Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Soil Selenium in Naidong District, Shannan City, Xizang
-
摘要:
硒是动物和人体所必需的微量元素之一,其丰缺与人和动植物的健康有着密切关系。近年来研究成果表明西藏缺硒土壤主要分布在雅鲁藏布江(简称“雅江”)以北地区,而雅江以南存在土壤全硒含量较高且面积较大区域。西藏山南市乃东区位于青藏高原中南部雅江流域,为雅鲁藏布江流域重要的农业区,也是西藏粮仓之一。本文以西藏山南市乃东区为研究对象,采用原子荧光光谱法(AFS)等方法测定了研究区1022件表层土壤、30组青稞籽实样及根系土壤样品中的硒等元素含量;同时对西藏山南市乃东区雅江两侧农用地及周边牧草地、林地表层土壤硒的分布特征和影响因素进行了研究。结果表明:雅江北侧土壤硒含量算术平均值为0.14mg/kg,接近西藏土壤硒含量平均值0.15mg/kg;雅江南侧土壤硒含量算术平均值为0.30mg/kg,高于西藏土壤硒含量平均值的一倍,略高于中国土壤硒含量平均值0.29mg/kg。乃东调查区不同土地利用类型土壤硒含量的平均值由大到小为:耕地(0.24mg/kg)>牧草地(0.22mg/kg)>林地(0.19mg/kg)。研究结果显示乃东调查区雅江两侧土壤硒含量差异较大;土壤硒元素含量除了受地质背景影响外,还与土壤酸碱度(pH)、有机质等因素有关。随着土壤中有机质含量上升,土壤硒含量明显升高;而随着土壤酸碱度的升高,土壤硒含量变低。此外雅江南侧存在富硒土壤,建议当地充分利用富硒土壤,研究不同品种的农作物对硒的吸收特征,通过农田养分管理,提高土壤中硒的有效性,促进当地发展富硒产业。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Selenium is one of the essential trace elements for animals and humans, and its abundance is closely related to the health of humans, animals and plants. Selenium deficiency is common in Chinese soil, especially in Xizang. Research results in recent years have shown that the selenium-deficient soils in Xizang are mainly distributed in the north of the Yarlung Zangbo River (referred to as "Yajiang"), while there are areas with high total selenium content and a large area in the south of the Yajiang River. Naidong district is located in the Yajiang River valley in the central and southern parts of the Xizang Plateau. It is one of the important agricultural areas in Xizang and one of the granaries of Xizang.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in different areas and different land utilization types on both sides of the Yajiang River in Naidong District, Shannan City, Xizang.
METHODS The contents of selenium and other elements in 1022 topsoil, 30 groups of highland barley seed samples and root soil samples in the Naidong District were determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS). Correlation analysis was used to study the influencing factors of soil selenium.
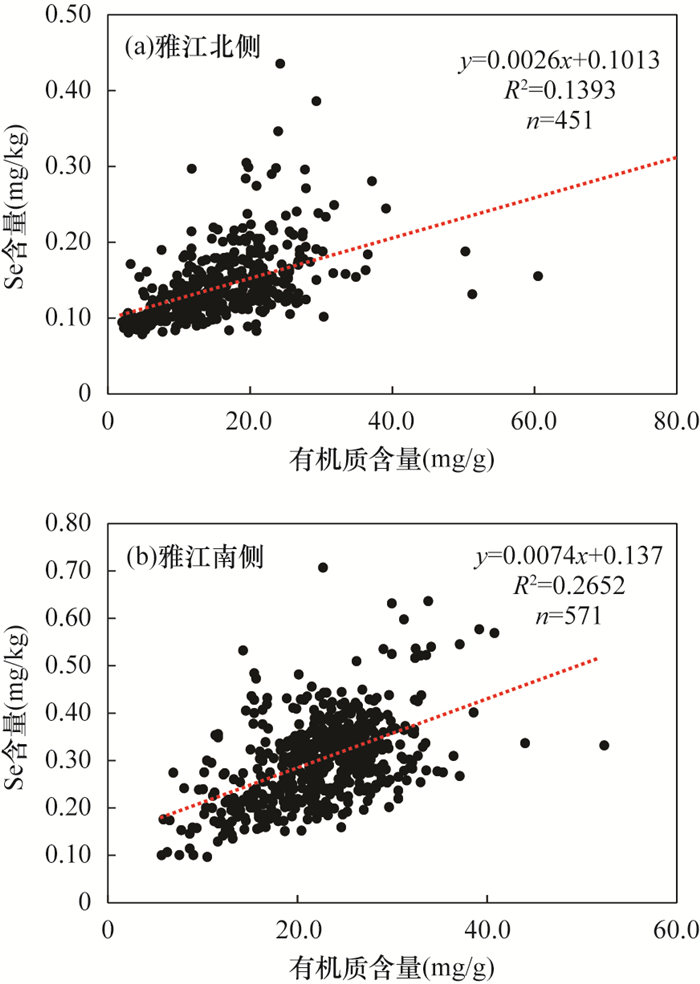
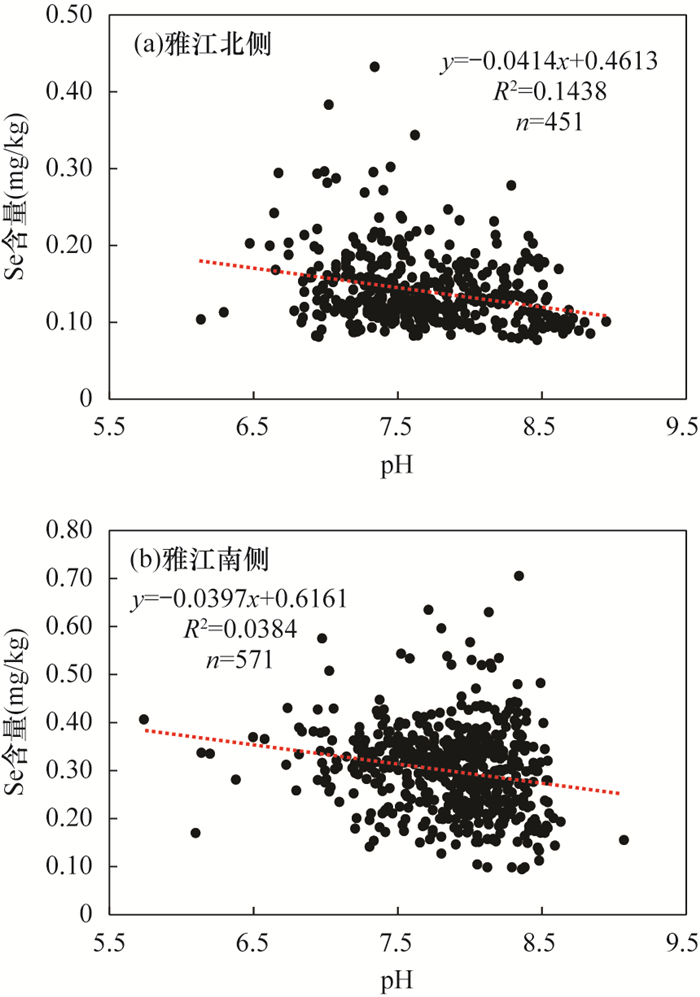
RESULTS The data showed that the arithmetic mean of selenium content in the soil on the north side of the Yajiang River was 0.14mg/kg, which was close to the mean value of selenium in the soil of Xizang (0.15mg/kg). The arithmetic mean of selenium content in the soil on the southern side of the Yajiang River was 0.30mg/kg, which was twice the mean value of soil selenium content in Xizang, and slightly higher than the mean soil selenium content in China (0.29mg/kg). The average selenium content in different land utilization types in the Naidong survey area was cultivated land (0.24mg/kg)>pasture land (0.22mg/kg)>forest land (0.19mg/kg). The research results showed that the soil selenium content on both sides of the Yajiang River in the Naidong survey area was quite different, and there was selenium-rich soil on the south side of the Yajiang River. The factors controlling soil selenium content were not only affected by geological background, but also related to soil pH, organic matter and other factors. Soil Se content increased significantly with the increase of soil organic matter content, but decreased with the increase of soil pH.
CONCLUSIONS It is suggested to make full use of the selenium-enriched soil in Naidong District, and study the absorption of selenium by different crops to improve the availability of selenium in the soil through farmland nutrient management, and promote the development of the local selenium-enriched industry.
-
Key words:
- Naidong District /
- soil /
- Se /
- atomic fluorescence spectrometry /
- influencing factors /
- land utilization type
-

-
表 1 调查区土壤样品硒元素含量参数统计
Table 1. Se content parameter statistics of soil samples in the investigation area
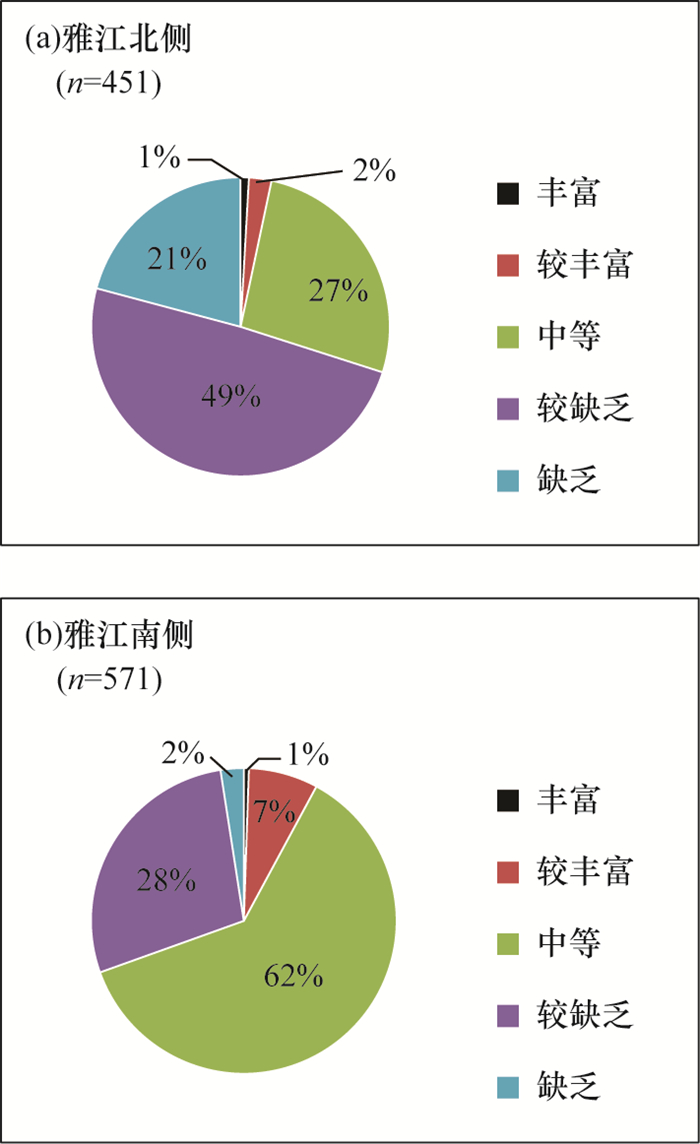
调查区部位 样本数量(件) 硒含量(mg/kg) 富集系数 变异系数 最小值 最大值 平均值 中位数 标准离差 乃东调查区 1022 0.08 0.71 0.23 0.21 0.11 3.74 0.47 雅江北侧 451 0.08 0.44 0.14 0.13 0.05 2.28 0.33 雅江南侧 571 0.1 0.71 0.30 0.31 0.09 4.90 0.29 表 2 调查区土壤样品富硒样品数量情况统计
Table 2. Statistics of soil samples riched in selenium in the investigation area
硒含量指标
(mg/kg)乃东调查区 雅江北侧 雅江南侧 样数
(件)比例
(%)样数
(件)比例
(%)样数
(件)比例
(%)过剩(>3.0) 0 0 0 0 0 0 高(0.40~3.0) 63 6.16 1 0.22 62 10.83 适量(0.175~0.40) 555 54.31 81 17.96 474 83.01 边缘(0.125~0.175) 198 19.37 168 37.25 29 5.06 缺乏(≤ 0.125) 206 20.16 201 44.57 6 1.10 表 3 调查区不同用地类型土壤硒含量特征参数统计
Table 3. Statistics of characteristic parameters of soil selenium content in different land utilization types
土地利用类型 调查区范围 样品数量
(件)硒含量(mg/kg) 富集系数 变异系数 最小值 最大值 平均值 中位数 标准离差 乃东调查区 709 0.08 0.64 0.24 0.24 0.1 3.92 0.43 耕地 雅江北侧 291 0.08 0.44 0.14 0.13 0.04 2.31 0.3 雅江南侧 418 0.13 0.64 0.31 0.32 0.07 5.04 0.24 乃东调查区 186 0.08 0.71 0.22 0.18 0.12 3.48 0.54 牧草地 雅江北侧 85 0.08 0.30 0.14 0.12 0.06 2.27 0.4 雅江南侧 101 0.1 0.71 0.28 0.26 0.12 4.5 0.42 乃东调查区 127 0.08 0.64 0.19 0.17 0.11 3.14 0.55 林地 雅江北侧 75 0.08 0.28 0.14 0.12 0.05 2.19 0.34 雅江南侧 52 0.10 0.64 0.28 0.27 0.11 4.51 0.41 -
[1] 吕瑶瑶, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 等. 大骨节病区硒元素分布的调控机理研究——以四川省阿坝地区为例[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(7): 935-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201207000.htm
Lyu Y Y, Yu T, Yang Z F, et al. The regulation mechanism of selenium distribution in Kaschin-Beck disease area: A case study in Aba area, Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(7): 935-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201207000.htm
[2] 熊咏民, 杨晓莉, 张丹丹, 等. 硒的生物学效应与环境相关性疾病的研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1105-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806008.htm
Xiong Y M, Yang X L, Zhang D D, et al. Research progress in biological function of selenium and environmentally associated diseases[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1105-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201806008.htm
[3] 迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201605017.htm
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201605017.htm
[4] 曲航, 尼玛扎西, 韦泽秀, 等. 西藏青稞产区土壤和籽粒硒含量调查研究[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2020, 40(7): 890-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MLZW202007016.htm
Qu H, Ni M T S, Wei Z X, et al. Investigation on selenium content in soil and Hulless Barley grains in Xizang[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2020, 40(7): 890-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MLZW202007016.htm
[5] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 371.
Environmental Monitoring in China. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 1990: 371.
[6] 王学求, 柳青青, 刘汉粮, 等. 关键元素与生命健康: 中国耕地缺硒吗?[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(3): 421-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202103035.htm
Wang X Q, Liu Q Q, Liu H L, et al. Key elements and human health: Is China's arable land selenium-deficient?[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(3): 421-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202103035.htm
[7] 张晓平, 张玉霞. 西藏土壤中硒的含量及分布[J]. 土壤学报, 2000, 37(4): 558-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.04.018
Zhang X P, Zhang Y X. Content and distribution of selenium in soils of Xizang[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2000, 37(4): 558-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2000.04.018
[8] 杨林生, 吕瑶, 李海蓉, 等. 西藏大骨节病区的地理环境[J]. 地理科学, 2006, 26(4): 466-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2006.04.014
Yang L S, Lyu Y, Li H R, et al. Features of geographical environment of Kaschin-Beck Disease (KBD) affected region in Xizang[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2006, 26(4): 466-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2006.04.014
[9] 钱薇, 唐昊冶, 王如海, 等. 一次消解土壤样品测定汞、砷和硒[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(8): 1215-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201708024.htm
Qian W, Tang H Y, Wang R H, et al. Determination of mercury, arsenic and selenium in soils by one-time digestion[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(8): 1215-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201708024.htm
[10] 李蕾, 苏园, 程楚国, 等. 微敞开体系快速石墨消解-原子荧光法测定食品及土壤中的硒[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1098-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004026.htm
Li L, Su Y, Chen C G, et al. Fast determination of selenium in food and soils by micro-open graphite digestion-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1098-1104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202004026.htm
[11] 王琪, 刘禹含, 杨景娜, 等. 新疆伊犁土壤硒资源分布及与土壤性质的关系分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6): 555-559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ201406013.htm
Wang Q, Liu Y H, Yang J N, et al. Analysis on the distribution of selenium resources and its relationships with soil properties of Ili District, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6): 555-559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ201406013.htm
[12] Li S J, Li W, Hu X, et al. Soil selenium concentration and Kashin-Beck disease prevalence in Xizang, China[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering in China, 2009, 3(1): 62-68. doi: 10.1007/s11783-009-0009-4
[13] 刘冰权, 沙珉, 谢长瑜, 等. 江西赣县清溪地区土壤硒地球化学特征和水稻根系土硒生物有效性影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(5): 740-750. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202107230082
Liu B Q, Sha M, Xie C Y, et al. Geochemical of soil selenium and influencing factors of selenium bioavailability in rice root soils in Qingxi area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(5): 740-750. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202107230082
[14] 杨妍萍, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等. 川西高原地区岩石中硒的地球化学和影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(1): 115-126. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201808290098
Yang Y P, Liu X D, Liu J C, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in rocks from the western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(1): 115-126. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201808290098
[15] 周国华. 富硒土壤资源研究进展与评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 319-336. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911140158
[16] 魏振山, 涂其军, 唐蜀虹, 等. 天山北坡乌鲁木齐至沙湾地区富硒土壤地球化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(5): 893-898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201605008.htm
Wei Z S, Tu Q J, Tang S H, et al. A discussion on the geochemical features and origin of selenium-rich soil on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains from Urumqi to Shawan County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(5): 893-898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201605008.htm
[17] 袁宏, 赵利, 王茂丽, 等. 西藏拉萨至曲水拉萨河沿岸农用地土壤硒锗空间分布与评价[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2): 427-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA202002028.htm
Yuan H, Zhao L, Wang M L, et al. Spatial distribution and evaluation of selenium and germanium in farmland soils from Lhasa to Qushui along the Lhasa River in Xizang[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(2): 427-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA202002028.htm
[18] 曾庆良, 余涛, 王锐. 土壤硒含量影响因素及富硒土地资源区划研究——以湖北恩施沙地为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1): 105-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201801011.htm
Zeng Q L, Yu T, Wang R. The influencing factors of selenium in soils and classifying the selenium-rich soil resources in the typical area of Enshi, Hubei[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(1): 105-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201801011.htm
[19] 陈娟, 宋帅, 史雅娟, 等. 富硒农业生产基地土壤硒资源空间分布特征及评价[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(12): 2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
Chen J, Song S, Shi Y J, et al. Spatial distribution and assessment of selenium in soils of a Se-enrich agricultural production base[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12): 2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
[20] 李明伟, 黄飞岳, 胡蔚红. 恩施茶园土壤硒含量及与茶叶吸收量的相关关系[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2010, 49(4): 832-834. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2010.04.020
Li M W, Huang F Y, Hu W H. Correlations on Se content of tea plantation's soil and Se absorption of tea leaves in Enshi Autonomous Prefecture[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 49(4): 832-834. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2010.04.020
[21] 韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等. 富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系: 以江西丰城为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6): 1177-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201806017.htm
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al. Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6): 1177-1183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201806017.htm
[22] 周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘—梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of South Jiangxi Province: A typical area of Qingtang—Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806017.htm
[23] 饶孝沛, 王明琼, 冉露, 等. 利川市耕地硒资源分布研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(13): 201-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.13.065
Rao X P, Wang M Q, Ran L, et al. Distribution of selenium resources in cultivated land of Lichuan City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agriculture Science, 2016, 44(13): 201-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.13.065
[24] 周殷竹, 刘义, 王彪, 等. 青海省囊谦县农耕区土壤硒的富集因素[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1952-1959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012011.htm
Zhou Y Z, Liu Y, Wang B, et al. Influence factors of soil selenium in cultivated area of Nangqian County, Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1952-1959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012011.htm
[25] 冯辉, 张学君, 张群, 等. 北京大清河流域生态涵养区富硒土壤资源分布和来源解析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 693-704. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905270071
Feng H, Zhang X J, Zhang Q, el al. Distribution characteristics and sources identification of selenium-rich soils in the ecological conservation area of the Daqinghe River Watershed, Beijing[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 693-704. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905270071
[26] 杨志忠, 周文龙, 罗勇军, 等. 贵州镇远县耕地土壤中硒的分布特征及控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 434-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102013.htm
Yang Z Z, Zhou W L, Luo Y J, et al. Distribution of soil selenium of the cultivated land and its controlling factors in Zhenyuan of Guizhou Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(2): 434-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102013.htm
[27] 李晓慧, 高宁, 赵万伏, 等. 宁夏青铜峡农耕土壤硒含量分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2018, 35(5): 422-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ201805006.htm
Li X H, Gao N, Zhao W F, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium in cultivated soil and its influencing factors in Qingtongxia City of Ningxia[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2018, 35(5): 422-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHFZ201805006.htm
[28] 谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等. 中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控与评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3): 273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al. Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in southern China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3): 273-281. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610100152
[29] 顾涛, 赵信文, 雷晓庆, 等. 珠江三角洲崖门镇地区水稻田土壤-植物系统中硒元素分布特征及迁移规律研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(5): 545-555. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201811030118
Gu T, Zhao X W, Lei X Q, et al. Distribution and migration characteristics of selenium in the soil-plant system of paddy fields in the Pearl River Delta, Yamen Town[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(5): 545-555. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201811030118
[30] 郭亚楠, 李海蓉, 杨林生, 等. 雅鲁藏布江两岸环境硒分布特征及与大骨节病发病的关系[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 2017, 36(7): 494-497. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2017.07.007
Guo Y N, Li H R, Yang L S, et al. The relationship be-tween environment selenium characteristics and distribution of Kaschin-Bebk disease in the Yarlung Zangbo River Banks[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 2017, 36(7): 494-497. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4255.2017.07.007
-



 下载:
下载: