THE CORRECTION OF RUGGED SEABED BASED ON STRUCTURAL SIMILARITY
-
摘要:
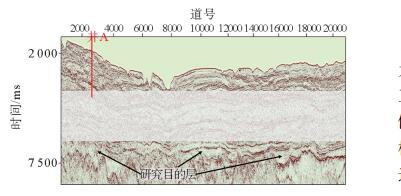
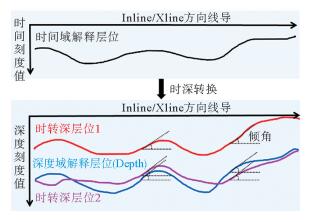
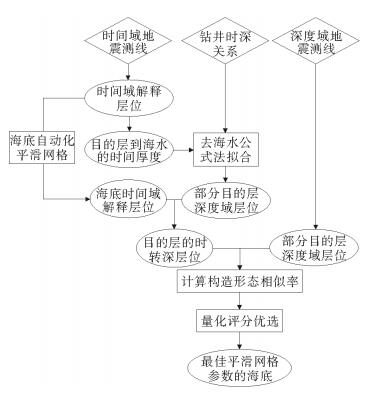
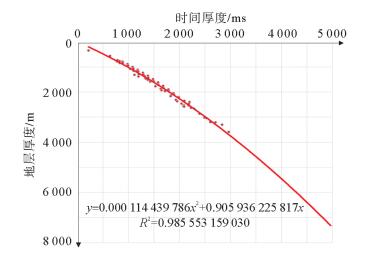
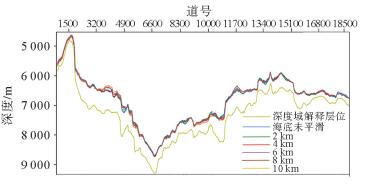
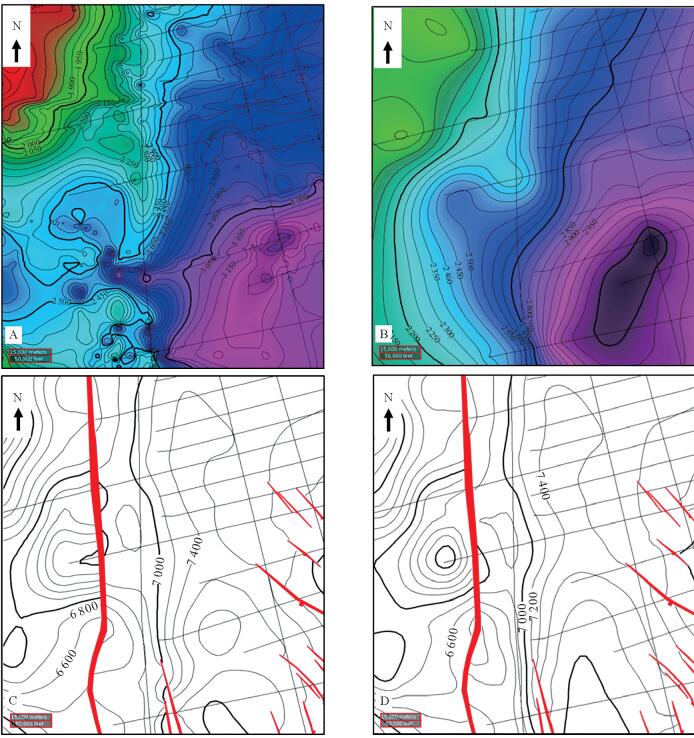
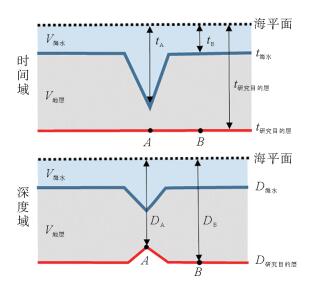
研究区位于深水低勘探区,崎岖海底等普遍存在,受地震、钻井和速度等资料条件的限制,只能采用去海水的拟合公式法进行时深转换。然而去海水拟合公式法时深转换会因崎岖海底而造成假构造现象,且常规的崎岖海底填平校正方法存在一定的不足。用去海水拟合公式法计算出时转深层位,并比较时转深层位与深度域地震资料的横向构造形态变化,引入了构造形态相似率的概念,建立了崎岖海底填平量化评分模板来对崎岖海底进行填平校正,最后根据最高得分值来确定最佳平滑网格的海底和合适的时转深层位,在一定程度上消除了崎岖海底造成的假构造现象和支持了构造成图的需求。
Abstract:Abstract: The time-depth conversion faces many difficulties in some special conditions, such as rugged seabed, deep-water and the areas of low exploration degree, owing to the deficiency in seismic, sha-llow drilling and improper velocity data. The fitting formula by removing water depth was the only method for time-depth conversion. However, the practice may lead to pseudo-structures because of rugged seabed,and the conventional correction method by filling up the sea bottom has similar shortcomings. The method used in this paper calculate the time-to-depth horizon first, and then compare the horizons in depth-domain for the change in the transverse structures. This method introduced in the concept of structure similarity rate and quantitative templates are built up for filling up the sea bottom for correction of the rugged seabed. Based on the highest score value, the suitable sea bottom and time-to-depth horizons are determined. To some extent, it can eliminate the pseudo-structures caused by rugged seabed and better support the requirements of structural mapping.
-

-
表 2 2号测线上不同网格平滑参数的构造形态相似率
Table 2. Structural similarity rate of different mesh smoothing parameters of Line2
海底层位的网格
平滑参数/km误差容忍度 高 中 低 未平滑 0.675 0.850 0.907 2 0.715 0.834 0.894 4 0.685 0.869 0.936 6 0.723 0.904 0.952 8 0.762 0.920 0.951 10 0.740 0.907 0.958 表 1 号测线上不同网格平滑参数的构造形态相似率
Table 1. Structural similarity rate of different mesh smoothing parameters of Line1
海底层位的网格
平滑参数/km误差容忍度 高 中 低 未平滑 0.378 0.642 0.774 2 0.522 0.743 0.866 4 0.574 0.782 0.877 6 0.547 0.781 0.877 8 0.554 0.777 0.872 10 0.539 0.773 0.882 表 3 1号测线上不同网格平滑参数的评分模板
Table 3. Score value template of different mesh smoothing parameters of Line1
海底层位的网格
平滑参数/km误差容忍度 3 2 1 合计分数 未平滑 1 1 1 6 2 2 2 2 12 4 6 6 5 35 6 4 5 4 26 8 5 4 3 26 10 3 3 6 21 表 4 2号测线上不同网格平滑参数的评分模板
Table 4. Score value template of different mesh smoothing parameters of Line2
海底层位的网格
平滑参数/km误差容忍度 3 2 1 合计分数 未平滑 1 2 2 9 2 3 1 1 12 4 2 3 3 15 6 4 4 5 25 6 6 4 3 34 10 5 5 6 31 -
[1] 张英德,彭佳勇,郝立业,等.海外深水复杂地质条件下时深转换难点及技术对策[J].地球物理学进展,2012,27(4):1484-1492. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxjz201204023
[2] 喻英梅,张英德,彭佳勇.海底峡谷对深部地层时深转换的影响及其消除方法[J].中国海上油气,2008,20(4):236-238. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zghsyq-gc200804005
[3] 徐立恒,鲜波,薛玉英,等.高精度地震时深转换方法研究及应用[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(5):1712-1719. http://xuebao.jlu.edu.cn/dxb/CN/Y2014/V44/I5/1712
[4] 李军.三维地震资料解释中时深转换方法对比分析及应用[J].海洋石油,2014,34(1):36-40. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95970A/201401/48981334.html
[5] 张国栋,廖仪,马光克.速度体高精度建模法在深水M气田时深转换中的应用[J].地球物理学进展,2016,31(5):2246-2254. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxjz201605050
[6] 黄兆林,王兴芝,李添才,等.变速成图技术在南海西部地区的应用[J].海洋地质前沿,2011,27(11):55-59. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98440A/201111/40244109.html
[7] 刘杰,秦成岗,全志臻,等.一种识别陆架坡折带“隐形构造”的时深转换方法[J].石油地球物理勘探,2013,48(1):128-133. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/sydqwlkt201301020
[8] 胡青琴.叠加速度在稀疏二维工区速度场建立中的应用[J].吉林地质,2016,35(3):85,87,105. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96381X/201603/670255643.html
[9] 刘道理,汪瑞良,秦成岗,等.利用特色叠前深度偏移技术消除崎岖海底影响———以珠江口盆地番禺—流花地区应用为例[J].海相油气地质,2013,18(1):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.01.010 http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/hxyqdz201301010
[10] 陈海清,戴晓云,潘良云,等.时间剖面上的假构造及其解决方法[J].石油地球物理勘探,2009,44(5):590-602. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2009.05.014
[11] 杨东升,赵志刚,杨海长,等.深水崎岖海底区构造解释与圈闭落实方法———以琼东南盆地深水区宝岛凹陷为例[J].石油学报,2018,39(7):767-774.
-



 下载:
下载: