TECTONIC EVOLUTION AND ITS BEARING ON HYDROCARBON DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTION IN OUTENIQUE BASIN, SOUTH AFRICA
-
摘要:
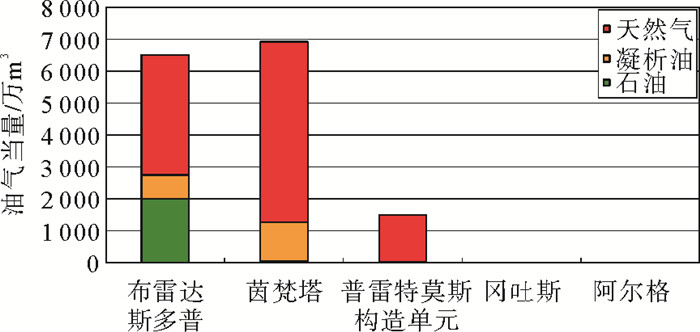
奥坦尼瓜盆地位于非洲大陆最南端,为典型被动大陆边缘盆地。晚侏罗世,盆地随着东西冈瓦纳大陆的解体,由非洲、南美和南极洲三大板块的裂开而形成。盆地经历了裂谷期(J3-K1凡兰吟期)、过渡期(凡兰吟期)和漂移期(K1欧特里夫期至今)三大构造演化阶段,发育漂移期下白垩统欧特里夫阶和巴雷姆—阿普特阶2套烃源岩,以Ⅱ2/Ⅲ型干酪根为主,偏生气。主要储集层为下白垩统凡兰吟阶浅海相砂岩,其次为下白垩统阿尔比阶深水浊积砂岩。圈闭发育具有典型的两分特征,裂谷期以构造圈闭为主,漂移期以构造—岩性圈闭为主。截至2014年,盆地已发现41个油气田/藏,石油可采储量2 042万m3, 凝析油可采储量2 016万m3, 天然气可采储量1160亿m3。平面上, 油气呈现西多东少的特点;垂向上,绝大多数油气发现集中在裂谷期顶部凡兰吟阶储层中。通过对盆地南部阿古拉斯走滑带的分析认为,阿古拉斯走滑带的活动是造成盆地东、西部油气富集差异的主要因素。在对盆地油气分布特征基础上,认为勘探前景区应聚焦盆地西部。
Abstract:The Outenique Basin, located in the very south of the Africa continent, is a typical passive continent margin basin. The Gondawana continent begun to break-up in late Jurassic. The Outenique Basin was then developed with the drifting of the three plates, Africa, South America and Antarctica. The basin has undergone three tectonic evolution stages, rifting, transition and drifting. The Hauterivian and Barremian- Aptian (K1) deposits are the major source rock, which is of II2/III kerogen and prior to gas. The Valangnian (K1) shallow marine sandstone is the major reservoir and the Albian deep-water turbidite sandstone the second. Structural-stratigraphic traps are well developed in the drifting strata, but the structural traps mainly in the rifting stage. Traps formed in rifting stage are rather different with those formed in the drifting period. Up to 2014, 41 oil and gas fields/reservoirs have been discovered. 2.04×107m3 of oil, 2.02×107m3 of condensate and 1.16×1011m3 of recoverable gas reserves have been proved. Facts of discovered oil and gas show that great amount of oil and gas are accumulated in the Valangnian reservoir instead of others, and more reserves have been found in the west of the basin. The analysis of Agulhas fracture suggests that the difference of tectonic activity patterns between the east and west are the main controlling factor of oil and gas distribution in the Outenique basin. Future exploration should focus on the western part of the basin.
-
Key words:
- Outenique Basin /
- Agulhas fracture /
- tectonic evolution /
- oil and gas distribution
-

-
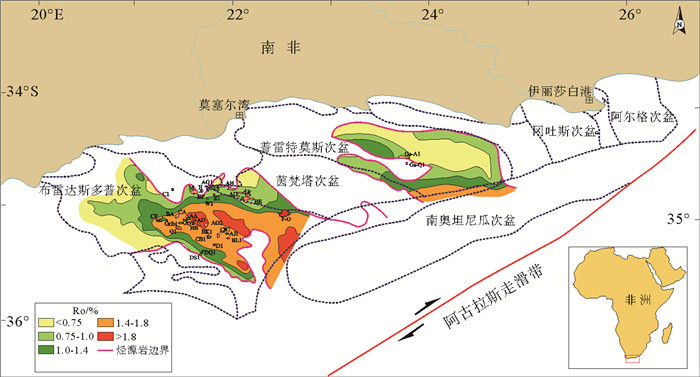
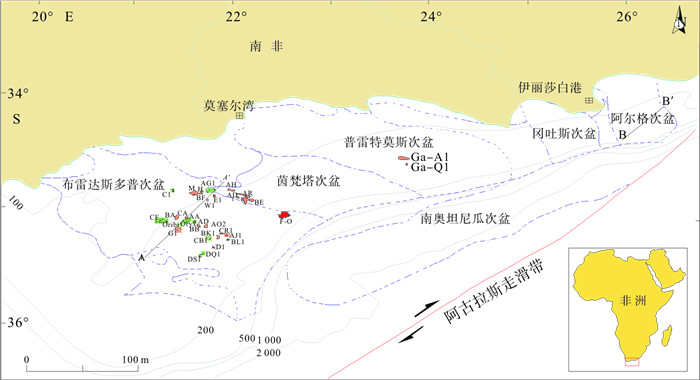
图 1 奥坦尼瓜盆地构造单元划分(据文献[1]修改)
Figure 1.
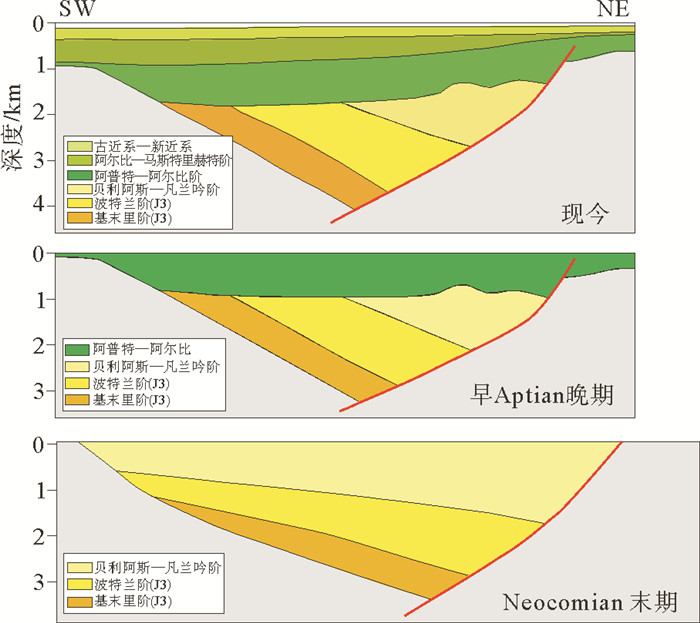
图 2 阿尔格次盆地构造演化(剖面位置见图 1 B-B')
Figure 2.
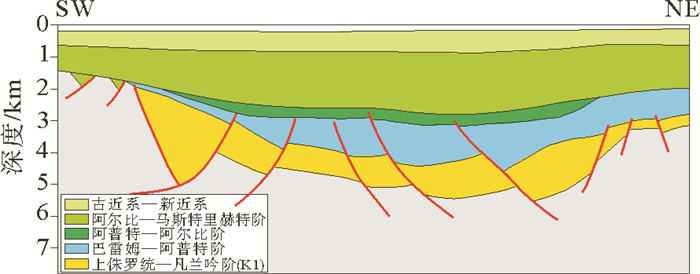
图 3 过布雷达斯多普次盆地质剖面(剖面位置见图 1 A-A')
Figure 3.
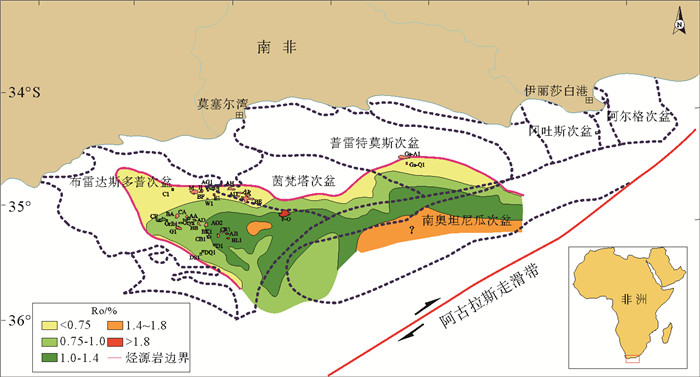
图 5 下白垩统欧特里夫阶烃源岩顶面现今成熟度(据文献[1]修改)
Figure 5.
图 6 下白垩统巴雷姆—阿普特阶烃源岩顶面现今成熟度(据文献[1]修改)
Figure 6.
-
[1] IHS Energy Group. International petroleum exploration and production database[DB]. IHS Energy Group, 2012.
[2] Dingle R V, Scrutton R A. Continental breakup and the development of Post-Paleozoic sedimentary basins around southern Africa [J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1974, 85(9): 1467-1474. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1974)85<1467:CBATDO>2.0.CO;2
[3] Roberts D G. Regional Geology and Tectonics: Phanerozoic Passive Margins, Cratonic Basins and Global Tectonic Maps [M]. Oxford: Elsevier's Science and Technology Rights Department, 2012: 534-564.
[4] Thomson K. Role of continental break-up mantle plume developments and fault reactivation in the evolution of the Gamtoos Basin, South Africa [J]. Marine Petroleum Geology, 1999, 16: 409-429. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00010-0
[5] Hugh J S. Assessment controls on reservoir performance and the affects of granulation seam mechanics in the Bredasdorp Basin, South Africa [D]. Western Cape: University of the Western Cape, 2005.
[6] Singh V, Brink G J, Winter H, et al. New interpretation reveals potential in onshore Algoa basin, South Africa [J]. Oil and Gas Journal, 2005, 103(1): 34-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=aac1041ab18c19809355ff569965f67e
[7] Van Der M R, Fouche J. Inversion tectonics in the Bredasdorp Basin, offshore South Africa [C]//De Wit M J, Ransome I G D. Inversion Tectonics of the Cape Fold Belt, Karoo and Cretaceous Basins of Southern Africa, Cape Town: Proceedings of the Conference on Inversion Tectonics of The Cape Fold Belt, 1992: 49-59.
[8] Davies C P N. Hydrocarbon evolution of the bredasdorp basin, offshore south africa: from source to reservoir [D]. Western Cape: University of Stellenbosch, 1997.
[9] Akinlua A, Sigedle A, Buthelezi T, et al. Trace element geochemistry of crude oils and condensates from South African Basins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 286-293. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.07.023
[10] Van Der S D. Aptian source rocks in some South African, Cretaceous basins [C]//Arthur T J, Macgregor D S, Cameron N R. Petroleum Geology of Africa: New Themes and Developing Technologies. London: The Geological Society of London, 2003, 207: 185-202.
[11] Ojongokpoko H M. Porosity and permeability distribution in the deep marine play of the central bredasdorp basin, block 9, offshore South Africa[D]. Western Cape: University of the Western Cape, 2006.
https: //www.researchgate.net/publication/30758573_Porosity_and_permeability_distribution_in_the_deep_marine_play_of_the_central_Bredasdorp_Basin_Block_9_offshore_South_Africa -



 下载:
下载: