A Review of Research Progress on Provenance Indication of Rare Earth Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry Hyphenated Techniques
-
摘要:
稀土元素(REEs)不仅是重要的战略资源,而且因其特有的地球化学属性,在追踪岩石、矿物、沉积物等物质的来源方面具有重要研究意义。近年来,随着REEs在现代社会的广泛应用,人为源REEs作为潜在新兴污染物,在自然环境中的出现频率及浓度水平明显提高。然而,相比于地质源REEs,目前关于人为源REEs研究相对较少,且受检测技术的制约直接测定人为源REEs较为困难。随着仪器分析技术的发展,高选择性的离子色谱(IC)分离技术与高灵敏的电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)技术的联用在人为源REEs分析中发挥了重要作用,该技术的元素形态分析能力使其成为人为源REEs分析的重要研究工具之一。ICP-MS及其联用技术等高精度分析技术发展,使REEs物源指示方面的研究取得革命性突破。本文系统阐述了REEs分异特征、同位素分馏、赋存形态等地球化学特征在识别物质来源、解析关键过程、示踪环境行为等方面的研究进展,主要包括:①REEs配分模式、同位素分异特征在传统物源指示方面有着广泛应用,研究主要基于REEs丰度或同位素分馏信息,结合相关数理统计模型,完成岩石、矿物等物质的溯源研究;②REEs形态特征能够为指示人类活动提供重要依据,譬如,由于使用的核磁共振钆对比剂(GBCAs)种类存在地域差异,人为源REEs赋存形态在不同地区也存在明显的不同,德国等地区自然水体中大环型GBCAs检出率较高,线型检出率较低。在此基础上,系统回顾了ICP-MS及其联用技术在REEs物源示踪研究中的相关应用进程,归纳总结了REEs在追踪物质来源、指示人类活动方面的主要研究情况,对REEs物源示踪研究发展前景作了展望。在这些分析技术中,激光剥蚀多接收等离子体质谱技术(LA-MC-ICP-MS)可以原位获得样品内部REEs同位素组成的空间分布信息;基于亲水离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用技术(HILIC-ICP-MS)的形态分析方法可为人为源REEs研究提供“多维”数据。针对目前技术方法体系存在的不足,本文提出了开发快速便携分析技术、整合多维信息进行示踪研究、综合考虑人类活动影响的研究展望。
Abstract:Rare earth elements (REEs) are not only important strategic resources, but also have important research significance in tracing the sources of rocks, minerals, sediments, and other materials due to their unique geochemical properties. In recent years, with the increasing use of REEs in modern society, anthropogenic REEs have attracted widespread attention from scholars at home and abroad through different pathways into environmental media such as the atmosphere, water and soil. Gadolinium (Gd), one of the most widely used REEs, is commonly used as Gd-based constrast agents (GBCAs). Since the application of GBCAs in the 1980s, their use has increased year by year. However, GBCAs are highly hydrophilic and stable, and they are difficult to remove in conventional wastewater treatment; the vast majority of them can directly enter urban and surrounding waters. Since Bau and Dulski first reported positive Gd anomalies in the Rhine River in Germany in 1996, anthropogenic Gd, an emerging contaminant, has now been detected in surface waters worldwide. However, there are relatively few studies on anthropogenic REEs, and the direct determination of them is difficult due to the constraints of detection techniques, and traditional methods for estimating anthropogenic REEs are inevitably subject to varying degrees of error.
Since its introduction in the 1980s, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has shown great potential for trace multi-element analysis due to its high sensitivity, low detection limits and wide linearity range. The technique combines a plasma ion source with high ionization efficiency and a mass spectrometer with the advantages of high sensitivity, rapid multi-element detection and less mass interference compared to spectroscopy in a special interface, making it a highly efficient technique for simultaneous multi-element analysis. The development of high-precision ICP-MS and its coupling techniques, has led to a revolutionary breakthrough in the study of REEs provenance indication. The combination of highly selective separation techniques such as ion chromatography and highly sensitive ICP-MS has played an important role in the analysis of anthropogenic REEs, and the elemental speciation analysis capabilities of it make this one of the key research tools for the analysis of anthropogenic REEs.
The progress of geochemical features of REEs such as isotopes in identifying material sources, resolving key processes and tracing environmental behavior, is summarized in this study, mainly including: (1)REEs fractionation patterns and isotopic features have been widely used in traditional provenance indication, and research is mainly based on REEs content or isotope information, combined with relevant mathematical and statistical models; (2) The speciation of REEs can provide an important basis for indicating anthropogenic activities, for example, due to the regional differences in the types of GBCAs used, there are obvious geographical differences in the speciation of anthropogenic REEs, with a high detection rate of macrocyclic GBCAs and a low detection rate of linear GBCAs in natural waters in regions such as Germany. On this basis, the application of ICP-MS and its coupling techniques in the source tracing of REEs is systematically reviewed, the main studies on REEs for tracing the sources of substances and indicating human activities are summarized, and the prospects for the development of source tracing of REEs are outlined. Among these analytical techniques, laser ablation multicollector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS) can be used to obtain in-situ information on the spatial distribution of the isotopic composition of REEs within samples. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (HILIC-ICP-MS) has become an important tool for the analysis of the speciation of anthropogenic REEs in waters.
To address the shortcomings of the current technical approach, a research outlook for the development of rapid and portable analytical techniques, the integration of multidimensional information for tracer studies, and the integrated consideration of the effects of human activitiesis proposed. It is worth noting that the frequency and concentration levels of anthropogenic REEs in the natural environment have increased significantly, which may affect the distribution characteristics of geogenic REEs and thus reduce the accuracy of traditional source tracing studies. Therefore, future studies need to consider whether human activities in the vicinity have significantly influenced the study area before conducting conventional provenance indication analyses.
-

-
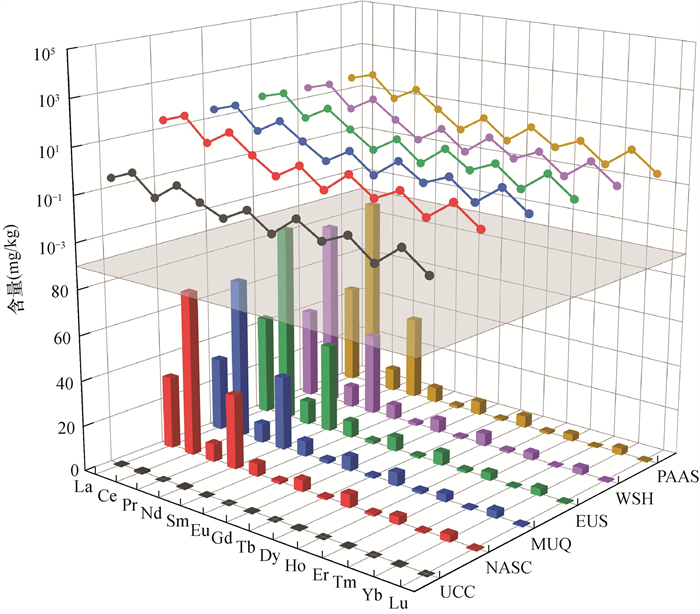
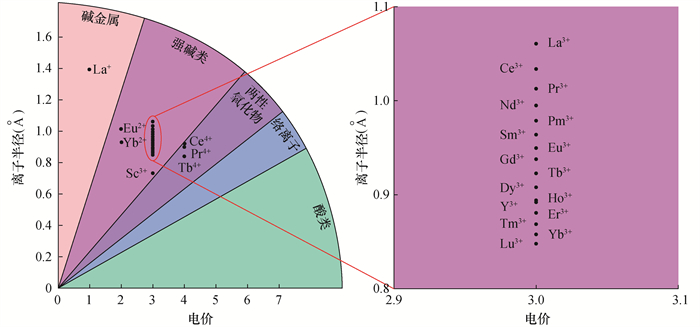
图 1 REEs的离子电位与化学性质关系图[3]
Figure 1.
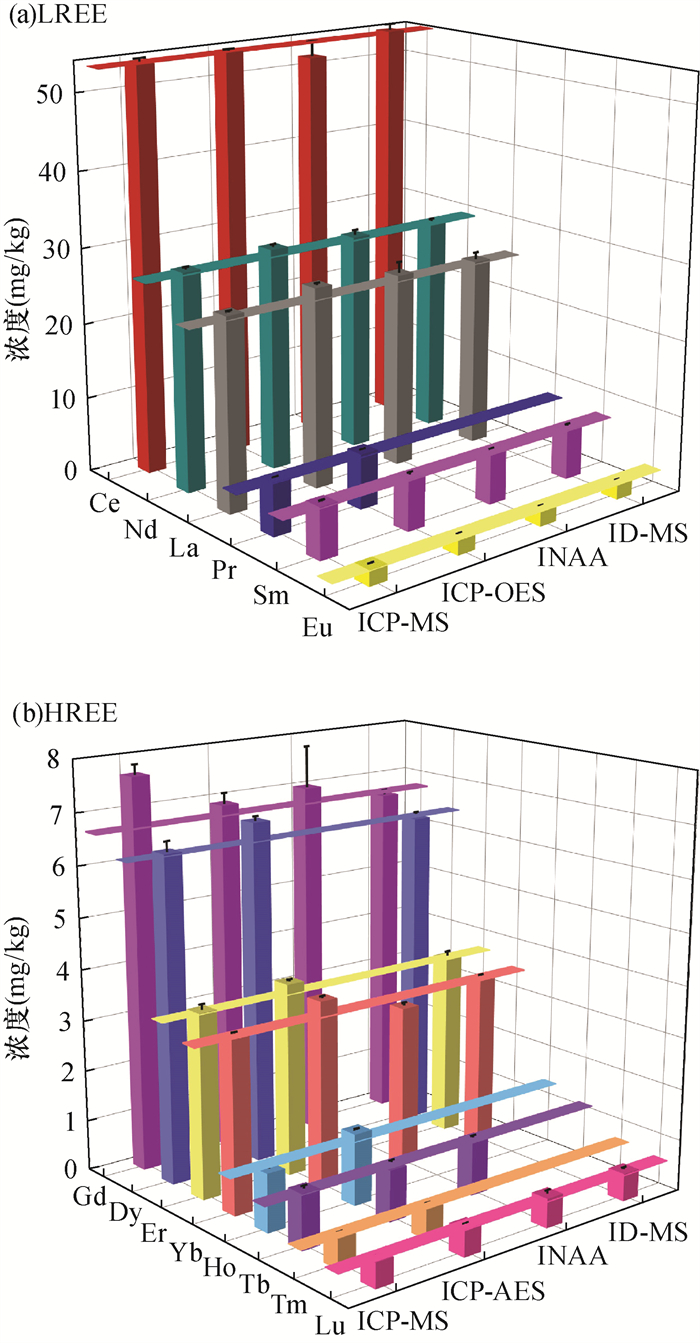
图 5 不同分析方法获得的玄武岩标准物质BCR-1(USGS)的REEs数据[44]
Figure 5.
-
[1] Garzanti E, Andò S. Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands: Implications for provenance interpretation[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58: 517-545.
[2] 张瀚之, 鹿化煜, 周亚利, 等. 渭河流域沉积矿物组合定量分析及示踪[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(4): 944-956. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.021
Zhang H Z, Lu H Y, Zhou Y L, et al. Quantitative analysis of the clastic mineral composition in sediments from the Weihe River Basin by scanning electron microscope and its implication for provenance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(4): 944-956. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2022.021
[3] 陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990: 1-263.
Chen D Q, Chen G. Practical rare earth element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1990: 1-263.
[4] Bau M, Koschinsky A, Dulski P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferro-manganese crusts and seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60: 1709-1725. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00063-4
[5] Liu H, Guo H, Pourret O, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements in sediments of the North China Plain: A probe of sedimentation process[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 134: 105089. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105089
[6] 密蓓蓓, 刘升发, 窦衍光, 等. 东海周边中小型河流沉积物锶钕铅同位素组成及其物源示踪意义[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(4): 440-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB201704012.htm
Mi B B, Liu S F, Dou Y G, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic composition in the sediments of the middle and small rivers around the East China Sea and the implications for tracing sediment sources[J] Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(4): 440-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB201704012.htm
[7] Wang S Y, Xiong Z N, Wang L Q, et al. Potential hot spots contaminated with exogenous, rare earth elements originating from e-waste dismantling and recycling[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 309: 119717. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119717
[8] 王咏梅, 赵仕林, 赵凡, 等. 农用稀土肥料对环境影响的研究[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 27(2): 202-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSD200402022.htm
Wang Y M, Zhao S L, Zhao F, et al. Study on the effect of agricultural rare earth fertilizers on environment[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 27(2): 202-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSD200402022.htm
[9] Klaver G, Verheul M, Bakker I, et al. Anthropogenic rare earth element in rivers: Gadolinium and lanthanum partitioning between the dissolved and particulate phases in the Rhine River and spatial propagation through the Rhine-Meuse Delta (the Netherlands)[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 47: 186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.05.020
[10] Bau M, Dulski P. Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 143: 245-255. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00127-6
[11] Wang T, Wu Q X, Wang Z H, et al. Anthropogenic gadolinium accumulation and rare earth element anomalies of river water from the middle reach of Yangtze River Basin, China[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2021, 5: 3130-3139. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00238
[12] Dulski P, Moeller P, Pekdeger A. Comparison of gado-pentetic acid (Gd-DTPA) and bromide in a dual-tracer field experiment[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2011, 19: 823-834. doi: 10.1007/s10040-011-0713-6
[13] Künnemeyer J, Terborg L, Meermann B, et al. Speciation analysis of gadolinium chelates in hospital effluents and wastewater treatment plant sewage by a novel HILIC/ICP-MS method[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2009, 43: 2884-2890. doi: 10.1021/es803278n
[14] Li X C, Yang K F, Spandler C, et al. The effect of fluid-aided modification on the Sm-Nd and Th-Pb geochronology of monazite and bastnasite: Implication for resolving complex isotopic age data in REE ore systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 300: 1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.02.028
[15] Balaram V. Rare earth elements: A review of applica-tions, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 10(4): 1285-1303. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.12.005
[16] 张珏. 贵阳市地表水中溶解态稀土元素和抗生素分布特征与相关关系研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2021: 3-7.
Zhang Y. Distribution characteristics and correlation of dissolved rare earth elements and antibiotics in surface water of Guiyang City[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2021: 3-7.
[17] Pourmand A, Dauphas N, Ireland T J. A novel extraction chromatography and MC-ICP-MS technique for rapid analysis of REE, Sc and Y: Revising CI-chondrite and Post-Archean Australian Shale (PAAS) abundances[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 291: 38-54. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.08.011
[18] Mclennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200.
[19] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4): 57-72.
[20] Kamber B S, Greig A, Collerson K D. A new estimate for the composition of weathered young upper continental crust from alluvial sediments, Queensland, Australia[J]. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69: 1041-1058. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.020
[21] Bau M, Schmidt K, Pack A, et al. The European Shale: An improved data set for normalisation of rare earth element and yttrium concentrations in environmental and biological samples from Europe[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 90: 142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.01.008
[22] 杨守业, 李从先. 长江与黄河沉积物REE地球化学及示踪作用[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(4): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199904008.htm
Yang S Y, Li C X. REE geochemistry and tracing application in the Yangtze River and the Yellow River sediments[J]. Geochemistry, 1999, 28(4): 374-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199904008.htm
[23] 魏亮, 郭华明, 谢振华, 等. 北京平原沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(6): 72-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006009.htm
Wei L, Guo H M, Xie Z H, et al. Rare earth elements geochemistry and its implication for sediment provenance in the Beijing Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(6): 72-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006009.htm
[24] 陈晓薇, 陈秀玲, 周笑笑, 等. 霍童溪表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源示踪分析[J]. 地球环境学报, 2021, 12(5): 526-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHJ202105006.htm
Chen X W, Chen X L, Zhou X X, et al. Characteristics and trace analysis of rare earth elements in surface sediment of Huotong River[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2021, 12(5): 526-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHJ202105006.htm
[25] Wang L Q, Han X X, Liang T, et al. Discrimination of rare earth element geochemistry and co-occurrence in sediment from Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 217: 851-857.
[26] 高永娟, 凌文黎, 邱啸飞, 等. La-Ce同位素体系应用现状和研究进展[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(1): 33-42, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201101005.htm
Gao Y J, Ling W L, Qiu X F, et al. La-Ce isotopic system: Application status and advances[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(1): 33-42, 52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201101005.htm
[27] 李超, 孙鹏程, 孟会明, 等. 一种新的稀有金属矿床定年技术: 微区原位Sm-Nd定年[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(2): 445-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202202009.htm
Li C, Sun P C, Meng H M, et al. A new age determination technique for rare metal deposits: In situ Sm-Nd dating[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(2): 445-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202202009.htm
[28] Kaczor-Kurzawa D, Wysocka I, Porowski A, et al. The occurrence and distribution of rare earth elements in mineral and thermal waters in the Polish Lowlands[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 237: 106984.
[29] 王汾连. 太平洋深海粘土的REE和Nd同位素特征及物源意义[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(S1): 201-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2017S1098.htm
Wang F L. The characteristics of REE and Nd isotopes and their provenance significance of the pelagic sediments from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(S1): 201-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2017S1098.htm
[30] Liu Y Z, Masuda A, Inoue M. Measurement of isotopes of light rare earth elements in the form of oxide ions: A new development in thermal ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2000, 72(13): 3001-3005.
[31] Migaszewski Z M, Gałuszka A. The characteristics, occurrence, and geochemical behavior of rare earth elements in the environment: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 45: 429-471.
[32] 李梅. 稀土元素及其分析化学[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009: 1-30.
Li M. Rare earth elements and their analytical chemistry[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009: 1-30.
[33] 王玉洁, 刘蓓蓓, 万全, 等. 稀土元素在土壤中的释放与迁移研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(3): 644-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ202103023.htm
Wang Y J, Liu B B, Wan Q, et al. The release and transport behavior of rare earth elements in soil: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(3): 644-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ202103023.htm
[34] 韩松, 黄忠祥, 贾秀勤, 等. 云南个旧打磨山钙质夕卡岩及石榴石的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(2): 192-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302009.htm
Han S, Huang Z X, Jia X Q, et al. The geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in skarns and their garnets from Damoshan area, Gejiu District, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(2): 192-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199302009.htm
[35] Millero F J. Stability constants for the formation of rare earth inorganic complexes as a function of ionic strength[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56: 3123-3132.
[36] 孟秀丽. 赣南小流域水体中溶解态稀土元素地球化学及微量元素组成[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2008: 1-9.
Meng X L. Geochemistry and trace element composition of dissolved rare earth elements in a small watershed in southern Jiangxi[D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2008: 1-9.
[37] Tweed S O, Weaver T R, Cartwright I, et al. Behavior of rare earth elements in groundwater during flow and mixing in fractured rock aquifers: An example from the Dandenong Ranges, southeast Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 234: 291-307.
[38] Dulski P, Moeller P, Pekdeger A. Comparison of gadopentetic acid (Gd-DTPA) and bromide in a dual-tracer field experiment[J]. Hydrogeology, 2011, 19(4): 823-834.
[39] Horstmann M, de Vega R G, Bishop D P, et al. Determination of gadolinium MRI contrast agents in fresh and oceanic waters of Australia employing micro-solid phase extraction, HILIC-ICP-MS and bandpass mass filtering[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2021, 36(4): 767-775.
[40] Okabayashi S, Kawane L, Mrabawani N Y, et al. Specia-tion analysis of gadolinium-based contrast agents using aqueous eluent-hydrophilic interaction liquid chromato-graphy hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2021, 222: 121531.
[41] 王金土. 黄海表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 1990(1): 44-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199001004.htm
Wang J T. REE geochemistry of surficial sediments from the Yellow Sea of China[J]. Geochemistry, 1990(1): 44-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199001004.htm
[42] 唐诵六, 孙景信, 屠树德, 等. 广州土壤中的稀土元素[J]. 土壤学报, 1980, 17(4): 299-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198004000.htm
Tang S L, Sun D X, Tu S D, et al. Rare earth elements in some soils from Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Soil, 1980, 17(4): 299-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB198004000.htm
[43] 龚子珊. 电感耦合等离子体质谱生物样品基质效应和分析方法的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020: 1-14.
Gong Z S. Study on matrix effect and analysis methods in biological samples by in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020: 1-14.
[44] Balaram V. Recent trends in the instrumental analysis of rare earth elements in geological and industrial materials[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 1996, 15: 475-486.
[45] 张祎玮, 蒋俊平, 李浩, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤中稀土元素条件优化[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(3): 605-613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202103015.htm
Zhang Y W, Jiang J P, Li H, et al. Optimization of microwave digestion inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for determination of rare earth elements in soil[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2021, 40(3): 605-613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202103015.htm
[46] 高娟琴, 于扬, 李以科, 等. 内蒙白云鄂博稀土矿土壤-植物稀土元素及重金属分布特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 871-882. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202102210026
Gao J Q, Yu Y, Li Y K, et al. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements and heavy metals in a soil-plant system at Bayan Obo rare earth mine, Inner Mongolia[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 871-882. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202102210026
[47] 何伟, 吴亮, 魏向成, 等. 宁东煤田中侏罗统延安组稀有稀散稀土元素地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(6): 962-977. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111080169
He W, Wu L, Wei X C, et al. Geochemical characteristics of three kinds of rare elements in middle Jurassic Yan' an Formation of Ningdong coalfield and their indicative significance to sedimentary environment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(6): 962-977. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111080169
[48] 贾玉衡, 钱建平. 电子探针-电感耦合等离子体质谱法研究不同种类石榴石的稀土元素配分和矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 886-895. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060007
Jia Y H, Qian J P. Study on REE distribution and mineralogical characteristics of different garnets by electron probe and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 886-895. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060007
[49] 郭东旭, 刘琰, 李自静, 等. 应用电感耦合等离子体质谱技术研究牦牛坪矿床霓长岩化蚀变矿物微量元素特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 896-907. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060003
Guo D X, Liu Y, Li Z J, et al. Determination of trace element compositions of altered minerals in fenitization veins by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 896-907. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060003
[50] 高永娟. La-Ce同位素分析技术及其在岩浆侵位和沉积过程氧化环境研究中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010: 1-32.
Gao Y J. La-Ce isotope analytical method and its application to oxidizing environment study during magmatic intrusion and sedimentary processes[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2010: 1-32.
[51] Sindern S. Analysis of rare earth elements in rock and mineral samples by ICP-MS and LA-ICP-MS[J]. Physical Sciences Reviews, 2017, 2(2): 20160066.
[52] 杨岳衡, 杨进辉, 吴福元, 等. 激光原位LA-MC-ICP-MS测定地质样品Sm-Nd同位素方法新进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(3): 422-431, 401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201603005.htm
Yang Y H, Yang J H, Wu F Y, et al. New progresses in analytical methods of in situ Sm-Nd isotope measurement of natural geological samples by laser ablation multi-collector ICP mass spectrometry[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2016, 35(3): 422-431, 401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201603005.htm
[53] Foster G L, Vance D. In situ Nd isotopic analysis of geological materials by laser ablation MC-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(3): 288-296.
[54] Foster G L, Carter A. Insights into the patterns and locations of erosion in the Himalaya-A combined fission-track and in situ Sm-Nd isotopic study of detrital apatite[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 257(3-4): 407-418.
[55] 王艳萍, 郭于枫, 张玲帆. IC-ICP-MS联用技术同时测定饮用水中砷、铬、碘、溴四种元素的不同形态[J]. 分析试验室, 2021, 40(7): 827-831. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202107012.htm
Wang Y P, Guo Y F, Zhang L F. Simultaneous determination for elements species of arsenic, chromium, iodide and bromine in drinking water by IC-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2021, 40(7): 827-831. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202107012.htm
[56] Idee J M, Port M, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and biological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: A review[J]. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology, 2006, 21: 335-335.
[57] Raju C S K, Cossmer A, Scharf H, et al. Speciation of gadolinium based MRI contrast agents in environmental water samples using hydrophilic interaction chromatography hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2010, 25: 55-61.
[58] Lindner U, Lingott J, Richter S, et al. Analysis of gad-olinium-based contrast agents in tap water with a new hydrophilic interaction chromatography (ZIC-cHILIC) hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 407: 2415-2422.
[59] 黄颖. 中亚热带地区加积型红土稀土元素分馏特征及环境意义[D]. 杭州: 浙江师范大学, 2020: 1-28.
Huang Y. Rare earth elements fractionation charateristics and its envrionmental significance of aggradation red earth in middle subtropical area[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Normal University, 2020: 1-28.
[60] 齐文菁, 李小艳, 范德江, 等. 印度洋东经90°海岭现代沉积物稀土元素组成及其物源示踪意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(2): 92-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202202009.htm
Qi W J, Li X Y, Fan D J, et al. Rare earth element composition of the surface sediments from the ninety east ridge and its implications for provenance[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(2): 92-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202202009.htm
[61] Guo Y L, Li C, Wang C Y, et al. Sediment routing and anthropogenic impact in the Huanghe River catchment, China: An investigation using Nd isotopes of river sediments[J]. Water Resources Research, 2021, 57(9): e2020WR028444.
[62] 汤振权, 刘刚, 许文年. 稀土元素示踪技术及其在土壤侵蚀研究中的应用[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2011, 29(5): 515-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB201105002.htm
Tang Z Q, Liu G, Xu W N. REE tracing method and application in soil erosion[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2011, 29(5): 515-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB201105002.htm
[63] Wang L Q, Liang T, Kleinman P J A, et al. An experimental study on using rare earth elements to trace phosphorous losses from nonpoint sources[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 85: 1075-1079.
[64] Han R, Wang Z, Shen Y, et al. Anthropogenic Gd in urban river water: A case study in Guiyang, SW China[J]. Elementa-Science of the Anthropocene, 2021, 9(1): 00147.
[65] Macke M, Quarles C D, Sperling M, et al. Fast and auto-mated monitoring of gadolinium-based contrast agents in surface waters[J]. Water Research, 2021, 207: 117836.
[66] Brunjes R, Hofmann T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in fre-shwater and drinking water systems[J]. Water Research, 2020, 182: 115966.
[67] Liu Y, Wu Q, Jia H, et al. Anthropogenic rare earth elements in urban lakes: Their spatial distributions and tracing application[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 300: 134534.
[68] Kim I, Kim S H, Kim G. Anthropogenic gadolinium in lakes and rivers near metrocities in Korea[J]. Environmental Science-Processes and Impacts, 2020, 22: 144-151.
[69] da Costa A R B, Rousseau T C C, Maia P D, et al. Anthropogenic gadolinium in estuaries and tropical Atlantic coastal waters from Fortaleza, northeast Brazil[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 127: 104908.
[70] Sundriyal S, Shukla T, Tripathee L, et al. Natural versus anthropogenic influence on trace elemental concentration in precipitation at Dokriani Glacier, central Himalaya, India[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 27: 3462-3472.
[71] 贾会鹏. 武汉市地表水体中稀土元素分布特征及人为源Gd的来源研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020: 1-14.
Jia H P. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements and anthropogenic Gd in surface water in Wuhan City[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020: 1-14.
[72] Gao S L, Wang Z H, Wu Q X, et al. Urban geochemistry and human-impacted imprint of dissolved trace and rare earth elements in a high-tech industrial city, Suzhou[J]. Elementa-Science of the Anthropocene, 2021, 9: 00151.
[73] Wang L Q, Liang T. Accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements in atmospheric particulates around a mine tailing in Baotou, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 88: 23-29.
[74] Dang D H, Zhang Z. Hazardous motherboards: Changes in metal contamination related to the evolution of electronic technologies[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115731.
[75] Brewer A, Dror I, Berkowitz B. Electronic waste as a source of rare earth element pollution: Leaching, transport in porous media, and the effects of nanoparticles[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 132217.
[76] Ma L, Dang D H, Wang W, et al. Rare earth elements in the Pearl River Delta of China: Potential impacts of the REE industry on water, suspended particles and oysters[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 244: 190-201.
[77] Henríquez-Hernández L A, Boada L D, Carranza C, et al. Blood levels of toxic metals and rare earth elements commonly found in e-waste may exert subtle effects on hemoglobin concentration in sub-Saharan immigrants[J]. Environment International, 2017, 109: 20-28.
[78] 范广勤, 刘志刚, 郑辉烈, 等. 稀土暴露对儿童免疫功能影响的研究[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2002, 18(8): 952-953. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW200208029.htm
Fan G Q, Liu Z G, Zheng H L, et al. Study on effects of exposure to rare earth elements on function of immune system of children[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2002, 18(8): 952-953. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGW200208029.htm
[79] Nigro A, Sappa G, Barbieri M. Boron isotopes and rare earth elements in the groundwater of a landfill site[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 190: 200-206.
[80] Möller P, Morteani G, Dulski P. Anomalous gadolinium, cerium, and yttrium contents in the adige and isarco river waters and in the water of their tributaries (Provinces Trento and Bolzano/Bozen, NE Italy)[J]. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 2003, 31(3): 225-239.
[81] Pereto C, Coynel A, Lerat-Hardy A, et al. Corbicula flum-inea: A sentinel species for urban rare earth element origin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 732: 138552.
[82] Stojanovic A, Kogelnig D, Mitteregger B, et al. Major and trace element geochemistry of superficial sediments and suspended particulate matter of shallow saline lakes in eastern Austria[J]. Chemie Der Erde-Geochemistry, 2009, 69(3): 223-234.
[83] Lawrence M G, Bariel D G. Tracing treated wastewater in an inland catchment using anthropogenic gadolinium[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80(7): 794-799.
[84] Barbieri M, Andrei F, Nigro A, et al. The relationship between the concentration of rare earth elements in landfill soil and their distribution in the parent material: A case study from Cerreto, Roccasecca, central Italy[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 213: 106492.
[85] Amorim A M, Sodre F F, Rousseau T C C, et al. Assessing rare-earth elements and anthropogenic gadolinium in water samples from an urban artificial lake and its tributaries in the Brazilian Federal District[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2019, 148: 27-34.
-



 下载:
下载: