-
摘要: 铁是地球上丰度最高的变价元素,在自然界大量分布于各类矿物、岩石、流体和生物体中,并广泛参与成岩作用、成矿作用、热液活动和生命活动过程。铁同位素组成对地球化学、天体化学和生物化学方面提供重要的信息,是同位素地球化学研究领域的热点。铁同位素的精确测量是开展相关研究的重要基础。本文评述了铁同位素测试技术的研究进展,主要包括:①溶液法测试铁同位素样品纯化过程中阴离子树脂的改进;②质谱分析从传统的热电离质谱法发展为多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱法;③激光微区原位测试技术的研发等。在此基础上,对测试过程中会导致产生铁同位素分馏的步骤和校正方法进行了总结,并对各种测试方法的优缺点进行了评述。本文认为:溶液法分析流程长且复杂,但分析精度高(0.03‰,2SD)、方法稳定;微区原位分析方法从纳秒激光剥蚀发展为飞秒激光剥蚀,脉冲持续时间更短、脉冲峰值强度更高(可达1012W),聚焦强度超过1020W/cm2,使其具有分析速度快、空间分辨率高的优势。微区原位法可以从微观角度去讨论铁同位素变化的地球化学过程,但基体效应的存在限制了微区原位铁同位素的广泛应用。因此,缩短溶液法分析流程,开发系列基体匹配的标准样品,是铁同位素分析方法研发的方向。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDIron is the most abundant element on earth with variable valences. It is widely distributed in various minerals, rocks, fluids and organisms, and is involved in diagenesis, mineralization, hydrothermal activities and life activities. The study of iron isotope composition provides important information for geochemistry, astrochemistry and biochemistry. The accurate measurement of Fe isotopes is an important basis for the development of related research. OBJECTIVESTo summarize the research progress of Fe isotope measurement technology. METHODSThe current chemical separation and purification methods and main instrumental analysis techniques commonly used for iron isotopes, were compared and analyzed in this review, and the mechanism of different types of fractionations during mass spectrometry were discussed. These advances included:(1) Improvement of anion resin during determination of iron isotope by solution method; (2) Mass spectrometry development from traditional thermal ionization mass spectrometry to multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; (3) Development of laser in situ analytical technology. On this basis, the steps and calibration methods that would cause iron isotope fractionation during the analysis were summarized, and the advantages and disadvantages of different analytical methods were reviewed. RESULTSThe analysis process of solution method was long and complicated, but the precision was high (0.03‰, 2SD) and the method was stable. In situ iron isotope analysis method developed from nanosecond laser denudation to femtosecond laser denudation, with shorter pulse duration, higher pulse peak intensity (up to 1012W), and focusing intensity exceeding 1020W/cm2. In situ iron isotope analysis method was fast and had high spatial resolution, which can be used to discuss the geochemical process from the microscopic perspective. However, the presence of matrix effects limited the widespread use of iron isotopes. CONCLUSIONSShortening solution analysis process and developing a series of matrix-matched standard samples are the research direction of iron isotope analysis. -
Key words:
- iron isotope /
- chemical separation /
- solution method /
- mass spectrometry /
- laser ablation /
- matrix effect
-

-
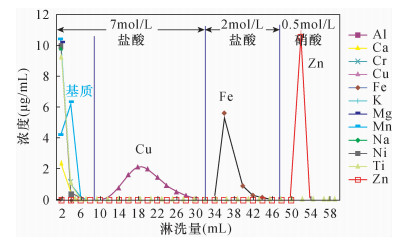
图 1 Fe与基质的化学分离淋洗曲线[33]
Figure 1.
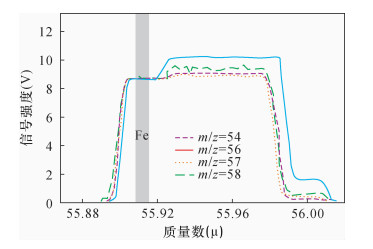
图 2 高分辨率模式下铁同位素与干扰峰的谱峰[33]
Figure 2.
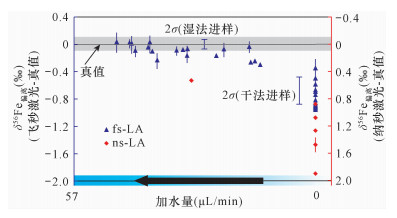
图 3 飞秒激光和纳秒激光剥蚀出气溶胶的粒径对比[91]
Figure 3.
图 4 水蒸汽对飞秒激光和纳秒激光基质效应的抑制对比[93]
Figure 4.
-
[1] Beard B L, Johnson C M.High precision iron isotope measurements of terrestrial and lunar materials[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(11-12):1653-1660. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00089-7
[2] 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟.元素地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1984.
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L.Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1984.
[3] 牟保磊.元素地球化学[M]北京:北京大学出版社, 1999.
Mu B L.Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing:Peking University Press, 1999.
[4] Dauphas N, John S G, Rouxel O.Iron isotope systematics[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2017, 82(1):415-510. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2017.82.11
[5] 何永胜, 胡东平, 朱传卫.地球科学中铁同位素研究进展[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(5):54-71. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201505004
He Y S, Hu D P, Zhu C W.Progress of iron isotope geochemistry in geoscience[J.Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(5):54-71. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201505004
[6] Beard B L, Johnson C M, Skulan J L, et al.Application of Fe isotopes to tracing the geochemical and biological cycling of Fe[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 195(1):87-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=844fae4abeb031e1d538eb65e08bd2f2
[7] Johnson C M, Beard B L, Roden E E.The iron isotope fingerprints of redox and biogeochemical cycling in modern and ancient earth[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2008, 36(1):457-493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.36.031207.124139
[8] Dauphas N, Rouxel O.Mass spectrometry and natural va-riations of iron isotopes[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2006, 25:515-550. doi: 10.1002/mas.20078
[9] Beard B L, Johnson C M, von Damm K L, et al.Iron isotope constraints on Fe cycling and mass balance in oxygenated Earth oceans[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(7):629-632. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0629:IICOFC>2.0.CO;2
[10] Kodolányi J, Stephan T, Trappitsch R, et al.Iron and nickel isotope compositions of presolar silicon carbide grains from supernovae[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 221:127-144. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.05.029
[11] Conway T M, John S G.Quantification of dissolved iron sources to the North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Nature, 2014, 511(7508):212-215. doi: 10.1038/nature13482
[12] Anbar A D.Iron stable isotopes:Beyond biosignatures[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 217(3):223-236. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ025852629/
[13] Labidi J.Iron Isotope Composition of Depleted MORB[C]//Proceedings of Agu Fall Meeting (AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts), 2015.
[14] Teng F Z, Dauphas N, Huang S, et al.Iron isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 107:12-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.12.027
[15] Sossi P A, Nebel O, Anand M, et al.On the iron isotope composition of Mars and volatile depletion in the terrestrial planets[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 449:360-371. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.05.030
[16] Sossi P A, O'Neill H St C.The effect of bonding environment on iron isotope fractionation between minerals at high temperature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 196:121-143. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=941cca5adb4430ecca32fd1de9314be6
[17] Rouxel O, Toner B M, Manganini S J, et al.Geochemistry and iron isotope systematics of hydrothermal plume fall-out at East Pacific Rise 9°50'N[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 441:212-234. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.08.027
[18] Weyer S, Ionov D A.Partial melting and melt percolation in the mantle:The message from Fe isotopes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 259:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.033
[19] Zhao Y, Xue C J, Liu S A, et al.Redox reactions control Cu and Fe isotope fractionation in a magmatic Ni-Cu mineralization system[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 249(15):42-58.
[20] Syverson D D, Luhmann A J, Tan C, et al.Fe isotope fractionation between chalcopyrite and dissolved Fe during hydrothermal recrystallization:An experimental study at 350℃ and 500bars[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 200:87-109. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.12.002
[21] Williams K B, Krawczynski M J, Nie N X, et al.The Role of Differentiation Processes in Mare Basalt Iron Isotope Signatures[C]//Proceedings of Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2016.
[22] Bau M, von Blanckenburg F, Ohmoto H.Iron isotope stratification of Late Archean Seawater:Evidence from dolomites and banded iron-formations[J]. Nature Immunology, 2017, 16 (5):467-75.
[23] McCoy V E, Asael D, Planavsky N.Benthic iron cycling in a high-oxygen environment:Implications for interpreting the Archean sedimentary iron isotope record[J]. Geobiology, 2017, 15(5):619-627. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12247
[24] Liu K, Wu L L, Couture R M, et al.Iron isotope fractionation in sediments of an oligotrophic freshwater lake[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 423:164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.05.010
[25] Kurzweil F, Pasava J, Drost K, et al.Molybdenum (Mo) and Iron (Fe) Isotope Evidence of Tepla-Barrandian Black Shales against Widespread Deep Ocean Oxygenation in the Late Neoproterozoic[C]//Proceedings of the Fall Meeting 2014.American Geophysical Union, 2014.
[26] Severmann S, Lyons T W, Anbar A, et al.Modern iron isotope perspective on the benthic iron shuttle and the redox evolution of ancient oceans[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(6):487-490. doi: 10.1130/G24670A.1
[27] Shollenberger Q R, Brennecka G A, Schuth S, et al.Iron Isotope Systematics of Refractory Inclusions and the Search for the Source of Nucleosynthetic Anomalies[C]//Proceedings of the 48th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2017.
[28] Poitrasson F, Halliday A N, Lee D C, et al.Iron isotope differences between Earth, Moon, Mars and Vesta as possible records of contrasted accretion mechanisms[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(3-4):0-266.
[29] Belshaw N S, Zhu X K, Guo Y, et al.High precision measurement of iron isotopes by plasma source mass spectrometry[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2000, 197(1-3):191-195. doi: 10.1016/S1387-3806(99)00245-6
[30] 唐索寒, 朱祥坤, 李津, 等.用于多接收器等离子体质谱测定的铁铜锌同位素标准溶液研制[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(2):127-133. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.02.003
Tang S H, Zhu X K, Li J, et al.New standard solutions for measurement of iron, copper and zinc isotopic compositions by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(2):127-133. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.02.003
[31] 孙剑, 朱祥坤, 陈岳龙.碳酸盐矿物铁同位素测试的选择性溶解方法研究——以白云鄂博矿床赋矿白云岩为例[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(1):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.01.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/9f80e74f-058d-418d-b894-e133d46d0a1a
Sun J, Zhu X K, Chen Y L.The selective dissolution of carbonate minerals for Fe isotope determination:A case study on the ore-hosting dolomite marble in the Bayan Obo ore deposit[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(1):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.01.005 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/9f80e74f-058d-418d-b894-e133d46d0a1a
[32] 唐索寒, 闫斌, 朱祥坤, 等.玄武岩标准样品铁铜锌同位素组成[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(2):218-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.02.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120204
Tang S H, Yan B, Zhu X K, et al.Iron, copper and zinc isotopic compositions of basaltic standard reference materials[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(2):218-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.02.004 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20120204
[33] 侯可军, 秦燕, 李延河.Fe同位素的MC-ICP-MS测试方法[J].地球学报, 2012, 33(6):885-892. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201206008
Hou K J, Qin Y, Li Y H.High-precision measurements of Fe isotopes using MC-ICP-MS[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2012, 33(6):885-892. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201206008
[34] Zhu X K, Guo Y, Williams R J P, et al.Mass fractionation processes of transition metal isotopes[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 200(1-2):47-62. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00615-5
[35] Rosman K J R, Taylor P D P.Isotopic compositions of the elements 1997 (Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1998, 70(1):217-235. doi: 10.1351/pac199870010217
[36] Kraus K A, Moore G E.Anion exchange studies:The divalent transition elements manganese to zinc in hydrochloric acid[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1953, 75:1460-1462. doi: 10.1021/ja01102a054
[37] Kosler J, Pedersen R B, Kruber C, et al.Comment on "Analysis of Fe isotopes in sulfides and iron meteorites by laser ablation high-mass resolution multi-collector-ICP mass spectrometry"—Reply[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(2):214-216. doi: 10.1039/B512647A
[38] Strelow F W E.Improved separation of iron from copper and other elements by anion-exchange chromatography on a 4% cross-linked resin with high concentrations of hydrochloric acid[J]. Talanta, 1980, 27(9):727-732. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(80)80166-4
[39] Anbar A D.Nonbiological fractionation of iron isotopes[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5463):126-128. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5463.126
[40] Dauphas N, Janney P E, Mendybaev R A, et al. Chromatographic separation and multicollection ICPMS analysis of iron.Investigating mass-dependent and independent isotope effects[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 76(19):5855-5863. doi: 10.1021/ac0497095
[41] van der Walt T N, Strelow F W E, Haasbroek F J.Separation of iron-52 from chromium cyclotron targets on the 2% cross-linked anion-exchange resin AG1-X2 in hydrochloric acid[J]. Talanta, 1985, 32(4):313-317. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(85)80086-2
[42] Marechal C N.Precise analysis of copper and zinc isotopic compositions by plasma-source mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 156(1-4):251-273. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00191-0
[43] Archer C, Vance D.Mass discrimination correction in multiple-collector plasma source mass spectrometry:An example using Cu and Zn isotopes[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(5):656-665. doi: 10.1039/b315853e
[44] Sossi P A, Halverson G P, Nebel O, et al.Combined separation of Cu, Fe and Zn from rock matrices and improved analytical protocols for stable isotope determination[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2015, 39(2):129-149. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.00298.x
[45] Poitrasson F, Freydier R.Heavy iron isotope composition of granites determined by high resolution MC-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 222(1):132-147.
[46] 唐索寒, 闫斌, 李津.少量AG1-X4阴离子交换树脂分离地质标样中的铁及铁同位素测定[J].地球化学, 2013(1):46-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.01.006
Tang S H, Yan B, Li J.Separation of Fe using a small amount of AG1-X4 anion exchange resin and Fe isotope compositions of geological reference materials[J]. Geochimica, 2013(1):46-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.01.006
[47] 马信江, 梁细荣, 涂相林, 等.AG MP-1M阴离子分离Cu、Fe、Zn及其在Fe同位素测定上的应用[J].地球化学, 2009, 38(5):70-76. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx200905007
Ma X J, Liang X R, Tu X L, et al.Separation of Cu, Fe and Zn using AG MP-1M anion exchange resin and applications for Fe isotope determination[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(5):70-76. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx200905007
[48] 孙剑, 朱祥坤, 唐索寒, 等.AG MP-1阴离子交换树脂元素分离方法再研究[J].高校地质学报, 2006, 24(3):398-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.03.014
Sun J, Zhu X K, Tang S H, et al.Further investigation on elemental separation using AG MP-1 anion exchange resin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 24(3):398-403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.03.014
[49] Craddock P R, Dauphas N.Iron isotopic compositions of geological reference materials and chondrites[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2011, 35(1):101-123. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2010.00085.x
[50] Sossi P A, Halverson G P, Nebel O, et al.Combined separation of Cu, Fe and Zn from rock matrices and improved analytical protocols for stable isotope determination[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2015, 39(2):129-149. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.00298.x
[51] Liu S A, Li D, Li S, et al.High-precision copper and iron isotope analysis of igneous rock standards by MC-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2013, 29(1):122-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=be3cff31ad013d50e69a4d2225615a6b
[52] Taylor P D P, Maeck R, Bièvre P D.Determination of the absolute isotopic composition and atomic weight of a reference sample of natural iron[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 1992, 121(1-2):111-125. doi: 10.1016/0168-1176(92)80075-C
[53] Rudge J F, Reynolds B C, Bourdon B.The double spike toolbox[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 265(3-4):0-431. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e97d8b2ef9fa6c95a32479f7de88e1bb
[54] Zhu X K, Makishima A, Guo Y, et al.High precision measurement of titanium isotope ratios by plasma source mass spectrometry[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2002, 220(1):21-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9099dd076fb6a250206f149ef5360336
[55] Kehm K, Hauri E H, Alexander C M O, et al.High precision iron isotope measurements of meteoritic material by cold plasma ICP-MS[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(15):2879-2891. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00080-2
[56] Weyer S, Schwieters J.High precision Fe isotope measurements with high mass resolution MC-ICPMS[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2003, 226:355-368. doi: 10.1016/S1387-3806(03)00078-2
[57] 朱祥坤, 李志红, 赵新苗, 等.铁同位素的MC-ICP-MS测定方法与地质标准物质的铁同位素组成[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2008, 27(4):263-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.04.001
Zhu X K, Li Z H, Zhao X M, et al.High-precision measurement of Fe isotopes isotopes using MC-ICP-MS and Fe isotope compositons of geological regerence materials[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2008, 27(4):263-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2008.04.001
[58] 唐索寒, 朱祥坤, 蔡俊军, 等.用于多接收器等离子体质谱铜铁锌同位素测定的离子交换分离方法[J].岩矿测试, 2006, 25(1):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.01.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20060102
Tang S H, Zhu X K, Cai J J, et al.Chromatographic separation of Cu, Fe and Zn using AG MP-1 anion exchange resin for isotope determination by MC-ICPMS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2006, 25(1):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.01.002 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20060102
[59] Zhu X K, O'Nions R K, Guo Y, et al.Determination of natural Cu-isotope variation by plasma-source mass spectrometry:Implications for use as geochemical tracers[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 163(1):139-149.
[60] Arnold T, Markovic T, Kirk G J D, et al.Iron and zinc isotope fractionation during uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa) grown in oxic and anoxic soils[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2015, 347(7-8):397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2015.05.005
[61] Dideriksen K, Baker J A, Stipp S L S.Iron isotopes in natural carbonate minerals determined by MC-ICP-MS with a 58Fe-54Fe double spike[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(1):0-132. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bd9632e7ee81087155324249c10d032b
[62] Rudge J F, Reynolds B C, Bourdon B.The double-spike toolbox[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 265(3-4):420-431. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.010
[63] Dauphas N, Pourmand A, Teng F Z.Routine isotopic analysis of iron by HR-MC-ICPMS:How precise and how accurate?[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 267(3-4):0-184.
[64] 丁悌平.激光探针稳定同位素分析技术的现状及发展前景[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(2):263-268. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.02.001
Ding T P.The present status and prospect on laser-microprobe analysis techiques for stable isotopes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(2):263-268. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.02.001
[65] Gray A L.Solid sample introduction by laser ablation for inductively coupled plasma source mass spectrometry[J]. Analyst, 1985, 110:551. doi: 10.1039/an9851000551
[66] Horn I, Hinton R W, Jackson S E, et al.Ultra-trace element analysis of NIST SRM 616 and 614 using laser ablation microprobe-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LAM-ICP-MS):A comparison with secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS)[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 21(2):191-203.
[67] Horn I, Rudnick R L, Mcdonough W F.Precise elemen-tal and isotope ratio determination by simultaneous solution nebulization and laser ablation-ICP-MS:Application to U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 164(3):281-301.
[68] Mank A J G, Mason P R D.A critical assessment of laser ablation ICP-MS as an analytical tool for depth analysis in silica-based glass samples[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1999, 14(8):1143-1153. doi: 10.1039/a903304a
[69] Günther D, Heinrich C A.Enhanced sensitivity in laser ablation-ICP mass spectrometry using helium-argon mixtures as aerosol carrier[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1999, 14(9):1363-1368. doi: 10.1039/A901648A
[70] Arrowsmith P.Laser ablation of solids for elemental analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1987, 59:10(10):1437-1444. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1021-ac00137a014/
[71] Norman M D, Pearson N J, Sharma A, et al.Quantitative analysis of trace elements in geological materials by laser ablation ICPMS:Instrumental operating conditions and calibration values of NIST glasses[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 20(2):247-261. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1111-j.1751-908X.1996.tb00186.x/
[72] Horn I, von Blanckenburg F, Schoenberg R, et al.In situ iron isotope ratio determination using UV-femtosecond laser ablation with application to hydrothermal ore formation processes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70:3677-3688. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.05.002
[73] Hirata T, Ohno T.In-situ isotopic ratio analysis of iron using laser ablation-multiple collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS)[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2001, 16(5):487-491. doi: 10.1039/b100946j
[74] Graham S, Pearson N, Jackson S, et al.Tracing Cu and Fe from source to porphyry:In situ determination of Cu and Fe isotope ratios in sulfides from the Grasberg Cu-Au deposit[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 207(3):147-169.
[75] Kosler J, Pedersen R B, Kruber C, et al.Analysis of Fe isotopes in sulfides and iron meteorites by laser ablation high-mass resolution multi-collector ICP mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2005, 21:192-199. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fbe86928b9161dcc69d2fd2ceeda6743
[76] Horn I, Schoenberg R, Blanckenburg F V.Comment on "Analysis of Fe isotopes in sulfides and iron meteorites by laser ablation high-mass resolution multi-collector-ICP mass spectrometry" by J.Košler, R.B.Pedersen, C.Kruber and P.J.Sylvester[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(2):211-213. doi: 10.1039/B504720J
[77] d'Abzac F X, Beard B L, Czaja A D, et al.Iron isotope composition of particles produced by UV-femtosecond laser ablation of natural oxides, sulfides, and carbononates[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(24):11885-11892. doi: 10.1021/ac402722t
[78] d'Abzac F X, Czaja A D, Beard B L, et al.Iron dis-tribution in size-resolved aerosols generated by UV-femtosecond laser ablation:Influence of cell geometry and implications for in situ isotopic determination by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2014, 38 (3):293-309. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.00281.x
[79] Oeser M, Weyer S, Horn I, et al.High-precision Fe and Mg isotope ratios of silicate reference glasses determined in situ by femtosecond LA-MC-ICP-MS and by solution nebulisation MC-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2014, 38:311-328. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.00288.x
[80] Oeser M, Dohmen R, Horn I, et al.Processes and time scales of magmatic evolution as revealed by Fe-Mg chemical and isotopic zoning in natural olivines[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 154:130-150. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.01.025
[81] Teng F Z, Dauphas N, Helz R T, et al.Diffusion-driven magnesium and iron isotope fractionation in Hawaiian olivine[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 308(3-4):0-324. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=026e55831e6dece4fad57dbaa02498a1
[82] Corliss K I S, Dauphas N.Thermal and crystallization histories of magmatic bodies by Monte Carlo inversion of Mg-Fe isotopic profiles in olivine[J]. Geology, 2017, 45(1):67-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4058f6d0500f4241e8d4196792fd28e9
[83] Collinet M, Charlier B, Namur O, et al.Crystallization history of enriched shergottites from Fe and Mg isotope fractionation in olivine megacrysts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 207:277-297. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.03.029
[84] Horn I, von Blanckenburg F.Investigation on elemental and isotopic fractionation during 196nm femtosecond laser ablation multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Spectrochim Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2007, 62:410-422. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2007.03.034
[85] Öder H R.Laser-generated aerosols in laser ablation for inductively coupled plasma spectrometry[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2006, 61(3):284-300. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.02.001
[86] Momma C, Chichkov B N, Nolte S, et al.Short-pulse laser ablation of solid targets[J]. Optics Communications, 1996, 129(1-2):134-142. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(96)00250-7
[87] Russo R E, Mao X, Gonzalez J J, et al.Femtosecond vs.nanosecond laser pulse duration for laser ablation chemical analysis[J]. Spectroscopy, 2013, 28(1):24-39.
[88] Günther D, Hattendorf B.Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2005, 24(3):255-265. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2004.11.017
[89] Koch J, von Bohlen A, Hergenröder R, et al.Particle size distributions and compositions of aerosols produced by near-IR femto- and nanosecond laser ablation of brass[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(2):267-272. doi: 10.1039/B310512A
[90] 陈开运, 范超, 袁洪林, 等.飞秒激光剥蚀-多接收电感耦合等离子质谱原位微区分析青铜中铅同位素组成——以古铜钱币为例[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 32(5):1342-1349. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)05-1342-08
Chen K Y, Fan C, Yuan H L, et al.High-precision in situ analysis of the lead isotopic composition in copper using femtosecond laser ablation MC-ICP-MS and the application in ancient coins[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):1342-1349. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)05-1342-08
[91] 杨文武, 史光宇, 商琦, 等.飞秒激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱在地球科学中的应用进展[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(7):208-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201707036
Yang W W, Shi G Y, Shang Q, et al.Applications of femtosecond (fs) laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in Earth sciences[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(7):208-214. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gpxygpfx201707036
[92] Zheng X Y, Beard B L, Lee S, et al.Contrasting particle size distributions and Fe isotope fractionations during nanosecond and femtosecond laser ablation of Fe minerals:Implications for LA-MC-ICP-MS analysis of stable isotopes[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 450:235-247. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.12.038
[93] Zheng X Y, Beard B L, Johnson C M.Assessment of matrix effects associated with Fe isotope analysis using 266nm femtosecond and 193nm nanosecond laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2018, 33:68-83. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00272F
[94] Teng F Z, Li W Y, Ke S, et al.Magnesium isotopic com-position of the Earth and chondrites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(14):4150-4166. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.04.019
[95] Janney P E, Richter F M, Mendybaev R A, et al.Matrix effects in the analysis of Mg and Si isotope ratios in natural and synthetic glasses by laser ablation-multicollector ICPMS:A comparison of single- and double-focusing mass spectrometers[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 281(1-2):26-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.11.026
[96] Sio C K I, Dauphas N, Teng F Z, et al.Discerning crystal growth from diffusion profiles in zoned olivine by in situ Mg-Fe isotopic analyses[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 123(2):302-321. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=313c4f174cc4f182644f09f4292f62ad
-

| 引用本文: | 秦燕, 徐衍明, 侯可军, 李延河, 陈蕾. 铁同位素分析测试技术研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2): 151-161. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908120120 |
| Citation: | Yan QIN, Yan-ming XU, Ke-jun HOU, Yan-he LI, Lei CHEN. Progress of Analytical Techniques for Stable Iron Isotopes[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2): 151-161. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908120120 |
- Figure 1. Elution curve for Fe element separation
- Figure 2. Peak shape of Fe isotopes and interfering signals at high-resolution mode[33]
- Figure 3. Comparison of aerosols from femtosecond laser ablation and nanosecond laser ablation in ilmenite[91]
- Figure 4. Comparison of nature of matrix effects during in-situ Fe isotope analysis between fs-laser and ns-laser ablation[93]


 下载:
下载: