A Review of Research Progress on Fractionation Characteristics and Acquisition Methods of Rare Earth Elements in Carbonate Minerals
-
摘要:
古地表水中自生沉积的碳酸盐矿物能够较完整地保留沉积时水体稀土元素的分馏特征,这些特征主要受水体环境条件的影响,因此可以作为沉积水体古环境信息的良好指标。本文根据前人研究,综述了古地表水pH、盐度、溶氧量和热液输入等环境因素对稀土元素分馏特征的影响,总结了碳酸盐矿物稀土元素分馏特征示踪沉积水体古环境信息和主要获取碳酸盐矿物中稀土元素分馏特征信息的方法。目前,激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法(LA-ICP-MS)和酸溶-电感耦合等离子体质谱法是主要的获取碳酸盐矿物中稀土元素分馏特征的分析方法。单纯只含碳酸盐矿物的样品较少见,出露地表的通常是碳酸盐岩,其在形成过程中会不可避免地混入陆源矿物(如黏土、石英、长石等)和自生沉积的非碳酸盐矿物,这些矿物带入的稀土元素会扰乱碳酸盐矿物中原始稀土元素分馏特征,而这两种方法均未能找到有效地避免这些非碳酸盐矿物干扰的途径。因此,未来稀土元素分馏特征示踪古环境信息的研究首先应该探究能准确获取碳酸盐岩中碳酸盐矿物稀土元素分馏特征的方法。
-
关键词:
- 碳酸盐矿物 /
- 稀土元素 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 分馏特征
Abstract:BACKGROUND Authigenic carbonate minerals deposited from paleo-surface water can retain the fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements in water when deposited. The environmental conditions of the water at the time affect these characteristics. Therefore, these characteristics can be used as a reliable indicator for the paleo-environmental information of deposited water.
OBJECTIVES Based on previous studies, the influence of pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen and hydrothermal input of paleo-surface water on the fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements are reviewed, and the methods of tracing the paleo-environment information and obtaining the characteristics information of rare earth elements in carbonate minerals are summarized.
METHODS At present, laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and acid dissolution-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry are the mainstream analytical methods used to obtain the fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements in carbonate minerals.
RESULTS It is rare to find samples that only contain carbonate minerals, so samples are usually carbonate rocks exposed on the earth's surface. However, carbonate rocks have been inevitably mixed with terrigenous minerals (such as clay, quartz, feldspar) and authigenic non-carbonate minerals during their formation, which will disturb the original rare earth elements fractionation characteristics of the carbonate minerals. Unfortunately, neither method mentioned earlier was successful in avoiding this interference.
CONCLUSIONS The future study on the fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements should first explore the methods to accurately obtain the fractionation characteristics of carbonate minerals in carbonate rocks.
-

-
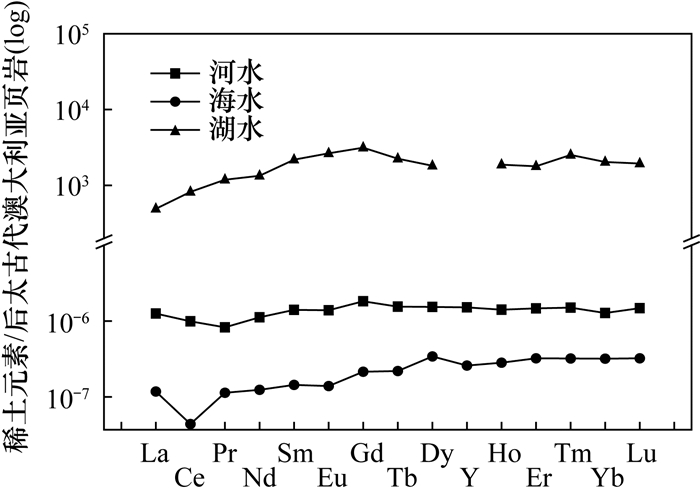
表 1 各类地表水稀土元素分馏特征
Table 1. Fractionation characteristics of rare earth elements in various surface waters
-
[1] 陈道公. 地球化学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009: 203-206.
Chen D G. Geochemistry[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009: 203-206.
[2] 赵平, 李爱民, 刘建中, 等. 应用ICP-MS研究黔西南地区构造蚀变体稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1): 89-96. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.013
Zhao P, Li A M, Liu J Z, et al. Application of ICP-MS to study REE geochemistry of structure alteration rocks in southwestern Guizhou Province, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1): 89-96. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.013
[3] 陈莹, 王晓蓉, 彭安. 稀土元素分馏作用研究进展[J]. 环境科学进展, 1999, 7(1): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ901.001.htm
Cheng Y, Wang X R, Peng A. The research progress of fractionation among the rare earth elements[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1999, 7(1): 10-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ901.001.htm
[4] 佘海东, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 稀土元素在热液中的迁移与沉淀[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12): 3567-3581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201812008.htm
She H D, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Migration and precipitation of rare earth elements in the hydrothermal fluids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(12): 3567-3581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201812008.htm
[5] 王宇航, 朱园园, 黄建东, 等. 海相碳酸盐岩稀土元素在古环境研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(9): 922-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201809006.htm
Wang Y H, Zhu Y Y, Huang J D, et al. Application of rare earth elements of the marine carbonate rocks in paleoenvironmental researches[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(9): 922-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201809006.htm
[6] Taylor S R. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964, 28(8): 1273-1285. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(64)90129-2
[7] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2): 241-265. doi: 10.1029/95RG00262
[8] Zhong S, Mucci A. Partitioning of rare earth elements (REEs) between calcite and seawater solutions at 25℃ and 1atm, and high dissolved REE concentrations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(3): 443-453. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)00381-U
[9] 万友利, 王剑, 万方, 等. 羌塘盆地南部古油藏带布曲组碳酸盐岩稀土元素特征及意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(5): 655-665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201705011.htm
Wan Y L, Wang J, Wan F, et al. Characteristics and indications of rare earth elements in carbonates in the Buqu Formation, southern Qiangtang Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(5): 655-665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201705011.htm
[10] 杜洋, 樊太亮, 高志前. 塔里木盆地中下奥陶统碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及其对成岩环境的指示——以巴楚大板塔格剖面和阿克苏蓬莱坝剖面为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(8): 1509-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201608018.htm
Du Y, Fan T L, Gao Z Q. Geochemical characteristics and their implications to diagenetic environment of lower-middle Ordovician carbonate rocks, Tarim Basin, China: A case study of Bachu Dabantage outcrop and Aksu Penglaiba outcrop[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(8): 1509-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201608018.htm
[11] Liu H Y, Pourret O, Guo H M, et al. Rare earth elements sorption to iron oxyhydroxide: Model development and application to groundwater[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2017, 87: 158-166. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.10.020
[12] Sholkovitz E R. The geochemistry of rare earth elements in the Amazon River estuary[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(10): 2181-2190. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90559-F
[13] Morton P L, Landing W M, Shiller A M, et al. Shelf inputs and lateral transport of Mn, Co, and Ce in the western North Pacific Ocean[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2019, 6: 1-25. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00001
[14] Zhang L Y, Tao C H, Su X, et al. Characteristics of rare earth elements in the surface sediments of southwest Indian Ridge: Implication of grain size for the identification of hydrothermal activity[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2022, 42: 7. doi: 10.1007/s00367-022-00729-8
[15] Zhou X X, Lu X X, Liu C. Geochemical characteristics of carbonates and indicative significance of the sedimentary environment based on carbon-oxygen isotopes, trace elements and rare earth elements: Case study of the lower Paleozoic carbonates in the Gucheng area, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14: 1341. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-07574-6
[16] 刘阳, 邵铁全, 刘云焕, 等. 陕南西乡寒武纪梅树村期微古生物群产出层位的地球化学特征及古环境和古气候条件研究[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(1): 309-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202201023.htm
Liu Y, Shao T Q, Liu Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and palaeo-environment and palaeoclimate conditions of early Cambrian Meishucun micropalaeontological strata in Xixiang, southern Shaanxi[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(1): 309-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202201023.htm
[17] 贾文博, 关平, 刘沛显, 等. 湖相碳酸盐岩元素测试方法研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(4): 842-852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201804019.htm
Jia W B, Guan P, Liu P X, et al. Study on the testing method for elemental composition of lacustrine carbonates[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(4): 842-852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201804019.htm
[18] 吴石头, 许春雪, 陈宗定, 等. LA-ICP-MS结合超高压粉末压片技术快速分析碳酸盐岩中Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba和轻稀土元素[J]. 分析试验室, 2019, 38(9): 1089-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201909018.htm
Wu S T, Xu C X, Chen Z D, et al. Rapid determination of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba and LREEs in carbonate by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in combination with high pressure tableting technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2019, 38(9): 1089-1094. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201909018.htm
[19] 樊连杰, 裴建国, 赵良杰, 等. 利用ICP-MS研究桂林寨底地下河系统中碳酸盐岩稀土元素特征及其形成环境[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3): 251-258. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.006
Fan L J, Pei J G, Zhao L J, et al. Rare earth element composition of carbonate rocks afforded by ICP-MS and formation environment of the Zhaidi underground river in Guilin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3): 251-258. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.006
[20] 陈琳莹, 李崇瑛, 陈多福. 泥灰岩中自生方解石的稀土元素酸溶方法研究[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 43(6): 647-654. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2014.06.009
Chen L Y, Li C Y, Chen D F. Dissolution method of authigenic calcites in marls for rare earth elements analysis[J]. Geochimica, 2014, 43(6): 647-654. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2014.06.009
[21] Zhang K, Zhu X K, Yan B. A refined dissolution method for rare earth element studies of bulk carbonate rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 412: 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.07.027
[22] Chen D F, Huang Y Y, Yuan X L, et al. Seep carbonates and preserved methane oxidizing archaea and sulfate reducing bacteria fossils suggest recent gas venting on the seafloor in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Marine Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22(5): 613-621. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.05.002
[23] Quinn K A, Byrne R H, Schijf J. Comparative scavenging of yttrium and the rare earth elements in seawater: Competitive influences of solution and surface chemistry[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 2004, 10(1-2): 59-80.
[24] Falcone E E, Federico C, Boudoire G. Geochemistry of trace metals and rare earth elements in shallow marine water affected by hydrothermal fluids at Vulcano (Aeolian Islands, Italy)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2022, 593: 120756. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.120756
[25] Ghosh R, Baidya T K. Using BIF magnetite of the Badampahar greenstone belt, iron ore group, East Indian Shield to reconstruct the water chemistry of a 3.3-3.1Ga sea during iron oxyhydroxides precipitation[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 301: 102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.09.006
[26] Surya P L, Ray D, Paropkari A L, et al. Distribution of REEs and yttrium among major geochemical phases of marine Fe-Mn-oxides: Comparative study between hydrogenous and hydrothermal deposits[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 312-313: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.03.024
[27] Liu H Y, Pourret O, Guo H M, et al. Impact of hydrous manganese and ferric oxides on the behavior of aqueous rare earth elements (REE): Evidence from a modeling approach and implication for the sink of REE[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(12): 2837. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122837
[28] Ohta A, Kawabe I. REE(Ⅲ) adsorption onto Mn dioxide (δ-MnO2) and Fe oxyhydroxide: Ce(Ⅲ) oxidation by δ-MnO2[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(5): 695-703. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00578-0
[29] Casse M, Montero-Serrano J C, St-Onge G, et al. REE distribution and Nd isotope composition of estuarine waters and bulk sediment leachates tracing lithogenic inputs in eastern Canada[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2019, 211: 117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2019.03.012
[30] Kim T, Kim H, Kim G. Tracing river water versus wastewater sources of trace elements using rare earth elements in the Nakdong River estuarine waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 160: 111589. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111589
[31] 王中良, 刘丛强. 长江口水体混合过程中溶解态稀土元素分布特征[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(12): 1322-1326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.12.018
Wang Z L, Liu C Q. Distribution characteristics of dissolved rare earth elements during water mixing in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(12): 1322-1326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.12.018
[32] Arienzo M, Ferrara L, Trifuoggi M, et al. Advances in the fate of rare earth elements, REE, in transitional environments: Coasts and estuaries[J]. Water, 2022, 14(3): 401. doi: 10.3390/w14030401
[33] 赵思凡, 顾尚义, 沈洪娟, 等. 华南地区南沱冰期海洋氧化还原环境研究——来自贵州松桃南沱组白云岩稀土元素地球化学的指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(6): 1140-1151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202006002.htm
Zhao S F, Gu S Y, Shen H J, et al. Ocean redox environment in the Nantuo Ice Age of South China: An indication of the rare earth element geochemistry in the dolomites from the Nantuo Formation in Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(6): 1140-1151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202006002.htm
[34] Garcia-Solsona E, Jeandel C. Balancing rare earth element distributions in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 532: 119372. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119372
[35] German C R, Elderfield H. Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: The ground rules[J]. Paleoceanography, 1990, 5(5): 823-833. doi: 10.1029/PA005i005p00823
[36] Liang T, Bao Z D, Zhu X E, et al. Rare earth elements in dolostones and limestones from the Mesoproterozoic Gaoyuzhuang Formation, North China: Implications for penecontem poraneous dolomitization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 196: 104374. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104374
[37] 魏浩天, 刘刚, 韩孝辉, 等. 珊瑚礁对热液流体的地球化学记录——来自南海西沙永兴岛珊瑚礁稀土元素的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4): 78-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202004007.htm
Wei H T, Liu G, Han X H, et al. Geochemical records of hydrothermal fluids in corals: Evidence of rare earth elements from coral reefs in the Yongxing Island, Xisha, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 78-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202004007.htm
[38] Debruyne D, Hulsbosch N, Muchez P. Unraveling rare earth element signatures in hydrothermal carbonate minerals using a source-sink system[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 232-252. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.022
[39] 赵彦彦, 李三忠, 李达, 等. 碳酸盐(岩)的稀土元素特征及其古环境指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(1): 141-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htm
Zhao Y Y, Li S Z, Li D, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of carbonate and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2019, 43(1): 141-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htm
[40] Johannessen K C, Vander Roost J, Dahle H, et al. Environmental controls on biomineralization and Fe-mound formation in a low-temperature hydrothermal system at the Jan Mayen Vent Fields[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 202: 101-123. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.12.016
[41] Johannesson K H, Lyons W B, Yelken M A, et al. Geochemistry of the rare-earth elements in hypersaline and dilute acidic natural terrestrial waters: Complexation behavior and middle rare-earth element enrichments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133(1-4): 125-144. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00072-1
[42] 黄清华, 席党鹏, 王辉, 等. 松辽盆地北部中二叠统碳酸盐岩元素和稳定同位素地球化学特征与古环境[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(5): 1282-1295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202105012.htm
Huang Q H, Xi D P, Wang H, et al. Element and isotope geochemical characteristics of middle Permian carbon-ates and paleoenvironment in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(5): 1282-1295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202105012.htm
[43] 史冀忠, 牛亚卓, 许伟, 等. 银额盆地石板泉西石炭系白山组碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(3): 680-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202103004.htm
Shi J Z, Niu Y Z, Xu W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of Carboniferous Baishan Formation carbonate in Shibanquanxi of Yingen—Ejin Banner Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51(3): 680-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202103004.htm
[44] 陈聪, 林良彪, 余瑜, 等. 四川盆地南部CLD1井龙潭组地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(2): 225-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG202202010.htm
Chen C, Lin L B, Yu Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleo-environmental significance of Longtan Formation in Well CLD1 in southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 49(2): 225-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG202202010.htm
[45] Li Y, Zhao L, Chen Z Q, et al. Oceanic environmental changes on a shallow carbonate platform (Yangou, Jiangxi Province, South China) during the Permian— Triassic transition: Evidence from rare earth elements in conodont bioapatite[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeo-climatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 486: 6-16.
[46] Zhao Y Y, Wei W, Li S Z, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of carbonates as a proxy for deep-time environmental reconstruction[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 574: 110443.
[47] 赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 430-431.
Zhao Z H. Principles of trace element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 430-431.
[48] Fee J A, Gaudette H E, Lyons W B, et al. Rare-earth element distribution in Lake Tyrrell groundwaters, Victoria, Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 96(1): 67-93.
[49] 余新亚, 李平平, 邹华耀, 等. 川北元坝气田二叠系长兴组白云岩稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(3): 309-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201503003.htm
Yu X Y, Li P P, Zou H Y, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of dolostones and its indicative significance of the Permian Changxing Formation in Yuanba Gasfield, northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2015, 17(3): 309-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201503003.htm
[50] Zhang K, Shields G A. Sedimentary Ce anomalies: Secular change and implications for paleoenvironmental evolution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 229: 104015.
[51] Ling H F, Li C F, Chu Z Y, et al. Cerium anomaly variations in Ediacaran—earliest Cambrian carbonates from the Yangtze Gorges area, South China: Implications for oxygenation of coeval shallow seawater[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 225: 110-127.
[52] Chen J B, Algeo T J, Zhao L S, et al. Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by bioapatite, with an example from lower Triassic conodonts of South China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 149: 181-202.
[53] 江冉, 付勇, 王富良, 等. 应用去除碳酸盐法研究滇黔地区"白泥塘层"硅质成分的来源[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3): 236-244. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.004
Jiang R, Fu Y, Wang F L, et al. Application of the removing carbonate method to study the origin of silica in "Bainitangceng" of Yunnan—Guizhou area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3): 236-244. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.03.004
[54] Ye Y T, Wang H J, Wang X M, et al. Elemental geochemistry of lower Cambrian phosphate nodules in Guizhou Province, South China: An integrated study by LA-ICP-MS mapping and solution ICP-MS[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 538: 109459.
[55] Rieger P, Magnall J M, Gleeson S A, et al. Differentiating between hydrothermal and diagenetic carbonate using rare earth element and yttrium (REE+Y) geochemistry: A case study from the Paleoproterozoic George Fisher massive sulfide Zn deposit, Mount Isa, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2022, 57(2): 187-206.
[56] Nozaki Y, Zhang J, Amakawa H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148: 329-340.
[57] Kamber B S, Webb G E. The geochemistry of late Archaean microbial carbonate: Implications for ocean chemistry and continental erosion history[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(15): 2509-2525.
[58] Li F, Webb G E, Algeo T J, et al. Modern carbonate ooids preserve ambient aqueous REE signatures[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 509: 163-177.
[59] Lawrence M G, Greig A, Collerson K D, et al. Rare earth element and yttrium variability in South East Queensland Waterways[J]. Aquatic Geochemistry, 2006, 12: 39-72.
[60] 施泽进, 张瑾, 李文杰, 等. 四川盆地Guadalupian统碳酸盐岩稀土元素和碳-锶同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4): 1095-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201904008.htm
Shi Z J, Zhang J, Li W J, et al. Characteristics of rare earth element and carbon-strontium isotope and their geological significance of Guadalupian carbonate in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1095-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201904008.htm
[61] Kamber B S, Webb G E, Gallagher M. The rare earth element signal in Archaean microbial carbonate: Information on ocean redox and biogenicity[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2014, 171(6): 745-763.
[62] Goldstein S J, Jacobsen S B. Rare earth elements in river waters[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 89(1): 35-47.
[63] Zhao M Y, Zheng Y F. A geochemical framework for retrieving the linked depositional and diagenetic histories of marine carbonates[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 460: 213-221.
[64] Bolhar R, Hofmann A, Siahi M, et al. A trace element and Pb isotopic investigation into the provenance and deposition of stromatolitic carbonates, ironstones and associated shales of the ~3.0Ga Pongola Supergroup, Kaapvaal Craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 158: 57-78.
[65] Caetano-Filho S, Paula-Santos G M, Dias-Brito D. Carbonate REE+Y signatures from the restricted early marine phase of South Atlantic Ocean (late Aptian—Albian): The influence of early anoxic diagenesis on shale-normalized REE+Y patterns of ancient carbonate rocks[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 500: 69-83. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040264531610_4cd8.html
[66] Zhao Y M, Zheng F Y. Marine carbonate records of terrigenous input into Paleotethyan seawater: Geochemical constraints from Carboniferous limestones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 141: 508-531.
[67] 兰叶芳, 任传建, 李小彩, 等. 黔西北毕节地区中二叠统碳酸盐岩岩石学、地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 3(5): 309-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202203006.htm
Lan Y F, Ren C J, Li X C, et al. Petrological and geochemical characteristics and their significance of middle permian carbonate rocks in Bijie area, northwestern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 3(5): 309-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202203006.htm
[68] 杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999(2): 63-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ902.009.htm
Yang S Y, Li C X. Research progress in REE tracer for sediment source[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 1999(2): 63-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ902.009.htm
[69] 郭晓强, 李好斌, 魏荣珠, 等. 山西沁水盆地西缘寒武系碳酸盐岩的元素地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(2): 349-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202002013.htm
Guo X Q, Li H B, Wei R Z, et al. Characteristics of elemental geochemistry of the Cambrian carbonate rocks and their palaeoenvironmental implication in western margin of Qinshui Basin, Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2020, 22(2): 349-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202002013.htm
[70] Feng D, Lin Z J, Bian Y Y, et al. Rare earth elements of seep carbonates: Indication for redox variations and microbiological processes at modern seep sites[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 65: 27-33.
[71] Nothdurft L D, Webb G E, Kamber B S. Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, Canning Basin, western Australia: Confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(2): 263-283.
[72] Ward J F, Verdel C, Campbell M J, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Neoproterozoic carbonate: Constraints on the Neoproterozoic oxygenation events[J]. Precambrian Research, 2019, 335: 105471.
[73] Gong Q L, Li F, Lu C J, et al. Tracing seawater- and terrestrial-sourced REE signatures in detritally contaminated, diagenetically altered carbonate rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 570: 120169.
[74] Della P G, Webb G E, Mcdonald I. REE patterns of microbial carbonate and cements from Sinemurian (lower Jurassic) siliceous sponge mounds (Djebel Bou Dahar, High Atlas, Morocco)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 400: 65-86.
[75] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1-9.
[76] Auer G, Reuter M, Hauzenberger C A, et al. The impact of transport processes on rare earth element patterns in marine authigenic and biogenic phosphates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 203: 140-156.
[77] 娄方炬, 顾尚义. 贵州织金寒武纪磷块岩中磷灰石和白云石稀土元素的LA-ICP-MS分析: 对沉积环境和成岩过程的指示意义[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2020, 38(2): 225-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB202002013.htm
Lou F J, Gu S Y. LA-ICP-MS REE analyses for phosphates and dolomites in cambrian phosphorite in Zhijin, Guizhou Province: Implication for depositional conditions and diagenetic processes[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(2): 225-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB202002013.htm
[78] Baldwin G J, Thurston P C, Kamber B S. High-precision rare earth element, nickel, and chromium chemistry of chert microbands pre-screened with in-situ analysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 285(1): 133-143.
[79] Loope G R, Kump L R, Arthur M A. Shallow water redox conditions from the Permian—Triassic boundary microbialite: The rare earth element and iodine geochemistry of carbonates from Turkey and South China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 351: 195-208.
[80] Bi D, Shi X, Huang M, et al. Geochemical and miner-alogical characteristics of deep-sea sediments from the western North Pacific Ocean: Constraints on the enrichment processes of rare earth elements[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 138: 104318.
[81] Mishra P K, Mohanty S P. Geochemistry of carbonate rocks of the Chilpi Group, Bastar Craton, India: Implications on ocean paleoredox conditions at the late Paleoproterozoic Era[J]. Precambrian Reserach, 2021, 353: 106023.
[82] Tostevin R, Shields G A, Tarbuck G M, et al. Effective use of cerium anomalies as a redox proxy in carbonate-dominated marine settings[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 438: 146-162.
-



 下载:
下载: