Concentration of Heavy Metals in Soils and Rice and Its Influence by Soil pH in Jinqu Basin
-
摘要:
作物对土壤中重金属的吸收受作物种类、采集部位及土壤理化性质等多方面因素的影响。近年来,金衢盆地土壤酸化面积逐年增大,酸化程度逐渐加深,其对土壤-作物系统中重金属元素的活动影响尚不明确。本文基于金衢盆地典型地区264组根系土壤-稻米样品分析数据,开展土壤、作物的重金属含量特征及其影响因素的研究,重点讨论了土壤pH对作物吸收重金属的影响。结果表明:①264件土壤中多数重金属元素的变异系数大于0.5,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni和Zn元素之间呈显著正相关(P < 0.01)。土壤Cd超标样品23件,超标率为8.7%;As、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb和Zn超标样品均未超过2件。②稻米中Cu、Zn与Cd含量呈显著正相关,Cd的富集系数(BCF)高于植物营养元素Cu、Zn。③稻米中Zn和Cu在P < 0.1水平上与pH值呈显著正相关。Cd、Cr、Hg的BCF与pH值之间存在一定的负相关性。研究认为,适当调低土壤的酸碱度会削减土壤中Cd、Hg等重金属元素的活性,从而减少农作物对重金属的吸收转运。研究结果可为当地粮食安全生产决策提供科学数据,为土地管护提供参考依据。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The absorption of heavy metals in soil by crops is affected by various factors such as crop types, collection sites and physical and chemical soil properties. In recent years, soil acidification of an area in the Jinqu Basin has increased year by year, and the degree of acidification has gradually deepened.
OBJECTIVES In order to find out the content characteristics of heavy metals in soil and crops, the influence of soil acidification on the absorption of heavy metals by crops was studied.
METHODS Based on 264 samples of root soil-rice samples from a typical area of the Jinqu Basin, the characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal content in soil and crops were studied.
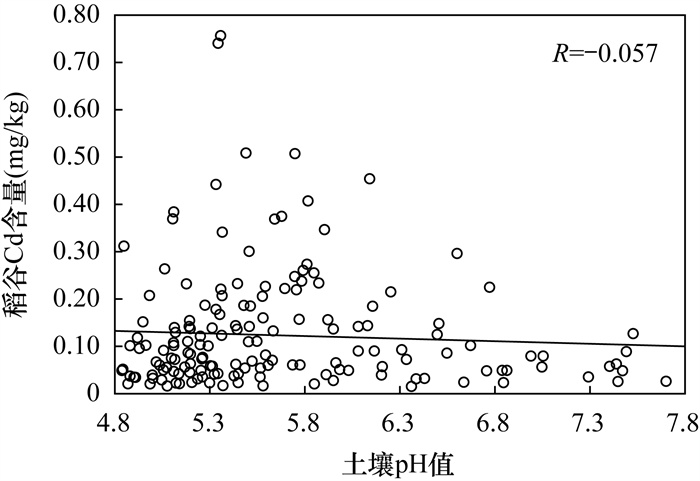
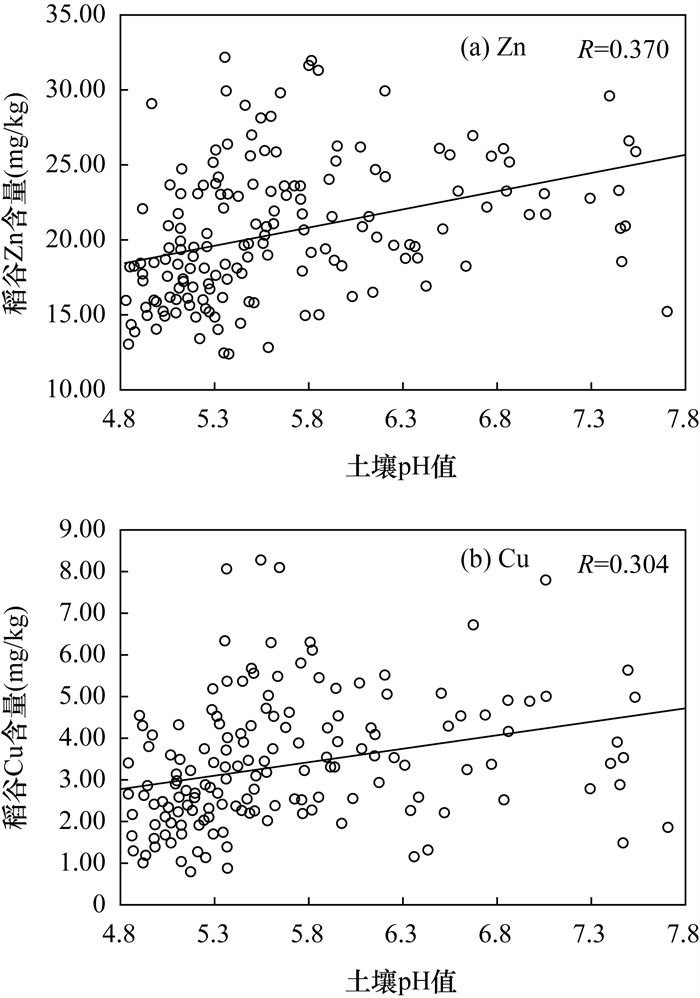
RESULTS The results showed that: (1) The variation coefficient of most heavy metal elements in 264 soil samples was greater than 0.5. Significant positive correlations (P < 0.01) occurred among the elements of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, and Zn in soil. 23 soil samples of Cd exceeded the standard, and the over-standard rate was 8.7%. The soil samples number of other elements(As, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn) exceeding the standard were no more than 2. (2) The contents of Cu, Zn and Cd in rice were positively correlated, and the enrichment coefficient of the toxic heavy metal element Cd was higher than that of plant nutrient elements Cu and Zn. (3) Zn and Cu in rice were positively correlated with soil pH at P < 0.1. Bioconcentration factor (BCF) of Cd, Cr and Hg were negatively correlated with pH.
CONCLUSIONS It is believed that adjusting soil acidity will reduce the activity of Cd, Hg and other heavy metal elements in the soil, in order to achieve the goal of minimizing the absorption and transport of heavy metal elements in crops. The research results provide scientific data for local food production safety decision and reference for land management and protection.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- crops /
- heavy metal content /
- bioconcentration factor /
- influencing factors
-

-
表 1 土壤及作物样品分析方法
Table 1. Analysis methods of the soil and rice samples
样品类型 测定指标或元素 分析方法 检出限 标样合格率(%) 重复样合格率(%) 土壤 pH 电位法 0.1 100.0 100.0 As HG-AFS 1 100.0 100.0 Cd ICP-MS 30 100.0 100.0 Cr 压片制样,XRF 5 100.0 100.0 Cu ICP-MS 1 100.0 100.0 Hg CV-AFS 0.5 100.0 100.0 Ni ICP-MS 2 100.0 100.0 Pb ICP-MS 2 100.0 100.0 Zn ICP-MS 2 100.0 100.0 作物 As 微波消解,AFS 0.1 100.0 100.0 Cd 微波消解,ICP-MS 10 100.0 100.0 Cr 微波消解,ICP-MS 0.2 100.0 100.0 Cu 微波消解,ICP-MS 1 100.0 100.0 Hg 微波消解,ICP-MS 0.5 100.0 100.0 Ni 微波消解,ICP-MS 0.2 100.0 100.0 Pb 微波消解,ICP-MS 0.5 100.0 100.0 Zn 微波消解,ICP-OES 2 100.0 100.0 注:Cd、Hg元素含量检出限单位为ng/g,其余元素均为mg/kg。 表 2 土壤中重金属元素统计值(N=264)、区域背景值与标准限值
Table 2. Concentrations of heavy metals from study area, regional background and the safety limits
统计量 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 最大值(mg/kg) 39.6 2.65 223.2 113.3 2.02 77.5 127.3 583.7 最小值(mg/kg) 1.5 0.10 11.6 6.1 0.02 1.03 21.8 42.9 平均值(mg/kg) 6.0 0.28 50.7 22.6 0.13 17.9 36.2 84.8 中位数(mg/kg) 4.8 0.23 44.3 20.4 0.11 14.2 35.1 76.3 标准差(mg/kg) 4.0 0.24 28.7 12.3 0.14 11.7 9.7 46.1 变异系数(%) 0.67 0.83 0.57 0.55 1.02 0.65 0.27 0.54 全国土壤背景值(mg/kg) 11.2 0.097 53.9 20.0 0.047 23.4 23.6 67.7 金衢盆地背景值(mg/kg) 6.49 0.19 39.1 18.03 0.098 12.45 35.12 72.13 污染累积指数范围(平均值) 0.23~6.10(0.93) 0.51~13.67(1.46) 0.30~5.71(1.30) 0.34~6.28(1.26) 0.23~20.65(1.34) 0.00~6.22(1.44) 0.62~3.63(1.03) 0.59~8.09(1.18) 单项污染指数范围(平均值) 0.05~1.32(0.24) 0.29~3.11(0.76) 0.07~0.72(0.19) 0.12~2.27(0.41) 0.08~4.05(0.29) 0.00~0.89(0.25) 0.12~0.64(0.39) 0.23~1.87(0.40) 表 3 土壤重金属之间的Pearson相关系数
Table 3. Pearson correlation coefficients of heavy metals in soils
重金属元素 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn As 1 - - - - - - - Cd 0.179** 1 - - - - - - Cr 0.298** 0.360** 1 - - - - - Cu 0.192** 0.555** 0.630** 1 - - - - Hg 0.113 0.186** 0.062 0.099 1 - - - Ni 0.243** 0.404** 0.764** 0.625** 0.121 1 - - Pb 0.094 0.581** -0.033 0.173** 0.162** 0.044 1 - Zn 0.164** 0.719** 0.367** 0.613** 0.047 0.451** 0.525** 1 注:标注“**”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 4 稻米重金属含量与超标情况统计(N=264)
Table 4. Contents and statistical characteristics of heavy metals in rices
统计项目 As Cd Cr Cu Hg Ni Pb Zn 含量平均值(mg/kg) 0.154 0.125 0.196 3.157 0.005 0.428 0.071 20.308 稻米安全标准值(mg/kg) - 0.2 1 - 0.02 - 0.2 - 超标件数(件) - 55 1 - 0 - 6 - 稻米超标率(%) - 20.83 0.38 - 0 - 2.27 - 平均富集系数 0.033 0.543 0.005 0.161 0.049 0.031 0.002 0.266 -
[1] 赵其国, 骆永明. 论我国土壤保护宏观战略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2015, 30(4): 452-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201504004.htm
Zhao Q G, Luo Y M. The macro strategy of soil protection in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015, 30(4): 452-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201504004.htm
[2] 徐建明, 孟俊, 刘杏梅, 等. 我国农田土壤重金属污染防治与粮食安全保障[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 153-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201802006.htm
Xu J M, Meng J, Liu X M, et al. Control of heavy metal pollution in farmland of China in terms of food security[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 153-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201802006.htm
[3] 庄国泰. 我国土壤污染现状与防控策略[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2015, 30(4): 476-483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201504007.htm
Zhuang G T. Current situation of national soil pollution and strategies on prevention and control[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015, 30(4): 476-483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX201504007.htm
[4] 赵其国, 黄国勤, 钱海燕. 生态农业与食品安全[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(6): 1127-1134. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.06.024
Zhao Q G, Huang G Q, Qian H Y. Ecological agriculture and food safety[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(6): 1127-1134. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2007.06.024
[5] 张桃林. 科学认识和防治耕地土壤重金属污染[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(3): 435-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201503001.htm
Zhang T L. More comprehensive understanding and effective control of heavy metal pollution of cultivated soils in China[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(3): 435-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201503001.htm
[6] 黎承波. 重金属在土壤-植物系统中的迁移转化研究进展[J]. 山东化工, 2017, 46(14): 186-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2017.14.075
Li C B. Research advance in the migration and transformation of heavy metals in soil-plant system[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(14): 186-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2017.14.075
[7] 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 安溪土壤-茶叶铅含量关系与土壤铅临界值研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201601026.htm
Zhou G H, Sun B B, He L, et al. The relationship of lead concentration between soils and tea leaves and the critical value of lead for soil in Anxi, Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201601026.htm
[8] 赵东杰, 王学求. 滇黔桂岩溶区河漫滩土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028
Zhao D J, Wang X Q. Distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the floodplain soils of the Karst area of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028
[9] 李坤权, 刘建国, 陆小龙, 等. 水稻不同品种对镉的吸收及分配的差异[J]. 农业环境科学报, 2003, 22(5): 529-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200305003.htm
Li K Q, Liu J G, Lu X L, et al. Uptake and distribution of cadmium in different rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2003, 22(5): 529-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200305003.htm
[10] 周国华, 汪庆华, 董岩翔, 等. 土壤-农产品系统中重金属含量关系的影响因素分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2007, 29(1): 227-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT2007S1052.htm
Zhou G H, Wang Q H, Dong Y X, et al. Factors affecting heavy metal concentrations in the soil-agricultural product system[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 29(1): 227-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT2007S1052.htm
[11] Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A. Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced exogenous humic substances[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 52(1): 265-275. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00185-1
[12] Romero F M, Villalobos M, Aguirre R, et al. Solid-phase control on lead bioaccessibility in smelter-impacted soils[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 55: 566-575. doi: 10.1007/s00244-008-9152-3
[13] Madrid F, Diaz-Barrientos E, Madrid L. Availability and bio-accessibility of metals in the clay fraction of urban soils of Sevilla[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 156(3): 605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.023
[14] Moreno A M, Quintana J R, Pérez L, et al. Factors influencing lead sorption-desorption at variable added metal concentrations in rhodoxeralfs[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 64: 758-763. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.058
[15] Vega F A, Covelo E F, Andrade M L. Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils: Influence of mine soil characteristics[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2006, 298(2): 582-592. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S002197970600018X&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1432650164&md5=e525c248d4626a3d2e9e9dee8d068b9f
[16] 夏伟, 吴冬妹, 袁知洋. 土壤-农作物系统中重金属元素迁移转化规律研究——以湖北宣恩县为例[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4): 563-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201804010.htm
Xia W, Wu D M, Yuan Z Y. Study on the migration and transformation law of heavy metals in soil-crop system[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4): 563-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201804010.htm
[17] 李杰, 朱立新, 康志强. 南宁市郊周边农田土壤-农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201801006.htm
Li J, Zhu L X, Kang Z Q. Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system of peri-urban agricultural soils of Nanning, South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201801006.htm
[18] 刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊燕, 等. 西南高镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2877-2884. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906045.htm
Liu Y Z, Xiao T F, Xiong Y, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium, southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2877-2884. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201906045.htm
[19] 潘永敏, 廖启林, 华明, 等. 江苏南部典型地区耕作层土壤及农作物中重金属评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(2): 319-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201402020.htm
Pan Y M, Liao Q L, Hua M, et al. An evaluation of the heavy metal content in the plough layer and crops in southern Jiangsu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(2): 319-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201402020.htm
[20] 温晓华, 张琢, 何中发. 根系土中重金属元素分布特征及在农作物中的迁移[J]. 上海国土资源, 2012(2): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.010
Wen X H, Zhang Z, He Z F. The distribution of heavy metals in the rhizosphere and their migration in crops[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2012(2): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.02.010
[21] 胡留杰, 廖敦秀, 马连杰, 等. 西南茶区土壤-茶树系统重金属研究现状与趋势[J]. 农学学报, 2017(11): 19-22. doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17040010
Hu L J, Liao D X, Ma L J, et al. Heavy metals of soil-tea system in southwest tea area: Research status and trend[J]. Chinese Countryside Well-off Technology, 2017(11): 19-22. doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17040010
[22] 曹宁, 孙彬彬, 曾道明, 等. 珠江三角洲西部典型乡镇稻米与根系土重金属元素含量关系研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 739-752. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912240177
Cao N, Sun B B, Zeng D M, et al. Study on the relationship between the contents of heavy metals in rice and root soils in typical townships in the western Pearl River Delta[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 739-752. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912240177
[23] 王腾云, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 等. 福建沿海地区土壤-稻谷重金属含量关系及影响因素研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3): 295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.013
Wang T Y, Zhou G H, Sun B B, et al. The relationship between heavy metal contents of soils and rice in coastal areas, Fujian Province, including influencing factors[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3): 295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.013
[24] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 郭飞, 等. 广西典型岩溶区农田土壤-作物系统Cd迁移富集影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 42(3): 1514-1522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103055.htm
Ma H H, Peng M, Guo F, et al. Factors affecting the translocation and accumulation of cadmium in a soil-crop system in a typical karst area of Guangxi Province, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 42(3): 1514-1522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202103055.htm
[25] 周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104047.htm
Zhou Y L, Yang Z B, Wang Q L, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil-crop system in Xiong'an New District[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104047.htm
[26] 章明奎, 常悦畅. 近50年浙江省耕作土壤有机质和酸碱度的变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(11): 4399-4404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201311042.htm
Zhang M K, Chang Y C. Changing characteristics of organic matter and pH of cultivated soils in Zhejiang Province over the last 50 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2013, 34(11): 4399-4404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201311042.htm
[27] 朱真令. 基于GIS的龙游县土壤pH值时空演变[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2020, 61(1): 183-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNX202001053.htm
Zhu Z L. Temporal and spatial changing of farmland pH value in Longyou Country based on GIS[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 61(1): 183-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNX202001053.htm
[28] 汪庆华, 董岩翔, 周国华, 等. 浙江省土壤地球化学基准值与环境背景值[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2007, 26(5): 591-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCST200702016.htm
Wang Q H, Dong Y X, Zhou G H, et al. Soil geochemical baseline and environmental background values of agricultural regions in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2007, 26(5): 591-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCST200702016.htm
[29] 魏复盛, 陈静生. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 1991, 12(4): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ199104006.htm
Wei F S, Chen J S. Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 1991, 12(4): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ199104006.htm
[30] Liu Y Z, Xiao T F, Ning Z P, et al. High cadmium concentratio n in soil in the Three Gorges Region: Geogenic source and potential bioavailability[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 37: 149-156. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ning_Zengping/publication/258725493_High_cadmium_concentration_in_soil_in_the_Three_Gorges_region_Geogenic_source_and_potential_bioavailability/links/57eb9c4808ae66664092e072.pdf
[31] Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, et al. Cadmium sorption and desorption in soils: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2012, 42: 489-533.
[32] Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, et al. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 90-105.
[33] Li X H, Zhou Q X, Sun X Y, et al. Effects of cadmium on uptake and translocation of nutrient elements in different welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L. ) cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 194: 101-110. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wenjie_Ren2/publication/282638502_Effects_of_cadmium_on_uptake_and_translocation_of_nutrient_elements_in_different_welsh_onion_Allium_fistulosum_L_cultivars/links/566d13e808aea0892c5010b0.pdf
[34] 鄢明才, 迟清华. 中国东部地壳元素丰度与岩石平均化学组成研究[J]. 物探与化探, 1997, 21(6): 451-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH199706008.htm
Yan M C, Chi Q H. Chemical compositions of continental crust and rocks in eastern China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997, 21(6): 451-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH199706008.htm
[35] 周通, 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 等. 南方几种水稻土重金属污染下的土壤呼吸及微生物学效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(12): 2568-2573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200912025.htm
Zhou T, Pan G X, Li L Q, et al. Effects of heavy metals on soil respiration and microbial indices in paddy field of South China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(12): 2568-2573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200912025.htm
[36] 谢丹, 徐仁扣, 蒋新, 等. 不同体系中不同土壤对Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)吸附能力的比较[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005, 25(3): 704-710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200505013.htm
Xie D, Xu R K, Jiang X, et al. Adsorption ability for Cu(Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ) and Cd(Ⅱ) among different soils under different systems[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2005, 25(3): 704-710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200505013.htm
[37] 王岚, 王亚平, 许春雪, 等. 水稻土中重金属元素Cd、Pb的竞争吸附——以长株潭地区水稻土为例[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(4): 601-607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201204013.htm
Wang L, Wang Y P, Xu C X, et al. Competitive adsorption of cadmium and lead in paddy soils: A case study of paddy soils in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan area of Hunan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(4): 601-607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201204013.htm
[38] Zhang J R, Li H Z, Zhou Y Z, et al. Bioavailability and soil-to-crop transfer of heavy metals in farmland soils: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 235: 710-719.
[39] Hu Y N, Cheng H F, Tao S. The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: A critical review[J]. Environment International, 2016, 92: 515-532. http://60.247.50.249/uploadCms/file/20600/papers_upload/20161008090810421440.pdf
[40] 魏建宏, 罗琳, 刘艳, 等. 赤泥颗粒和赤泥对污染土壤镉形态分布及水稻吸收的效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(2): 318-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201202018.htm
Wei J H, Luo L, Liu Y, et al. Effects of red mud granules and red mud on the distribution of Cd fractions and Cd uptake by the paddy rice in a contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(2): 318-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201202018.htm
[41] Chang C Y, Yu H Y, Chen J J, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in leaf vegetables from agricultural soils and associated potential health risks in the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186: 1547-1560.
[42] 王亚婷, 党媛, 杜焰玲, 等. 成都平原典型稻作土壤重金属镉有效性及主要驱动机制[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(1): 225-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY202001042.htm
Wang Y T, Dang Y, Du Y L, et al. Availability and main driving mechanism of heavy metal Cd in typical paddy soils in Chengdu Plain[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(1): 225-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY202001042.htm
-



 下载:
下载: