An Effective Artificial Beachon Muddy Coast: the Case of Jinshan City Beach of Shanghai
-
摘要:
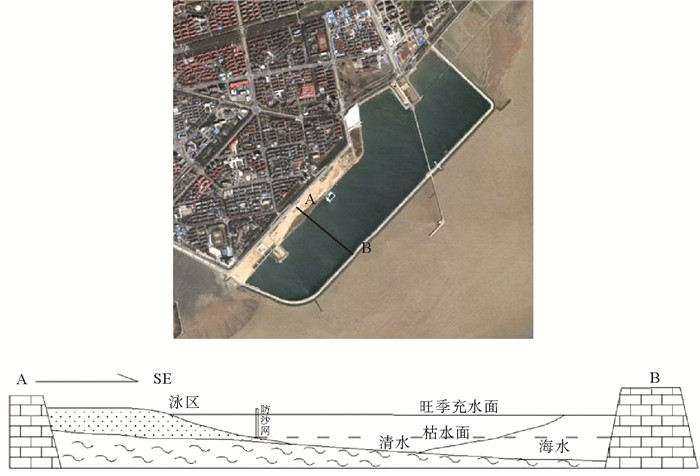
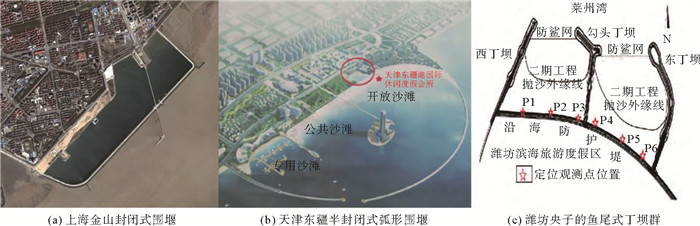
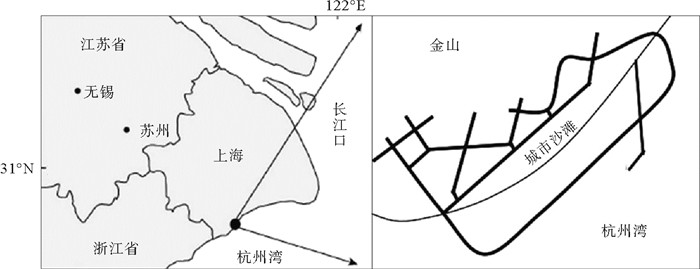
上海市金山区位于杭州湾北岸,发育典型的粉砂淤泥质海岸,潮滩低平、颗粒极细,下陷0.1~0.2 m,且风暴潮期间海水泥沙含量极高,泥层易滑塌。2005年,在金山潮滩构筑3.3 km封闭式围堰围海成湖1.72 km2,近岸抛沙15.6万m3并设防泥网建成长度1.4 km的人造沙滩进行跳相养滩,后经多次补沙和围堰加固,将“黄水黑滩”变为“碧海金沙”,成为金山城市沙滩。该人造沙滩是中国首个泥岸养滩成功案例,后有天津东疆浴场、潍坊央子人造沙滩、南通启东碧海银滩等10余个人造沙滩建成。金山城市沙滩封闭式围堰消浪护沙、稳定沙滩,结合“沉泥碧水”技术维持海水清洁且防止新滩泥化;固定式防泥网较为坚固,保证游人安全。其围海成湖、沉泥碧水、抛沙建滩及泥沙界网等工程技术为中国粉砂淤泥质海岸人造沙滩建设提供了实践经验。
Abstract:The Jinshan District of Shanghai, located on the north bank of Hangzhou Bay, has a well developed silty and muddy coast with a low and smooth tidal flat covered by fine sediment in shape of a sink 0.1~0.2 m in depth. The content of sea water in the sediment is extremely high during storm surge so that the mud layers are easy to slide. In 2005, a 3.3 km closed cofferdam was constructed on the Jinshan tidal flat and a lake of 1.72 km2 was formed. A sediment net was setting up and an 1.4 km long artificial beach was constructed by throwing 156 000 m3 of sand from offshore. After many times of sand replenishment and cofferdam reinforcement, the "Yellow Water covered Black Beach" finally turned into a beach of "Blue Water with Golden Sand", which is called Jinshan City Beach since then. The artificial beach is the first successful case in China to turn a muddy flat into a sand beach. After it, more than ten artificial beaches, such as the Tianjin Dongjiang Beach, Weifang Yangzi Artificial Beach, and Nantong Qidong Beach were built up successively. In the case of the Jinshan City Beach, closed cofferdam is used to eliminate wave and protect sand from erosion, make the beach more stable, keep sea water clean and prevent the deposition of beach mud with the technology of sinking sediment and clean water. The fixed mud net is strong enough to ensure the safety of visitors. Its engineering techniques, such as encircling the sea into a lake, sinking mud to clean water, sand nourishment, beach construction and keeping the mud boundary stable, etc., have provided useful samples for construction of artificial sand beaches in China.
-

-
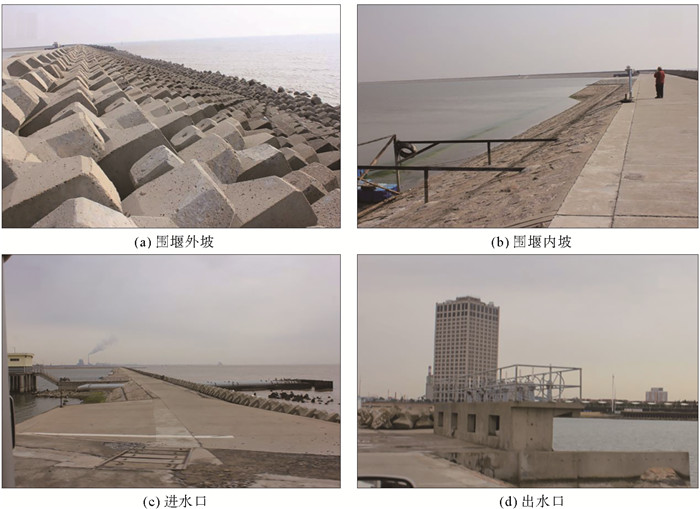
图 6 人造沙滩围堰工程(引自文献[11])
Figure 6.
-
[1] Cai F, Su X Z, Liu J H, et al. Coastal erosion in China under the condition of global climate change and measures for its prevention[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(4):415-426. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.05.034
[2] Dar I A, Dar M A. Prediction of shoreline recession using geospatial technology: a case study of Chennai coast, Tamil Nadu, India[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2009, 25(6): 1276-1286. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27752777
[3] Komar P D. Beach processes and sedimentation (2nd edition)[M]. New Jersey:Prentice Hall, 1998: 543.
[4] 庄振业, 王永红, 包敏, 等.海滩养护过程和工程技术[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(5):1019-1024. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb200905025
[5] 刘锡清.中国海洋环境地质学[M].北京:海洋出版社, 2006.
[6] 庄振业, 曹立华, 李兵, 等.我国海滩养护现状[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(3):133-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201103017
[7] 杜运才.浅议低滩围垦大堤技术管理构建[J].上海水务, 2015, 31(4):25-29. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/97649X/201504/667174427.html
[8] 王永庆.金山城市沙滩工程创新设计[J].水利规划与设计, 2014(7):93-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2014.07.030
[9] 阮龙飞.上海市金山城市沙滩水库堤坝防渗设计[C]//第十三届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集, 2007: 692-697.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6553695 [10] 王兆飞.简析城市沙滩以西保滩工程几项结构优化措施[J].山西建筑, 2015, 41(31):204-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2015.31.108
[11] 庄振业, 刘修锦, 邱若峰, 等.泥岸养滩技术与效益评估——以天津东疆浴场建设和评估为例[J].海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(4):51-57. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201604008
[12] 周军, 庄振业, 李建华, 等.潮滩上的人造沙滩——潍坊滨海旅游区沙滩构建始末[J].海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(3):64-70. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201403008
[13] 黄锦林, 程永东.海堤和护岸消浪型式选择[J].广东水利水电, 2009(4):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0112.2009.04.010
[14] 陈兆林.不同结构离岸式潜堤消浪效果试验研究[J].海岸工程, 2005, 24(2):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2005.02.001
[15] 张甲波, 杨燕雄, 庄振业, 等.离岸潜堤在海滩养护中的作用[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2010(4):111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2010.04.016
-



 下载:
下载: