Rapid Determination of Sulfur in Nickel-Lead-Zinc Ore by High-frequency Infrared Carbon and Sulfur Analyzer
-
摘要:
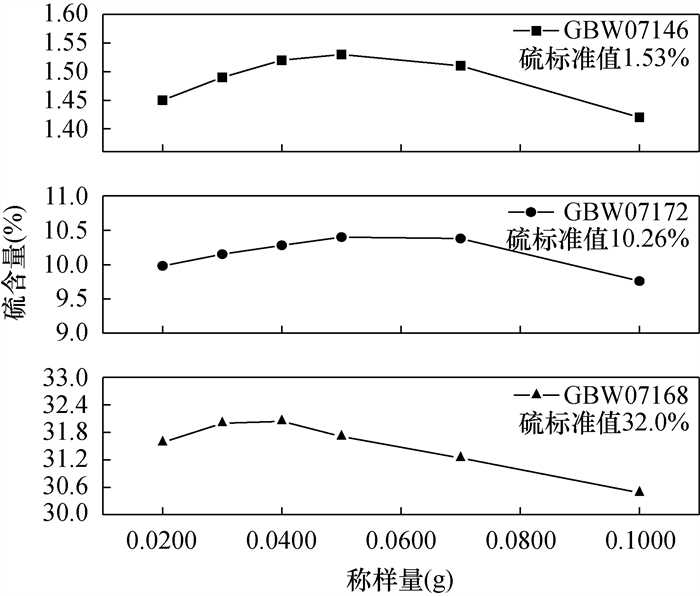
高频红外碳硫仪测定不同矿石种类中的硫含量,测定速度快,稳定性好,但当测定范围宽、样品种类多时,受助熔剂、氧化温度和氧化时间影响较大。本文应用高频红外碳硫分析仪,研究了实验条件对分析结果的影响,通过优化样品称样量、助熔剂添加量和分析时间,建立了矿石样品中质量分数为0.74%~32.0%的硫含量检测方法,分析条件为:分析氧气流速2.8L/min,样品称样量0.0400g,纯铁助熔剂0.50g,纯钨助熔剂2.0g,分析时间45s。通过国家标准物质验证该方法的检出限为0.185%,定量限为0.739%,标准曲线线性相关系数大于0.9995,测定结果的相对标准偏差小于3%(n=11),与标准值的相对误差小于2%,且均小于DZ/T 0130—2006中对矿石样品分析要求的相对误差允许限。采用本方法与传统燃烧碘量法对实际样品进行测定,两种方法测定值的绝对误差小于0.5%,测定结果之间呈极显著线性关系(R2=0.9995),表明两种方法具有良好的一致性。
-
关键词:
- 镍矿石 /
- 铅矿石 /
- 锌矿石 /
- 硫 /
- 高频燃烧-红外吸收光谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUND High-frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer can be used to rapidly analyze the sulfur content in different ores with good stability. However, the analysis is greatly affected by the flux type, oxidation temperature and time for various sulfur contents and sample types.
OBJECTIVES To expand the detection range of sulfur and improve the detection efficiency.
METHODS A high-frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer was used to study the influence of experimental conditions on the analysis results. By optimizing the sample weight, the amount of flux, and the analysis time, a method for determination of sulfur with a content of 0.74% to 32.0% in ore samples was established.
RESULTS The optimized conditions were 2.8L/min oxygen flow, 45s analysis time, sample weight of 0.0400g, 0.50g pure iron and 2.0g pure tungsten as flux. The detection limit of the method verified by national standard material was 0.185%, and the limit of quantification was 0.739%. The linear correlation coefficient of calibration curve was better than 0.9995, the relative standard deviations were less than 3% (n=11) and the relative errors were less than 2%. The relative errors were all less than the allowance limit for the ores analysis of relative error obtained in accordance with DZ/T 0130—2006. The actual samples of the laboratory were determined by this method and the traditional iodine combustion method. The absolute error of the measured values between the two methods was less than 0.5%, with an extremely significant linear relationship (R2=0.9995), indicating good agreement between the two methods.
CONCLUSIONS The method has high precision and low relative error. The detection limit, precision and accuracy of the established method meet the analytical requirements of the ores.
-
Key words:
- nickel ore /
- lead ore /
- zinc ore /
- sulfur /
- high frequency combustion-infrared absorption spectrometry
-

-
表 1 纯铁加入量对硫测量值的影响
Table 1. Effect of pure iron addition on the sulfur detection
纯铁加入量(g) GBW07146硫含量 GBW07168硫含量 标准值(%) 测定值(%) 标准值(%) 测定值(%) 0.20 1.44 31.51 0.35 1.47 31.78 0.50 1.53±0.06 1.52 32.0±0.3 32.04 0.60 1.54 31.88 0.75 1.48 31.75 表 2 不同分析时间下硫含量测定结果
Table 2. Results of sulfur content in different analysis time
分析时间(s) GBW07147硫含量 GBW07172硫含量 GBW07168硫含量 标准值(%) 测定值(%) 标准值(%) 测定值(%) 标准值(%) 测定值(%) 30 3.78±0.07 3.65 10.26±0.19 9.52 32.0±0.3 28.05 35 3.73 9.83 30.21 40 3.82 10.40 31.57 45 3.78 10.28 32.04 50 3.87 10.60 32.21 55 3.89 10.61 32.28 表 3 方法精密度和准确度
Table 3. Precision and accuracy tests of the method
标准物质编号 硫含量标准值(%) 硫含量测定值(%) 硫含量测定平均值(%) RSD (%) RE (%) YB (%) GBW(E)070077 2.90 2.86 2.85 3.01 2.97 2.88 2.91 2.99 2.92 3.02 2.89 2.93 2.93 2.04 1.03 2.32 GBW07163 6.74 6.85 6.66 6.68 6.80 6.84 6.85 6.82 6.70 6.72 6.80 6.78 6.77 1.04 0.49 1.72 GBW07172 10.26 10.28 10.40 10.15 10.22 10.26 10.36 10.26 10.29 10.45 10.31 10.35 10.30 0.82 0.42 1.44 GBW(E)070080 15.62 15.65 15.45 15.52 15.36 15.97 15.90 15.83 15.85 15.72 15.68 15.83 15.71 1.25 0.55 1.18 GBW07165 29.00 29.25 28.65 28.82 28.77 29.15 28.85 29.02 28.93 28.72 29.28 28.99 28.95 0.73 -0.18 0.82 GBW07168 32.00 32.30 32.17 32.21 32.01 31.85 32.06 31.95 32.03 31.95 32.24 31.81 32.05 0.50 0.16 0.77 表 4 两种方法硫含量结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of sulfur content determined with two methods
实际样品编号 硫含量测定平均值(%) 绝对误差(%) 实际样品编号 硫含量测定平均值(%) 绝对误差(%) 高频红外碳硫仪法 燃烧碘量法 高频红外碳硫仪法 燃烧碘量法 1 5.96 6.21 -0.25 11 2.23 2.05 0.18 2 26.09 25.60 0.49 12 24.62 24.85 -0.23 3 4.83 4.72 0.11 13 2.82 2.72 0.10 4 2.17 1.96 0.21 14 30.41 30.36 0.05 5 2.24 2.09 0.15 15 3.10 2.99 0.11 6 6.94 7.12 -0.18 16 5.23 5.00 0.23 7 4.12 4.08 0.04 17 2.17 2.02 0.15 8 2.47 2.20 0.27 18 15.73 15.88 -0.15 9 3.30 3.28 0.02 19 13.40 13.07 0.33 10 1.34 1.31 0.03 20 17.57 17.09 0.48 -
[1] 陈薇. 硫化铅锌矿选矿工程设计特征分析[J]. 现代矿业, 2021(3): 114-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202103032.htm
Chen W. Analysis on design characteristics of beneficiation engineering of sulfide lead-zinc ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2021(3): 114-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202103032.htm
[2] 韩洁. ICP-AES法测定金属矿石中的铜、铅、锌含量研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019(20): 185-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.20.104
Han J. Determination of copper, lead and zinc in metal ores by ICP-AES[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2019(20): 185-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.20.104
[3] 罗继锋, 王莹, 祁雨凡, 等. 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法快速测定铜铅锌矿石中的硫[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016(10): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201610063.htm
Luo J F, Wang Y, Qi Y F, et al. Rapid determination of sulfur in copper lead zinc ores by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2016(10): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201610063.htm
[4] Eksteen J J, Oraby E A, Nguyen V. Leaching and ion exchange based recovery of nickel and cobalt from a low grade, serpentine-rich sulfide ore using an alkaline glycine lixiviant system[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 145: 106073. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106073
[5] 钟华, 刘凤君, 聂梅影, 等. 高频燃烧红外吸收法测定石灰石和白云石中硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2017, 37(9): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201709007.htm
Zhong H, Liu F J, Nie M Y, et al. Determination of sulfur in limestone and dolomite by high frequency furnace combustion infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2017, 37(9): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201709007.htm
[6] 杨旭龙. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤中硫的方法优化[J]. 化学工程师, 2021(3): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXGC202103024.htm
Yang X L. Optimization of the method of high-frequency infrared carbon-sulfur analyzer for determining sulfur in soil[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2021(3): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXGC202103024.htm
[7] 龚仓, 付桂花, 黄艳波. 高频燃烧-红外碳硫仪测定岩心钻探样品中碳硫[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(12): 77-80. doi: 10.11792/hj20161219
Gong C, Fu G H, Huang Y B. Determination of carbon and sulfur in drilling core samples by high frequency combustion-infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer[J]. Gold, 2016, 37(12): 77-80. doi: 10.11792/hj20161219
[8] 许刚. X射线荧光光谱与碳硫仪联用测定土壤样品中的硫[J]. 化学与粘合, 2019, 41(6): 486-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0017.2019.06.022
Xu G. Determination of sulfur in soil samples by the X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and carbon sulfur analyzer[J]. Chemistry and Adhesion, 2019, 41(6): 486-488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0017.2019.06.022
[9] 耶曼, 张华, 李湘, 等. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤、水系沉积物和矿石中的硫[J]. 化学分析计量, 2021, 30(6): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ202106013.htm
Ye M, Zhang H, Li X, et al. Determination of sulfur in soil, stream sediment and ore by high frequency infrared carbon sulfur meter[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2021, 30(6): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ202106013.htm
[10] 殷陶刚, 窦向丽, 张旺强, 等. 应用高频红外碳硫仪测定农用地土壤样品中有机质含量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 631-638. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905110061
Yin T G, Dou X L, Zhang W Q, et al. Determination of organic matter content in farm land soil by high frequency infrared carbon-sulfur analyzer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 631-638. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905110061
[11] 欧阳泉根, 李晓燕, 白静梅, 等. 盐酸预处理-高频燃烧红外吸收法测定铀岩石中有机碳[J]. 冶金分析, 2020, 40(2): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202002004.htm
Ouyang Q G, Li X Y, Bai J M, et al. Determination of organic carbon in uranium-bearing rock by high frequency combustion infrared absorption with hydro-chloric acid pretreatment[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2020, 40(2): 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202002004.htm
[12] 张庸, 杨丽, 詹秀嫣, 等. 高频燃烧红外吸收法测定镍基高温合金中碳的助熔剂影响探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2016, 36(1): 52-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201601010.htm
Zhang Y, Yang L, Zhan X Y, et al. Influence of flux on the determination of carbon in nickel-based superalloy by high frequency combustion infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2016, 36(1): 52-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201601010.htm
[13] 殷艺丹, 李晖, 张健康, 等. 高频燃烧红外吸收光谱法测定高纯铝粉中碳含量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2021, 11(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202101014.htm
Yin Y D, Liu H, Zhang J K, et al. Determination of carbon in high purity aluminum powder by high-frequency combustion infrared absorption spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 11(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202101014.htm
[14] 张亚菲, 李啸寅. 红外碳硫仪在地质矿物元素含量测定中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2021(4): 207-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO202104098.htm
Zhang Y F, Li X Y. Application of infrared carbon sulfur analyzer in the determination of elements in geological minerals[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2021(4): 207-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO202104098.htm
[15] 杨小莉, 杨小丽, 曾美云, 等. 高频燃烧红外吸收法测定铜铅锌矿石中硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2020, 40(3): 44-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202003009.htm
Yang X L, Yang X L, Zeng M Y, et al. Determination of sulfur in copper-lead-zinc ore by high frequency combustion infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2020, 40(3): 44-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202003009.htm
[16] 黄启华, 徐志强, 杨玮玮. 高频红外碳硫仪测定重晶石和黄铁矿中的硫[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2): 130-135. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.006
Huang Q H, Xu Z Q, Yang W W. Determination of sulfur in barite and pyrite by high frequency infrared carbon-sulfur spectrometer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2): 130-135. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.02.006
[17] 张鑫. 高频燃烧红外吸收光谱法测定铀矿石中的硫[J]. 湿法冶金, 2017, 36(2): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ201702016.htm
Zhang X. Determination of sulfur in uranium ore by high frequency combustion infrared absorption spectroscopy[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2017, 36(2): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ201702016.htm
[18] 周富强, 刘松, 罗天林. 高频燃烧红外吸收法测定矿产品中硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2016, 36(11): 46-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201611008.htm
Zhou F Q, Liu S, Luo T L. Determination of sulfur content in mineral products by high frequency combustion infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2016, 36(11): 46-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201611008.htm
[19] 王宝玲. 高频红外吸收法快速测定硫精矿中高含量硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2013, 33(8): 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201308010.htm
Wang B L. High frequency infrared absorption method for rapid determination of high-content sulfur in sulfur concentrate[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(8): 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201308010.htm
[20] 吕新明, 孙振泽, 王东, 等. 高频燃烧-红外吸收光谱法同时测定铬铁矿石中碳和硫含量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2018, 8(3): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201803006.htm
Lyu X M, Sun Z Z, Wang D, et al. Simultaneous determination of carbon and sulfur in chromium ores by high frequency combustion-infrared absorption spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 8(3): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX201803006.htm
[21] 方雅琴, 贾正勋, 于晓琪, 等. 助熔剂对高频红外碳硫仪分析结果的影响分析[J]. 山东化工, 2021, 50(14): 118-120, 123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG202114051.htm
Fang Y Q, Jia Z X, Yu X Q, et al. Analysis of the influence of flux on the analysis results of high frequency infrared carbon sulfur analyzer[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(14): 118-120, 123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG202114051.htm
[22] 郭飞飞, 万双, 魏中凯, 等. 无水硫酸钠校准-高频燃烧红外吸收法测定铜精矿中高含量硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2015, 35(10): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201510019.htm
Guo F F, Wan S, Wei Z K, et al. Determination of high content sulfur in copper concentrate by high frequency combustion-infrared absorption method with anhydrous sodium sulfate calibration[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(10): 73-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201510019.htm
[23] 李帅. LECO-高频红外碳硫仪测定铁矿石中硫[J]. 山东化工, 2019, 48(24): 58-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201924023.htm
Li S. Determination of sulfur in iron ore by LECO-high frequency infrared carbon sulfur analyzer[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(24): 58-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201924023.htm
[24] 张彦甫, 蒋晓光, 韩峰. 高频燃烧红外吸收法测定高硫铜磁铁矿中硫含量[J]. 冶金分析, 2015, 35(6): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201506011.htm
Zhang Y F, Jiang X G, Han F. Determination of sulfur in high sulfur copper magnetite by high frequency combustion infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(6): 44-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX201506011.htm
[25] 王小松, 陈曦, 王小强. 高频燃烧-红外吸收光谱法测定钼矿石和镍矿石中的高含量硫[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(4): 581-585. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/07e697e5-6dcf-4413-a1dc-61f67853b4a0
Wang X S, Chen X, Wang X Q, et al. Determination of high content sulfur in molybdenum ore and nickel ore using high frequency combustion-infrared absorption spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(4): 581-585. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/07e697e5-6dcf-4413-a1dc-61f67853b4a0
[26] 陈伟锐. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤和水系沉积物中的硫实验条件改进[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(1): 123-128. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045
Chen W R. Improvement of experimental conditions for the determination of sulfur in soil and stream sediments by high-frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(1): 123-128. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045
[27] 于汀汀, 王玮, 许俊玉, 等. 红外碳硫仪测定矿石中高含量硫[J]. 分析试验室, 2016, 35(6): 695-699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201606018.htm
Yu T T, Wang W, Xu J Y, et al. Determination of high-content sulfur in ore by IR-absorption spectrometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2016, 35(6): 695-699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201606018.htm
[28] 李杰阳. 全自动红外吸收光谱法测定硫化矿矿石中全硫量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2021, 11(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202102009.htm
Li J Y. Determination of total sulfur in sulfide ore by automatic infrared absorption spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 11(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJFX202102009.htm
[29] 宾曦, 王娟, 刁正斌. 高频炉燃烧红外吸收法测定钛精矿中硫[J]. 冶金分析, 2020, 40(8): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202008015.htm
Bin X, Wang J, Diao Z B. Determination of sulfur in titanium concentrate by high frequency furnace combustion and infrared absorption method[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2020, 40(8): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX202008015.htm
[30] 詹会霞, 董亚红, 靳心怡. 红外线吸收法测定铁矿石中硫的准确性研究[J]. 现代科学仪器, 2019(4): 71-74, 83.
Zhan H X, Dong Y H, Jin X Y. Study on the accuracy of infrared absorption method for the determination of sulfur in iron ore[J]. Modern Scientific Instruments, 2019(4): 71-74, 83.
-



 下载:
下载: