TEMPORAL AND SPATIAL VARIATION OF SUSPENDED SEDIMENT CONCENTRATION IN THE NEARSHORE WATERS OF WESTERN YANTAI AND ITS TRANSPORT CHARACTERISTICS IN WINTER
-
摘要:
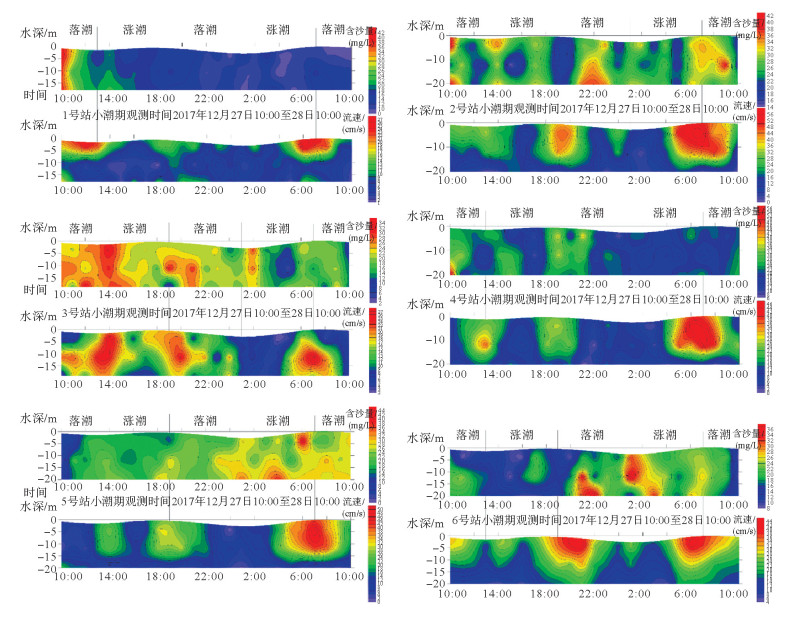
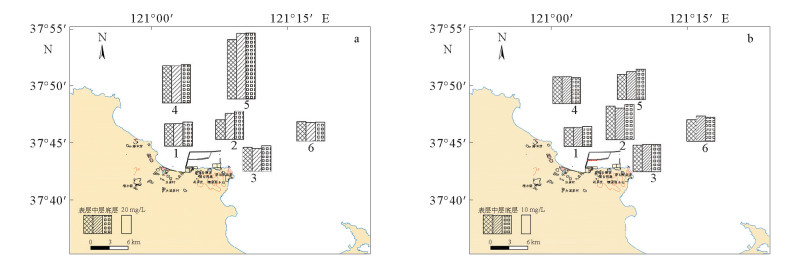
基于2017年12月在烟台港近岸海域6个站位大、小潮期的海流和悬沙同步观测资料,分析了悬浮泥沙浓度的时空变化规律,利用悬浮泥沙通量机制分解方法计算了研究区的悬浮泥沙输运通量,并初步讨论了潮流作用下悬浮泥沙的输运机制。结果表明,研究区各站位悬浮泥沙含量大潮期大于小潮期;大潮期各站位悬浮泥沙浓度多出现2~4个峰值,小潮期各站位悬浮泥沙浓度变化较为复杂,其规律性较弱;悬浮泥沙变化一般滞后于流速变化1~2 h。从平面分布上来看,研究区大潮期各站位悬浮泥沙浓度差异较大,小潮期差异较小;垂向上,大小潮期各层位悬浮泥沙含量变化不大,层化现象较弱。研究区水体的平流输运项主导着这一区域的悬浮泥沙输运,垂向净环流项起辅助作用,其他输沙项的贡献很小,研究区悬浮泥沙净输运方向与余流方向大致一致。大潮期垂向净环流项对悬浮泥沙输运的贡献略大于小潮期,小潮期平流输运项对悬浮泥沙输运的贡献略大于大潮期,大小潮变化对研究区泥沙输运影响显著。
Abstract:Based on the simultaneous observation of currents and suspended matters in spring and neap tides at six stations in the coastal waters of Yantai Port in December 2017, this paper studied the temporal and spatial variation in suspended sediment concentrations. The transport flux of suspended matter was calculated, and the transport mechanism of suspended sediment under tidal currents discussed. The results show that the suspended sediment content in the spring tide is greater than that in the neap tide; and the concentration of suspended matter at each station has 2~4 peaks during the spring tide period, whereas that in the neap tide is more complicated and lack of regularity. The change in suspended sediment generally lags behind the flow rate change for 1~2 hours. From the view of plane distribution, the concentration of suspended sediment at different stations in the study period is quite different, and the difference in neap tide period is rather small. In the vertical direction, however, the suspended sediment content in each layer of the spring and neap tides has little change, and the stratification phenomenon is not obvious. The advection transport of the water in the study area dominates the suspended sediment transport, while the vertical net circulation plays a supporting role, and the contribution of other sediment transport modes is rather small. The net transport direction and residual flow of suspended sediment in the study area are roughly the same. The contribution of the vertical net circulation to the suspended sediment transport during the spring tide period is slightly larger than that during the neap tide period. The contribution of the advection transport in the neap tidal period to the suspended sediment transport is slightly greater than that during the spring tide period, and the influence of the fluctuation of spring and neap tides on the sediment transport is significant in the area.
-

-
表 1 大、小潮期间海流观测特征值
Table 1. Characteristic values of current observation during the spring tide and neap tide
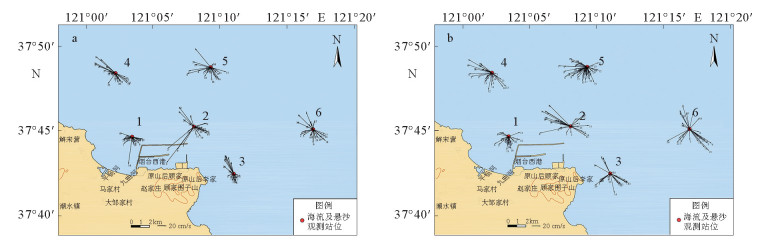
流速/(cm/s),流向/(°) 测站 平均流速 涨潮最大流速 落潮最大流速 大潮 小潮 大潮 小潮 大潮 小潮 表层
流速底层
流速表层
流速底层
流速表层 底层 表层 底层 表层 底层 表层 底层 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 流速 流向 1 22.5 12.6 12.9 7.7 41.5 130.1 18.1 307.8 24 116.2 18.8 164 51.1 285.9 17.2 317.6 26.4 259.3 12.4 232.2 2 45.4 15.6 21.1 7.8 51.3 104.1 14.5 114.1 33 123.3 15 251.7 126.1 289.7 86.7 142.2 56 299.4 15.6 36.6 3 21.2 15.4 12.1 12.3 33.4 313.9 17.9 340.8 25.9 197.8 20 115.4 54.5 338.5 34.7 332.4 21.8 44.7 19.2 342.4 4 34.9 10.1 18.2 8.7 52.6 134.2 16.1 112.7 24.8 137.3 14.9 325.1 78.2 306 14.3 325 45.2 281.5 14.3 287.9 5 33 9.9 19.4 7.5 50 126 17.5 75.8 25.6 146 20.9 184.7 89.1 322.8 19.2 123.9 48.3 308.4 12.9 249.2 6 28.3 20.6 20.6 18.9 41 326.7 31.9 99.5 43.2 305.4 41 299.5 75.6 321.5 51.7 301.6 31.6 298.6 28.9 301.2 表 2 2017年12月大、小潮期各站位潮余流分布特征
Table 2. Distribution characteristics of tidal currents at stations in the spring tide and neap tide periods in December 2017
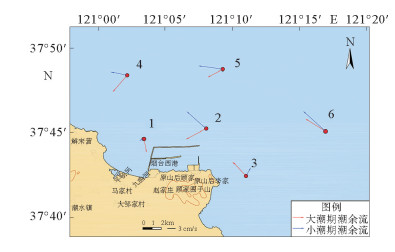
流速/(cm/s),方向/(°) 测站 大潮 小潮 表层 中层 底层 平均 表层 中层 底层 平均 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 流速 方向 1 8.7 167.9 2.9 197.1 3.7 144.5 5.1 169.8 3.7 199.5 0.8 208.8 0.5 340.9 1.7 249.7 2 11 309.7 7.4 338.7 6.3 78.9 8.2 242.4 13.1 319.8 11.5 300.4 3.6 315.1 9.4 311.8 3 9.4 312.3 6.3 317.5 5.5 321.5 7.1 317.1 3.6 62.7 3.2 12.4 3.7 14.8 3.5 30 4 11 263.1 11.9 271.5 1.4 128.3 8.1 221 7.8 278.7 7.3 264.6 3.2 301.8 6.1 281.7 5 9.4 315.2 8.1 319.4 1.2 93.6 6.2 242.7 12.2 295.5 11.9 295.3 2.5 242.6 8.9 277.8 6 10 312.8 8.7 310.7 7 282.1 8.6 301.9 9.5 284 13 353.8 10.2 298.4 10.9 312.1 表 3 大、小潮期各站涨落潮阶段平均悬浮泥沙含量
Table 3. Average suspended sediment content during the rising and falling tides in spring tide and neap tide
/(mg/L) 站号 大潮 小潮 落潮垂
向平均涨潮垂
向平均涨落潮垂
向悬浮泥
沙含量之比落潮垂
向平均涨潮垂
向平均涨落潮垂向
悬浮泥沙
含量之比2 27.2 26.5 0.97 27.2 26.5 0.97 3 21.4 21.8 1.02 21.4 21.8 1.02 4 23.2 19.4 0.84 23.2 19.4 0.84 5 21.3 23.5 1.1 21.3 23.5 1.1 6 19.2 19.1 0.99 19.2 19.1 0.99 平均值 21.5 20.8 0.97 21.5 20.8 0.97 注:涨落潮阶段平均悬浮泥沙含量分别为涨潮阶段、落潮阶段各层位悬浮泥沙含量的平均值。 表 4 大、小潮期间各站位悬沙浓度
Table 4. Suspended sediment concentration in spring and neap tides
/(mg/L) 站位 平均悬浮泥沙浓度 垂线平均最大悬沙浓度 大潮期 小潮期 大潮期 小潮期 1 24.9 15.7 30.0 29.0 2 26.4 26.8 36.0 34.1 3 25.3 21.6 37.9 30.6 4 40.7 21.3 54.1 31.8 5 68.6 22.4 88.0 32.7 6 20.5 19.2 28.0 28.7 表 5 各站位各层平均悬浮泥沙含量(大、小潮)
Table 5. Average suspended sediment content (spring tide and neap tide) in each layer at each station
/(mg/L) 站位 大潮 小潮 落潮 涨潮 落潮 涨潮 表层 中层 底层 表/底 表层 中层 底层 表/底 表层 中层 底层 表/底 表层 中层 底层 表/底 1 24.5 24.9 26 0.9 23.8 24.1 26.1 0.9 16.1 16.8 17 0.9 14.5 14 15.4 0.9 2 18.5 24 29.7 0.6 23.8 31.5 30.7 0.8 26.4 26.6 28.7 0.9 27.5 23.9 28 1 3 25.4 24.7 28.6 0.9 23.7 23.8 25.9 0.9 20.5 22.1 21.6 0.9 22.2 21.4 21.7 1 4 35.4 37.4 39.1 0.9 45.5 42.6 44 1 23.1 24.3 22.1 1 19.8 18.8 19.7 1 5 61.2 69.1 69.1 0.9 66.5 72.5 73 0.9 18.5 22.9 22.4 0.8 22.1 21.8 26.5 0.8 6 21.3 19.1 21.5 1 20.7 21 19.3 1.1 16 20.6 21.1 0.8 19 20.6 17.6 1.1 注:表中的表底比值为同一潮阶段表层与底层平均悬浮泥沙含量的比值 表 6 各站悬沙输运项及单宽悬沙净输运率(大、小潮)和矢量
Table 6. Net transport capacity of suspended sediments and single-width suspended sediment transport rate (spring tide and neap tide)
/(g·m-1·s-1),角度/(°) 站位 计算
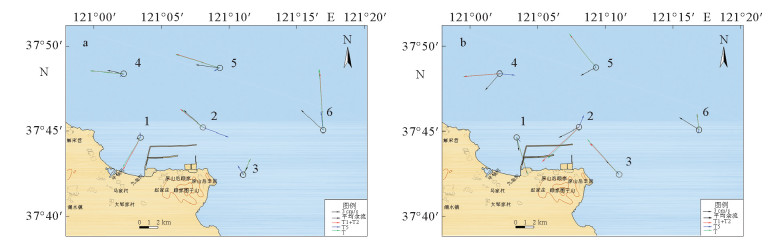
结果大潮 小潮 T1 T2 T5 T1+T2 T3+T4 T6+T7+T8 T T1 T2 T5 T1+T2 T3+T4 T6+T7+T8 T 1 和矢量 14.02 0.09 0.22 13.93 0.01 0 14.14 1.37 0.07 0.02 1.34 0.08 0.01 1.26 角度 163.6 325 138.3 163.7 135.7 48 163.3 206 322 356.1 208.7 1 287.5 211.2 2 和矢量 32.88 0.61 4.74 32.37 0.12 0.11 36.75 20.96 0.17 0.99 21.1 0.04 0.01 20.12 角度 5.2 217.4 22.4 4.6 122.1 204.6 7 309.2 277.3 110.8 309 118.3 228.6 309.8 3 和矢量 15.75 0.24 1.58 15.59 0.04 0.01 17.19 6.37 0.07 0.04 6.38 0.02 0 6.39 角度 317.8 185 327.2 317.1 1.7 297 318.1 26.1 306.8 331.3 25.5 182.9 305.7 25.2 4 和矢量 27.23 0.63 0.56 26.69 0.12 0.16 26.17 12.01 0.18 0.09 12.17 0.02 0.01 12.24 角度 266.2 117.5 95.9 265.5 121.2 300.1 265.3 274.5 307.5 231.9 275 299.6 91.6 274.7 5 和矢量 29.67 0.65 1.41 30.28 0.14 0.04 31.55 16.63 0.07 0.26 16.67 0.03 0.01 16.86 角度 322 300.6 328.1 321.5 126.3 240.2 321.8 287.9 235 240.8 287.7 328.2 100.2 287.2 6 和矢量 21.02 0.18 1.35 20.85 0.03 0.03 22.14 6.4 0.57 0.07 5.93 0.09 0.02 5.96 角度 356.3 153.6 352.7 356.5 211 179.1 356.2 350.1 138 201.3 353 331.2 304.5 352.3 表 7 大小潮期各站位潮余流、悬浮泥沙输运方向一览表
Table 7. List of tidal currents and suspended sediment transport directions at each station in the period of spring and neap tides
/(°) 站位 大潮期 小潮期 潮余流方向 悬沙输运方向 潮余流方向 悬沙输运方向 1 169.8 163.2 249.7 211.2 2 242.4 7.0 311.8 309.8 3 317.1 318.1 30.0 25.2 4 220.9 265.2 281.7 274.7 5 242.7 321.8 277.8 287.1 6 301.8 356.2 312.0 352.3 -
[1] 余佳.黄海悬浮体分布及季节性变化[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
[2] 杨作升, 王兆祥, 郑爱芬, 等.黄河口毗邻渤海陆架区悬浮体成分[J].青岛海洋大学学报, 1990, 20(1): 26-40.
[3] 乔璐璐.冬季大风事件下渤黄海环流及泥沙输运过程研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
[4] Zhang J, Liu S M, Xu H, et al.Riverine sources and estuarine fates of particulate organic carbon from North China in late summer[J].Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Sciences, 1998, 46(3):439-448. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0277
[5] Ma M, Feng Z, Guan C, et al.Pah and Pcb in sediments from the intertidal zone of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2001, 42 (2):132-136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e4012328789303378ca8d3a6df3f71c4
[6] 刘雪.基于遥感的中国东部海域悬浮泥沙季节变化研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[7] Bi N, Yang Z, Wang H, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3):239-247. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272771411000886
[8] 江文胜, 苏健, 杨华, 等.渤海悬浮物浓度分布和水动力特征的关系[J].海洋学报, 2002(S1):212-217. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1000451372
[9] 李爱超, 乔璐璐, 万修全, 等.渤海海峡悬浮体分布、通量及其季节变化[J].海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2):310-318. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201602003
[10] Zhang J, Huang W W, Martin J M. Trace metals distribution in Huanghe (Yellow River) estuarine sediments[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 1988, 26(5):499-516. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(88)90003-0
[11] 秦蕴珊, 李凡, 郑铁民, 等.南黄海冬季海水中悬浮体的研究[J].海洋科学, 1986, 10(6):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYKX198606000.htm
[12] 鲍献文, 李真, 王勇智, 等.冬、夏季北黄海悬浮物分布特征[J].泥沙研究, 2010(2):48-56. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/nsyj201002008
[13] 吴祥柏, 汪亚平, 潘少明.长江河口悬沙与盐分输运机制分析[J].海洋学研究, 2008, 26(4):8-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2008.04.002
[14] 杨林.废黄河口海域悬沙时空变化及输移特征[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018.
[15] 张存勇.连云港近岸海域沉积物再悬浮及悬沙动力研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.
[16] 杜家笔, 裴艳东, 高建华, 等.弱动力浅海中的悬沙输运机制:以天津港附近海域为例[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2012, 34(1):136-144. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyxb201201017
[17] 林纪江, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等.潮流作用下蓬莱近岸海域悬浮泥沙的时空分布及变化特征[J].海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(12):13-23. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=49c3c1d2-9280-4f19-8425-233e25efb493
[18] 张伟, 周连成, 吴建政, 等.渤海海峡南部海域表层沉积物分布特征及控制因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):19-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505004
[19] 刘成, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等.庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境分区及沉积物输运趋势[J].海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(8):26-35. http://hydt.cbpt.cnki.net/WKA/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=c31dc0d2-9adb-46a7-a6e9-274567b9be2c
[20] 李爱超, 乔璐璐, 万修全, 等.渤海海峡悬浮体分布、通量及其季节变化[J].海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(2):310-318. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hyyhz201602003
[21] Jiang S H, Hu R J, Feng X L, et al. Influence of the construction of the Yantai West Port on the dynamic sedimentary environment[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2017:1-9. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1064119X.2017.1278809
[22] 董有强, 周锋.烟台港西港区规划锚地锚泊安全研究[J].中国水运, 2010(4):26-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsy201004014
[23] 秦福寿, 王钺, 张国建, 等.烟台港西港区规划设计建设中关键技术问题回顾[J].港工技术, 2014(2):13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9592.2014.02.004
[24] 胡日军, 吴建政, 朱龙海, 等.东海舟山群岛海域表层沉积物运移特性[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3):495-500, 442. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb200903027
[25] Yu Q, Wang Y P, Flemming B, et al. Tide-induced suspended sediment transport: Depth-averaged concentrations and horizontal residual fluxes[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 34:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.11.015
[26] Xie D F, Gao S, Wang Z B, et al. Numerical modeling of tidal currents, sediment transport and morphological evolution in Hangzhou Bay, China[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2013, 28(3):316-328. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(13)60042-6
[27] 陈斌, 刘健, 高飞.莱州湾悬沙输运机制研究[J].水科学进展, 2015, 26(6):857-866. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/skxjz201506012
[28] 陈斌, 高飞, 刘健.夏季浙江沿岸陆架区泥沙输运机制[J].海洋学报(中文版), 2017, 39(3):96-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.03.009
[29] Ingram R G. Characteristics of the Great Whale River Plume[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1981, 86(C3): 2017-2023. doi: 10.1029/JC086iC03p02017
[30] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 1985, 8(3):256-269. doi: 10.2307/1351486
[31] 唐建华, 梁摇斌, 李若华.强潮河口悬浮泥沙浓度垂向结构分析——以杭州湾乍浦水域大潮期为例[J].水利水运工程学报, 2009(2):39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2009.02.007
[32] 冷星, 朱龙海, 胡日军.山东半岛东部海域泥质区冬季悬浮泥沙时空变化及输运机制[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(4):106-116. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qdhydxxb201904012
[33] 杨晓东, 姚炎明, 蒋国俊, 等.乐清湾悬沙输移机制分析[J].海洋通报, 2011, 30(1):53-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.01.009
-



 下载:
下载: