High-precision Measurement of Strontium and Neodymium Isotopic Composition by Multi-collector Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry with Microwave Digestion
-
摘要: 应用多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(MC-ICP-MS)测定地质样品中锶、钕同位素组成时,化学前处理流程冗长、复杂,且容易出现样品未完全溶解的现象。本文采用微波消解法消解样品,在保证消解效果的前提下有效地缩短了溶样时间,在此基础上研究了锶、钕化学分离和质谱测试流程,重点考察了树脂柱的回收率和记忆效应。结果表明:树脂经10次使用后的锶、钕流程空白均低于1.0 ng,但回收率明显下降,分别由原来的98%和90%降到20%和50%,若待测样品中锶、钕含量较低,所接收的锶、钕则达不到质谱仪测试范围,因此建议锶特效树脂使用次数不超过5次,AG50W-X8稀土柱和Ln树脂使用次数不超过10次。整套流程应用于国际地质标准样品(BCR-2、W-2a、BHVO-2、AGV-2)的锶、钕分离,MC-ICP-MS所得的87Sr/86Sr、143Nd/144Nd测定值与文献报道值一致,仪器的内精度2SE(n=50)和方法的外精度2SD(n=6)均优于0.0015%,表明该流程可以满足地质样品中锶、钕同位素高精度测定的要求。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDDetermination of strontium (Sr) and neodymium (Nd) isotopic composition in geological samples by Multi-collector Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS) needs a lengthy and complex chemical preparation procedure. Moreover, samples cannot be dissolved completely. OBJECTIVESTo effectively digest samples and eliminate interferences from the experimental process. METHODSGeological samples were dissolved by microwave digestion. The processes of Sr, Nd chemical separation and mass spectrometry analyses were studied. In particular, the recovery and memory effect of resin column were investigated. RESULTSThe research shows that after ten times usages Sr and Nd procedure, blanks of the resin are less than 1.0 ng. However, the recovery decreases significantly from 98% to 20% and 90% to 50%, respectively. If the analyzed samples contain low concentrations of Sr and Nd, which are insufficient for mass spectrometry analysis, it is suggested that Sr special effect resin should be used no more than 5 times and AG50W-X8 and Ln resin should be used no more than 10 times. The entire procedure is applied in the separation of Sr and Nd of international standard geological samples (BCR-2, W-2a, BHVO-2, AGV-2). The acquired 87Sr/86Sr and 143Nd/144Nd ratios are consistent with those in the literature, and the instrumental internal precision 2SE (n=50) and methodological external precision 2SD (n=6) are better than 0.0015%. CONCLUSIONSThe proposed method meets the requirement of high-precision measurement of Sr and Nd isotopic composition in geological samples. -

-
表 1 微波消解程序
Table 1. Program of the microwave digestion
步骤 温度
(℃)功率
(W)加热时间
(min)保持时间
(min)1 120 400 5 2 2 160 800 5 5 3 180 1200 4 10 表 2 MC-ICP-MS仪器工作参数
Table 2. Working parameters of MC-ICP-MS
工作参数 设定值 冷却气流量 16 L/min 辅助气流量 0.8 L/min 雾化气气压 2.6×105 Pa (via DSN) 射频功率 1100 W 每次测量积分时间 0.4194 s 每组测量次数 10 测量组数 5 表 3 离子交换柱分离锶和钕的流程
Table 3. Procedure of Sr and Nd separation
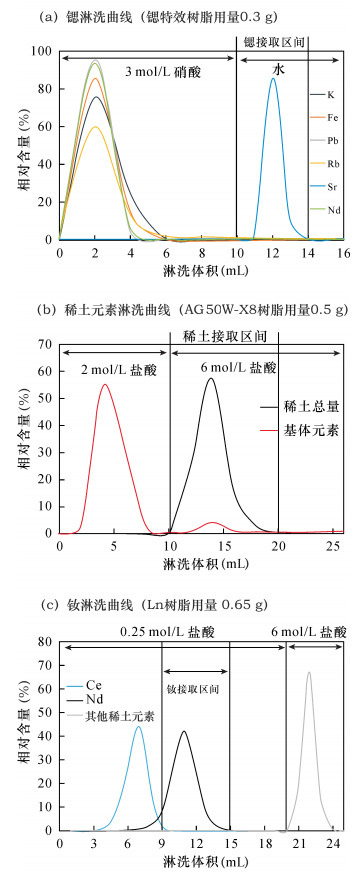
步骤 项目 使用试剂和用量 样品引入 离心后上清液 1 洗脱基体 3 mol/L硝酸,6 mL 洗脱基体 3 mol/L硝酸,4 mL 收集锶 Milli-Q水,4 mL 样品引入 离心后上清液 2 洗脱基体 2 mol/L盐酸,10 mL 收集稀土 6 mol/L盐酸,12 mL 样品引入 离心后上清液 3 洗脱基体 0.25 mol/L盐酸,9 mL 收集钕 0.25 mol/L盐酸,6 mL 注:步骤2中样品为步骤1中前6 mL 3 mol/L硝酸淋洗液蒸干后转为2 mol/L盐酸介质的溶液,步骤3中样品为步骤2收集到的稀土馏分蒸干后转为0.25 mol/L盐酸介质的溶液。 表 4 树脂不同使用次数的流程空白和回收率(n=5)
Table 4. Procedure blanks and recoveries of resin with different times of use (n=5)
树脂使用次数 空白(ng) 回收率(%) Sr Nd Sr Nd 0 0.47 0.34 98 91 5 0.88 0.61 52 73 10 0.92 0.63 23 50 表 5 87Sr/86Sr和143Nd/144Nd测定结果与文献报道值对比
Table 5. Comparison of 87Sr/86Sr and 143Nd/144Nd in standard samples with the reported values
标样编号 87Sr/86Sr同位素测定 143Nd/144Nd同位素测定 fRb/Sr Sr含量
(μg)87Sr/86Sr测试值 内精度
(2SE)87Sr/86Sr平均值 外精度
(2SD)数据来源 fCe/Nd Nd含量
(μg)143Nd/144Nd测试值 内精度
(2SE)143Nd/144Nd平均值 外精度
(2SD)数据来源 BCR-2 0.137 3.21 0.705042 0.000008 0.705046 0.000008 本文 1.89 1.34 0.512642 0.000003 0.512636 0.000004 本文 5.77 0.705056 0.000007 2.40 0.512638 0.000004 6.90 0.705035 0.000009 2.87 0.512632 0.000004 8.67 0.705043 0.000008 3.60 0.512636 0.000005 10.53 0.705047 0.000006 4.37 0.512632 0.000004 13.80 0.705052 0.000006 5.73 0.512633 0.000003 - - - 0.705019 0.000008 Dominique等[16] - - - 0.512634 0.000006 Dominique等[16] BHVO-2 0.025 3.75 0.703488 0.000008 0.703504 0.000013 本文 1.54 1.16 0.512993 0.000004 0.512989 0.000005 本文 6.73 0.703518 0.000009 2.08 0.512984 0.000005 8.05 0.703504 0.000009 2.49 0.512983 0.000005 10.12 0.703521 0.000010 3.13 0.512993 0.000005 12.29 0.703498 0.000008 3.80 0.512984 0.000006 16.10 0.703495 0.000007 4.98 0.512996 0.000006 - - - 0.703487 0.000007 Dominique等[16] - - - 0.512981 0.000006 Dominique等[16] W-2A 0.103 1.85 0.706996 0.000009 0.707003 0.000010 本文 1.77 0.63 0.512503 0.000007 0.512502 0.000003 本文 3.32 0.707011 0.000009 1.14 0.512506 0.000005 3.97 0.707011 0.000007 1.36 0.512502 0.000008 4.99 0.706992 0.000008 1.71 0.512505 0.000007 6.06 0.706995 0.000007 2.07 0.512499 0.000008 7.94 0.707014 0.000010 2.72 0.512499 0.000007 - - - 0.706973 0.000006 Li等[11] - - - 0.512518 0.000004 Li等[11] AGV-2 0.102 6.28 0.704023 0.000010 0.704026 0.000006 本文 2.28 1.43 0.512776 0.000005 0.512784 0.000008 本文 11.26 0.704021 0.000009 2.57 0.512795 0.000005 13.48 0.704031 0.000011 3.08 0.512776 0.000005 16.94 0.704029 0.000006 3.87 0.512784 0.000006 20.56 0.704031 0.000006 4.69 0.512794 0.000006 26.94 0.704018 0.000008 6.15 0.512776 0.000006 - - - 0.703987 0.000009 Dominique等[16] - - - 0.512790 0.000006 Dominique等[16] 注:fRb/Sr为该标样中铷和锶含量的质量比,Sr含量(μg)为样品引入时锶的理论质量。
fCe/Nd为该标样中铈和钕含量的质量比,Nd含量(μg)为样品引入时钕的理论质量。 -
[1] 王文元, 高建国, 侬阳霞, 等.云南禄劝噜鲁铅锌矿床铷-锶同位素年代学与硫、铅同位素地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(7):1294-1304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.07.019
Wang W Y, Gao J G, Nong Y X, et al.Rb-Sr isotopic geochronology and geochemical characteristics of S and Pb isotopes of the Lulu Pb-Zn deposit in Luquan, Yunnan Province[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(7):1294-1304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.07.019
[2] Deng K, Li Q G, Chen Y J, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of the Early Jurassic granodiorite from the Sankuanggou intrusion, Heilongjiang Province, Northeastern China:Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications[J].Lithos, 2018, 296-299:113-128. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.10.016
[3] 刘贤荣, 林晓辉, 于瑞莲, 等.铅-锶-钕同位素示踪技术在PM2.5源解析中的应用[J].环境科学导刊, 2016, 35(5):55-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2016.05.013
Liu X R, Lin X H, Yu R L, et al.Application of Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic tracing technique in the recognition and analysis of PM2.5 pollution sources[J].Environmental Science Survey, 2016, 35(5):55-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9655.2016.05.013
[4] 邵磊, 李长安, 张玉芬, 等.长江上游水系沉积物锶-钕同位素组成及物源示踪[J].沉积学报, 2014, 32(2):290-295. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201402012
Shao L, Li C A, Zhang Y F, et al.Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the upper Yangtze River sediments:Implications for tracing sediment sources[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinca, 2014, 32(2):290-295. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201402012
[5] 刘家军, 吕志成, 吴胜华, 等.南秦岭大巴山大型钡成矿带中锶同位素组成及其成因意义[J].地学前缘, 2014, 21(5):23-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201405003
Liu J J, Lü Z C, Wu S H, et al.Strontium isotopic composition and its genetic significance of the Dabashan large barium metallogenic belt in Southern Qingling mountains[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(5):23-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201405003
[6] 蔡伊, 张乾, 张永斌, 等.桂中镇圩碳酸盐岩型滑石矿床热液方解石的锶同位素研究[J].地球化学, 2015, 44(5):427-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2015.05.003
Cai Y, Zhang Q, Zhang Y B, et al.Strontium isotopic geochemistry of hydrothermal calcites in carbonate-hosted talc deposits at Zhengxu in central Guangxi Province, South China[J].Geochemical, 2015, 44(5):427-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2015.05.003
[7] 侯可军, 秦燕, 李延河, 等.磷灰石Sr-Nd同位素的激光剥蚀-多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱微区分析[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(4):547-554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.04.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/7329324d-bf21-4909-9e66-40d4fb8e7e0d
Hou K J, Qin Y, Li Y H, et al.In situ Sr-Nd isotopic measurement of apatite using laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(4):547-554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.04.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/7329324d-bf21-4909-9e66-40d4fb8e7e0d
[8] Bao Z A, Yuan H L, Zong C L, et al.Simultaneous determination of trace elements and lead isotopes in fused silicate rock powders using a boron nitride vessel and fs LA-(MC)-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31:1012-1022. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00410A
[9] 李杨, 杨岳衡, 焦淑娟, 等.金红石Hf同位素激光原位多接收等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS)测定[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(6):857-869. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201606010.htm
Li Y, Yang Y H, Jiao S J, et al.In situ determination of hafnium isotopes from rutile using LA-MC-ICP-MS[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2015, 58:2134-2144. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201606010.htm
[10] 何连花, 刘季花, 张俊, 等.MC-ICP-MS测定富钴结壳中的铜锌同位素的化学分离方法研究[J].分析测试学报, 2016, 35(10):1347-1350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2016.10.023
He L H, Liu J H, Zhang J, et al.Separation of Cu and Zn in cobalt-rich crusts for isotope determination by MC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2016, 35(10):1347-1350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2016.10.023
[11] Li C F, Li X H, Li Q L, et al.Rapid and precise determination of Sr and Nd isotopic ratios in geological samples from the same filament loading by thermal ionization mass spectrometry employing a single-step separation scheme[J].Analytical Chemical Acta, 2012, 727:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.03.040
[12] Liu H C, Chung C H, You C F, et al.Determination of 87Sr/86Sr and δ88Sr/86Sr ratios in plant materials using MC-ICP-MS[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408:387-397. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9070-y
[13] 宗春蕾, 袁洪林, 戴梦宁.一次溶样分离地质样品中Pb-Sr-Nd方法的可行性研究[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):945-949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120606
Zong C L, Yuan H L, Dai M N.A feasibility study on chemical separation of Pb, Sr and Nd from the same single dissolution of geological sample[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):945-949. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120606
[14] 苟龙飞, 金章东, 邓丽, 等.高效分离Li及其同位素的MC-ICP-MS精确测定[J].地球化学, 2017, 46(6):528-537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.06.003
Gou L F, Jin Z D, Deng L, et al.Efficient purification for Li and high-precision and accuracy determination of Li isotopic compositions by MC-ICP-MS[J].Geochemical, 2017, 46(6):528-537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.06.003
[15] de Carvalho G G A, Oliveira P V, Yang L.Determination of europium isotope ratios in natural waters by MC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32:987-995. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00020K
[16] Dominique W, Bruno K, Claude M, et al.High-precision isotopic characterization of USGS reference materials by TIMS and MC-ICP-MS[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(8):1-30. https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/highprecision-isotopic-characterization-usgs-reference-materials-tims-mcicpms/
[17] 袁永海, 元志红.微波消解-磷钼蓝分光光度法测定钨矿石中的磷含量[J].中国无机分析化学, 2015, 5(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.01.007
Yuan Y H, Yuan Z H.Determination of phosphorus in tungsten ores by microwave digestion-phosphorus molybdenum blue spectrophotometry[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 5(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.01.007
[18] 袁永海, 尹昌慧, 元志红, 等.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法同时测定锡矿石中的砷和锑[J].冶金分析, 2016, 36(3):39-43. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YJFX201603010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Yuan Y H, Yin C H, Yuan Z H, et al.Determination of arsenic and antimony in tin ore by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2016, 36(3):39-43. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YJFX201603010&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[19] 黎卫亮, 程秀花, 李忠煜, 等.碱熔共沉淀-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定橄榄岩中的稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):468-473. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201607130099
Li W L, Cheng X H, Li Z Y, et al.Determination of rare earth elements in peridotite by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry after alkali fusion and Mg(OH)2 and Fe(OH)3 coprecipitation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):468-473. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201607130099
[20] 李潮峰, 李献华, 郭敬辉, 等.微量岩石样品中Rb-Sr和Pb一步分离及高精度热电离质谱测试[J].地球化学, 2011, 40(5):399-406. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201105001
Li C F, Li X H, Guo J H, et al.Single-step separation of Rb-Sr and Pb from minor rock samples and high precision determination using thermal ionization mass spectrometry[J].Geochemical, 2011, 40(5):399-406. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201105001
-



 下载:
下载: