PREDICTION OF HIGH QUALITY SOURCE ROCKS BASED ON SEQUENCE STRATIGRAPHIC FRAMEWORK OF WENCHANG FORMATION, PANYU 4 DEPRESSION, THE PEARL RIVER MOUTH BASIN
-
摘要:
珠江口盆地番禺4洼“小而肥”,目前的探明石油地质储量已超出早期估算的地质资源量,早期对烃源岩的认识不足可能是其主要原因,尤其是对优质烃源岩的分布范围仍缺少精确刻画,在很大程度上限制了对该洼陷勘探潜力的认知。以该难点问题为切入点,利用最新钻井和地震资料,采取层序地层学开展了番禺4洼烃源岩的预测工作。通过地震资料上识别的各种反射特征,结合区内已有钻井资料识别的旋回特征,将番禺4洼文昌组划分5个三级层序,进而建立了等时地层格架。在此基础上,综合运用地震沉积学最新技术手段,精细揭示了番禺4洼文昌组文三段优质烃源岩的分布范围。研究结果表明,番禺4洼优质烃源岩分布面积较为广泛,尤其在北次洼和西次洼,优质源岩面积均超过了以往预期。这一研究成果对本区和珠江口盆地油气勘探具有一定指导意义。
Abstract:The Panyu 4 Depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin is rather small but rich in hydrocarbon, and the current proved geological reserves have exceeded the early-estimated geological resources. Lacking of source rock knowledges, especially lacking of accurate description of high-quality source rocks, may be the main reason that greatly limited the recognition of the exploration potential of the depression. Taking this difficult problem as the standpoint to seek for breakthrough, this paper uses the latest drilling and seismic data and adopts the unique perspective of sequence stratigraphy to systematically make prediction of source rocks in the depression. According to the various reflection characteristics identified from seismic data and the cyclic characteristics from drilling data, the Wenchang Formation in Panyu 4 Depression is divided into five third-order sequences, and the isochronous stratigraphic framework is then established. On this basis, the distribution area of high-quality source rocks in the third sequence of Wenchang Formation in Panyu 4 Depression is revealed by using the latest seismic sedimentology techniques. The results show that the area of high-quality source rocks in the Panyu 4 Depression is relatively wide, especially in the North Sub-depression and the West Sub-depression, the area of high-quality source rocks exceeds previous expectations. The research results of this paper may provide clues for oil and gas exploration in this region and the Pearl River Mouth Basin.
-

-
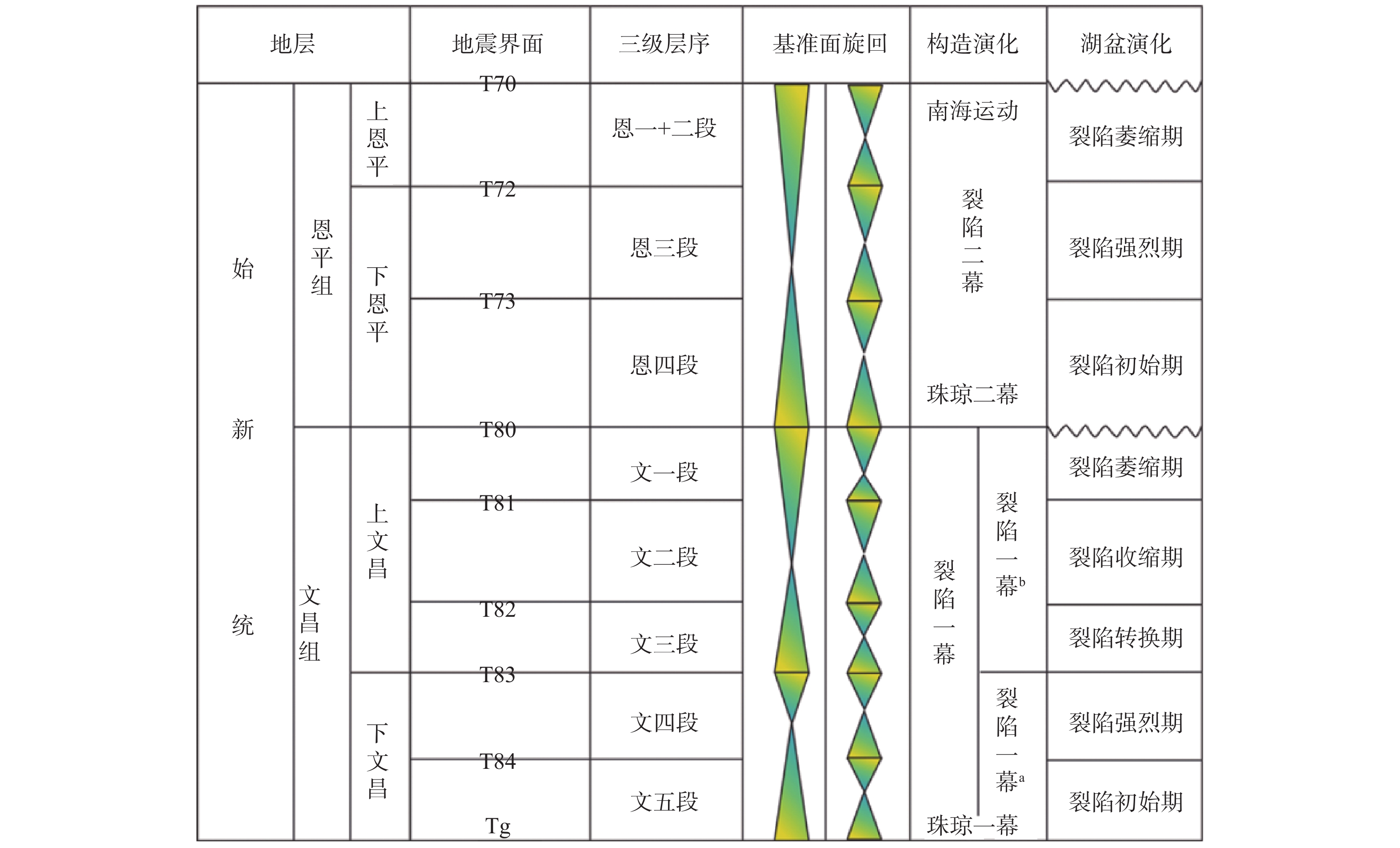
图 2 番禺4洼古近系层序地层格架[13]
Figure 2.
表 1 烃源岩地球化学特征统计表
Table 1. Statistics of geochemical characteristics of source rocks
样品深度/m 样品数 TOC/% S1+S2/(mg/g) HI/(mg/g) Tmax/℃ 氯仿沥青“A”/% 干酪根类型 Ro/% 3 273~3 639 15
1.6~10.5
2.31~76.08
136.3~696.2424~444
0.39~0.965Ⅱ1 0.63~0.66 -
[1] 代一丁. 珠江口盆地西江南洼古近系构造演化与沉积特征[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(3):1-7.
[2] 朱筱敏,黄捍东,代一丁,等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼文昌组层序格架与沉积体系研究[J]. 岩性油气藏,2014,26(4):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.04.001
[3] 杨玲,陈开远,魏谋杰,等. 珠江口盆地番禺4洼陷文昌组层序地层划分[J]. 石油天然气学报,2008(2):187-190,647.
[4] 张水昌,高志勇,李建军,等. 塔里木盆地寒武系—奥陶系海相烃源岩识别与分布预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2012,39(3):285-294.
[5] 张寒,朱光有. 利用地震和测井信息预测和评价烃源岩:以渤海湾盆地富油凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2007,34(1):55-59. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2007.01.011
[6] 赵宏伟. 利用测井和地震响应特征识别优质烃源岩:以松南新区断陷群为例[J]. 石油天然气学报,2013,35(8):7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2013.08.002
[7] 吴玉坤,胡明毅,柯岭,等. 利用地震相识别优质烃源岩:以辽中凹陷沙三段为例[J]. 沉积学报,2013,31(2):366-373.
[8] 徐海,都小芳,高君,等. 基于波形聚类的沉积微相定量解释技术研究:以中东地区X油田为例[J]. 石油物探,2018,57(5):744-755. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.05.014
[9] 刘爱群,陈殿远,任科英. 分频与波形聚类分析技术在莺歌海盆地中深层气田区的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2013,28(1):338-344. doi: 10.6038/pg20130137
[10] 杨飞, 章学刚, 雷海飞. 地震沉积学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 92-96.
[11] 舒誉,施和生,杜家元,等. 珠一坳陷古近系油气成藏特征及勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气,2014,26(3):37-42.
[12] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M], 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 1-4.
[13] 米立军,张向涛,陈维涛,等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系油气富集规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气,2018,30(6):1-13.
[14] 卓海腾,王英民,徐强,等. 南海北部陆坡分类及成因分析[J]. 地质学报,2014,88(3):327-336.
[15] VAIL P R,MITCHUM P M. Seismic stratigraphic and global changes in sea leavel. Parts Ⅰ-Ⅱ[J]. AAPG Memoir,1977,26:51-212.
[16] MITCHUM P M, SANGEREE J B, VAIL P R, et al. Recognizing sequences and systems tracts from well logs, seismic data and biostratigraphy: examples from the late Cenozoic, siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy[J]. AAPG Memoir 58, 1993: 163-199.
[17] BROWN L F. Sequence stratigraphy in offshore South African divergent basin[J]. AAPG Studies in Geology,1996,41:184.
[18] MITCHUM R M,VAN WAGONER J C. High-frequency sequences and their stacking patterns:sequence-stratigraphic evidence of high frequency eustatic cycle[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1991,70:131-160. doi: 10.1016/0037-0738(91)90139-5
[19] 张世奇,纪发亮. 陆相断陷湖盆层序地层学模式探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1996(5):20-23,82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1996.05.001
[20] 蔡希源, 李思田. 陆相盆地高精度层序地层学: 隐蔽油气藏勘探基础、方法与实践[M], 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 45-53.
[21] 朱红涛,李森,刘浩冉,等. 陆相断陷湖盆迁移型层序构型及意义:以珠Ⅰ坳陷古近系文昌组为例[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(3):361-372.
[22] 施和生,杜家元,梅廉夫,等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(3):447-461.
[23] 卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 200-206.
[24] 程克明, 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 等. 烃源岩地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995.83-88.
[25] 朱光有,金强. 有效烃源岩的识别方法[J]. 石油大学学报,2003,27(2):6-10.
[26] 张功成,梁建设,徐建永,等. 中国近海潜在富烃凹陷评价方法与烃源岩识别[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(1):13-19,102.
-




 下载:
下载: