Distribution and Enrichment Characteristics of Selenium in Soil and Crops in Luoyang City, Henan Province
-
摘要:
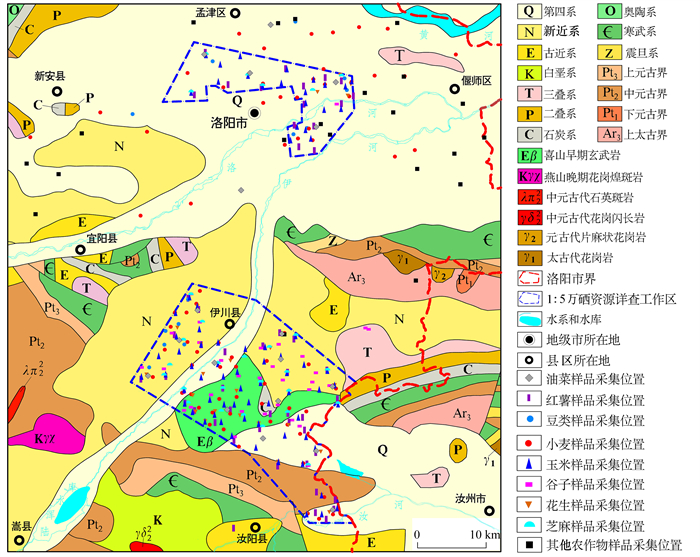
研究分析某一地区种植的各种农作物中的硒富集特征,同时对施硒肥农作物硒含量进行调查评价,可以为富硒特色农业开发提供依据。查明不同农作物中硒含量影响因素,对于开发富硒农产品具有重要的意义。本文以河南省洛阳市硒资源详查项目区及其他农业种植区为研究对象,通过采集区内22种大田种植的农作物及其根系土,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定土壤和农作物硒含量,研究了不同农作物中硒富集特征。结果表明:研究区土壤硒平均值均接近河南省富硒土壤标准,在酸性土壤中富硒点位占比28.61%,中性土壤中富硒点位占比43.72%,碱性土壤中富硒点位占比41.99%,总体土壤富硒点位占比40.56%。根据各类作物的硒富集系数评价,研究区适合开发富硒豆类、油料类、小麦、谷子、红薯等特色农作物和富硒中药材银条,不适宜开发富硒玉米。不同农作物中硒含量与土壤硒含量和酸碱度(pH)的相关性研究表明,土壤硒含量是农作物中硒含量的决定因素,其次是土壤酸碱度。为促进研究区开发富硒农产品,可以通过施硒肥改善农作物硒含量水平,低硒背景土壤种植的农作物特别是水果适合施加硒肥,高硒背景土壤种植的谷子不适合施加硒肥。
-
关键词:
- 洛阳市 /
- 农作物 /
- 硒 /
- 富集系数 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法
Abstract:BACKGROUND The analysis of selenium enrichment characteristics in various crops planted in a certain area and investigation and evaluation of selenium content in selenium fertilizer crops can provide a basis for the development of selenium-enriched characteristic agriculture. It is important to find out the influencing factors of selenium content in different crops for developing selenium-enriched agricultural products.
OBJECTIVES To understand the distribution and enrichment characteristics of Se in soil and crops in Luoyang City.
METHODS The selenium resources detailed investigation project area and other agricultural planting areas in Luoyang City, Henan Province were chosen as the research object. The selenium content of 22 kinds of crops and their root soil were measured by ICP-MS, and the selenium enrichment characteristics of different crops were studied.
RESULTS The average value of soil selenium in the study area was close to the standard of selenium-enriched soil in Henan Province. The selenium-enriched sites in acidic soil, neutral soil, alkaline soil, and overall soil accounted for 28.61%, 43.72%, 41.99%, and 40.56%, respectively. According to the evaluation of selenium enrichment coefficient of various crops, the study area was suitable for the development of selenium-enriched beans, oil-bearing crops, wheat, millet, sweet potato and other characteristic crops and selenium-enriched traditional Chinese medicine Stachys floridana Schuttl.ex Benth, but not suitable for the development of selenium-enriched corn. The correlation of selenium content in different crops with soil selenium content and pH showed that soil selenium content was the decisive factor of selenium content in crops, followed by soil pH.
CONCLUSIONS In order to promote the development of selenium-enriched agricultural products in the study area, selenium fertilizer can be applied to improve the selenium content of crops. Crops planted in low selenium background soil, especially fruits, are suitable for applying selenium fertilizer, while millet planted in high selenium background soil is not suitable for applying selenium fertilizer.
-
Key words:
- Luoyang /
- crops /
- selenium /
- enrichment factor /
- inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry
-

-
表 1 不同酸碱性土壤硒元素地球化学特征值
Table 1. Geochemical characteristic values of selenium in different acid and alkaline soils
土壤酸碱性 样品数量(件) 占比(%) 硒含量平均值(mg/kg) 变异系数 富硒点数 富硒率(%) 河南省富硒土壤硒含量标准(mg/kg) 酸性(pH < 6.5) 727 12.55 0.33 0.332 208 28.61 ≥0.35 中性(pH 6.5~7.5) 828 14.29 0.315 0.429 362 43.72 ≥0.32 碱性(pH > 7.5) 4239 73.16 0.288 0.478 1780 41.99 ≥0.30 全区 5794 100 0.297 0.454 2350 40.56 - 表 2 洛阳市不同农作物及根系土硒含量和富集特征
Table 2. Selenium content and enrichment characteristics of different crops and root soils in Luoyang City
农作物种类 样品数量(件) 根系土硒含量平均值(mg/kg) 根系土硒含量范围(mg/kg) 农作物硒含量平均值(mg/kg) 农作物硒含量范围(mg/kg) BCF (%) BCF范围(%) 黄豆 20 0.38 0.15~0.59 0.13 0.03~0.58 32.39 16.61~98.81 绿豆 4 0.32 0.26~0.37 0.12 0.08~0.16 36.86 25.75~45.47 油菜籽 15 0.31 0.23~0.50 0.11 0.04~0.67 35.44 10.44~204.06 花生 49 0.344 0.11~0.70 0.10 0.017~0.99 29.75 8.42~73.47 豇豆 1 0.29 - 0.085 - 29.24 - 芝麻 35 0.32 0.22~0.42 0.081 0.01~0.20 26.08 3.87~79.72 小麦 174 0.42 0.074~0.96 0.08 0.009~0.52 18.38 2.62~99.72 黑豆 4 0.19 0.13~0.29 0.071 0.05~0.12 36.18 26.73~43.45 谷子 34 0.31 0.16~0.48 0.060 0.024~0.12 19.46 7.67~44.45 红小豆 1 0.34 - 0.053 - 15.54 - 银条 17 0.24 0.11~0.31 0.042 0.002~0.011 4.3 1.02~8.81 玉米 175 0.40 0.15~1.28 0.040 0.003~0.74 7.55 0.66~73.80 红薯 125 0.40 0.126~1.59 0.022 0.006~0.22 2.80 1.37~67.78 毛豆 1 0.56 - 0.016 - 2.89 - 大蒜 16 0.20 0.13~0.24 0.013 0.003~0.028 6.46 1.41~12.56 沙梨 3 0.14 0.12~0.16 0.012 0.0001~0.032 9.42 0.07~26.33 豆角 2 0.16 0.15~0.17 0.010 0.009~0.011 5.90 5.13~6.67 樱桃 2 0.26 0.24~0.27 0.0083 0.008~0.0086 3.32 3.03~3.61 辣椒 2 0.25 0.25~0.26 0.0085 0.006~0.011 3.28 2.14~4.40 梨 17 0.21 0.13~0.33 0.003 0.0003~0.007 1.58 0.11~4.47 苹果 17 0.17 0.081~0.84 0.0028 0.0001~0.0051 2.27 0.04~4.52 秋葵 1 0.24 - 0.002 - 0.81 - 硒肥谷子 40 0.31 0.12~0.40 1.52 0.075~4.92 507.83 22.35~1503.36 硒肥玉米 2 0.50 0.32~0.67 0.34 0.0078~0.68 51.52 2.40~100.64 硒肥红薯 6 0.24 0.14~0.30 0.13 0.07~0.23 54.09 28.88~87.75 硒肥石榴 3 0.15 0.11~0.19 0.067 0.054~0.077 47.20 36.48~37.22 硒肥葡萄 3 0.48 0.47~0.51 0.013 0.010~0.016 2.66 2.07~3.38 硒肥梨 3 0.064 0.05~0.076 0.006 0.0036~0.0073 9.59 5.57~14.51 硒肥苹果 4 0.076 0.064~0.089 0.0055 0.0006~0.010 7.24 0.92~13.21 表 3 洛阳市与其他地区不同农作物硒含量对比
Table 3. Comparison of selenium content of different crops in Luoyang City and other areas
样品类型 本区硒含量(mg/kg) 其他地区硒含量(mg/kg) 参考文献 样品类型 本区硒含量(mg/kg) 其他地区硒含量(mg/kg) 参考文献 土壤 0.297 0.34(成都) [8] 油菜籽 0.11 0.153(陕西) [12] 0.267(陕西) [12] 大蒜 0.013 0.059(陕西) [12] 0.35(海口) [25] 豆角 0.01 0.018(陕西) [12] 0.32(绥化) [26] 花生 0.101 0.243(海口) [25] 小麦 0.08 0.075(成都) [8] 芝麻 0.081 0.194(海口) [25] 0.159(陕西) [12] 豆类 0.13 0.132(海口) [25] 0.073(湖北) [27] 红薯 0.022 0.01(邢台威县) [28] 小麦BCF 18.38% 19.51%(成都) [8] 0.009(海南澄迈县) [28] 玉米 0.04 0.028(成都) [8] 辣椒 0.008 0.01陕西) [12] 0.064(陕西) [12] 0.057(海口) [25] 0.028(绥化) [26] 黄豆 0.132 0.111(湖北) [27] 0.036(湖北) [27] 玉米BCF 7.55% 0.28%(成都) [8] 谷子 0.06 0.084(河南、河北、山西、山东) [29] 表 4 洛阳市不同农作物硒含量与其他省富硒标准对比
Table 4. Comparison of selenium content of different crops in Luoyang City with selenium enrichment standard of other provinces
农作物种类 农作物名称 样本 根系土硒含量平均值(mg/kg) 农作物硒含量平均值(mg/kg) BCF (%) 陕西省硒含量① (mg/kg) 江西省硒含量② (mg/kg) 重庆市硒含量③ (mg/kg) 洛阳市硒含量④ (mg/kg) 豆类 黄豆 20 0.38 0.132 32.39 ≥0.02 0.07~0.3 0.05~0.3 0.2~2 绿豆 4 0.32 0.117 36.86 黑豆 4 0.19 0.07 36.18 油料类 油菜籽 15 0.31 0.11 35.44 ≥0.02 0.07~0.3 0.02~0.30 0.3~5 花生 40 0.34 0.101 24.89 0.05~0.30 芝麻 35 0.32 0.081 26.08 0.02~0.30 粮食类 小麦 174 0.42 0.08 18.38 ≥0.05 0.07~0.3 稻谷(0.04~0.30)
玉米(0.02~0.30)0.2~2 谷子 34 0.31 0.06 19.46 玉米 175 0.4 0.04 7.55 硒肥玉米 2 0.498 0.343 51.52 硒肥谷子 40 0.31 1.52 507.83 蔬菜类 大蒜⑤ 16 0.2 0.0131 6.46 ≥0.03 ≥0.03 ≥0.03 ≥0.03 豆角 2 0.16 0.0096 5.9 ≥0.02 0.01~0.1 0.02~0.1 0.05~0.2 辣椒 2 0.25 0.008 3.28 根茎类 红薯 124 0.4 0.022 2.8 ≥0.02 0.05~0.1 0.02~0.1 0.05~0.2 硒肥红薯 6 0.24 0.128 54.09 中草药 偃师银条 17 0.24 0.042 4.3 ≥0.02 - - 0.3~5 水果类 樱桃 2 0.26 0.0083 3.32 ≥0.02 0.01~0.05 0.01~0.5 0.05~0.2 沙梨 3 0.143 0.012 9.4 苹果 17 0.15 0.0033 3.22 梨 20 0.21 0.003 1.58 硒肥石榴 3 0.15 0.067 47.2 硒肥葡萄 3 0.48 0.0128 2.66 硒肥梨 3 0.064 0.006 9.59 硒肥苹果 4 0.076 0.0055 7.24 注:①陕西省地方标准,《富硒含硒食品与相关产品硒含量标准》(DB61/T 556—2018);②江西省地方标准,《富硒食品硒含量分类标准》(DB36/T 566—2017);③重庆市地方标准,《富硒农产品》(DB50/T 705—2016);④洛阳市行业标准,《富硒农产品及其加工品硒含量标准》(T/LRSIA001—2019);⑤大蒜采用农业行业标准《富硒大蒜》(NY/T 3115—2017)。 表 5 研究区不同土壤和农作物系统中硒迁移回归方程
Table 5. Regression equation of selenium migration in different soil and crop systems in the study area
农作物 样品数(件) 土壤硒与农作物硒回归模型 R pH与农作物硒BCF回归模型 R 黑豆 4 y=0.442x-0.0151 0.909 y=10.718x-40.584 0.616 绿豆 4 y=0.5789x-0.0654 0.695 y=11.31x-50.705 0.450 黄豆 20 y=0.5486x-0.0756 0.651 y=9.6159x-41.261 0.185 小麦 174 y=0.2847x-0.0405 0.558 y=7.5657x-40.355 0.344 玉米 175 y=0.2211x-0.0461 0.530 y=0.8204x+3.5075 0.055 大蒜 16 y=0.0501x+0.0029 0.228 y=6.8545x-49.566 0.468 花生 49 y=0.163x+0.0451 0.111 y=-4.5654x+63.554 -0.079 红薯 125 y=-0.0234x+0.0358 -0.077 y=16.03x-109.04 0.082 银条 17 y=0.6785x-2.4652 0.075 y=-0.0227x+0.0113 -0.446 油菜籽 15 y=0.0641x+0.0893 0.026 y=35.208x-223.24 0.314 谷子 34 y=-0.0042x+0.0592 -0.010 y=-5.799x+63.439 -0.368 梨 17 y=0.0002x+0.0031 0.006 y=-1.0955x+10.248 -0.364 苹果 17 y= 0.00004x+0.0028 0.004 y=1.2637x-7.5582 0.522 芝麻 35 y=-0.0008x+0.0812 -0.001 y=3.9044x-3.4176 0.161 -
[1] 王磊, 杜菲, 孙卉, 等. 人体硒代谢与硒营养研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2015, 5(4): 285-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2015.04.06
Wang L, Du F, Sun H, et al. Progress on selenium metabolism and nutrition in human[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2015, 5(4): 285-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2015.04.06
[2] 胡婷, 吴文良, 赵桂慎, 等. 我国富硒农产品及食品标准体系发展与展望[J]. 检测认证, 2019, 6(1): 136-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGBZ201911036.htm
Hu T, Wu W L, Zhao G S, et al. Development and prospect of selenium-enriched agricultural products and foods standards in China[J]. Certification Testing, 2019, 6(1): 136-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGBZ201911036.htm
[3] 李傲瑞, 乔新星, 赵飞飞, 等. 硒与人体健康关系研究进展[J]. 绿色科技, 2020(12): 121-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LVKJ202012044.htm
Li A R, Qiao X X, Zhao F F, et al. Research progress on the relationship between selenium and human health[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2020(12): 121-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LVKJ202012044.htm
[4] 张勇胜, 李仁兰, 刘妍, 等. 硒对人体健康作用的研究进展[J]. 内科, 2018, 13(4): 623-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKYT201804026.htm
Zhang Y S, Li R L, Liu Y, et al. Research progress of selenium on human health[J]. Internal Medicine, 2018, 13(4): 623-625. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NKYT201804026.htm
[5] 自然资源部中国地质调查局. 中国耕地地球化学调查报告(2015年)[R]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2015.
China Geological Survey, Ministry of National Resources. Geochemical survey report of cultivation land in China (2015)[R]. Beijing: China Geological Survey, 2015.
[6] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
[7] 韩笑, 周越, 吴文良. 富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6): 1177-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201806017.htm
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al. Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6): 1177-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201806017.htm
[8] 金兴钰, 王胜华, 包雨函, 等. 成都经济区土壤及经济植物硒含量特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(3): 322-331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2010.03.015
Jin X Y, Wang S H, Bao Y H, et al. Survey and research of selenium content in soil and economic plants from the Chengdu Economic Areas, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2010, 37(3): 322-331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2010.03.015
[9] 王锐, 余涛, 曾庆良, 等. 我国主要农耕区土壤硒含量分布特征、来源及影响因素[J]. 生物技术进展, 2010, 37(3): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705006.htm
Wang R, Yu T, Zeng Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics, origin and influencing factors of soil selenium concentration of main farming areas in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2010, 37(3): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWJZ201705006.htm
[10] 姬丙艳, 沈骁, 姚振, 等. 青海柴达木盆地绿洲农业区硒地球化学特征——以诺木洪绿洲为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1): 199-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202001026.htm
Ji B Y, Shen X, Yao Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in the oasis agricultural area of Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province: Exemplified by Nomhon Oasis[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 199-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202001026.htm
[11] 张立, 刘国栋, 吕石佳, 等. 黑龙江省海伦市农耕区土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5): 1046-1054. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201905012.htm
Zhang L, Liu G D, Lyu S J, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium cultivated soil and its influencing factors in Hailun County of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(5): 1046-1054. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201905012.htm
[12] 乔新星, 晁旭, 任蕊, 等. 陕西关中富硒土壤研究及开发利用——以三原—阎良地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 45(1): 230-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101028.htm
Qiao X X, Chao X, Ren R, et al. Research development and utilization of selenium rich soil of Shaanxi: A case study of Sanyuan—Yanliang area[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 45(1): 230-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101028.htm
[13] 张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5): 1138-1144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201905026.htm
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5): 1138-1144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201905026.htm
[14] 周小娟, 张嫣, 祝莉玲, 等. 武汉市侏儒—消泗地区农田系统中硒的分布特征及有效性研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4): 158-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201604025.htm
Zhou X J, Zhang Y, Zhu L L, et al. Research on selenium distribution and effectiveness in the farm system in Zhuru and Xiaosi areas, Wuhan City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4): 158-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201604025.htm
[15] 张立, 姜侠, 崔玉军, 等. 松嫩平原吕大火房垂直剖面中硒赋存形态及影响因素分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 603-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202006016.htm
Zhang L, Jiang X, Cui Y J, et al. Analysis on the occurrence forms of selenium of and influencing factors in Lvdahuofang vertical section of Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 603-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202006016.htm
[16] 张百忍, 解松峰. 陕西秦巴山区不同农田农作物硒含量变化规律分析[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2011, 42(10): 128-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDN201110031.htm
Zhang B R, Xie S F. Analysis of selenium concentrations in different crops and croplands in Qinba Mountain areas, Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2011, 42(10): 128-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDN201110031.htm
[17] 陈清清, 张泽洲, 袁林喜, 等. 富硒西兰花中硒的赋存形态及其抗氧化性[J]. 宜春学院学报, 2020, 42(12): 90-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-380X.2020.12.021
Chen Q Q, Zhang Z Z, Yuan L X, et al. Study on the distribution and combined speciation of selenium in Se-enriched broccoli and their antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Yichun University, 2020, 42(12): 90-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-380X.2020.12.021
[18] 卢鹏飞, 高志强, 孙敏, 等. 外源硒肥对小麦籽粒产量及植株硒元素积累的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2020, 43(3): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT202003004.htm
Lu P F, Gao Z Q, Sun M, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium fertilizer on grain yield and selenium accumulation in wheat[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020, 43(3): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CULT202003004.htm
[19] 成东梅, 尹国红, 赵伟峰, 等. 外源硒在绿色优质小麦生产中的应用研究[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 41(1): 20-29.
Cheng D M, Yin G H, Zhao W F, et al. Study on the application of exogenous selenium in the production of green and high quality wheat[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 41(1): 20-29.
[20] 袁知洋, 项剑桥, 吴冬妹, 等. 恩施富硒土壤区主要农作物硒镉特征以及和根系土硒镉关系研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2017, 31(6): 706-712. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201706008.htm
Yuan Z Y, Xiang J Q, Wu D M, et al. The characteristics of selenium and cadmium in crops and its root soil in the area of Se and Cd-enriched soil in Enshi[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2017, 31(6): 706-712. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201706008.htm
[21] 唐世琪, 万能, 曾明中, 等. 恩施地区土壤与农作物硒镉地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3): 607-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202003018.htm
Tang S Q, Wan N, Zeng M Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and cadmium in soil and crops in Enshi area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3): 607-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202003018.htm
[22] 朱帅, 沈亚婷, 贾静, 等. 液相色谱-高分辨质谱法在中国东北地区农作物有机硒形态分析中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(2): 262-272. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005130070
Zhu S, Shen Y T, Jia J, et al. Determination of organic selenium compounds in crops by liquid chromatography-quadrupole/electrostatic field orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(2): 262-272. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005130070
[23] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京. 地质出版社, 2020: 26-41, 17.
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 26-41, 17.
[24] 袁知洋, 许克元, 黄彬, 等. 恩施富硒土壤区绿色富硒农作物筛选研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4): 569-575. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201804011.htm
Yuan Z Y, Xu K Y, Huang B, et al. Screening of high quality crops in selenium rich and high cadmium soil area of Enshi[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4): 569-575. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201804011.htm
[25] 李福燕, 漆智平, 李许明. 海口市农田土壤硒含量特征与农作物硒特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(3): 630-635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201603019.htm
Li F Y, Qi Z P, Li X M. Survey and research of selenium contents in farmland soil and crops of Haikou[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3): 630-635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201603019.htm
[26] 张立, 杨晨梦, 孙广义, 等. 黑龙江绥化大宗农作物硒含量特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(5): 510-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202105006.htm
Zhang L, Yang C M, Sun G Y, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of selenium content of staple crops in Suihua area of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(5): 510-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202105006.htm
[27] 闫加力, 徐春燕, 杨军, 等. 湖北省不同农作物对土壤硒吸收富集规律的研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2019, 33(4): 481-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201904009.htm
Yan J L, Xu C Y, Yang J, et al. Study on soil selenium absorption and enrichment of different crops in Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2019, 33(4): 481-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201904009.htm
[28] 刘芳, 张磊, 张晓彬, 等. 威县枣园乡魏家寨村红薯中硒含量的测定[J]. 农产品加工, 2019(6): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCPJ201912019.htm
Liu F, Zhang L, Zhang X B, et al. Two methods for determination of selenium content in sweet potato of Weijiazhai Village in Weixian County[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2019(6): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCPJ201912019.htm
[29] 赵宇, 崔纪菡, 李顺国, 等. 不同品种(系)和地区对小米硒含量的影响[J]. 河北农业科学, 2017(4): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBKO201704001.htm
Zhao Y, Cui J H, Li S G, et al. Effects of different varieties and regions on selenium content in Foxtail Millet[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2017(4): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBKO201704001.htm
[30] 王祖伟, 李宗梅, 王景刚, 等. 天津污灌区土壤重金属含量与理化性质对小麦吸收重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(4): 1406-1410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200704044.htm
Wang Z W, Li Z M, Wang J G, et al. Absorption to heavy metals by wheat and influencing features in sewage-irrigated soil in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(4): 1406-1410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200704044.htm
[31] 郭素霞, 程志号, 孙佩光, 等. 海南17a宿根巴西蕉园土壤微生物特征及土壤pH周年变化特征分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(8): 2413-2421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDZX202108038.htm
Guo S X, Cheng Z H, Sun P G, et al. Soil microbial flora and pH annual change characteristics of 17 years continuous cropping banana field in Hainan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(8): 2413-2421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDZX202108038.htm
[32] 吴小芳, 张振山, 范琼, 等. 海南省果园土壤肥力综合评价研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(7): 2109-2118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDZX202107039.htm
Wu X F, Zhang Z S, Fan Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility in orchards of Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(7): 2109-2118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDZX202107039.htm
[33] 李福燕, 李许明. 海口市农用地土壤硒含量与土壤理化性质的相关性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(14): 42-47, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY202014014.htm
Li F Y, Li X M. Soil selenium contents in relation to soil physicochemical properties in agricultural land of Haikou[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(14): 42-47, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY202014014.htm
[34] 鲁晋秀, 闫秋艳, 杨峰, 等. 土壤硒含量显著影响黑小麦与普通小麦的硒吸收[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(10): 1966-1971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201810023.htm
Lu J X, Yan Q Y, Yang F, et al. Soil selenium content affects selenium accumulation in seeds of triticale and bread wheat[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(10): 1966-1971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201810023.htm
[35] 廖彪. 玉米硒含量与土壤硒含量的相关性[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2021, 49(1): 34-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GATE202101006.htm
Liao B. Correlation between corn and soil Se content[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(1): 34-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GATE202101006.htm
-



 下载:
下载: