EXPERIMENTAL SIMULATION OF SEABED HYDROCARBON GAS SEEPAGE:VARIATION OF CONTENT AND MOLECULAR COMPOSITION OF THE HYDROCARBON GAS AND RECONSTRUCTION OF SEEPAGE PROCESS
-
摘要:
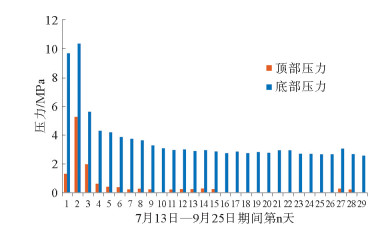
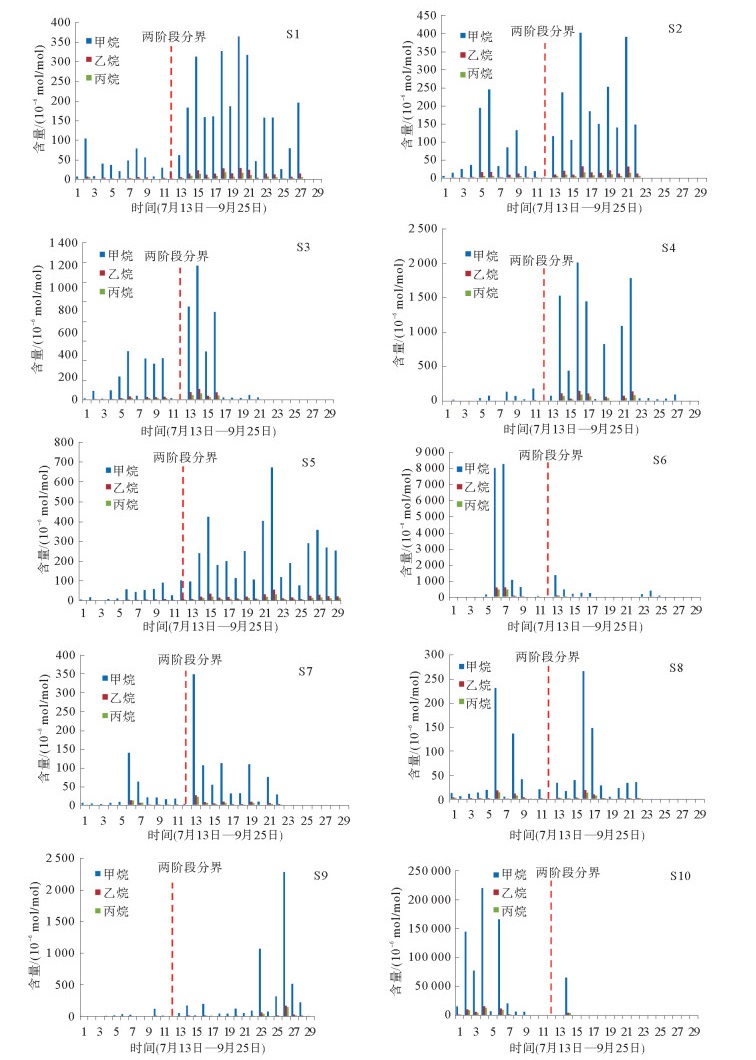
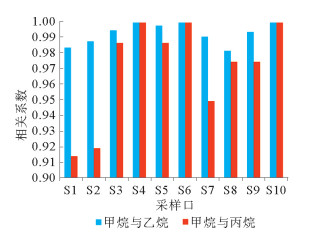
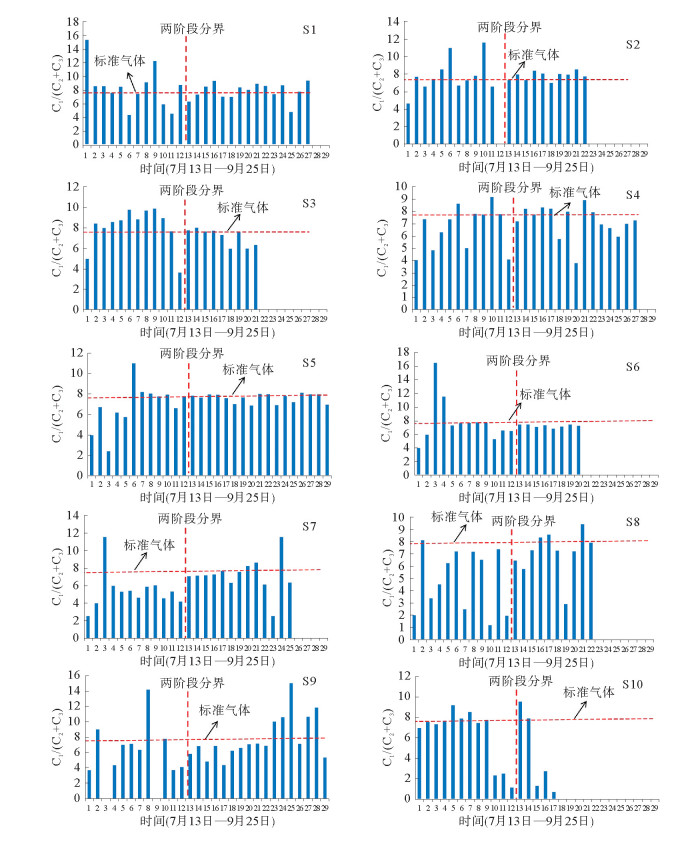
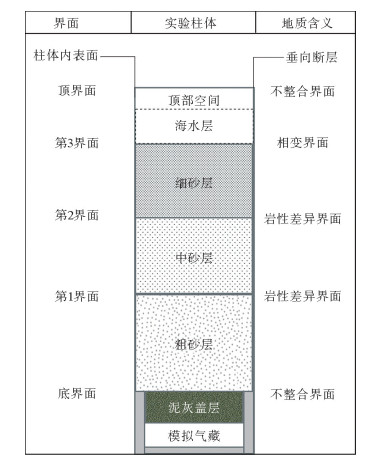
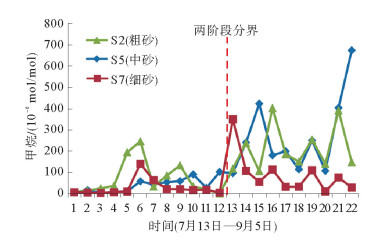
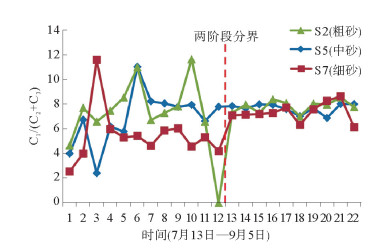
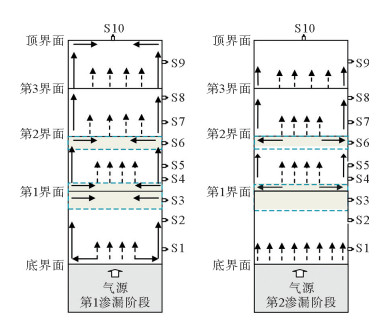
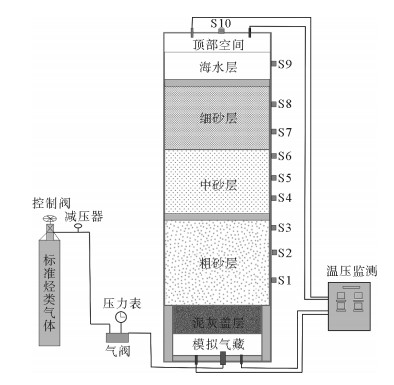
利用海底烃类气体渗漏实验模拟装置对海底烃类气体渗漏过程进行了实验模拟。通过10个采样口样品采集和分析测试,探讨了各采样口在渗漏过程中烃类气体含量和分子组成变化。各采样口烃类气体含量和分子组成随时间具有明显阶段变化,总体显示了两阶段渗漏特征:第1渗漏阶段从7月13日到8月5日,第2渗漏阶段从8月6日到9月25日。根据各采样口烃类气体在两阶段渗漏强度可分为3类:第1类包括S1、S2、S5、S7和S8,表现为在第1阶段和第2阶段渗漏强度均不高,属于微渗漏类型;第2类包括S3、S4和S9,表现为在第1阶段渗漏强度低,属于微渗漏类型,在第2阶段渗漏强度高,属于宏渗漏类型;第3类包括S6和S10,表现为在第1阶段和第2阶段均属于宏渗漏类型。烃类气体渗漏主要受实验柱体内各种界面和沉积物粒度等因素控制,而且不同采样口渗漏烃类气体含量变化的控制因素也不尽相同。模拟结果为研究海底烃类气体渗漏过程中,断裂构造、地层不整合界面、岩性差异界面,以及沉积物粒度变化等对海底烃类气体渗漏控制机理提供了实验依据。
Abstract:The experimental simulation for seabed hydrocarbon gases seepage was carried out by the authors. The changes in contents of hydrocarbon gases and their molecular compositions during the seepage were studied through sample collection and analysis at 10 sampling outlets.It is found that the hydrocarbon gas content and molecular composition of each sampling outlets have obvious phase changes with time. There are two stages of seepages in general, the first stage from July 13 to August 5, and the second stage from August 5 to September 25. According to the intensity of seepage, the sampling outlets can be divided into three categories. The first category includes S1, S2, S5, S7 and S8, during which the seepage intensity is not high and thus named as the micro-seepage type in the first and second seepage stages.The second category includes S3, S4 and S9, of which the seepage intensity is low and belonging to micro-seepage type in the first seepage stage, and high in second seepage stage and thus named the type of macro-seepage in this paper. The third category includes S6 and S10 with high seepage intensity and belongs to macro-seepage type. In the process of experimental simulation, hydrocarbon gas seepage is mainly controlled by various interfaces inside the experimental column and sediment grain size.The control factors for hydrocarbon gas seepage at different sampling outlets are different.The simulation results provided the experimental basis to the study of controlling factors and mechanisms of hydrocarbon gas seepage on seabed, such as fault structures, unconformities, lithological boundaries as well as changes in grain size.
-

-
表 1 用于实验模拟的标准气体构成
Table 1. Standard gas composition for theexperimental simulation
烃类气
体组分含量/
(10-6 mol/mol)甲烷 696 000 异丁烷 2 400 乙烷 52 000 正丁烷 2 800 乙烯 800 异戊烷 2 400 丙烷 40 000 正戊烷 2 800 丙烯 800 表 2 采样口烃类气体含量(10-6 mol/mol)变化范围
Table 2. Variation range of hydrocarbon gas content (10-6 mol/mol) at sampling outlets
采样口 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 异丁烷 正丁烷 异戊烷 正戊烷 S1 7.02~363.80/
122.670.46~28.84/
10.070~18.38/
5.380~1.53/
0.300~2.77/
0.550~0.38/
0.130~3.05/
0.42S2 1.77~400.71/
139.340.73~32.57/
11.790~15.45/
5.410~0.70/
0.240.03~0.69/
0.260~0.33/
0.100~1.47/
0.32S3 0.86~1 192.69/
280.530.10~94.96/
21.740.14~54.57/
12.600~3.03/
0.690~2.31/
0.570~0.34/
0.120~2.77/
0.41S4 3.33~2 007.26/
415.880.53~150.11/
31.830.07~91.80/
19.330~5.51/
1.120~4.02/
0.890~2.40/
0.340~5.37/
0.89S5 1.41~670.79/
173.030.12~54.24/
14.510.47~29.98/
7.810~1.00/
0.300~1.00/
0.310~0.35/
0.100~1.33/
0.24S6 3.61~8254.72/
1 344.860.22~598.32/
99.580~484.59/
78.060~34.00/
5.370~33.35/
5.150~24.34/
3.750~35.68/
5.61S7 2.93~347.88/
65.270.25~26.73/
5.510~22.62
4.320~2.14/
0.620~1.54/
0.250~1.37/
0.250~2.63/
0.48S8 0.91~265.11/
57.960.18~18.63/
4.610.14~13.70/
3.400~1.03/
0.300~0.85/
0.250~0.48/
0.120~5.84/
1.02S9 1.69~2 275.05/
252.880~173.10/
18.650~147.29/
13.800~10.27/
0.970~11.14/
0.930~0.27/
0.080~12.67/
0.96S10 0.48~219 410.40/
49 786.230.22~15 614.03/
3 537.830.05~12 937.34/
2 939.230~896.51/
200.690.03~933.42/
213.180~500.14/
119.560.03~962.00/
215.95 -
[1] Judd A G, Hovland M. Seabed Fluid Flow: the Impact on Geology, Biology and the Marine Environment[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007:475.
[2] Judd A G, Hovland M, Dimitrov L I, et al.The geological methane budget at continental margins and its influence on climate change[J].Geofluids, 2002, 2:109-126. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00027.x
[3] Judd A G, Davies G, Wilson J, et al.Contributions to atmospheric methane by natural seepages on the UK continental shelf [J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 137: 42-55. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0025-3227(96)00087-4/
[4] Hovland M, Judd A G, Burke R A. The global production of methane from shallow submarine sources[J]. Chemosphere, 1993, 26(5):59-78. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/027843439290082U
[5] Logan G A, Jones A T, Kennard J M, et al. Australian offshore natural hydrocarbon seepage studies, a review and re-evaluation[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 22:26-45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=38d0feacf2f312fa0d29eaccf7c484ea
[6] Traynor J J, Sladen C. Seepage in Vietnam-onshore and offshore examples[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1997, 14: 345-362. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(96)00040-2
[7] Chow J, Lee J S, Liu C S, et al. A submarine canyon as the cause of a mud volcano-Liuchienuyu Island in Taiwan[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 176: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00157-8
[8] Huang B J, Xiao X M, Dong W L. Multiphase natural gas migration and accumulation and its relationship to diapir structures in the DF1-1 gas field, South China Sea [J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19: 861-872. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(02)00109-5
[9] Huang B J, Xiao X M, Li X S, et al. Spatial distribution and geochemistry of the nearshore gas seepages and their implications to natural gas migration in the Yinggehai Basin, offshore South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26:928-935. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.04.009
[10] 关进安, 樊栓狮, 梁德青, 等.南海琼东南盆地渗漏系统甲烷水合物生长速度[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3):765-775. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb200903020
[11] Butenko J, Milliman J D, Ye Y C. Geomorphology, shallow structure, and geological hazards inn the East China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1985, 4:121-141. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(85)90025-1
[12] Yin P, Berne′ S, Vagner P, et al. Mud volcanoes at the shelf margin of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 194:135-149. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00678-3
[13] 赵铁虎, 张训华, 王修田, 等, 南黄海盆地北部坳陷海底油气渗漏的声学探测[J].石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(2):195-199. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf200902009
[14] 王建强, 李双林, 孙晶, 等.南黄海盆地北部坳陷海底烃类渗漏与深部油气属性[J].岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(5):122-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2015.05.021
[15] 李双林, 李兴, 赵青芳, 等.南黄海盆地北部凹陷海底沉积物酸解烃类气体及其碳同位素地球化学[J].石油天然气学报, 2012, 34(12):6-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2012.12.002
[16] Zhang S Y, Li S L, Dong H P, et al.An analysis of organic matter sources for surface sediments in the central South Yellow Sea, China: evidence based on macroelements and n-alkanes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 88:389-397 doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.07.064
[17] Li S L, Zhang S Y, Dong H P, et al. Presence of aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in near-surface sediments of an oil spill area in Bohai Sea[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 100:169-175. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.009
[18] Michael A A. Significance of hydrocarbon seepage relative to petroleum generation and entrapment[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2005, 22:457-477. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.08.003
[19] Michael A A, Nicola F D.Surface sediment hydrocarbons as indicators of subsurface hydrocarbons: field calibration of existing and new surface geochemistry methods in the Marco Polo area, Gulf of Mexico[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(11): 1907-1935. doi: 10.1306/03211110130
[20] Saunders D F, Burson K R, Thompson C K. Model for hydrocarbon microseepage and related near-surface alterations [J].AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83: 170-185. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=376c522b10032bcfa766c2539cf946fd
[21] 程同锦, 王国建, 范明, 等.油气藏垂向微渗漏的实验模拟[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(5):522-527. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.05.016
[22] 黄臣军, 王国建, 卢丽, 等.烃气在泥岩和砂岩中的微渗漏特征及油气勘探意义[J].石油实验地质, 2013, 35(4):445-448. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz201304015
[23] Wang J, Tang Y P, Cheng T J, et al. Laboratory simulation of the formation process of surface geochemical anomalies applied to hydrocarbon exploration[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(6):2149-2162. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13028
-



 下载:
下载: