Experimental Method and Application of Rapid and Continuous Extraction of Reduced Inorganic Sulfur from Sediments
-
摘要:
还原性无机硫是沉积物硫中最活跃的部分,其含量变化控制沉积物中铁、磷及重金属等元素的地球化学行为,在地质过程和环境污染方面都具有至关重要的影响。化学连续提取法是目前沉积物中硫形态提取基本方法,但常用的冷扩散法处理单个样品耗时长,难以实现对大批量样品的快速连续提取。为实现快速、准确地测定沉积物样品各形态还原性无机硫的含量,本文采用热蒸馏法,改进基于前人的三步提取过程,通过优化实验装置预先制备实验所需的二氯化铬溶液,实现了样品还原性无机硫形态的快速连续提取;以过氧化氢为氧化剂,将提取的各形态硫氧化为$\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}$后采用离子色谱进行检测。选取三峡库区沉积物样品进行重复实验检验,得到提取酸挥发性硫、黄铁矿硫、元素硫的标准偏差(RSD,n=3)分别为5.26%、1.22%和3.09%,重复性较好。进一步对酸挥发性硫、黄铁矿硫、元素硫的加标回收率进行测定,得到这三种硫形态的回收率分别为92.8%、93.6%、94.1%。本实验方法采用的热蒸馏法对单个硫形态提取时间为1.5h,用时较短,玻璃装置连接便捷、操作简单,分析检测准确度好,实现了一套装置对沉积物还原性无机硫形态的连续提取,可适用于大批量样品的硫形态快速提取与检测。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Sulfur is an active element with multiple chemical forms, which plays a vital role in the regulation of redox chemistry. Reduced inorganic sulfur (RIS) including acid volatile sulfur (AVS), elemental sulfur (ES) and pyrite sulfur (CRS) is the most active part of sulfur species in sediments and plays an important role in controlling the geochemical behavior of iron, phosphorus and heavy metals in sediments. Separation and determination of reduced inorganic sulfur in anoxic sediments are critical to ecological and geological studies of sulfur cycles.
Both distillation and diffusion methods can be effectively used to separate AVS, ES, and CRS in sediments. However, the current methods for extracting sulfur species are difficult to adapt to the large number of samples in geological and environmental research. Due to the reaction time, requirements of 24h for single sulfur species in the diffusion method limits the number of samples that can be processed on a timely basis. This limitation presents a problem for analyzing fresh anoxic sediment samples which have to be processed immediately to minimize the risk of sulfide re-oxidation. The detection method has the disadvantages of having a cumbersome testing process, long analysis time, and easy loss of sulfur components.
OBJECTIVES To achieve efficient and continuous determination of reduced inorganic sulfur forms in bulk sediment samples.
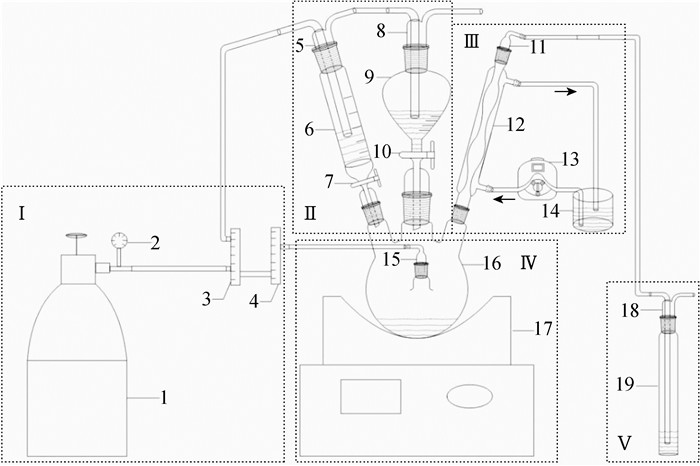
METHODS The method used in this experiment was improved based on the thermal distillation method, which was used to continuously extract the reduced inorganic sulfur from sediments. The reaction flask used in the experiment was a three-head round-bottom flask. A nitrogen flushing pipe, a condenser tube and two injection tubes were connected to each of the small necks. For the AVS procedure, 1.00g sediment sample reacted with 10mL of 6mol/L HCl under nitrogen gas at an elevated temperature (90℃) to convert reduced sulfur species into hydrogen sulfide which was subsequently carried by a nitrogen gas stream into a trap. For the CRS procedure, 20mL of CrCl2 solution was added to the sediment in the distillation flask after the AVS procedure, and 10mL of 6mol/L HCl was immediately placed in the flask at an elevated temperature (90℃), flushed with nitrogen. For the ES procedure, 20mL DMF were poured into the sample flask which contained acid and CrCl2 solutions from the previous procedure. 20mL of CrCl2 solution and 10mL of 6mol/L HCl were injected into the flask, and the reaction was allowed to take place at 90℃ purging with nitrogen. During the entire distillation process, H2S gas was absorbed by NaOH solution, and then oxidized by H2O2 to $\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}$. The concentrations of $\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}$ were obtained by ion chromatography.
RESULTS Repeatability experiments (n=3) were conducted on sediment samples from the Three Gorges Reservoir area and the mean values of acid volatile sulfur, elemental sulfur and pyrite sulfur were obtained as 0.19, 0.37 and 3.10μmol/g, respectively. The relative standard deviations (RSD) of the experimental results were 5.26%, 1.22% and 3.09%, respectively. In order to test the effectiveness of the distillation procedures, Na2S·9H2O, pyrite and S were added in the sediment to reveal the corresponding standard recoveries. An average of 92.8% of the added Na2S·9H2O was recovered by the AVS diffusion method. An average of 93.6% of the added pyrite was recovered by the CRS diffusion method. An average of 94.1% of the added elemental sulfur was recovered by the ES diffusion method. In the literature, recovery of AVS by the improved diffusion method ranged from 82.01% to 108.71%, and recovery of ES ranged from 92.25% to 98.08% (n=3), respectively.
The modified apparatus presented in this paper was an economic version which uses rubber and glass parts. The method provided the advantages of lower sample weighing, and simple operation. Compared with the diffusion method (24h), the extraction time for individual sulfur forms by our distillation method was just 1.5h. The recoveries achieved by the method are comparable to those reported for earlier methods. In addition, the results are more like the data on reduced inorganic sulfur content obtained by Hongbin Yin after measuring sediment samples from Taihu Lake using the modified cold diffusion method, indicating that the method designed in this study has a high degree of confidence.
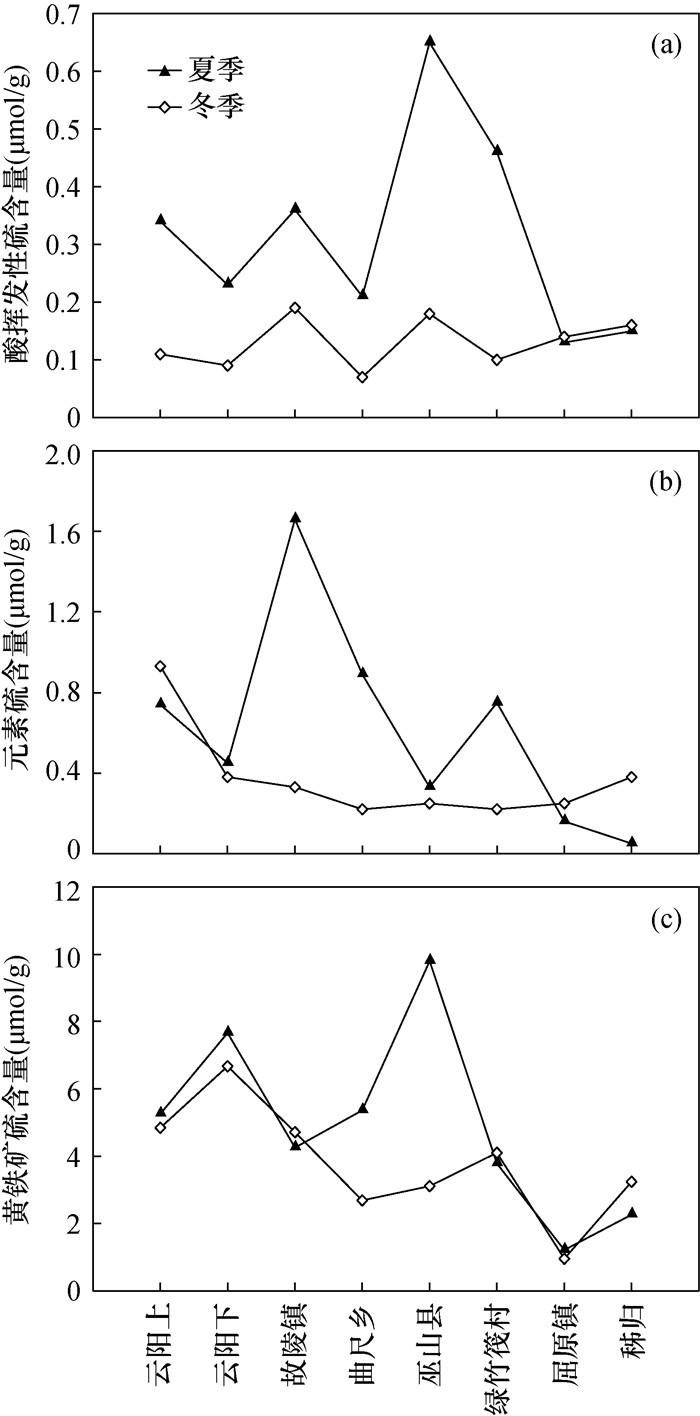
Geochemical processes of sulfur in river aquatic systems play a crucial role in environmental evolution. In this study, the distributions and seasonal variation of reduced inorganic sulfur (RIS) in the Three Gorges Reservoir area surface sediments were investigated. Surface sediment samples were collected from 8 points in the section from Yunyang to Zigui in the Three Gorges Reservoir area in August and December 2017. The result showed that the AVS and ES contents were higher in summer than in winter, and the trend of RIS in the section from Yunyang to Zigui was roughly decreasing, with obvious seasonal and spatial changes. Low sulfur pollution in the Three Gorges Reservoir area was observed.
CONCLUSIONS The improved thermal distillation method and apparatus in this study have significant advantages in the extraction efficiency of reduced inorganic sulfur from sediments. The extraction time of this study for individual sulfur form is 1.5h, less than the diffusion method. The established analytical method has good precision and accuracy, which is suitable for investigation studies with large numbers of samples such as environmental research and geological surveys.
-

-
图 3 (a) 三峡库区采样点分布;(b) 三峡沉积物与太湖表层沉积物还原性无机硫含量对比[30]
Figure 3.
表 1 重复实验与加标实验结果
Table 1. Results of repeated experiment and spike recovery in AVS, CRS, and ES procedures.
硫形态 重复实验 加标实验(回收率) 第一次实验(μmol/g) 第二次实验(μmol/g) 第三次实验(μmol/g) 平均值(μmol/g) RSD(%) 第一次实验(%) 第二次实验(%) 第三次实验(%) 平均值(%) RSD(%) 酸挥发性硫(AVS) 0.20 0.19 0.18 0.19 5.26 91.6 93.2 93.6 92.8 1.14 黄铁矿硫(CRS) 3.13 3.06 3.12 3.10 1.22 93.4 95.7 91.7 93.6 2.14 元素硫(ES) 0.38 0.38 0.36 0.37 3.09 94.6 93.8 93.9 94.1 0.46 -
[1] Wang J, Chen J, Guo J, et al. Speciation and transfor-mation of sulfur in freshwater sediments: A case study in southwest China[J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 2017, 228(10): 392. doi: 10.1007/s11270-017-3580-5
[2] 毛立, 孙志高, 陈冰冰, 等. 闽江河口互花米草入侵湿地土壤无机硫赋存形态及其影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(12): 4840-4852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202112018.htm
Mao L, Sun Z G, Chen B B, et al. Variations of inorganic sulfur fractions and main influencing factors in marsh soils with different years of spartina alterniflora invasion in the Min River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(12): 4840-4852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB202112018.htm
[3] Lu Q Q, Bai J H, Yan D H, et al. Sulfur forms in wetland soils with different flooding periods before and after flow-sediment regulation in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 276(8): 122969.
[4] 陈伟锐. 高频红外碳硫仪测定土壤和水系沉积物中的硫实验条件改进[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(1): 123-128. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045
Chen W R. Improvement of experimental conditions for the determination of sulfur in soil and stream sediments by high frequency infrared carbon and sulfur analyzer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(1): 123-128. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804160045
[5] Jiang M, Sheng Y Q, Liu Q Q, et al. Conversion mecha-nisms between organic sulfur and inorganic sulfur in surface sediments in coastal rivers[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 752: 141829. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141829
[6] 陈冰冰, 孙志高, 孙文广, 等. 外源氮输入对生长季黄河口碱蓬湿地土壤无机硫形态变化特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(5): 277-286. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2018.05.044
Chen B B, Sun Z G, Sun W G, et al. Effects of exogenous nitrogen enrichment on variations of inorganic sulfur fractions in soils of suaeda salsa marsh in the Yellow River Estuary during the growing season[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(5): 277-286. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2018.05.044
[7] Huerta-Diaz M A, Tessier A, Carignan R. Geochemistry of trace metals associated with reduced sulfur in freshwater sediments[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1998, 13(2): 213-233. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(97)00060-7
[8] 刘崴, 胡俊栋, 杨红霞, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱联用技术在元素形态分析中的应用进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 327-339. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006110089 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006110089
Liu W, Hu J D, Yang H X, et al. Research progress on elemental speciation analysis by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry hyphenated techniques[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 327-339. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006110089 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006110089
[9] 李力, 王小静, 刘季花. 沉积物中酸可挥发性硫化物的分析方法研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2015, 46(1): 96-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ201501012.htm
Li L, Wang X J, Liu J H. Analytical method of acid volatile sulfide in sediment[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2015, 46(1): 96-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ201501012.htm
[10] 徐程, 杨斌, 朱雪菁, 等. 大风江口海域沉积物酸可挥发性硫化物、重金属分布及风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(6): 1530-1538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202006026.htm
Xu C, Yang B, Zhu X Q, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of acid volatile sulfide and heavy metals in sediments of Dafengjiang River Estuary[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(6): 1530-1538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX202006026.htm
[11] Souza L R, Knöller K, Ladeira A C Q. Sulfur isotope fractionation and sequential extraction to assess metal contamination on lake and river sediments[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2016, 16: 1986-1994. doi: 10.1007/s11368-016-1410-9
[12] Nriagu J O, Soon Y K. Distribution and isotopic com-position of sulfur in lake sediments of northern Ontario[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(3): 823-834. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90175-9
[13] Duan W, Coleman M L, Pye K. Determination of reduced sulphur species in sediments—An evaluation and modified technique[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 141(3): 185-194.
[14] 曹爱丽, 周桂平, 胡姝, 等. 崇明东滩湿地沉积物中还原无机硫的形态特征[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2010, 49(5): 612-617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FDXB201005013.htm
Cao A L, Zhou G P, Hu S, et al. Morphological characteristics of reduced inorganic sulfur in sediments of Dongtan Wetland in Chongming[J]. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 2010, 49(5): 612-617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FDXB201005013.htm
[15] Hsieh Y P, Yang C H. Diffusion methods for the deter-mination of reduced inorganic sulfur species in sediments[J]. Limnology & Oceanography, 1989, 34(6): 1126-1130.
[16] Neretin L N, Böttcher M E, Jørgensen B B, et al. Pyriti-zation processes and greigite formation in the advancing sulfidization front in the upper Pleistocene sediments of the Black Sea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(9): 2081-2093.
[17] Burton E D, Sullivan L A, Bush R T, et al. A simple and inexpensive chromium-reducible sulfur method for acid-sulfate soils[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(9): 2759-2766.
[18] 黄志丁, 王军, 逯海, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定硫时不同形态硫的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(1): 77-82. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20120110
Huang Z D, Wang J, Lu H, et al. The effect on sulfur species during determination of sulfur by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(1): 77-82. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20120110
[19] 张媛媛, 林学辉, 贺行良, 等. 离子色谱法同时测定海洋沉积物中氯和硫[J]. 分析科学学报, 2015, 31(2): 249-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201502021.htm
Zhang Y Y, Lin X H, He X L, et al. Determination of chlorine and sulfur in marine sediment by ion chromatography[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2015, 31(2): 249-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXKX201502021.htm
[20] Chen Y Q, Ge J W, Huang T, et al. Restriction of sulfate reduction on the bioavailability and toxicity of trace metals in Antarctic lake sediments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 151: 110807.
[21] 石友昌, 陈贵仁, 赵萌生, 等. 酸溶-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法和燃烧-红外吸收法测定不同类型地球化学样品中的硫[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(4): 663-672. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108200104
Shi Y C, Chen G R, Zhao M S, et al. Determination of sulfur in different types of geochemical samples by ICP-OES with acid dissolution and combustion-infrared absorption spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(4): 663-672. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202108200104
[22] 姜云军, 李星, 姜海伦, 等. 四酸敞口溶解-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定土壤中的硫[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2): 152-158. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704010048
Jiang Y J, Li X, Jiang H L, et al. Determination of sulfurin soil by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry with four acids open dissolution[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2): 152-158. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201704010048
[23] Hsieh Y P, Shieh Y N. Analysis of reduced inorganic sulfur by diffusion methods: Improved apparatus and evaluation for sulfur isotopic studies[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 137(3): 255-261.
[24] 李肖, 赵新如, 周芬琦, 等. 安徽庐江钟山尾矿区河流水体硫形态及硫同位素分布特征[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(6): 1787-1794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202106016.htm
Li X, Zhao X R, Zhou F Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of sulfur species and isotopes in sediments of rivers around Zhongshan tailing at Lujiang County, Anhui Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(6): 1787-1794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202106016.htm
[25] 王小芳, 李方晓, 黄涛, 等. 安徽铜陵铜尾矿硫形态及硫同位素分布特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(4): 1664-1671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201904045.htm
Wang X F, Li F X, Huang T, et al. Distribution characteristics of sulfur species and isotopes in a copper tailing at Tongling, Anhui Province[J]. China Environ-mental Science, 2019, 39(4): 1664-1671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201904045.htm
[26] 程思海, 陈道华, 雷知生. 使用元素分析仪测定海洋沉积物中的硫化物[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(1): 63-66. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20110113
Cheng S H, Chen D H, Lei Z S. Determination of sulfide in marine sediments by elemental analyzer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(1): 63-66. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20110113
[27] Sheng Y Q, Sun Q Y, Shi W J, et al. Geochemistry of reduced inorganic sulfur, reactive iron, and organic carbon in fluvial and marine surface sediment in the Laizhou Bay region, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(2): 1151-1160.
[28] 吴松峻, 汪旋, 季秋忆, 等. 太湖西岸典型区域沉积物的硫铁分布特征及环境意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(4): 950-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201904006.htm
Luo S J, Wang X, Ji Q Y, et al. Iron-sulfur distribution and its environmental significance in three typical areas of western Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(4): 950-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201904006.htm
[29] Chen Y Q, Shen L L, Huang T, et al. Transformation of sulfur species in lake sediments at Ardley Island and Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctic Peninsula[J]. Science of tThe Total Environment, 2020, 703: 135591.
[30] 尹洪斌, 范成新, 丁士明, 等. 太湖沉积物中无机硫的化学特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2008, 28(2): 183-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200802019.htm
Yin H B, Fan C X, Ding S M, et al. The chemical characteristics of inorganic sulfur in Taihu Lake sediments[J]. China Environmental Science, 2008, 28(2): 183-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ200802019.htm
[31] Leonard E N, Mattson V R, Benoit D A, et al. Seasonal variation of acid volatile sulfide concentration in sediment cores from three northeastern Minnesota Lakes[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1993, 271(2): 87-95.
[32] 朱瑾灿, 吴雨琛, 尹洪斌. 太湖蓝藻聚集区沉积物硫形态的时空变异特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(12): 4690-4700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201712040.htm
Zhu J C, Wu Y C, Yin H B. Spatial and temporal variation of sulfur speciation in sediments from cyanobacteria accumulation in Taihu Lake, China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(12): 4690-4700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201712040.htm
[33] Howard D E, Evans R D. Acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) in a seasonally anoxic mesotrophic lake: Seasonal and spatial changes in sediment AVS[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 1993, 12(6): 1051-1057.
[34] Oehm N J, Luben T J, Ostrofsky M L. Spatial distribution of acid-volatile sulfur in the sediments of Canadohta Lake, PA[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1997, 345(1): 79-85.
-



 下载:
下载: