MICA SHAPE FACTOR AND ITS EQUIVALENT SEDIMENTATION IN THE SEDIMENTS OF THE YELLOW RIVER ESTUARY
-
摘要:
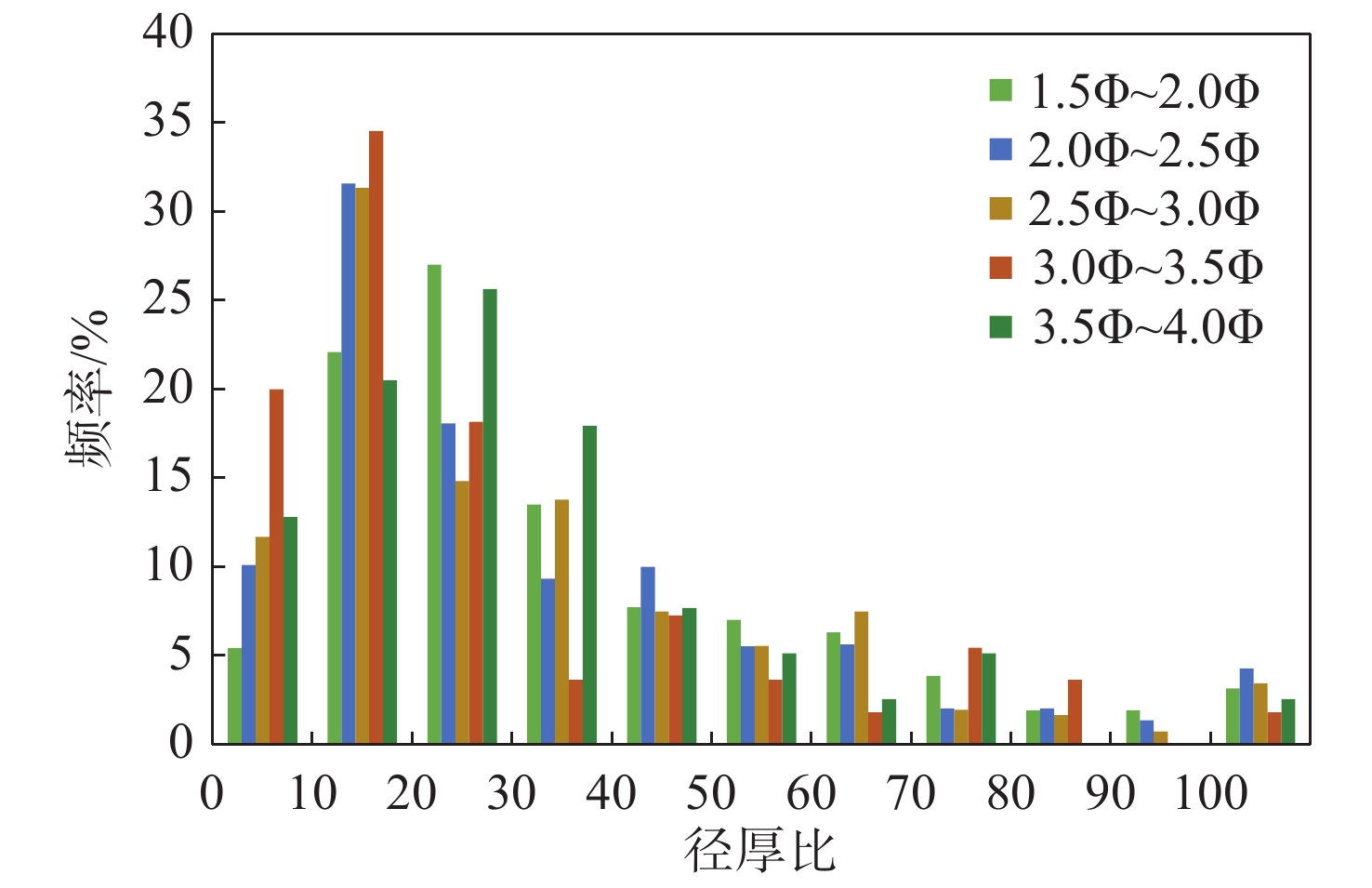
云母有着独特的片状结构和晶形,为了分析云母与其他粒状碎屑矿物的水力沉积差异,以黄河口段沉积物为对象,分粒级进行轻、重矿物鉴定,挑选出其中的白云母以及不同风化程度的黑云母,测量了5个样点、约12 000颗碎屑云母的粒径与厚度,以此比较片状云母与粒状石英和长石在水体中的等效沉积。结果表明,黄河口沉积物中云母含量约为1.8%~9.7%,其在不同样品和不同粒级之间差异很大,在1.5Φ~5.5Φ粒级之间云母含量由高至低急剧减少;云母厚度大都<20 μm,平均厚度仅8.93 μm,白云母的厚度一般小于黑云母;薄片状云母体积远小于相同粒径的粒状石英、长石,约为石英和长石的16%~55%;云母体积的变化可由其形状系数−径厚比来反映,云母的径厚比大都介于5~60。片状云母与粒状石英和长石在搬运与沉积过程中水力特性差异明显,等效沉积作用常使较大粒径云母与细粒泥质沉积密切共生。
Abstract:Mica has a unique sheet-like structure and crystal form. In order to study the hydraulic difference between mica and other granular detrital minerals, light and heavy minerals were identified for the sediments of different size taken from the Yellow River Estuary. Muscovite and the biotite with different weathering degree were selected as research objects. The particle size and thickness of about 12 000 detrital mica from 5 samples were measured to study the equivalent size for sheet-like mica and granular feldspar and quartz in water. The results show that the content of mica in the Yellow River sediments is about 1.8%~9.7% in general, which vary greatly between different samples and different grain size grades and the content of mica decreases sharply from high to low around the grain size of 1.5Φ~5.5Φ. The thickness of mica is mostly less than 20 μm with an average of 8.93 μm. Muscovite is generally thinner than biotite. The volume of sheet shaped mica is approximately 16% to 55% of granular minerals, which is much smaller than those of feldspar and quartz. The volume change of mica can be described with shape factor and the diameter-thickness ratio, which varies between 5~60. According to the Corey and Stokes law, for mica and granular minerals such as feldspar and quartz, the sedimentation rate of mica is only 0.12%~0.33% of that for feldspar and quartz if they are the same in grain size. If the sedimentation rates are same for the two kinds of sediments, the grain size distribution of mica is wider than that of feldspar and quartz, with a difference of about 1.0Φ~1.5Φ. Therefore, the hydraulic behavior of sheet-like mica and granular feldspar and quartz are obviously different in the process of transportation and deposition. Equivalent deposition often makes large-particles of mica deposited together with fine-grained muddy deposits.
-

-
表 1 黄河口沉积物代表性样品中各个粒级和全样中的云母含量
Table 1. The contents of mica in each fraction and bulk sample of representative sediments in the Yellow River Estuary
/% 样品编号 鉴定粒级/Φ 粒级含量 轻矿物含量 重矿物含量 轻矿物中白云母 轻矿物中风化黑云母 重矿物中白云母 重矿物中黑云母 LJ2 <1.5 0.02 100.00 0.00 13.92 8.86 0.00 0.00 1.5~2.0 0.05 100.00 0.00 0.59 3.26 0.00 0.00 2.0~2.5 0.03 100.00 0.00 17.25 45.32 0.00 0.00 2.5~3.0 0.24 97.81 2.19 36.13 50.32 3.83 86.90 3.0~3.5 1.30 99.61 0.39 11.68 20.96 2.71 48.98 3.5~4.0 38.86 99.56 0.44 2.13 2.44 0.68 8.54 4.0~4.5 49.10 99.15 0.85 0.57 1.14 0.00 0.81 4.5~5.0 6.95 97.82 2.18 1.55 0.62 0.00 0.79 5.0~6.0 2.06 99.99 0.01 4.00 0.92 0.21 0.00 ∑=98.61 云母加权平均值 1.535 1.966 0.001 0.026 HKZ9 <1.5 0.02 100.00 0.00 18.48 31.52 0.00 0.00 1.5~2.0 0.01 100.00 0.00 36.11 62.50 0.00 0.00 2.0~2.5 0.02 100.00 0.00 31.07 68.61 0.00 0.00 2.5~3.0 0.30 96.62 3.38 25.62 68.52 6.09 93.48 3.0~3.5 0.34 99.01 0.99 21.73 44.09 3.52 89.95 3.5~4.0 30.20 99.37 0.63 4.44 11.54 0.56 10.06 4.0~4.5 59.85 98.83 1.17 3.19 3.77 0.38 2.64 4.5~5.0 5.75 98.57 1.43 1.17 2.05 0.15 2.14 5.0~6.0 2.61 99.60 0.40 1.99 1.32 0.17 0.34 ∑=99.10 云母加权平均值 3.497 6.215 0.005 0.052 HH6 <2.0 0.01 99.63 0.37 37.70 62.30 1.89 96.23 2.0~2.5 0.02 95.93 4.07 35.08 64.92 2.08 95.83 2.5~3.0 0.05 95.47 4.53 30.15 60.57 3.74 92.52 3.0~3.5 2.57 98.66 1.34 3.98 6.82 5.61 69.91 3.5~4.0 39.01 98.49 1.51 0.24 1.18 0.24 10.12 4.0~4.5 44.67 94.29 5.71 0.60 1.00 0.15 0.15 4.5~5.0 4.52 89.07 10.93 2.07 1.81 0.00 0.00 5.0~6.0 0.30 89.95 10.05 1.06 2.90 0.55 0.91 ∑=91.16 云母加权平均值 0.559 1.182 0.007 0.091 HBZ12 <2.0 0.03 99.91 0.09 27.27 70.61 3.55 92.31 2.0~2.5 0.05 99.89 0.11 25.66 68.80 4.99 93.84 2.5~3.0 0.12 99.03 0.97 25.29 52.35 7.14 81.68 3.0~3.5 2.82 99.29 0.71 3.20 6.69 6.29 17.96 3.5~4.0 36.70 98.20 1.80 2.05 4.28 0.73 2.20 4.0~4.5 30.42 97.94 2.06 1.13 2.27 0.00 0.26 4.5~5.0 10.92 98.90 1.10 0.82 1.10 0.00 0.00 5.0~6.0 1.70 99.29 0.71 1.79 1.79 0.16 0.00 ∑=82.76 云母加权平均值 1.336 2.674 0.006 0.021 表 2 各样品云母平均粒径和厚度
Table 2. Average particle size and thickness of mica in each sample
/μm 矿物种类 筛分粒级/Φ HBZ13 HBZ12 HLJ2 HH6 HKZ9 平均粒径 平均厚度 平均粒径 平均厚度 平均粒径 平均厚度 平均粒径 平均厚度 平均粒径 平均厚度 白云母 1.5~2.0 303.39 13.26 316.66 10.87 302.01 9.79 299.84 8.34 306.65 12.94 2.0~2.5 186.85 10.82 202.29 7.56 208.60 9.14 208.67 9.29 209.86 10.83 2.5~3.0 159.04 10.08 157.64 8.74 153.52 8.02 158.77 9.21 159.04 10.08 3.0~3.5 115.66 7.44 114.07 5.64 112.92 8.17 113.34 2.30 110.53 7.57 3.5~4.0 85.71 4.24 80.56 3.27 79.44 4.15 77.05 4.78 75.83 4.18 弱风化黑云母 1.5~2.0 297.39 13.32 298.16 14.71 281.32 12.56 303.05 9.32 288.26 14.88 2.0~2.5 206.05 10.17 214.80 11.13 214.09 12.61 208.82 11.71 212.76 12.40 2.5~3.0 152.69 10.79 158.24 11.14 156.83 12.21 160.19 7.85 163.89 12.99 3.0~3.5 106.01 8.41 106.37 7.63 109.60 11.85 120.80 8.14 112.51 7.80 3.5~4.0 79.63 7.54 80.37 7.23 79.47 6.13 80.53 6.18 84.83 1.17 半风化黑云母 1.5~2.0 316.41 10.72 295.39 17.16 293.86 6.65 317.20 10.46 271.37 7.40 2.0~2.5 222.24 9.78 198.44 11.52 208.33 7.35 222.24 9.78 201.28 7.19 2.5~3.0 164.94 7.59 153.72 9.67 157.89 5.50 164.94 9.37 157.01 6.33 3.0~3.5 116.73 7.48 113.43 8.76 117.40 3.45 119.84 9.12 117.15 5.87 3.5~4.0 80.51 4.04 82.15 7.63 83.82 1.52 85.08 6.93 84.15 1.25 强风化黑云母 1.5~2.0 305.10 15.17 284.48 13.79 280.66 14.72 277.12 11.34 267.85 13.02 2.0~2.5 211.59 13.77 207.13 9.31 204.71 9.44 203.26 9.30 206.40 8.28 2.5~3.0 161.85 11.02 155.60 6.75 152.63 8.57 155.64 8.82 151.19 7.19 3.0~3.5 121.18 9.01 110.94 6.53 116.30 5.81 112.00 7.13 111.12 9.48 3.5~4.0 80.77 9.84 87.52 6.57 69.71 3.80 87.32 4.56 66.46 1.94 表 3 速度相同时云母与石英和长石粒径差异
Table 3. The particle size difference between mica and feldspar plus quartz at the same speed
D云母 D石英 粒度/μm 粒级/Φ 平均粒径/μm 平均粒径/μm 粒级/Φ 63~88 4.0~3.5 66.40~87.52 22.98~50.57 5.5~4.5 88~125 3.5~3.0 106.31~121.18 36.75~70.02 5.0~4.0 125~177 3.0~2.5 151.19~164.94 52.27~95.30 4.5~3.5 177~250 2.5~2.0 186.85~222.24 64.60~128.41 4.0~3.0 250~440 2.0~1.5 267.85~347.20 92.60~183.28 3.5~2.5 -
[1] 李玉中. 沉积分异作用与河口海洋沉积[J]. 地质学刊,2014,38(4):556-560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2014.04.556
[2] COLLINS M B,GAO S. Analysis of grain size trends,for defining sediment transport pathways in marine environments[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,1994,10(1):61-70.
[3] 任韧希子,陈沈良. 黄河下游至三角洲滨海区表层沉积物分异特征和规律[J]. 海洋科学进展,2010,28(1):24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2010.01.004
[4] 邓程文,张霞,林春明,等. 长江河口区末次冰期以来沉积物的粒度特征及水动力条件[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(6):185-198.
[5] 丛静艺,袁忠鹏,胡刚,等. 长江远端三角洲多源沉积分异作用及其动力机制[J]. 沉积学报,2020,38(3):528-537.
[6] 刘宝珺. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1980: 31-40.
[7] 张连杰,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 文登近岸海域重矿物组合分布及对沉积动力环境的指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(1):127-138.
[8] DOYLE L J,CLEAEY W J,PILKEY O H. Mica:Its use in determining shelf-depositional regimes[J]. Marine Geology,1968,6:381-389. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(68)90002-9
[9] 张富元,王秀昌. 东海表层沉积物中重矿物聚类分析及其动力分布特征[J]. 台湾海峡,1984,3(1):68-77.
[10] 王中波,杨守业,李日辉,等. 黄河水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及沉积动力环境约束[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(4):73-85.
[11] 于炳松, 梅冥相. 沉积岩岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2016: 120-126.
[12] 潘兆橹. 结晶学及矿物学下 第3版[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994: 169-196.
[13] 方霖,郭珍旭,刘长淼,等. 云母矿物浮选研究进展[J]. 中国矿业,2015,24(3):131-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.03.029
[14] 林晓彤,李巍然,时振波. 黄河物源碎屑沉积物的重矿物特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2003,23(3):17-21.
[15] JIN B F,WANG M Y,YUE W,et al. Heavy mineral variability in the Yellow River sediments as determined by the multiple-window strategy[J]. Minerals,2019,9(2):85-90. doi: 10.3390/min9020085
[16] TIANA S,LIB Z,WANGC Z,et al. Mineral composition and particle size distribution of river sediment and loess in the middle and lower Yellow River[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,2020,36(3):392-400.
[17] 卫晓锋, 潘东,阴元军等. 新疆阿克塔斯金矿床黑云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb和绢云母39Ar/40Ar测年及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质,2019,38(2):251-260.
[18] 曾广策. 晶体光学及光性矿物学, 第3版[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2017, 208-211.
[19] 白翠萍. 云母粉径厚比测定方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2008: 6-10.
[20] 乔志川,刘迪,刘钦甫. 层状矿物径厚比自动测算研究[J]. 煤炭技术,2017(5):306-308.
[21] TAO S,EGLINTON T I,MONTLUON D B,et al. Pre-aged soil organic carbon as a major component of the Yellow River suspended load:regional significance and global relevance[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,414(1):77-86.
[22] 水利部黄河水利委员会. 黄河年鉴[M]. 郑州: 黄河年鉴社, 2019: 5-9.
[23] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985: 14-44.
[24] GAO P,DENG J,CHAI X,et al. Dynamic sediment discharge in the Hekou-Longmen region of Yellow River and soil and water conservation implications[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,578:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.128
[25] MIKHAILOV V,MIKHAIOVA M. Natural and anthropogenic long-term variations of water runoff and suspended sediment load in the Huanghe River[J]. Water Resources,2017,44(6):793-807. doi: 10.1134/S0097807817060057
[26] 王臻,陈振宇,李建康,等. 云母矿物对仁里稀有金属伟晶岩矿床岩浆-热液演化过程的指示[J]. 矿床地质,2019,38(5):1039-1052.
[27] 陈丽蓉. 渤海、黄海、东海沉积物中矿物组合的研究[J]. 海洋科学,1989,13(2):1-8.
[28] LIU J,SAITO Y,WANG H,et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,236(3/4):165-187. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2006.10.031
[29] 张尧,韩宗珠,艾丽娜,等. 黄海全新世泥质体表层沉积物重矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(11):108-118.
[30] 胡邦琦,李军,李国刚,等. 长江和黄河入海沉积物的物源识别研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(6):147-156.
[31] 秦亚超,李日辉,姜学钧. 黄海中北部和渤海东部表层沉积物轻矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(3):611-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.03.15
[32] 张茂根,翁志学. 颗粒统计平均粒径及其分布的表征[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程,2000,16(5):1-4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7555.2000.05.001
[33] 白玉川. 河口泥沙运动力学[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2011: 9-20.
[34] 马在平,姜在兴. 我国热带亚热带部分地区花岗岩和片麻岩中黑云母风化研究[J]. 矿物岩石,1996,16(2):17-24.
[35] 王彦华,罗立峰. 花岗岩中黑云母风化的矿物变化机制[J]. 地球化学,1999,28(3):239-247.
[36] 王学潮, 向宏发. 聊城-兰考断裂综合研究及黄河下游河道稳定性分析[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2001: 94-105.
[37] 陆凯,秦亚超,王中波,等. 东海中南部海域表层沉积物碎屑重矿物组合分区及其物源分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019, 35(8):20-26.
[38] 张连杰,胡日军,朱龙海,等. 渤海湾碎屑矿物特征及其物源和沉积动力环境指示意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(5):60-70.
[39] COREY A T. Influence of the shape on the fall velocity of sand grains[M]. Colorado: Colorado State University, 1949: 10-30.
[40] KOMAR P D,REIMERS C E. Grain Shape Effects on Settling Rates[J]. The Journal of Geology,1978,86:193-209. doi: 10.1086/649674
[41] 魏德洲. 固体物料分选学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2015: 201-217.
[42] 袁竹林, 朱立平, 耿凡. 气固两相流动与数值模拟[M]. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 2013: 23-27.
-




 下载:
下载: