SEASONAL MONITORING OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS CHARACTERISTICS OF SCLERACTINIAN CORALS IN THE NORTHERN SOUTH CHINA SEA
-
摘要:
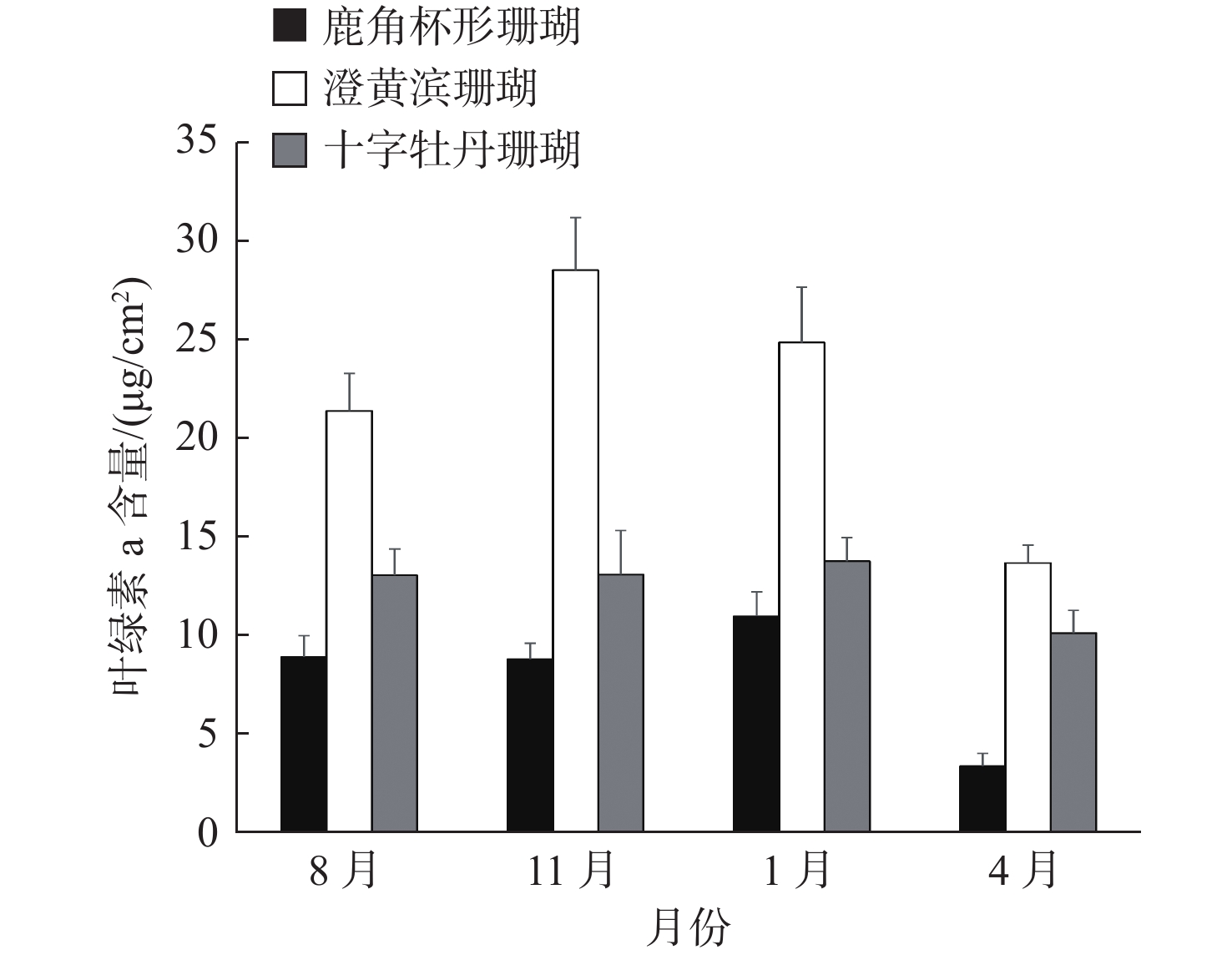
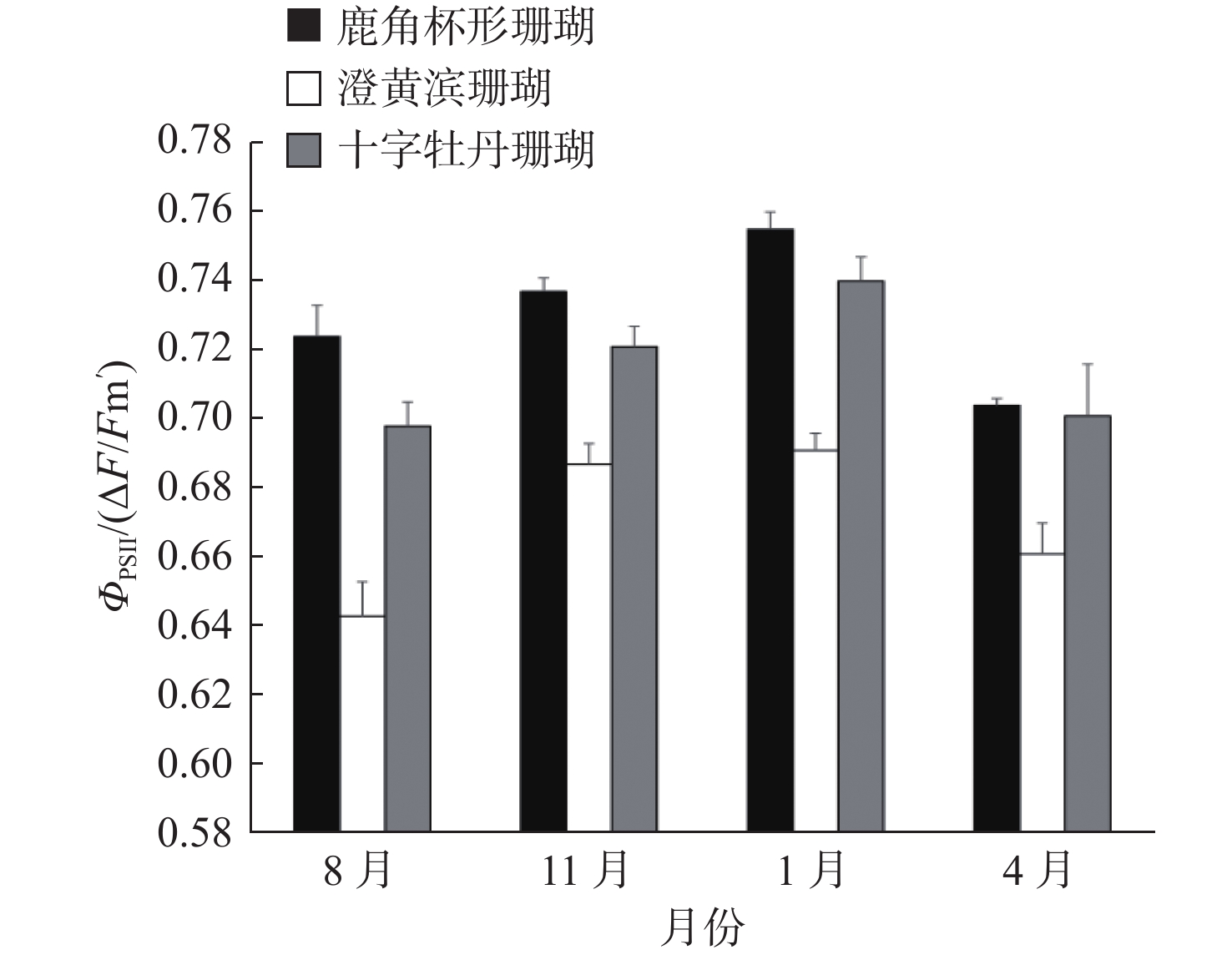
造礁珊瑚与虫黄藻共生是珊瑚礁最基本的生态特征。造礁珊瑚的生长乃至珊瑚礁生态系统的健康状况均与虫黄藻的光合作用密切相关。自然环境下造礁石珊瑚共生体光合作用特征研究仍相对缺乏,限制了珊瑚礁生态系统的健康评估与白化预警研究。在南海北部三亚鹿回头岸礁区选择鹿角杯形珊瑚(Pocillopora damicornis)、澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea)和十字牡丹珊瑚(Pavona decussata)3种不同形态珊瑚,对其共生藻密度、叶绿素a含量和有效量子产量(ΦPSII)进行了1年的跟踪监测调查。分析结果显示:① 3种形态不同的珊瑚共生体光合作用特征具有明显的种间差异,澄黄滨珊瑚有着最高的共生藻密度和叶绿素a含量,但ΦPSII最低。② 澄黄滨珊瑚的共生藻密度最低值出现在冬季,而鹿角杯形珊瑚和十字牡丹珊瑚的共生藻密度最低值出现在春季。3种珊瑚的叶绿素a含量和ΦPSII均表现出了相似的季节变化,秋冬偏高,春夏偏低。③ 珊瑚共生体的光合作用特征具有显著的种间差异和季节变化,与珊瑚礁生态健康状况息息相关,因此在珊瑚礁生态监测与健康评估过程中,所应用的指标需要认真考虑石珊瑚的种间差异性和环境的动态变化。
Abstract:Systematic investigations of scleractinian corals in the natural environment are relatively lacking since the global decline of coral reefs. In this study, we selected three corals with typical morphology from Sanya, including Pocillopora damicornis, Porites lutea and Pavona decussata. We investigated the symbiodinium density, chlorophyll-a content and effective quantum yield (Φ PSII) for one year. The results show that: ① There are significant interspecific differences among the three corals. The scleractinian density and chlorophyll-a content of P. lutea are the highest, while the Φ PSII is the lowest. ② About symbiodinium density, the lowest value of P. damicornis appeared in winter, while the lowest value of P. damicornis and P. decussata appeared in spring. The chlorophyll-a content and Φ PSII of the three corals show similar pattern of seasonal changes, higher in autumn and winter, lower in spring and summer. ③ The photosynthetic characteristics of corals are related closely to the ecological health of coral reefs, and have clear interspecific differences and seasonal differences. Therefore, the interspecific differences and environmental dynamic changes of scleractinian corals, as an important indicator, need serious consideration in the coral reef monitoring and health assessment.
-

-
[1] 赵美霞,余克服,张乔民. 珊瑚礁区的生物多样性及其生态功能[J]. 生态学报,2006(1):186-194. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.01.025
[2] PASCAL N,ALLENBACH M,BRATHWAITE A,et al. Economic valuation of coral reef ecosystem service of coastal protection:a pragmatic approach[J]. Ecosystem Services,2016,21:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.07.005
[3] 李扬,余克服,王英辉,等. 三亚鹿回头岸礁海域夏季表层海水营养盐年际变化特征[J]. 热带地理,2017,37(5):708-717.
[4] YU K F. Coral reefs in the South China Sea:their response to and records on past environmental changes[J]. Science China-Earth Sciences,2012,55(8):1217-1229. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4449-5
[5] HOEGH-GULDBERG O, POLOCZANSKA E S, SKIRVING W, et al. Coral reef ecosystems under climate change and ocean acidification[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science,2017,4:20.
[6] FINE M,HOEGH-GULDBERG O,MEROZ-FINE E,et al. Ecological changes over 90 years at Low Isles on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Nature Communications,2019,10:8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07894-4
[7] 李淑,余克服,施祺,等. 海南岛鹿回头石珊瑚对高温响应行为的实验研究[J]. 热带地理,2008,28(6):534-539. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2008.06.009
[8] 李淑,余克服,施祺,等. 造礁石珊瑚对低温的耐受能力及响应模式[J]. 应用生态学报,2009,20(9):2289-2295.
[9] HERON S F,MAYNARD J A,VAN HOOIDONK R,et al. Warming Trends and Bleaching Stress of the World's Coral Reefs 1985-2012[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0009-0
[10] HUGHES T P,KERRY J T,ALVAREZ-NORIEGA M,et al. Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals[J]. Nature,2017,543(7645):373. doi: 10.1038/nature21707
[11] DOWNS C A,KRAMARSKY-WINTER E,WOODLEY C M,et al. Cellular pathology and histopathology of hypo-salinity exposure on the coral Stylophora pistillata[J]. Science Of the Total Environment,2009,407(17):4838-4851. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.05.015
[12] THOMPSON J R,RIVERA H E,CLOSEK C J,et al. Microbes in the coral holobiont:partners through evolution,development,and ecological interactions[J]. Frontiers In Cellular And Infection Microbiology,2015,4:20.
[13] HUGHES T P,ANDERSON K D,CONNOLLY S R,et al. Spatial and temporal patterns of mass bleaching of corals in the Anthropocene[J]. Science,2018,359(6371):80. doi: 10.1126/science.aan8048
[14] MORRISON T H,HUGHES T P,ADGER W N,et al. Save reefs to rescue all ecosystems[J]. Nature,2019,573(7774):333-336. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-02737-8
[15] DUBINSKY Z, STAMBLER N. Zooxanthellae: The Yellow Symbionts Inside Animals[M]. Springer Netherlands, 2011: 87-106.
[16] WOOLDRIDGE S A. Breakdown of the coral-algae symbiosis:towards formalising a linkage between warm-water bleaching thresholds and the growth rate of the intracellular zooxanthellae[J]. Biogeosciences,2013,10(3):1647-1658. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-1647-2013
[17] ZHAO M X,YU K F,ZHANG Q M,et al. Age structure of massive Porites lutea corals at Luhuitou fringing reef (northern South China Sea) indicates recovery following severe anthropogenic disturbance[J]. Coral Reefs,2014,33(1):39-44. doi: 10.1007/s00338-013-1109-y
[18] 李淑,余克服. 珊瑚礁白化研究进展[J]. 生态学报,2007(5):2059-2069. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.05.047
[19] HINRICHS S,PATTEN N L,WAITE A M. Temporal variations in metabolic and autotrophic indices for acropora digitifera and acropora spicifera - implications for monitoring projects[J]. Plos One,2013,8(5):e63693.
[20] DOUGLAS A E. Coral bleaching - how and why?[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2003,46(4):385-392. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00037-7
[21] STIMSON J. The annual cycle of density of zooxanthellae in the tissues of field and laboratory-held Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology,1997,214(1/2):35-48.
[22] BROWN B E,DUNNE R P,AMBARSARI I,et al. Seasonal fluctuations in environmental factors and variations in symbiotic algae and chlorophyll pigments in four Indo-Pacific coral species[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series,1999,191:53-69. doi: 10.3354/meps191053
[23] FAGOONEE I,WILSON H B,HASSELL M P,et al. The dynamics of zooxanthellae populations:a long-term study in the field[J]. Science,1999,283(5403):843-845. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5403.843
[24] FITT W K,MCFARLAND F K,WARNER M E,et al. Seasonal patterns of tissue biomass and densities of symbiotic dinoflagellates in reef corals and relation to coral bleaching[J]. Limnology And Oceanography,2000,45(3):677-685. doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0677
[25] SAWALL Y,AL-SOFYANI A,BANGUERA-HINESTROZA E,et al. Spatio-temporal analyses of symbiodinium physiology of the coral pocillopora verrucosa along large-scale nutrient and temperature gradients in the Red Sea[J]. Plos One,2014,9(8):12.
[26] 李元超,陈海洲,郑新庆,等. 海南铜鼓岭国家级自然保护区海域珊瑚的分布及其健康状况评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2014,33(4):539-545. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.04.012
[27] ZHAO M X,YU K F,ZHANG Q M,et al. Long-term Decline of a Fringing Coral Reef in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2012,28(5):1088-1099. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00172.1
[28] CHEN T R,YU K F,SHI Q,et al. Twenty-five years of change in scleractinian coral communities of Daya Bay (northern South China Sea) and its response to the 2008 AD extreme cold climate event[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2009,54(12):2107-2117.
[29] YAN H Q,YU K F,SHI Q,et al. Seasonal variations of seawater pCO(2) and sea-air CO2 fluxes in a fringing coral reef,northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans,2016,121(1):998-1008. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011484
[30] 张乔民,施祺,陈刚,等. 海南三亚鹿回头珊瑚礁监测与管理策略[J]. 科学通报,2006,51(增刊II):71-77.
[31] 孙有方,雷新明,练健生,等. 三亚珊瑚礁保护区珊瑚礁生态系统现状及其健康状况评价[J]. 生物多样性,2018,26(3):258-265. doi: 10.17520/biods.2017312
[32] 黄德银, 施祺, 余克服, 等. 海南岛鹿回头珊瑚礁研究进展[J]. 海洋通报,2004,23(2):56-64.
[33] PINIAK G A,BROWN E K. Temporal variability in chlorophyll fluorescence of back-reef corals in Ofu,American Samoa[J]. Biological Bulletin,2009,216(1):55-67. doi: 10.1086/BBLv216n1p55
[34] 周洁,施祺,余克服. 三亚造礁石珊瑚虫黄藻光合作用效率的日周期及其调控因素[J]. 热带海洋学报,2014,33(1):81-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.011
[35] 许莉佳. 海南岛造礁石珊瑚共生藻的种间差异及季节变化特征[D]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 2017.
[36] 许莉佳,余克服,李淑. 海南岛澄黄滨珊瑚共生藻对环境变化的适应性[J]. 热带地理,2016,36(6):915-922.
[37] MARSH J A. Primary productivity of reef-building calcareous red algae[J]. Ecology,1970,51(2):254.
[38] KEMP D W,HERNANDEZ-PECH X,IGLESIAS-PRIETO R,et al. Community dynamics and physiology of Symbiodinium spp. before,during,and after a coral bleaching event[J]. Limnology And Oceanography,2014,59(3):788-797. doi: 10.4319/lo.2014.59.3.0788
[39] 刘丽,李泽鹏,申玉春,等. 四种环境因子对澄黄滨珊瑚和斯氏角孔珊瑚胁迫作用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报,2013,32(3):72-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.03.011
[40] JEFFREY S W,HUMPHREY G F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a,b,c1 and c2 in higher-plants,algae and natural phytoplankton[J]. Biochemie Und Physiologie Der Pflanzen,1975,167(2):191-194. doi: 10.1016/S0015-3796(17)30778-3
[41] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. HJ 897-2017 水质 叶绿素a的测定分光光度法[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2018.
[42] 雷新明,黄晖,王华接,等. 造礁石珊瑚共生藻对富营养的响应研究[J]. 海洋通报,2009,28(1):43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2009.01.007
[43] RODOLFO-METALPA R,REYNAUD S,ALLEMAND D,et al. Temporal and depth responses of two temperate corals,Cladocora caespitosa and Oculina patagonica,from the North Mediterranean Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series,2008,369:103-114. doi: 10.3354/meps07608
[44] WINTERS G,HOLZMAN R,BLEKHMAN A,et al. Photographic assessment of coral chlorophyll contents:implications for ecophysiological studies and coral monitoring[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology,2009,380(1/2):25-35.
[45] STIMSON J,SAKAI K,SEMBALI H. Interspecific comparison of the symbiotic relationship in corals with high and low rates of bleaching-induced mortality[J]. Coral Reefs,2002,21(4):409-421. doi: 10.1007/s00338-002-0264-3
[46] MEIKLE P,RICHARDS G N,YELLOWLEES D. Structural investigations on the mucus from 6 species of coral[J]. Marine Biology,1988,99(2):187-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00391980
[47] YU K F,ZHAO J X,LAWRENCE M G,et al. Timing and duration of growth hiatuses in mid Holocene massive Porites corals from the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science,2010,25(8):1284-1292. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1410
[48] 李淑,余克服,陈天然,等. 在细胞水平上对高温珊瑚白化的初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报,2011,30(2):33-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.005
[49] XU L J,YU K F,LI S,et al. Interseasonal and interspecies diversities of Symbiodinium density and effective photochemical efficiency in five dominant reef coral species from Luhuitou fringing reef,northern South China Sea[J]. Coral Reefs,2017,36(2):477-487. doi: 10.1007/s00338-016-1532-y
[50] ULSTRUP K E,HILL R,VAN OPPEN M J H,et al. Seasonal variation in the photo-physiology of homogeneous and heterogeneous Symbiodinium consortia in two scleractinian corals[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series,2008,361:139-150. doi: 10.3354/meps07360
[51] D'ANGELO C,WIEDENMANN J. Impacts of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs:new perspectives and implications for coastal management and reef survival[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability,2014,7:82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cosust.2013.11.029
-




 下载:
下载: