradient_GelElectrophoresis_Analysis_ofPolymerase_Chain_Reaction-Amplified_GenesCodingfor16SrRNA/links/00b7d528e7121b1532000000.pdf
[22] 陈晓洁, 曾永辉, 简纪常, 等.玛珥湖好氧不产氧光合细菌pufM基因DNA和mRNA的定量及多样性分析[J].微生物学通报, 2012, 39:1560-1572. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/WSWT201211001.htm
Chen X J, Zeng Y H, Jian J C, et al.Genetic diversity and quantification of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in Hugangyan Maar lake based on pufM DNA and mRNA analysis[J].Microbiology China, 2012, 39:1560-1572. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/WSWT201211001.htm
[23] Jin Z, Tai J, Pan G, et al.Comparison of soil organic carbon, microbial diversity and enzyme activity of wetlands and rice paddies in Jingjiang area of Hubei, China[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45:3773-3781. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZNYK201218011.htm
[24] William M, Lewis J.A revised classification of lakes based on mixing[J].Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1983, 40(10):1779-1787. doi: 10.1139/f83-207
[25] Ruhl N, Deangelis H, Crosby A M, et al.Applying a reservoir functional-zone paradigm to littoral bluegills:Differences in length and catch frequency?[J].PeerJ, 2014, 2:e528. doi: 10.7717/peerj.528
[26] 陈静生, 王飞越, 何大伟, 等.黄河水质地球化学[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(1):58-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200601009.htm
Chen J S, Wang F Y, He D W, et al.Geochemistry of water quality of the Yellow River basin[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(1):58-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200601009.htm
[27] 刘文. 亚热带不同地质背景水库碳转移过程的研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2015.
Liu W.A Study on Carbon Migration Processes in Reservoir with Different Geological Setting in Subtropical Areas, SW China[D].Chongqing:Southwest University, 2015.
[28] Zigah P K, Minor E C, Werne J P.Radiocarbon and stable-isotope geochemistry of organic and inorganic carbon in lake superior[J].Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2012, 26(1):1346. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258644619_Radiocarbon_and_stable-isotope_geochemistry_of_organic_and_inorganic_carbon_in_Lake_Superior
[29] Li W, Wu F, Liu C, et al.Temporal and spatial distributions of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in two small lakes on the Southwestern China plateau[J].Limnology, 2008, 9(2):163-171. doi: 10.1007/s10201-008-0241-9
[30] 蔡庆华, 刘建康.评价湖泊富营养化的一个综合模型[J].应用生态学报, 2002, 13(12):1674-1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.12.037
Cai Q H, Liu J K.A comprehensive model for assessing lake eutrophication[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(12):1674-1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2002.12.037
[31] 蔡庆华.湖泊富营养化综合评价方法[J].湖泊科学, 1997, 9(1):89-94. doi: 10.18307/1997.0114
Cai Q H.Method for assessing lake eutrophication[J].Journal of Lake Science, 1997, 9(1):89-94. doi: 10.18307/1997.0114
[32] 高坤乾, 顾继光, 韩博平.三座不同营养类型水库春季细菌生理群分布特征[J].生态环境, 2006, 15(3):469-474. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200603006.htm
Gao K Q, Gu J G, Han B P.Spatial distribution of heterotrophic bacteria, phosphobacteria and nitrogen-cycle bacteria among different types of reservoirs in spring[J].Geology and Environment, 2006, 15(3):469-474. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ200603006.htm
[33] 张朝能.水体中饱和溶解氧的求算方法探讨[J].环境科学研究, 1999, 12(2):54-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX902.012.htm
Zhang C N.Study on calculation method of saturation values of dissolved oxygen in waters[J].Research of Environmental Science, 1999, 12(2):54-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX902.012.htm
[34] Vähätalo A V, Wetzel R G.Long-term photochemical and microbial decomposition of wetland-derived dissolved organic matter with alteration of 13C:12C mass ratio[J].Limnology and Oceanography, 2008, 53(4):1387. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.4.1387
[35] Raymond P A, Bauer J E.Use of 14C and 13C natural abundances for evaluating riverine, estuarine, and coastal DOC and POC sources and cycling:A review and synthesis[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2001, 32(4):469-485. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00190-X
[36] Zigah P K, Minor E C, Werne J P, et al.Radiocarbon and stable carbon isotopic insights into provenance and cycling of carbon in lake superior[J].Limnology and Oceanography, 2011, 56(3):867-886. doi: 10.4319/lo.2011.56.3.0867
[37] Smith B N, Epstein S.Two categories of 13C/12C ratios for higher plants[J].Plant Physiology, 1971, 47(3):380-384. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.3.380
[38] 吴莹, 张经, 曹建平, 等.长江流域有机碳同位素地球化学特征[J].青岛海洋大学学报 (自然科学版), 2000, 30(2):309-314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY200002019.htm
Wu Y, Zhang J, Cao J P, et al.The character of carbon isotope geochemistry of the Changjiang drainage basin[J].Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao (Natural Science), 2000, 30(2):309-314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY200002019.htm
[39] 许斐, 杨守业, 展望, 等.三峡水库建设对长江下游颗粒有机碳通量及碳同位素组成的影响[J].地球化学, 2011, 40(2):199-208. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201102009.htm
Xu F, Yang S Y, Zhan W, et al.Influence of the impoundment of the Three Gorges reservoir on the flux and isotopic composition of particulate organic carbon in the lower Changjiang mainstream[J].Geochimica, 2011, 40(2):199-208. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201102009.htm
[40] 张彦鹏, 周爱国, 周建伟, 等.石家庄地区地下水中溶解性有机碳同位素特征及其环境指示意义[J].水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(3):12-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201303005.htm
Zhang Y P, Zhou A G, Zhou J W, et al.Characteristics of dissolved organic carbon isotope in groundwater in Shijiazhuang and its environmental implications[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(3):12-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201303005.htm
[41] 于志同, 王秀君, 赵成义, 等.基于多指标分析的博斯腾湖表层沉积物有机碳来源[J].湖泊科学, 2015, 27(5):983-990. doi: 10.18307/2015.0526
Yu Z T, Wang X J, Zhao C Y, et al.Source characterization of organic carbon using elemental, isotopic and nalkanes proxies in surface sediment from Lake Bosten, Xinjiang[J].Journal of Lake Science, 2015, 27(5):983-990. doi: 10.18307/2015.0526
[42] 张飞, 刘纪化, 李强, 等.从微型生物功能类群研究到海洋储碳机制的新认识——方法创新带动科学发现的一个典型案例[J].中国科学 (地球科学), 2016, 46(1):9-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201601002.htm
Zhang F, Liu J H, Li Q, et al.From the microbial function groups research to ocean carbon storage mechanism—A typical case of method innovation in new impetus scientific discovery[J].Science China:Earth Sciences, 2016, 46(1):9-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201601002.htm
[43] 陈晓洁. 湖光岩玛珥湖好氧不产氧光合细菌遗传多样性的分析[D]. 广州: 广东海洋大学, 2012.
Chen X J.Gentic Diversity of Aerobic Anoxgyenic Phototropic Bacteria in Huguangyan Maar Lake[D].Guangzhou:Guangdong Ocean University, 2012.
[44] Fauteux L, Cottrell M T, Kirchman D L, et al.Patterns in abundance, cell size and pigment content of aerobic anoxygenic ahototrophic bacteria along environmental gradients in Northern Lakes[J].PLoS One, 2015, 10(4):1-17. http://udspace.udel.edu/handle/19716/17608
[45] 焦念志, Michaele E S, 张瑶, 等.好氧不产氧光合异养细菌及其在海洋生态系统中的作用[J].科学通报, 2003, 48(6):530-534. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200306001.htm
Jiao N Z, Michael E S, Zhang Y, et al.Aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria and the role in ocean ecosystem[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(6):530-534. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200306001.htm
[46] Hauruseu D, Koblížek M.Influence of light on carbon utilization in aerobic anoxygenic phototrophs[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2012, 78(20):7414-7419. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01747-12
[47] Kirchman D L, Hanson T E.Bioenergetics of photoheter-otrophic bacteria in the oceans[J].Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2013, 5(2):188-199. doi: 10.1111/emi4.2013.5.issue-2
[48] 李强. 环境因子对AAPB的生长和色素表达的影响[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2006.
Li Q.Effects of Carbon Source and Salinity on Population Structure of Aerobic Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria in Lake Ulansuhai[D].Xiamen:Xiamen University, 2006.
[49] 赵吉睿. 碳源和盐度对乌梁素海水体好氧不产氧光合细菌群落结构影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2013: 37-41.
Zhao J R.Effects of Carbon Source and Salinity on Population Structure of Aerobic Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria in Lake Ulansuhai[D].Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2013:37-41.
[50] Jiao N Z, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, et al.Distinct distribution pattern of abundance and diversity of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in the global ocean[J].Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 9(12):3091-3099. doi: 10.1111/emi.2007.9.issue-12
[51] 焦念志, 骆庭伟, 张瑶, 等.海洋微型生物碳泵——从微型生物生态过程到碳循环机制效应[J].厦门大学学报 (自然科学版), 2011, 50(2):387-401. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZK201102028.htm
Jiao N Z, Luo T W, Zhang Y, et al.Microbial carbon pump in the oceanfrom microbial ecological process to carbon cycle mechanism[J].Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2011, 50(2):387-401. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDZK201102028.htm
[52] 赵子豪. 典型中国海好氧不产氧光合异养细菌 (AAPB) 生长动力学之研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2012.
Zhao Z H.Research of Aerobic Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria (AAPB) Growth Dynamic in Typical China Sea[D].Xiaomen:Xiamen University, 2012.
[53] 赵吉睿, 巩瑞红, 李畅游, 等.三种碳源对乌梁素海好氧不产氧光合细菌群落结构的影响[J].湖泊科学, 2014, 26(1):113-120. doi: 10.18307/2014.0114
Zhao J R, Gong R H, Li C Y, et al.Influence of three kinds of carbon source on community structure of aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria in Lake Ulansuhai[J].Journal of Lake Science, 2014, 26(1):113-120. doi: 10.18307/2014.0114
-




 下载:
下载: