APPLICATION AND PROSPECT OF ROV IN OFFSHORE OIL AND GAS FIELD DEVELOPMENT
-
摘要:
水下机器人(ROV)以其综合优势,在海上油气田勘探、开发和生产全生命周期中的各个阶段发挥着重要的作用。结合行业应用实际,系统介绍了ROV的原理和系统组成,以及海上油气田开发过程间各种作业类型中ROV的应用,对其工作内容、方式和风险进行了全面的详细论述和总结。同时,对ROV以后的技术发展趋势进行了展望。
Abstract:With its advantages, ROV played an important role in the lifecycle of offshore oil and gas exploration, development and production phases. Based on the practical applications in the industry, this paper systematically and comprehensively introduced the application of ROV in various operations during the development of offshore oil and gas fields, gave a detailed description of its scope of work, steps and summarized risks related with ROV. At the same time, the future development trend of ROV was forecasted.
-
Key words:
- ROV /
- offshore oil and gas field /
- risk of subsea operations /
- deep-sea route
-

-
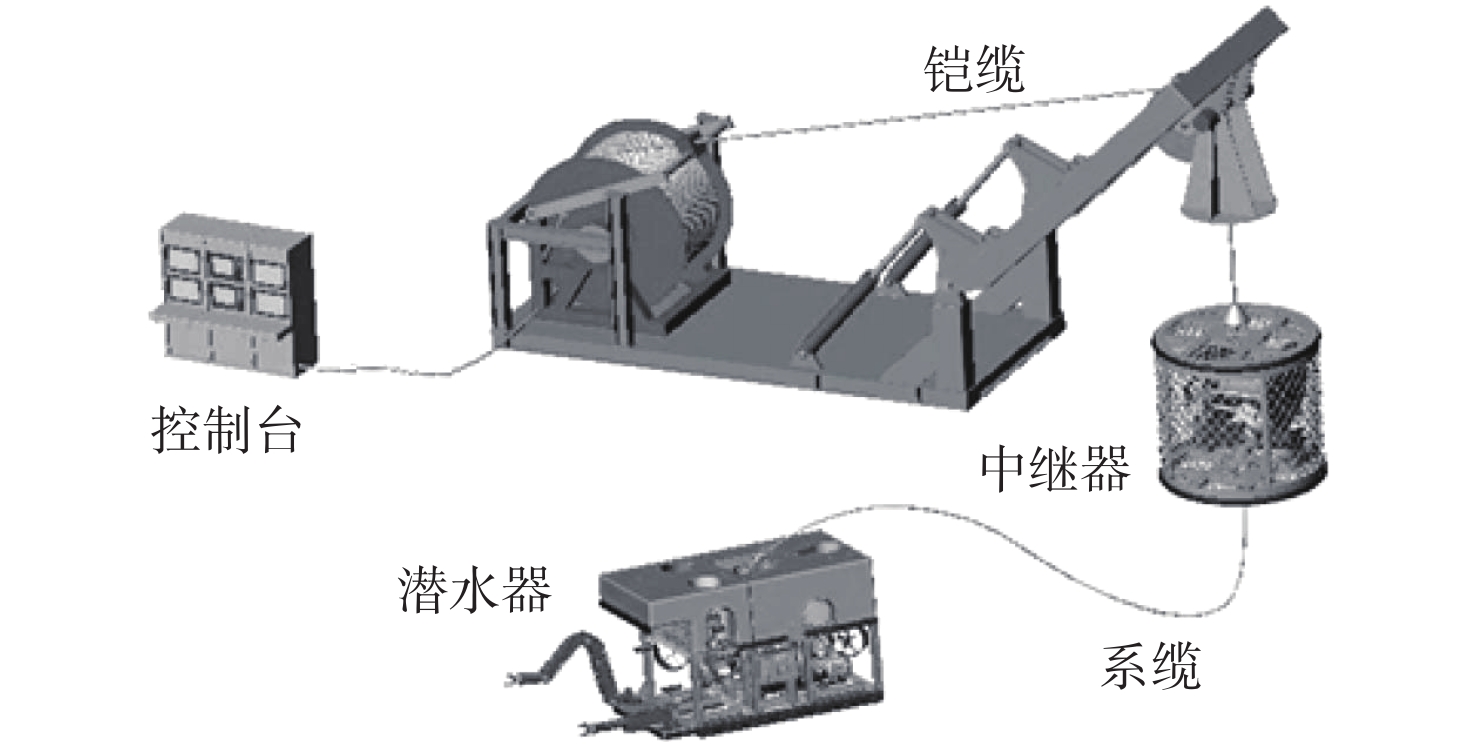
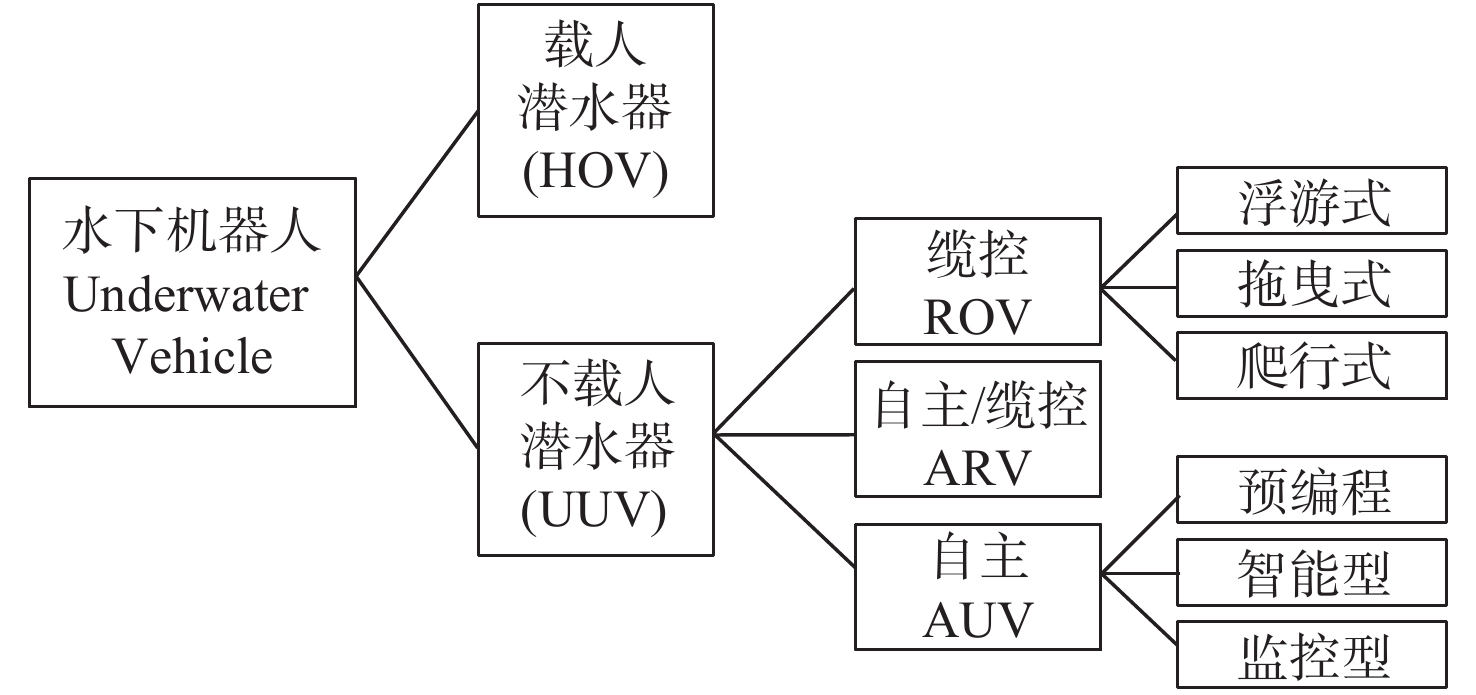
图 2 ROV系统组成示意图[6]
Figure 2.
表 1 国内主要深海潜器情况表
Table 1. Main deepwater vehicles in China
类型 名称 设计潜深/m 研发单位 HOV 蛟龙号 7 000 中国船舶集团 深海勇士号 4 500 奋斗者号 10 000 彩虹鱼号 11 000 上海海洋大学 AUV 潜龙一号 6 000 中国科学院 潜龙二号 4 500 潜龙三号 4 500 探索4500 4 500 ROV 海龙Ⅲ 6 000 上海交通大学 海马4500 4 500 上海交通大学 海星6000 6 000 中国科学院 海马11000 11 000 上海交通大学 ARV 北极号 4 000 中国科学院 海斗号 11 000 表 2 用于海洋油气领域的主要国外型号ROV基本参数
Table 2. The main manufacturers’ ROVs basic specification in overseas
生产厂家 国家 ROV名称及型号 级别 最大下潜深度/m 功率/HP 动力源 重量/kg 作业方式 Oceaneering 美国 MAGNUM 工作型 3 000 150 液压 3 000 TMS Forum(Perry&Sub-Atlantic) 美国 Perry Triton XLX 工作型 3 000 200 液压 4 900 TMS SMD 英国 Quasar 工作型 6 000 200 液压 4 500 TMS Technip-FMC(Schilling) 美国 Schilling UHD 工作型 5 000 200 液压 2 450 TMS Fugro 荷兰 FCV 3000C 工作型 3 000 200 液压 4 000 TMS Subsea 7(i-Tech) 英国 Centurion SP 工作型 4 000 230 液压 3 200 TMS IKM 挪威 WR200 工作型 3 000 200 电动 3 000 TMS ISE 加拿大 HYSUB130-4000 工作型 4 000 130 液压 3 400 自游式 SAAB(Seaeye) 英国 Seaeye Panther Plus 观察型 1 000 75 电动 500 自游式 -
[1] 谭界雄,田金章,王秘学,等. 水下机器人技术现状及在水利行业的应用前景[J]. 中国水利,2018(6):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2018.06.010
[2] 封锡盛. 从有缆遥控水下机器人到自治水下机器人[J]. 中国工程科学,2000,2(12):29-33,58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2000.12.005
[3] 范士波. 深海作业型ROV水动力试验及运动控制技术研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2013.
[4] 盛堰,谭鹰,陈宗恒,等. ROV在我国海洋区域地质调查中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2013,29(11):67-71.
[5] 陈宗恒,盛堰,陶军. 遥控水下机器人(ROV)结构综述—以hysub130-4000ROV为例[J]. 海洋地质,2009(3):67-71.
[6] 郭威,崔胜国,赵洋,等. 一种遥控潜水器控制系统的研究与应用[J]. 机器人,2008,30(5):398-403. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-0446.2008.05.003
[7] 赵俊海,张美荣,王帅,等. ROV中继器的应用研究及发展趋势[J]. 中国造船,2014,55(3):222-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4882.2014.03.025
[8] SHEPHERD K. Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs)[M]//STEELE J H. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2001: 2408-2413.
[9] AHMAD H, OMERDIC E, NOLAN S, et al. Integration and Testing of Multi-Purpose Platform Technologies System and High Resolution Multi-Beam Sonar on ROV[C]//8th IFAC Conference on Control Applications in Marine Systems, 2010:289-294.
[10] 黄明泉. 水下机器人ROV在海底管线检测中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(2):52-57.
[11] 刘春媚. 遥控式水下机器人运动控制技术的研究[D]. : 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2007.
[12] CHRIST R D, WERNLI R L. The ROV Manual: a User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles [M]. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth- Heinemann, 2013.
[13] 张洪欣,马龙,张丽婷,等. 水下机器人在海洋观测领域的应用进展[J]. 遥测遥控,2015,36(5):23-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1000.2015.05.004
[14] 陶军,陈宗恒. “海马”号无人遥控潜水器的研制与应用[J]. 工程研究,2016,8(2):185-191.
[15] 任福君,张岚,王殿君,等. 水下机器人的发展现状[J]. 佳木斯大学学报,2000,18(4):317-320.
[16] 张杰,纪文亮. ROV原理及在我国海洋石油工程中的应用[J]. 中国造船,2007,48(S1):132-136.
[17] 张杰,纪文亮. 在海洋石油工程项目中ROV的基本运作模式[J]. 中国造船,2007,48(S1):137-140.
[18] 李士涛. 机器人ROV在海洋工程水下施工中的应用技术研究[J]. 中国造船,2009,50(S1):222-228.
[19] 周凯,易杏甫. 水下机器人概述和发展应用前景[J]. 电子科技,2010(24):283-284.
[20] 刘阳,李军安. ROV在深水海底电缆铺设中的应用研究[J]. 湖南农机,2010,37(2):34-51.
[21] 率鹏. 水下机器人在海洋石油工程中的应用[J].石油和化工设备[J]. 石油化工设备,2019,22(5):63-65.
[22] 肖钢. 浅谈ROV在水下采油树检修中的应用[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2019,39(10):105-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2019.15.052
[23] SHUKLA A,KARKI H. Application of robotics in offshore oil and gas industry— A review Part II[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,2016(75):508-524.
[24] DENNIELOU B,DROZ L,BABONNEAU N,et al. Morphology,structure,composition and build-up processes of the active channel-mouth lobe complex of the Congo deep-sea fan with inputs from remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) multibeam and video surveys[J]. Deep–Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,2017(142):25-49.
[25] CAPOCCI R,DOOLY G,OMERDIĆ E,et al. Inspection-Class Remotely Operated Vehicles-A Review[J]. Marine Science and Engineering,2017,5(1):1-32.
[26] 田冷. 海洋石油开采工程[M]. 东营: 中国石油大学出版社, 2015: 62-63.
[27] YONG B, QIANG B. Pipeline Inspection, Maintenance and Repair[M]//YONG B, QIANG B. Subsea Pipelines and Risers. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005. 655-682.
[28] YONG B, QIANG B. ROV Intervention and Interface. Subsea Engineering Handbook Second Edition. 2019. 806-831.
[29] 刘彬,莫子翠,张杰,等. 双频识别声呐在浑浊海域ROV海管调查中的应用[J]. 广西科学院学报,2017,33(3):191-194.
[30] RICHARDS C. Technology Trends in the Offshore Oil & Gas Industry ROV Sensors & Subsystems[J]. Ocean News & Technology,2011,17(3):32-33.
[31] 庞维新,李清平,李迅科,等. 我国海洋油气ROV作业能力现状与展望[J]. 油气储运,2015,34(11):1157-1160.
[32] WERNIL R. The present and future capabilities of deep ROVs[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 1999-2000, 33(4): 26-40.
[33] CHEN H P, STAVINOHA S, WALKER M, et al. Opportunities and Challenges of Robotics and Automation in Offshore Oil & Gas Industry[J]. Intelligent Control and Automation, 2014, 5: 136-145.
[34] ROBERT D C, ROBERT L, WERNLI R L. The Future of ROV Technology[M]. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth- Heinemann, 2014: 643-661.
-



 下载:
下载: