Comprehensive Evaluation of Selenium-Enriched Land Resources in Changting County, Fujian Province Based on Niche Theory and AHP-TOPSIS Model
-
摘要:
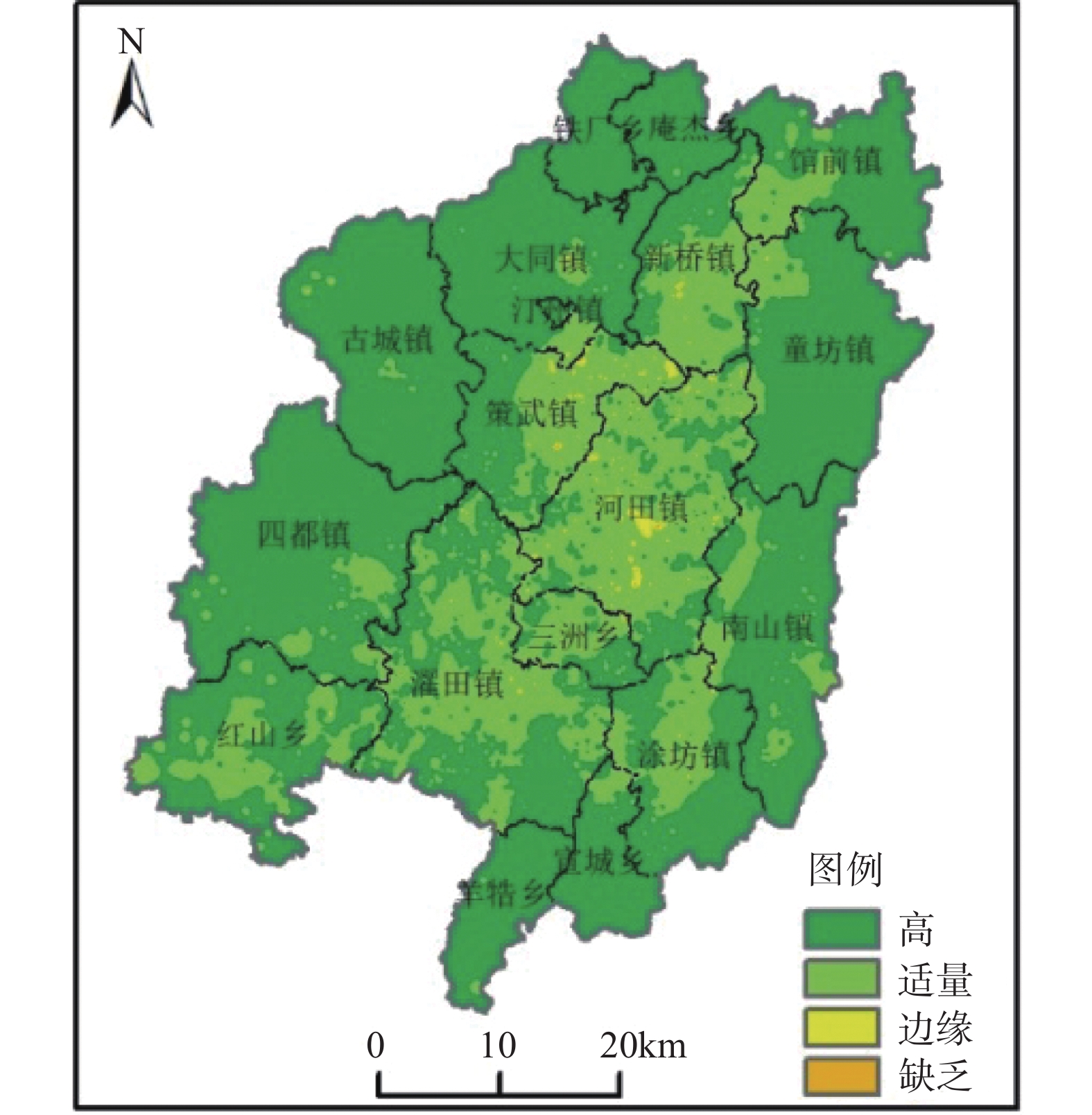
福建长汀县拥有丰富的富硒土地资源,因地制宜地综合评价该县富硒土地资源对于富硒土地资源的高效有序开发意义重大。现有的评价体系缺乏成熟的理论框架,评价结果难以有效地指导资源的开发。本文以生态位理论为基础,综合考虑长汀县富硒土地资源开发的主导因素、区位因素和限制因素构建评价指标体系。采用层次分析法(AHP)计算指标权重,以优劣解距离法(TOPSIS)求取加权综合指数进行综合等级划分。评价结果显示:长汀县土壤硒平均含量为0.46mg/kg,富硒土壤面积达2215.4km2,占全县总面积的71.36%,主要分布于长汀县东西部山区;按AHP-TOPSIS模型将长汀县富硒土地资源划分为适宜区、较适宜区、一般适宜区和不适宜区,面积分别为271.35km2、1116.96km2、1062.07km2、654.13km2,其中适宜区、较适宜区和一般适宜区与原有规范划定的富硒区基本吻合,反映了土壤硒含量在评价指标体系中的主导作用,将原富硒区细化的分区结果体现了区位因素和限制因素对富硒土地资源开发的约束作用。在基于生态位理论的AHP-TOPSIS模型中,以挖掘富硒土地资源开发的最适生态位为导向构建了评价指标体系,评价方法兼顾了指标对评价结果影响的差异性以及评价区域的资源禀赋条件,评价结果反映了长汀县富硒土地资源的开发潜力,相比原有规范有效地提升了评价的科学性。
-
关键词:
- 层次分析法(AHP) /
- 优劣解距离法(TOPSIS) /
- 生态位 /
- 长汀县 /
- 富硒土地
Abstract:Changting County in Fujian Province possesses abundant selenium-enriched land resources, and a comprehensive evaluation of them, based on local conditions is significant for the effective and structured utilization of these resources. Due to the absence of a well-established theoretical framework in existing evaluation systems, the evaluation results are difficult to effectively guide the development of resources. This article is based on the niche theory and comprehensively considers the dominant factors, geographical factors, and limiting factors of selenium-enriched land resource development in Changting County to formulate an evaluation index system. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP) is used to calculate the weight of indicators, and the technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution (TOPSIS) method is applied to determine the weighted comprehensive index for comprehensive grading. The evaluation results show that the average selenium content in the soil of Changting County is 0.46mg/kg, and the selenium-enriched soil area reaches 2215.4km2, accounting for 71.36% of the total county area, which is mainly distributed in the eastern and western mountainous areas of Changting County. Applying the AHP-TOPSIS model, the selenium-enriched land resources in Changting County are classified into suitable areas, relatively suitable areas, generally suitable areas, and unsuitable areas, with areas of 271.35km2, 1116.96km2, 1062.07km2, and 654.13km2, respectively. The suitable areas, relatively suitable areas, and generally suitable areas are approximately consistent with the selenium-enriched areas designated in previous specifications, reflecting the dominant role of soil selenium content in the evaluation index system. The refined zoning results of the original selenium-enriched areas reflect the constraining effect of geographical and limiting factors on the development of selenium-enriched land resources. In the AHP-TOPSIS model based on niche theory, an evaluation index system is constructed with the aim of identifying the optimal niche for the development of selenium-enriched land resources. The evaluation method takes into account the differences in the impact of indicators on the evaluation results and the resource endowment conditions of the evaluation area. The evaluation results reflect the development potential of selenium-enriched land resources in Changting County, effectively improving the science of the evaluation compared to previous standards.
-
Key words:
- AHP /
- TOPSIS /
- niche /
- Changting County /
- selenium-enriched land
-

-
表 1 分析方法质量监控
Table 1. Quality control table of analysis method
元素 分析方法 检出限
(mg/kg)报出率
(%)Se AFS 0.01 100 As AFS 0.2 100 Cd ICP-MS 0.02 100 Cr XRF 5.0 100 Cu ICP-MS 0.5 100 Hg AFS 0.005 100 Ni ICP-MS 0.1 100 Pb ICP-MS 0.1 100 Zn ICP-MS 2.0 100 pH 离子选择电极 0.01(无量纲) 100 有机质 红外碳硫仪 0.008(%) 100 速效磷 ICP-OES 0.25 100 有效钾 ICP-OES 1.25 100 表 2 土壤元素地球化学参数
Table 2. Geochemical parameters of elements in soil
指标 平均值 中位数 标准差 最小值 最大值 变异系数 全国背景值[8] K值 Se 0.46 0.43 0.20 0.05 1.06 44% 0.22 2.10 As 6.0 4.7 4.2 0.3 18.5 69% 9.1 0.66 Cd 0.058 0.052 0.029 0.022 0.144 50% 0.150 0.39 Cr 45 35 31 0.1 134 69% 63 0.71 Cu 15 10 13 0.1 53 84% 23 0.66 Hg 0.075 0.071 0.034 0.002 0.175 45% 50 1.50 Ni 15 11 11 1 48 71% 26 0.60 Pb 32 30 13 7 72 41% 25 1.29 Zn 48 46 23 6 117 48% 67 0.72 pH 4.51 4.49 0.25 3.77 5.25 6% 7.67 0.59 有机质 23.6 21.7 13.4 0.3 63.7 57% 18 1.28 有效磷 3.0 2.7 1.8 0.2 8.4 60% 速效钾 95 93 30 28 183 32% 注:有机质含量单位为g/kg,pH为无量纲,其余指标单位为mg/kg;K值为各指标平均值与全国背景值的比值。 表 3 准则层判断矩阵
Table 3. Criterion layer judgment matrix
参数 主导因素 区位因素 限制因素 指标权重 主导因素 1 5 2 0.58 区位因素 1/5 1 1/3 0.11 限制因素 1/2 3 1 0.31 表 4 区位因素判断矩阵
Table 4. Geographical factors judgment matrix
参数 海拔 坡度 地质背景 指标权重 海拔 1 1/5 1/3 0.10 坡度 5 1 3 0.64 地质背景 3 1/3 1 0.26 表 5 限制因素判断矩阵
Table 5. Judgment matrix of limiting factors
参数 有机质 有效磷 速效钾 环境质量 土地利用类型 水土流失程度 指标权重 有机质 1 3 3 1/2 1/4 1/3 0.11 有效磷 1/3 1 1 1/4 1/5 1/4 0.05 速效钾 1/3 1 1 1/4 1/5 1/4 0.05 环境质量 2 4 4 1 1/2 3 0.24 土地利用类型 4 5 5 2 1 4 0.39 水土流失程度 3 4 4 1/3 1/4 1 0.17 -
[1] 郝栗涛, 张湜溪, 雒昆利. 陕西省典型高硒土壤的空间分布及主要农作物硒的含量特征和主要来源研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2023, 36(5): 1032−1041. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2023.02.09
Hao L T, Zhang S X, Luo K L. Study on spatial distribution of typical high-selenium soil and content characteristics and main sources of selenium in main crops in Shannxi Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 36(5): 1032−1041. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2023.02.09
[2] 成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1367−1372. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2019.0187
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommendations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1367−1372. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2019.0187
[3] Yang H, Yang X F, Ning Z P, et al. The beneficial and hazardous effects of selenium on the health of the soil-plant-human system: An overview[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 422: 126876. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126876
[4] 周诗悦, 李茉, 周晨霓, 等. 硒在“土壤 — 作物 — 食品 — 人体”食物链中的流动[J]. 食品科学, 2023, 44(9): 231−244. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220716-184
Zhou S Y, Li M, Zhou C N, et al. Flow of selenium in the “soil — crop — food — human” chain[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(9): 231−244. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220716-184
[5] Sun G X, Liu X, Williams P N, et al. Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to grain and its speciation in paddy rice (Oiyza sativa L.)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(17): 6706−6711. doi: 10.1021/es101843x
[6] Chang C Y, Yin R S, Wang X, et al. Selenium translocation in the soil-rice system in the Enshi seleniferous area, Central China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 669(1): 83−90. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.451
[7] Dinh Q T, Cui Z W, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 2018, 112: 294−309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
[8] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020: 16-17.
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical parameters in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 16-17.
[9] 王学求, 周建, 徐善法, 等. 全国地球化学基准网建立与土壤地球化学基准值特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1469−1480. doi: 10.12029/gc20160501
Wang X Q, Zhou J, Xu S F, et al. China soil geochemical baselines networks: Data characteristics[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(5): 1469−1480. doi: 10.12029/gc20160501
[10] Bowen H J M. Environmental chemistry of the elements[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1979: 316.
[11] 谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病——生态化学地理研究[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996: 7−49.
Tan J A. Environmental life elements and Keshan disease— A study of ecological chemicogeography[M]. Beijing: China Medico-Pharmarceutical Science & Technology Publishing House, 1996: 7−49.
[12] Pan Z P, He S L, Li C J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium and evaluation of Se-rich land resources in the central area of Guiyang City, China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2017, 36: 240−249. doi: 10.1007/s11631-016-0136-0
[13] 刘冰权, 沙珉, 谢长瑜, 等. 江西赣县清溪地区土壤硒地球化学特征和水稻根系土硒生物有效性影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(5): 740−750. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202107230082
Liu B Q, Sha M, Xie C Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium and influencing factors of selenium bioavailability in rice root soils in Qingxi area, Ganxian County, Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(5): 740−750. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202107230082
[14] 成晓梦, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 四川省沐川县西部地区土壤硒含量特征及影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 808−819. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202106080072
Cheng X M, Sun B B, He L, et al. Content characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in Western Muchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 808−819. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202106080072
[15] 李明辉, 张笑蓉, 杜国强, 等. 安徽石台仙寓地区土壤硒地球化学特征及生物效应[J]. 华东地质, 2023, 44(2): 186−196. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.02.007
Li M H, Zhang X R, Du G Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics and biological effect of soil selenium in the Xianyu area, Shitai County of Anhui Province[J]. East China Geology, 2023, 44(2): 186−196. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2023.02.007
[16] 李婷婷, 贾黎黎, 朱鑫, 等. 雷州半岛富硒区土地质量地球化学评价及其利用区划研究——以城月地区为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(4): 481−489. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.051
Li T T, Jia L L, Zhu X, et al. Geochemical evaluation of the land quality and classification of the selenium-enriched soils in Chengyue area, Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(4): 481−489. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2022.50.051
[17] 陈国光, 周国华, 梁晓红, 等. 土地质量地球化学调查成果应用于永久基本农田划分方法技术[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(2/3): 437−442.
Chen G G, Zhou G H, Liang X H, et al. The application of land quality geochemical survey results to permanent basic farmland classification technology[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2019, 38(2/3): 437−442.
[18] 王惠艳, 曾道明, 郭志娟, 等. 天然富硒土地划定的富硒阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1): 333−342. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202005148
Wang H Y, Zeng D M, Guo Z J, et al. Selenium threshold for the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched land[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1): 333−342. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202005148
[19] 杨帆, 张舜尧, 宋云涛, 等. 云南省盐津县1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价方法研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6): 1318−1332. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.06.19
Yang F, Zhang S Y, Song Y T, et al. Research of 1∶50000 land quality geochemical assessment at Yanjin County in Yunnan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(6): 1318−1332. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.06.19
[20] 王亮, 王德伟, 龚仓, 等. 四川成都唐昌镇表层土壤元素地球化学特征及质量评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(6): 1082−1094. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202112270210
Wang L, Wang D W, Gong C, et al. Elemental geochemical characteristics of topsoil in Tangchang Town, Chengdu, Sichuan Province and quality evaluation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(6): 1082−1094. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202112270210
[21] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3): 319−336. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.20191114015
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3): 319−336. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.20191114015
[22] Liang R Y, Song S A, Shi Y J, et al. Comprehensive assessment of regional selenium resources in soils based on the analytic hierarchy process: Assessment system construction and case demonstration[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 605-606: 618−625. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.150
[23] 侯现慧, 王占岐, 杨俊. 富硒区耕地质量评价及利用分区研究——以福建省三元区为例[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(7): 1367−1375.
Hou X H, Wang Z Q, Yang J. Cultivated land quality evaluation using partition in the selenium-rich area of Sanyuan, Fujian Province[J]. Resources Science, 2015, 37(7): 1367−1375.
[24] 郭笑东, 陈利根, 毕如田, 等. 基于生态位理论的黄土丘陵区耕地整治优先度及模式研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(1): 184−190. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.01.030
Guo X F, Chen L G, Bi R T, et al. Priority and mode of cultivated land consolidation in loess hilly region based on niche-fitness model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(1): 184−190. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2019.01.030
[25] 张荣群, 王大海, 艾东, 等. 基于生态位和“反规划”思想的城市土地开发适宜性评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(3): 258−264. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.03.034
Zhang R Q, Wang D H, Ai D, et al. Suitability evaluation of urban land development based on niche and anti-planning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(3): 258−264. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.03.034
[26] Chen Y, Cai H S. Research on the suitability evaluation of the development and utilization of regional selenium-rich soil resources and spatial zoning based on niche theory[J]. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2023, 14(1): 67−83. doi: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2023.01.007
[27] 周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区富硒土地资源分布特征及开发利用评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(8): 3913−3921. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20220314.004
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics and utilization evaluation of selenium-rich land resources in Xiong’an New District[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(8): 3913−3921. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20220314.004
[28] 蔡海生, 陈艺, 张学玲. 基于生态位理论的富硒土壤资源开发利用适宜性评价及分区方法[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(24): 9208−9219. doi: 10.5846/stxb202002110229
Cai H S, Chen Y, Zhang X L. Suitability evaluation and zoning method research on development and utilization of selenium-rich soil resources based on niche theory[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(24): 9208−9219. doi: 10.5846/stxb202002110229
[29] Nyimbili P H, Erden T, Karaman H. Integration of GIS, AHP and TOPSIS for earthquake hazard analysis[J]. Natural Hazards, 2018, 92(3): 1523−1546. doi: 10.1007/s11069-018-3262-7
[30] 雷勋平, 邱广华. 基于熵权TOPSIS模型的区域资源环境承载力评价实证研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(1): 314−323. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0580
Lei X P, Qiu G H. Empirical study about the carrying capacity evaluation of regional resources and environment based on entropy-weight TOPSIS model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016, 36(1): 314−323. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0580
[31] 杨帆, 陈梓萌, 巩世彬. 基于AHP-熵权TOPSIS模型的辽宁省各城市土地承载力评价[J]. 水土保持通报, 2022, 42(1): 144−149. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2022.01.020
Yang F, Chen Z M, Gong S B. Evaluation of land resource carrying capacity in Liaoning Province based on AHP-entropy weight TOPSIS model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 42(1): 144−149. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2022.01.020
[32] 张克信, 潘桂棠, 何卫红, 等. 中国构造-地层大区划分新方案[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2): 206−233. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.016
Zhang K X, Pan G T, He W H, et al. New division of tectonic-strata super region in China[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(2): 206−233. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.016
[33] 陈国光, 刘红樱, 陈进全, 等. 福建长汀县水土流失的地质影响因素及防治对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6): 26−35. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202009027
Chen G G, Liu H Y, Chen J Q, et al. Geological influence factors of soil erosion in Changting County, Fujian Province and the countermeasures to prevent and control[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(6): 26−35. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202009027
[34] 李㛃, 朱金兆, 朱清科. 生态位理论及其测度研究进展[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2003, 25(1): 100−107. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.2003.01.02
Li J, Zhu J Z, Zhu Q K. A review on niche theory and niche metrics[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2003, 25(1): 100−107. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.2003.01.02
[35] 冯辉, 张学君, 张群, 等. 北京大清河流域生态涵养区富硒土壤资源分布特征和来源解析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 693−704. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905270071
Feng H, Zhang X J, Zhang Q, et al. Distribution characteristics and sources identification of selenium-rich soils in the ecological conservation area of the Daqinghe River Watershed, Beijing[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 693−704. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201905270071
[36] 唐志敏, 白晓, 湛龙, 等. 福建省长汀县重点水土流失区土壤元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 华东地质, 2022, 43(3): 324−335. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2022.03.008
Tang Z M, Bai X, Zhan L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its indicative significance of soil elements in key soil erosive areas of Changting County, Fujian Province[J]. East China Geology, 2022, 43(3): 324−335. doi: 10.16788/j.hddz.32-1865/P.2022.03.008
[37] 杨志, 李才文, 任正龑, 等. 基于熵权TOPSIS模型的宁夏土地利用绩效评价及障碍因子诊断[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2023, 45(4): 796−805. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2022.08039
Yang Z, Li C W, Ren Z Y, et al. Evaluation of land use performance in Ningxia, China based on entropy-weight topsis model and diagnosis of its obstacle factors[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2023, 45(4): 796−805. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2022.08039
[38] 陈春良, 鲍凯强, 王梦莹, 等. 植被去除对侵蚀环境土壤有机质和养分的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(5): 131−136. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.20220630.001
Chen C L, Bao K Q, Wang M Y, et al. Effects of vegetation removal on soil organic matter and nutrients in an erosive environment[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(5): 131−136. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.20220630.001
-



 下载:
下载:



