Identification of TiO2 Polymorphs of the Bauxite Deposit in Central Guangxi by Laser Raman Spectroscopy
-
摘要:
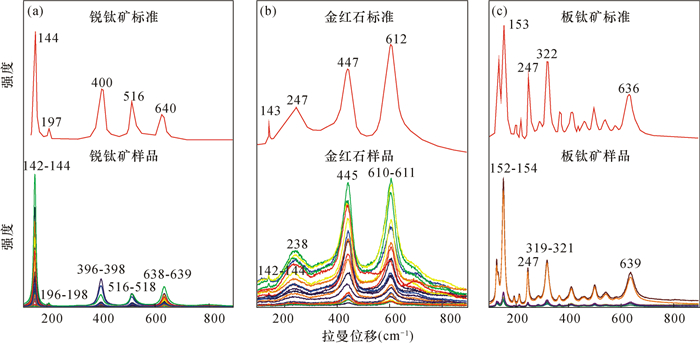
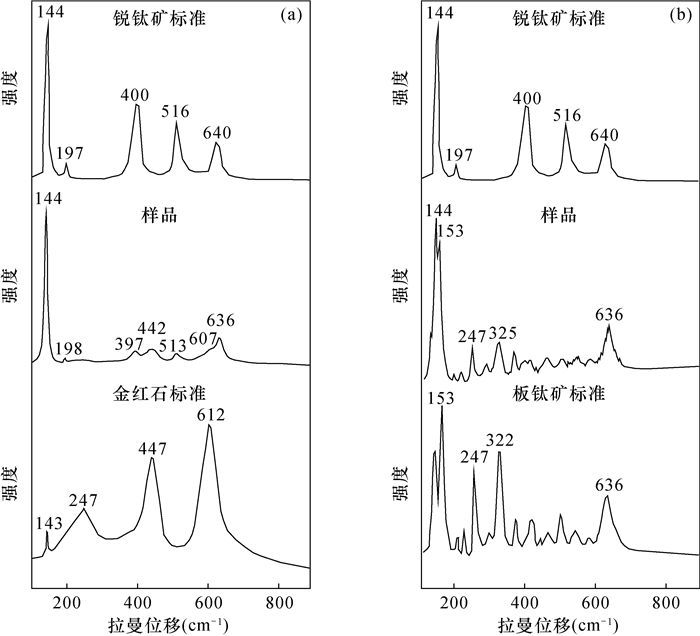
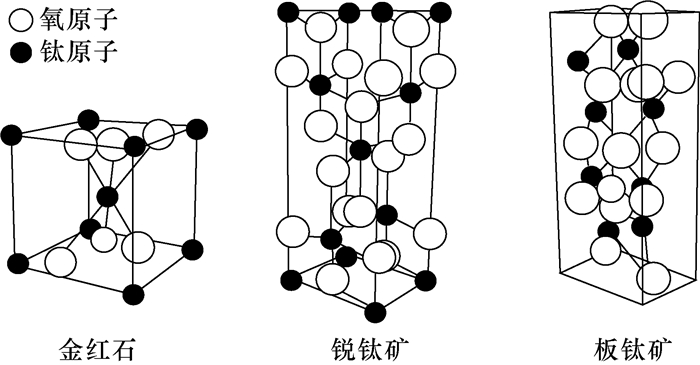
金红石、锐钛矿和板钛矿为TiO2的三种同质异象矿物。在进行金红石微区原位U-Pb定年时,通常主要依据电子探针数据、辅以阴极发光图像确定研究矿物为金红石,而电子探针数据和阴极发光图像有时并不能有效地区分金红石、锐钛矿和板钛矿,若用于进行定年的矿物中同时存在三种或其中两种TiO2矿物,获得的年龄可能是混合年龄,无显著地质意义。因此,对TiO2同质异象矿物的快速准确鉴别具有重要意义。本文以桂中铝土矿中TiO2矿物为研究对象,将激光拉曼光谱应用于TiO2同质异象矿物的鉴别,准确识别出桂中铝土矿TiO2矿物中存在四组不同特征的激光拉曼光谱谱线。前三组分别具有锐钛矿、金红石和板钛矿的激光拉曼光谱特征峰;第四组具有两种激光拉曼光谱特征谱线,第一种同时具有锐钛矿的特征峰144、198、397、513、636cm-1和金红石的特征峰442、607cm-1,第二种同时具有锐钛矿的特征峰144cm-1和板钛矿特征峰153、247、325、636cm-1。结果表明:桂中铝土矿TiO2矿物中除金红石、锐钛矿和板钛矿外,还存在同时具有两种矿物结构特征的中间矿物。分析认为研究区可能经历了后期的区域变质作用,导致TiO2同质异象矿物发生相变,这类中间矿物则记录了相变的过程。本文应用激光拉曼光谱快速准确地鉴别出桂中铝土矿TiO2同质异象矿物,为金红石微区原位U-Pb定年研究中矿物的鉴别提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- TiO2同质异象矿物 /
- 激光拉曼光谱 /
- 金红石 /
- 锐钛矿 /
- 板钛矿
Abstract:BACKGROUND Rutile, anatase and brookite are TiO2 polymorphs. In the rutile in-situ U-Pb dating, rutile was determined primarily on electron microprobe data and cathodoluminescence images, while these methods sometimes could not effectively distinguish rutile, anatase and brookite. If there are a small number of the TiO2 polymorphs in the sample, the obtained age may be a mixed age with no significant geological significance. Therefore, the identification of TiO2 polymorphs is very important.
OBJECTIVES To identify TiO2 polymorphs from the bauxite deposit in central Guangxi.
METHODS TiO2 minerals in bauxite from central Guangxi were used as the research object, and laser Raman spectroscopy was applied to the identification of TiO2 isomorphic minerals.
RESULTS Four groups of laser Raman spectral lines with different characteristics were identified. The first three groups have laser Raman spectral peaks of anatase, rutile and brookite, respectively. The fourth group has two kinds of laser Raman spectral characteristic lines, one has both anatase characteristic peaks of 144, 198, 397, 513, 636cm-1 and rutile characteristic peaks of 442, 607cm-1, the other has both anatase characteristic peak of 144cm-1 and brookite characteristic peak of 153, 247, 325, 636cm-1.
CONCLUSIONS The TiO2 polymorphs of the bauxite deposit includs rutile, anatase, brookite and intermediate minerals that undergo phase transformation. The study indicates that the bauxite deposit in central Guangxi may have undergone a later regional metamorphism, leading to the transformation of TiO2 polymorphs. The laser Raman spectroscopy provides a new method for the identification of TiO2 polymorphs andrutile for in-situ U-Pb dating.
-
Key words:
- TiO2 polymorphs /
- laser Raman spectroscopy /
- rutile /
- anatase /
- brookite
-

-
图 2 桂中铝土矿中锐钛矿、金红石及板钛矿激光拉曼光谱图(锐钛矿、金红石及板钛矿激光拉曼光谱标准曲线据Meinhold, 2010[27])
Figure 2.
图 3 桂中铝土矿第四组TiO2矿物激光拉曼光谱图(锐钛矿、金红石及板钛矿激光拉曼光谱标准曲线据Meinhold, 2010[27])
Figure 3.
表 1 桂中铝土矿TiO2同质异象矿物电子探针分析结果
Table 1. Electron microprobe analyses of TiO2 polymorphs from the bauxite deposit in central Guangxi
测点 锐钛矿(%) K2O UO2 CaO TiO2 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Cr2O3 MnO FeO ThO2 PbO Nb2O5 P2O5 Ta2O5 总计 1 0.02 0.08 0.10 98.84 0.03 0.00 0.21 0.31 0.00 0.02 0.18 0.01 0.00 0.27 0.00 0.14 100.20 2 0.00 0.00 0.08 98.55 0.01 0.00 0.09 0.22 0.00 0.02 0.14 0.02 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.01 99.28 3 0.01 0.02 0.02 98.07 0.00 0.01 0.81 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 99.27 4 0.01 0.00 0.05 98.66 0.03 0.00 0.04 0.17 0.01 0.01 0.15 0.02 0.00 0.18 0.00 0.00 99.35 5 0.01 0.00 0.03 99.39 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.15 0.00 0.03 99.74 6 0.00 0.02 0.09 99.48 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 0.23 0.01 0.11 100.20 测点 金红石(%) K2O UO2 CaO TiO2 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Cr2O3 MnO FeO ThO2 PbO Nb2O5 P2O5 Ta2O5 总计 1 0.00 0.09 0.00 97.57 0.01 0.01 0.15 0.21 0.06 0.00 0.61 0.05 0.00 0.16 0.00 0.04 98.96 2 0.00 0.00 0.01 98.18 0.00 0.00 0.18 0.10 0.03 0.01 0.42 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.00 0.00 99.17 3 0.23 0.00 0.04 97.76 0.00 0.07 0.66 1.09 0.03 0.01 0.19 0.04 0.00 0.18 0.00 0.00 100.30 4 0.02 0.05 0.01 99.15 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.21 0.01 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.09 99.66 5 0.00 0.00 0.01 99.22 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.48 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 99.80 6 0.02 0.02 0.00 98.17 0.00 0.01 0.05 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.58 0.05 0.00 0.99 0.01 0.09 100.10 测点 板钛矿(%) K2O UO2 CaO TiO2 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Cr2O3 MnO FeO ThO2 PbO Nb2O5 P2O5 Ta2O5 总计 1 0.00 0.00 0.00 98.40 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.16 0.00 0.00 0.91 0.02 0.07 99.67 2 0.00 0.00 0.04 98.48 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.29 0.00 0.01 0.58 0.00 0.08 99.55 3 0.00 0.04 0.01 99.82 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.09 0.01 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.00 100.10 测点 第四组矿物(%) K2O UO2 CaO TiO2 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Cr2O3 MnO FeO ThO2 PbO Nb2O5 P2O5 Ta2O5 总计 1 0.01 0.00 0.03 99.97 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.16 0.00 0.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.40 2 0.00 0.00 0.12 98.16 0.02 0.02 0.28 0.50 0.00 0.04 0.18 0.00 0.00 0.41 0.00 0.00 99.70 -
[1] 张雅, 李全忠, 闫峻, 等. LA-ICP-MS独居石U-Th-Pb测年方法研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(5): 637-649. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101130005
Zhang Y, Li Q Z, Yan J, et al. Analytical conditions for U-Th-Pb dating of monazite by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(5): 637-649. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101130005
[2] 周雄, 周玉, 孙宝伟, 等. 四川甲基卡稀有金属矿床134号脉锡石U-Pb定年与地质意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 156-164. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060006
Zhou X, Zhou Y, Sun B W, et al. Cassiterite U-Pb dating of No. 134 pegmatite vein in the Jiajika rare metal deposit, western Sichuan and its geological significances[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 156-164. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060006
[3] Dong Y, Ge W C, Yang H, et al. Geochemical and SIMS U-Pb rutile and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronological evidence of the tectonic evolution of the Mudanjiang ocean from amphibolites of the Heilongjiang complex, NE China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 69: 25-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.11.012
[4] Schmitt A K, Zack T, Kooijman E, et al. U-Pb ages of rare rutile inclusions in diamond indicate entrapment synchronous with kimberlite formation[J]. Lithos, 2019, 350-351: 105251. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105251
[5] 许康康, 刘晓阳, 孙凯, 等. 坦桑尼亚乌本迪带内花岗岩类的LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(1): 55-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.01.006
Xu K K, Liu X Y, Sun K, et al. Zircon U-Pb LA-MC-ICP-MS dating and geological significance of the granitoids in the Ubendian belt, southwestern Tanzania[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(1): 55-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.01.006
[6] 田辉, 李怀坤, 张健, 等. 天津蓟州东水厂中元古代高于庄组凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄——对中元古代生物-环境事件的制约[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2020, 43(2): 153-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.02.009
Tian H, Li H K, Zhang J, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb dating for zircons from the tuff bed of the Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Jixian Section, Tianjin, and its constraints on the Mesoproterozoic bio-environmental events[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2020, 43(2): 153-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.02.009
[7] 黄新鹏. 福建霞浦大湾钼铍矿区碱长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(5): 572-579. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710160165
Huang X P. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of alkali feldspar granites from the Dawan Mo-Be deposit, Xiapu, Fujian Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(5): 572-579. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710160165
[8] 张勇, 魏华, 陆太进, 等. 新疆奥米夏和田玉矿床成因及锆石LA-ICP-MS定年研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6): 695-704. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801170007
Zhang Y, Wei H, Lu T J, et al. The genesis and LA-ICP-MS zircon ages of the Omixia nephrite deposit, Xinjiang, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6): 695-704. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201801170007
[9] 郑奋, 刘琰, 张红清. 辽宁岫岩河磨玉岩石地球化学组成及锆石U-Pb定年研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(4): 438-448. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807310089
Zheng F, Liu Y, Zhang H Q. The petrogeochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of nephrith place deposit in Xiuyan, Liaoning[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(4): 438-448. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807310089
[10] 涂家润, 崔玉荣, 周红英, 等. 锡石U-Pb定年方法评述[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(4): 241-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201904002.htm
Tu J R, Cui Y R, Zhou H Y, et al. Review of U-Pb dating methods for cassiterite[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2019, 42(4): 241-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201904002.htm
[11] 李广旭, 曹汇, 王达, 等. 胶北粉子山群和荆山群三叠纪变质变形记录: 金红石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(11): 3246-3258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.11.017
Li G X, Cao H, Wang D, et al. Deformation and metamorphism of triassic fenzishan group and Jianshan Group in the Jianbei massif: Evidence from rutile U-Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(11): 3246-3258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.11.017
[12] 李秋立, 赵磊, 张艳斌, 等. 朝鲜甑山"群"变质岩中锆石-榍石-金红石U-Pb体系: 古元古代—中生代构造-热事件记录[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(10): 3019-3032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201610008.htm
Li Q L, Zhao L, Zhang Y B, et al. Zircon-titanite-rutile U-Pb system metamorphic rocks of Junshan "group" in Korea: Implication of tectno-thermal events from paleoproterozic to mesozoic[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(10): 3019-3032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201610008.htm
[13] 熊伯琴, 许文良, 李秋立, 等. 徐淮地区早白垩世adakitic岩石中榴辉岩类捕虏体中金红石的SIMS U-Pb定年: 对华北克拉通东部陆壳加厚时间的制约[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(5): 553-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201505001.htm
Xiong B Q, Xu W L, Li Q L, et al. SIMS U-Pb dating of rutile within eclogitic xenoliths in the early Cretaceous adakitic rocks of the Xuzhou—Huaibei area, China: Constraints on the timing of crustal thickening on the eastern North China Craton[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2015, 45(5): 553-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201505001.htm
[14] 张贵宾, 张立飞, 宁远煜, 等. 柴北缘超高压变质带的冷却历史: 来自副片麻岩中锆石、金红石的U-Pb年代学和温度信息[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(10): 2835-2842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201410004.htm
Zhang G B, Zhang L F, Ning Y Y, et al. Cooling history for North Qaidam UHPM belt: Constraints from zircon, rutile U-Pb dating and thermometry in paragneiss[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(10): 2835-2842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201410004.htm
[15] 赵一鸣, 李大新, 韩景仪, 等. 内蒙古羊蹄子山—磨石山钛铁矿、金红石和钛铁矿的矿物学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(4): 466-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200804003.htm
Zhao Y M, Li D X, Han J Y, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of anatase, rutile and ilmenite in Yangtizashan—Moshishan titanium ore deposit, Inner Mongolia[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(4): 466-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200804003.htm
[16] 赵一鸣, 李大新, 吴良士, 等. 内蒙古磨石山沉积型变质型钛铁矿矿床: 一个大型新类型钛矿床的发现、勘查和研究[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(9): 1350-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201209005.htm
Zhao Y M, Li D X, Wu L S, et al. Moshishan metamorphosed sedimentary antase deposit: Discovery, exploration, and study of a new genetic type large titanium deposit[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(9): 1350-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201209005.htm
[17] 肖益林, 黄建, 刘磊, 等. 金红石: 重要的地球化学"信息库"[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(2): 398-413. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201102005.htm
Xiao Y L, Huang J, Liu L, et al. Rutile: An important "reservoir" for geochemical information[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(2): 398-413. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201102005.htm
[18] Force E R. Geology of titanium-mineral deposits[J]. The Geological Society of America, 1991, 259: 1-112.
[19] Liu X F, Wang Q F, Deng J, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical investigations of the Dajia salento-type bauxite deposits, western Guangxi, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 105: 137-152.
[20] Hanaor D A H, Sorrell C C. Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2011, 46: 855-874.
[21] Dudek K, Jones F, Radomirovic T, et al. The effect of anatase, rutile and sodium titanate on the dissolution of boehmite and gibbsite at 90℃[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2009, 93: 135-140.
[22] Goresy A E, Chen M, Gillet P, et al. A natural shock-induced dense polymorph of rutile with α-PbO2 structure in the suevite from the ries crater in Germany[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 192: 485-495.
[23] 杜谷, 王坤阳, 冉敬, 等. 红外光谱/扫描电镜等现代大型仪器岩石矿物鉴定技术及其应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(5): 625-633. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/3980f0fc-b8e1-4632-be00-cf45aba72902
Du G, Wang K Y, Ran J, et al. Application of IR/SEM and other modern instrument for mineral identification[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(5): 625-633. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/3980f0fc-b8e1-4632-be00-cf45aba72902
[24] 范光, 葛祥坤. 微区X射线衍射在矿物鉴定中的应用实例[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2010, 27(2): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201002008.htm
Fan G, Ge X K. Application example of micro X-ray diffraction in mineral identification[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2010, 27(2): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201002008.htm
[25] Diebold U. The surface science of titanium dioxide[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2003, 48(5-8): 53-229.
[26] Landmann M, Raulse E, Schmidt W G. The electronic structure and optical response of rutile, anatase and brookite TiO2[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2012, 24: 195503.
[27] Meinhold G. Rutile and its applications in Earth sciences[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 102: 1-28.
[28] Hu Y, Tsai H L, Huang C L. Effect of brookite phase on the anatase-rutile transition in titania nanoparticles[J]. Journal of European Ceramic Society, 2003, 23: 691-696.
[29] Huberty J, Xu H. Kinetics study on phase transformation from titania polymorph brookite to rutile[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2008, 181: 508-514.
[30] Zhang M L, Chen T D, Wang Y J. Insights into TiO2 polymorphs: Highly selective synthesis, phase transition, and their polymorph-dependent properties[J]. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 2017, 7: 52755-52761.
[31] Gamaletsos P N, Godelitsas A, Kasama T. Nano-mineralogy and geochemistry of high-grade diasporic karst-type bauxite from Parnassos—Ghiona mines, Greece[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 84: 228-244.
[32] Zhang L, Park C Y, Wang G H, et al. Phase transformation processes in karst-type bauxite deposit from Yunnan area, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 89: 407-420.
[33] Hebert E, Gauthier M. Unconventional rutile deposits in the Quebec applialachians: Product of hypogene enrichment during low-grade metamorphism[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2007, 102(2): 319-326.
-



 下载:
下载: