DISTRIBUTION OF MAJOR ELEMENTS IN SURFACE SEDIMENTS OF BOHAI STRAIT AND ITS GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
-
摘要:
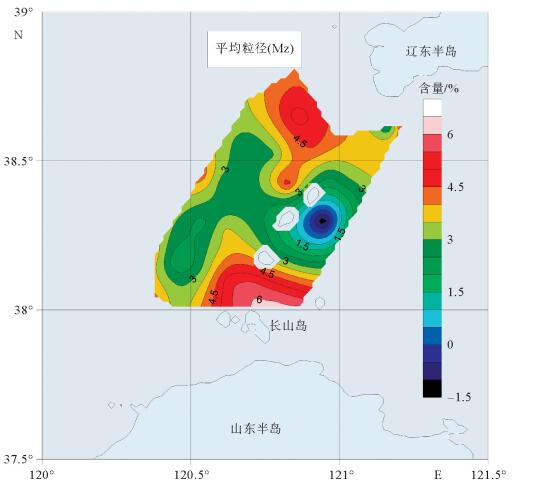
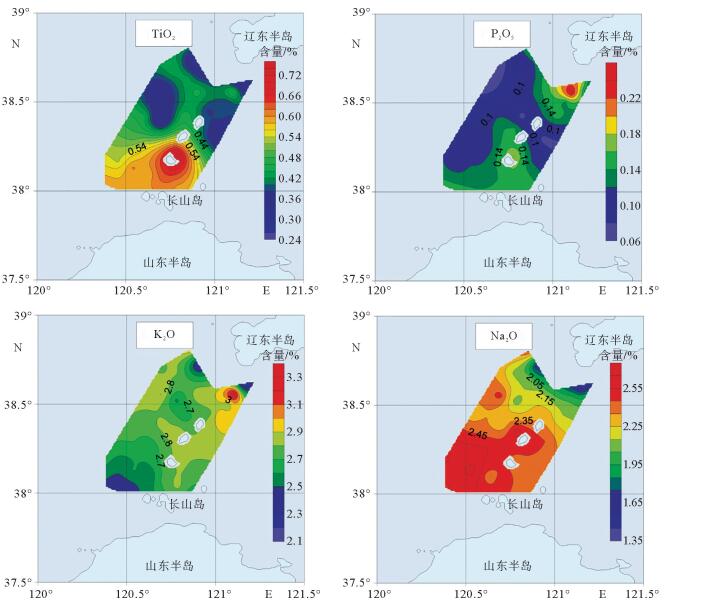
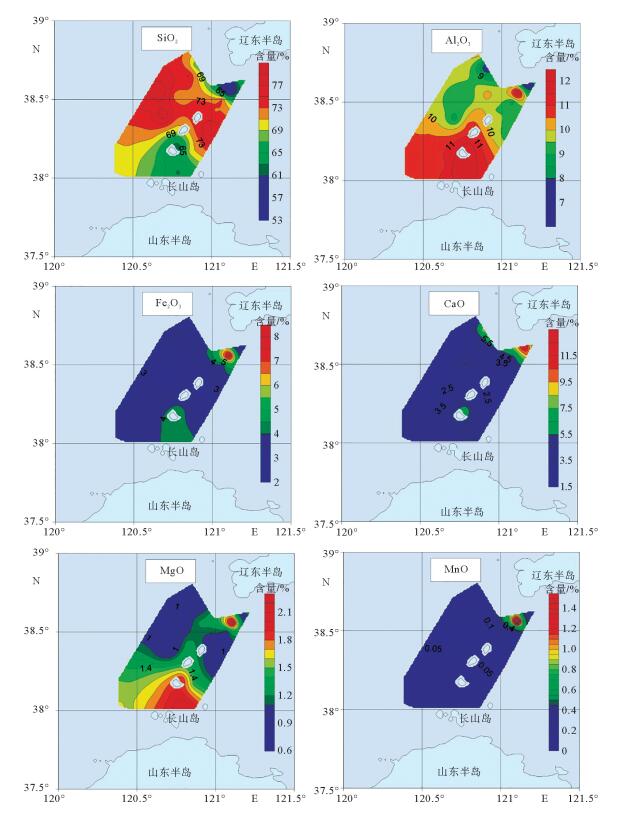
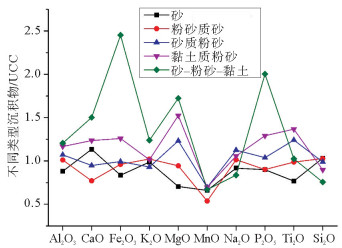
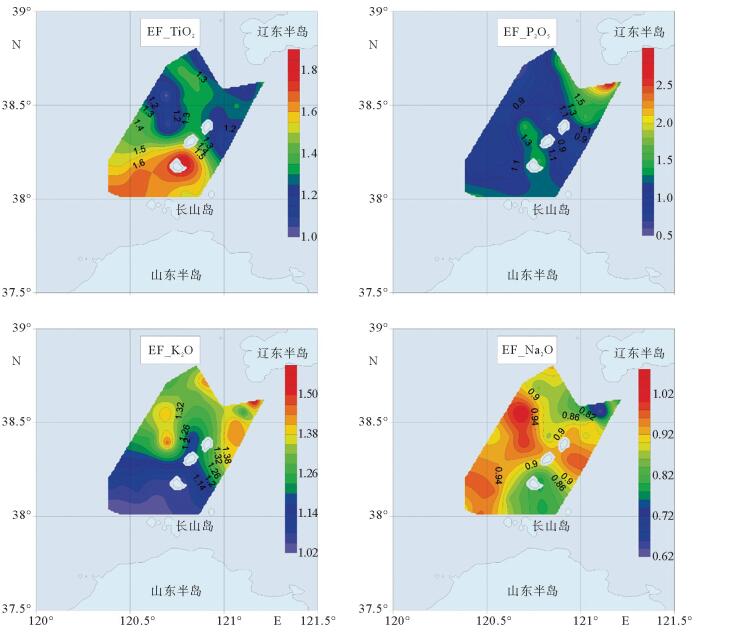
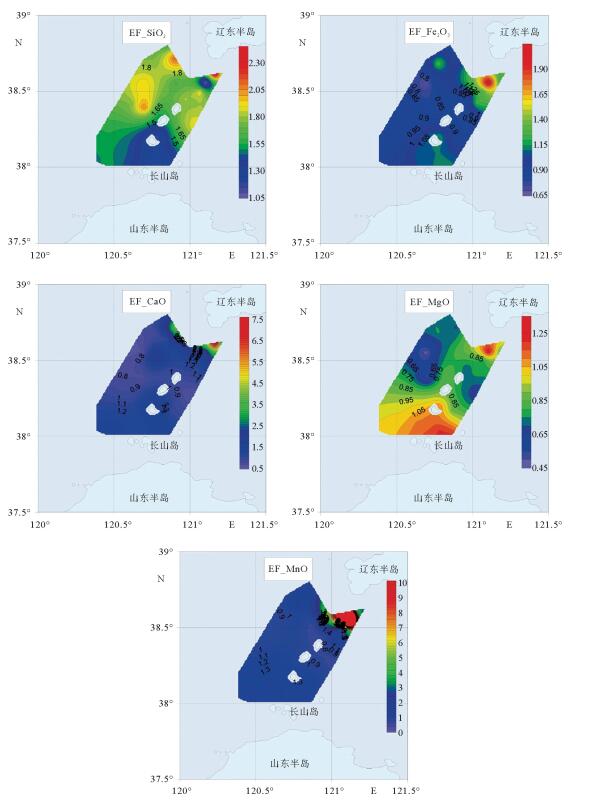
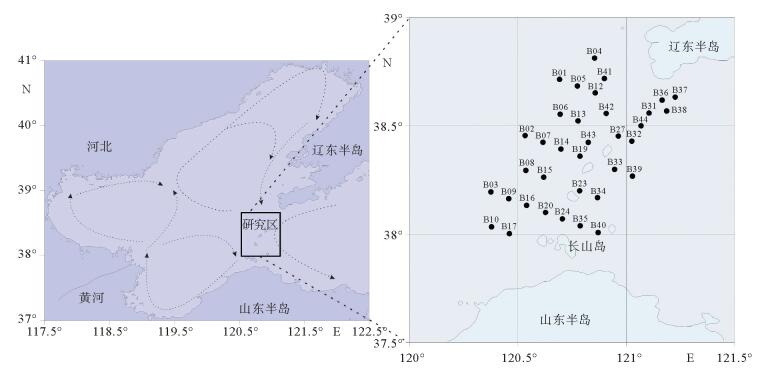
对采自渤海海峡北部海域35个站位表层沉积物进行常量元素分析,结果表明,研究区内表层沉积物常量元素主要由SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO、K2O、Na2O和MgO组成,约占沉积物总量的94.85%;其中SiO2、Al2O3和CaO的含量最高,平均含量分别达到70.44%、10.03%和3.96%,表明沉积物主要来源于陆源碎屑和黏土组分,其次是生物碎屑组分。SiO2与Mz呈较强负相关关系,在空间上分布与粗粒沉积物分布区相一致;Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5、TiO2在空间上分布相似,与细粒沉积物分布区相一致;此外,Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、Na2O、TiO2 5种常量元素之间呈明显的正相关关系,说明其分布受控因素较为相近。常量元素相关性和R型因子分析表明,研究区内常量元素可划分为3类,第1类包含了SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、MnO、P2O5、TiO2组成,代表了陆源碎屑沉积;第2类主要由CaO、Na2O组成,代表了海洋生物沉积作用;第3类K2O可能代表了海洋化学作用。
Abstract:The major elements of surface sediments in the northern Bohai Strait, according to the analyzing results of the samples collected from 35 stations, mainly consist of SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, CaO, K2O, Na2O and MgO, which account for more than 94.85% of the total. SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO dominate on average of 70.44%, 10.03% and 3.96%, respectively, suggesting the sediments of siliceous clasts and clays predominated by aluminosilicate minerals. SiO2 is strongly negatively correlated with Mz, and their spatial distribution is consistent with coarse-grained sediments. Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, P2O5 and TiO2 are similar in spatial distribution and consistent with that of fine-grained sediments. Moreover, there are obvious positive correlations among Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, Na2O and TiO2, indicating that their distribution is controlled by similar factors mentioned above. The correlation of major elements and R-factor analysis show that the major elements in the study area can be divided into three categories. The first category includes SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, MnO, P2O5, and TiO2, representing terrigenous clastic deposits; the second category mainly consists of CaO and NaO, representing marine biogenous sediments; and the third category of K2O may suggest the impact of marine authigenic sediment.
-
Key words:
- Bohai Strait /
- surface sediments /
- major elements /
- factor analysis
-

-
表 1 研究区表层沉积物常量元素含量数据统计
Table 1. Contents of major elements of the surface sediments in thestud
元素 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准偏差 变异系数 上地壳/UCC[14] SiO2/% 53.25 78.45 70.44 5.49 0.08 65.90 Al2O3/% 6.02 12.09 10.03 1.26 0.13 15.19 Fe2O3/% 2.09 8.37 3.42 1.08 0.32 5.00 CaO/% 1.77 12.41 3.96 2.31 0.58 4.20 MgO/% 0.64 2.23 1.29 0.42 0.32 2.21 MnO/% 0.03 1.57 0.11 0.25 2.19 0.08 TiO2/% 0.24 0.73 0.46 0.12 0.25 0.50 P2O5/% 0.06 0.25 0.12 0.04 0.30 0.16 K2O/% 2.10 3.37 2.72 0.22 0.08 3.37 Na2O/% 1.30 2.69 2.29 0.30 0.13 3.9 Mz/Φ -1.43 6.10 3.60 1.47 0.41 表 2 研究区表层沉积物常量元素富集因子
Table 2. Enrichment factor of major elements of the surface sediments in the study area
序号 元素 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准方差 变异系数 1 SiO2 1.01 2.42 1.65 0.28 0.17 2 Fe2O3 0.68 2.10 1.03 0.25 0.24 3 CaO 0.69 7.45 1.53 1.29 0.84 4 MgO 0.48 1.27 0.87 0.19 0.22 5 MnO 0.71 24.58 2.09 3.95 1.89 6 TiO2 1.02 1.86 1.39 0.20 0.15 7 P2O5 0.57 2.88 1.19 0.41 0.34 8 K2O 1.02 1.57 1.24 0.15 0.12 9 Na2O 0.62 1.04 0.89 0.08 0.09 表 3 表层沉积物的常量元素与平均粒径相关性分析(n=35)
Table 3. Correlation analysis of major elements and mean grain-size in the surface sediments(n=35)
Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO MnO Na2O P2O5 TiO2 SiO2 Mz Al2O3 1 CaO -0.415 1 Fe2O3 0.558 0.165 1 K2O 0.464 -0.509 0.488 1 MgO 0.822 0.097 0.740 0.134 1 MnO 0.164 0.450 0.818 0.296 0.441 1 Na2O 0.700 -0.683 -0.115 0.222 0.326 -0.272 1 P2O5 0.242 0.510 0.690 0.147 0.566 0.632 -0.236 1 TiO2 0.870 -0.168 0.418 0.044 0.842 0.012 0.629 0.251 1 SiO2 -0.314 -0.694 -0.745 0.040 -0.736 -0.621 0.288 -0.791 -0.392 1 Mz 0.239 0.111 0.340 -0.038 0.404 0.073 -0.153 0.193 0.262 -0.342 1 表 4 研究区表层沉积物常量元素因子分析
Table 4. R-factor analysis of major elements in the surface sediments of the study area
元素 F1 F2 F3 SiO2 -0.836 0.467 0.193 Al2O3 0.727 0.675 -0.037 CaO 0.206 -0.875 -0.338 Fe2O3 0.913 -0.124 0.298 K2O 0.331 0.365 0.808 MgO 0.922 0.208 -0.277 MnO 0.681 -0.337 0.550 Na2O 0.105 0.922 -0.139 P2O5 0.753 -0.421 0.063 TiO2 0.665 0.548 -0.453 Mz 0.406 -0.082 -0.326 方差贡献/% 42.846 27.990 14.625 累计贡献/% 42.846 70.836 85.460 -
[1] 刘振夏.黄海表层沉积物的分布规律[J].海洋通报, 1982, 1(1):43-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxkxyxb201702003
[2] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等.东海地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 1987.
[3] 王安国, 张训华, 李广雪, 等.山东半岛近岸海区全新世泥质沉积体研究现状[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(10):52-58. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzdt201310008
[4] 尹延鸿, 周青伟.渤海东部地区沉积物类型特征及其分布规律[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(2):47-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ402.004.htm
[5] 程鹏, 高抒.北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度物征和净输运趋势[J].海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(6):604-615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.004
[6] 李国刚, 胡邦琦, 李军, 等.山东半岛沿岸海域表层沉积物的常量元素及其地质意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3):45-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201203006
[7] 方海超, 黄朋, 周宇, 等.北黄海表层沉积物常量元素分布特征及其控制因素分析[J].海洋科学, 2015, 39(4):108-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201504016
[8] 崔振昂, 甘华阳, 刘文涛, 等.北部湾东部海域表层沉积物常量元素地球化学特征及其物源指示意义[J].物探化探计算技术, 2015, 37(4):522-531. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2015.04.18
[9] 蒋东辉, 高抒, 程鹏.渤海海峡沉积物输运的数值模拟[J].海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(5):553-561. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.05.013
[10] 李淑媛, 苗丰民, 赵全民, 等.辽东半岛西南及渤海中部海域表层沉积物的地球化学[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 34(4):124-130. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201004015
[11] 刘建国, 李安春, 陈木宏, 等.全新世渤海泥质沉积物地球化学特征[J].地球化学, 2007, 36(6):559-568. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2007.06.004
[12] 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 张志珣, 等.渤海东部与黄海北部表层沉积物的元素地球化学记录[J].地球学报, 2015, 36(6):718-728. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201506004
[13] 刘升发, 石学法, 刘焱光, 等.东海内陆架泥质区表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J].海洋科学进展, 2010, 28(1):80-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.011
[14] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M.The continental crust:its composition and evolution[J].The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4):57-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_7b034b121c08912757b660fdefe8747e
[15] 赵一阳, 鄢明才.中国浅海沉积物地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1994.
[16] 杜德文, 石学法, 孟宪伟, 等.黄海沉积物地球化学的粒度效应[J].海洋科学进展, 2003, 21(1):78-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.009
[17] 杨作升, 王海成, 乔淑卿.黄河与长江入海沉积物中碳酸盐含量和矿物颗粒形态特征及影响因素[J].海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(6):674-681. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2009.06.002
[18] 范德江, 杨作升, 王文正.长江、黄河沉积物中碳酸盐组成及差异[J].自然科学进展, 2002, 12(1):60-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2002.01.013
[19] 杨兢红, 王颖, 张振克, 等.苏北平原2.58Ma以来的海陆环境演变历史—宝应钻孔沉积物的常量元素记录[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(3):340-352. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dsjyj200603005
[20] 陈弘, 刘坚, 王宏斌.琼东南海域表层沉积物常量元素地球化学及其地质意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6):39-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200706006
[21] 郭志刚, 杨作升, 曲艳慧, 等.东海陆架泥质区沉积地球化学比较研究[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18(2):284-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.02.020
[22] 刘广虎, 李军, 陈道华, 等.台西南海域表层沉积物元素地球化学特征及其物源指示意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(5):61-68. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200605008
[23] Yang S Y, Jung H S, Li C X.Two unique weathering re-gimes in the Changjiang and Huanghe drainage basins:ge-ochemical evidence from river sediments[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 164(1/2):19-34.
-



 下载:
下载: