Tectonic evolution and division of structural units of Sureste Basin in the continental margin of Mexico
-
摘要:
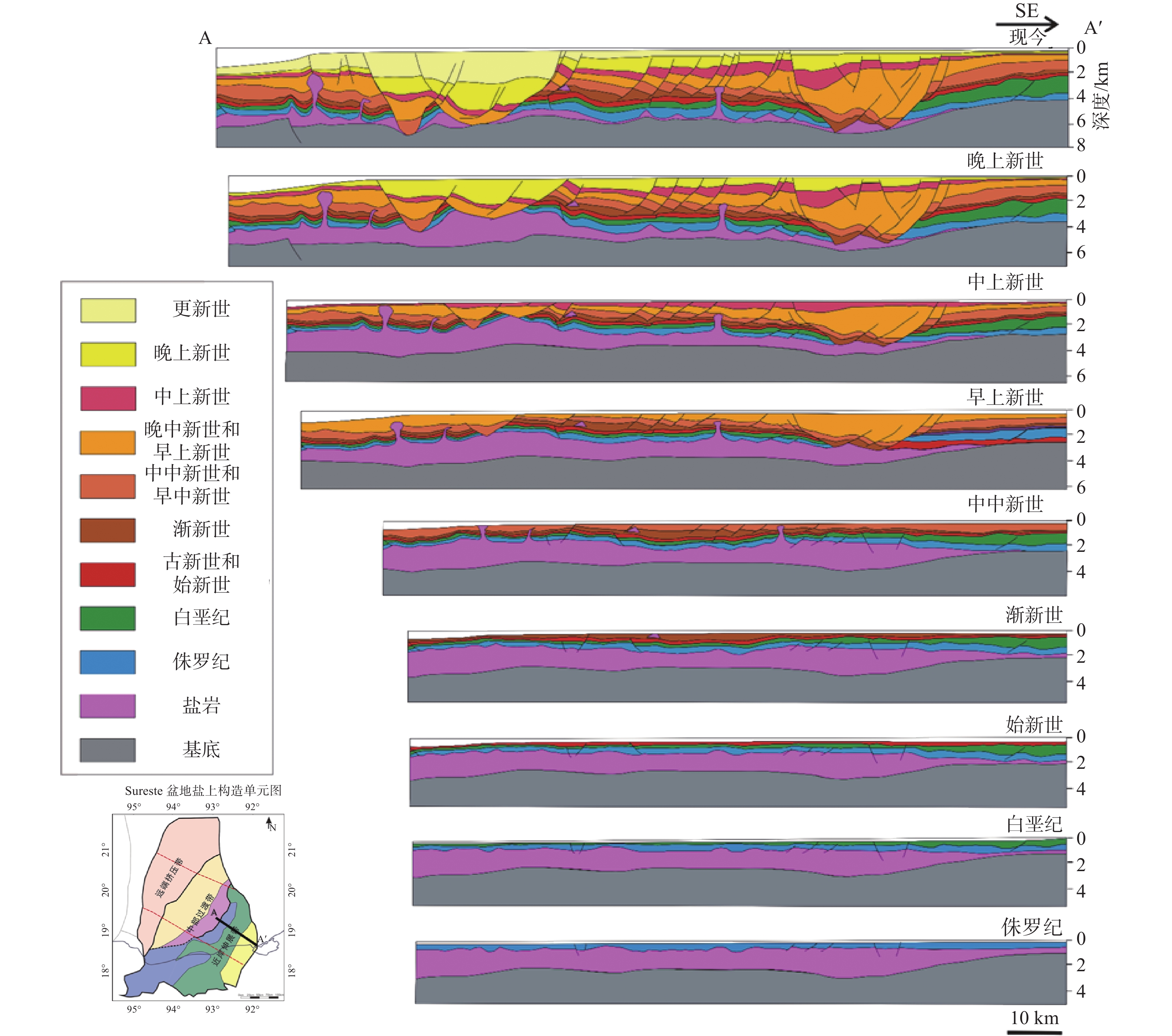
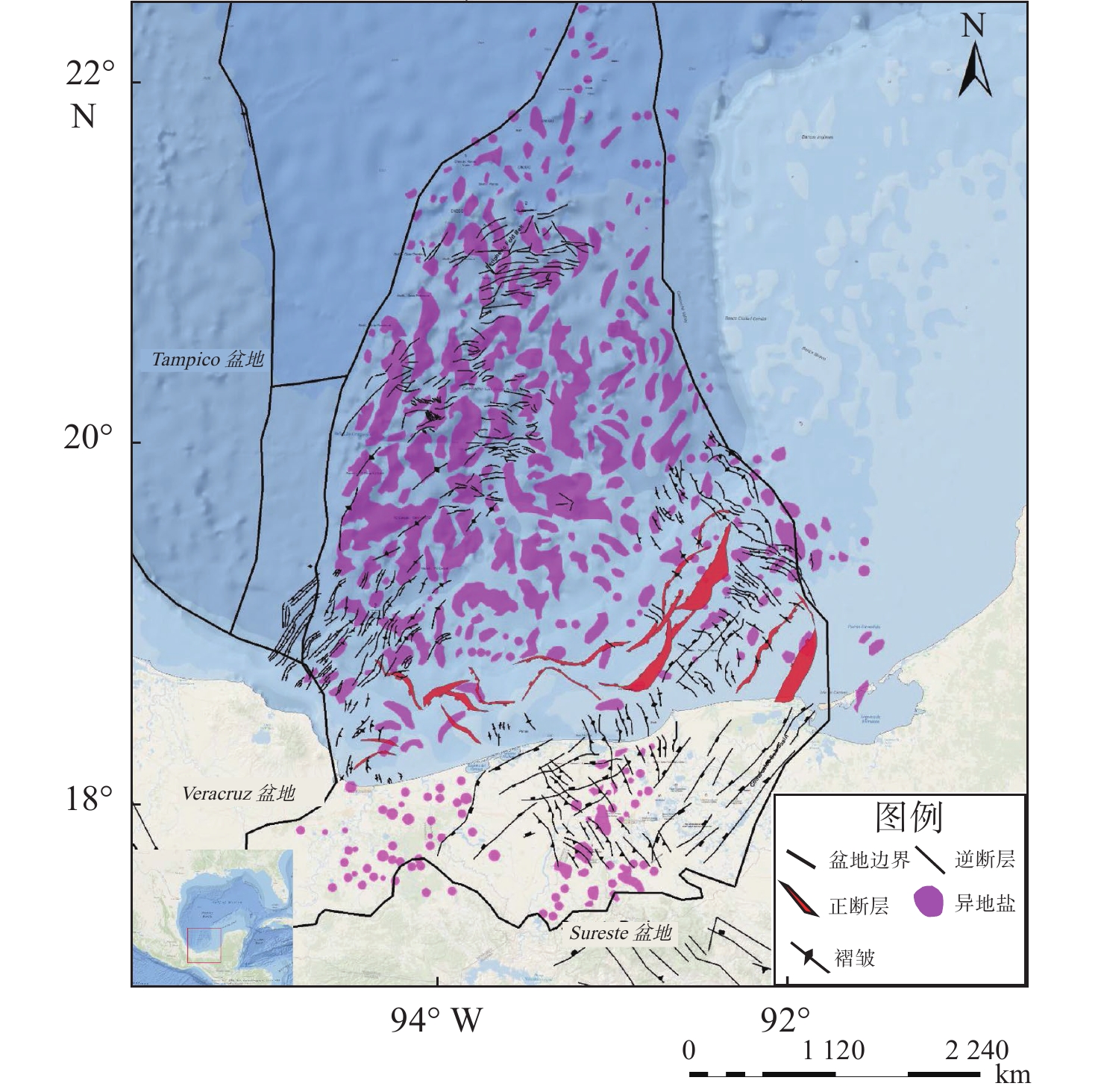
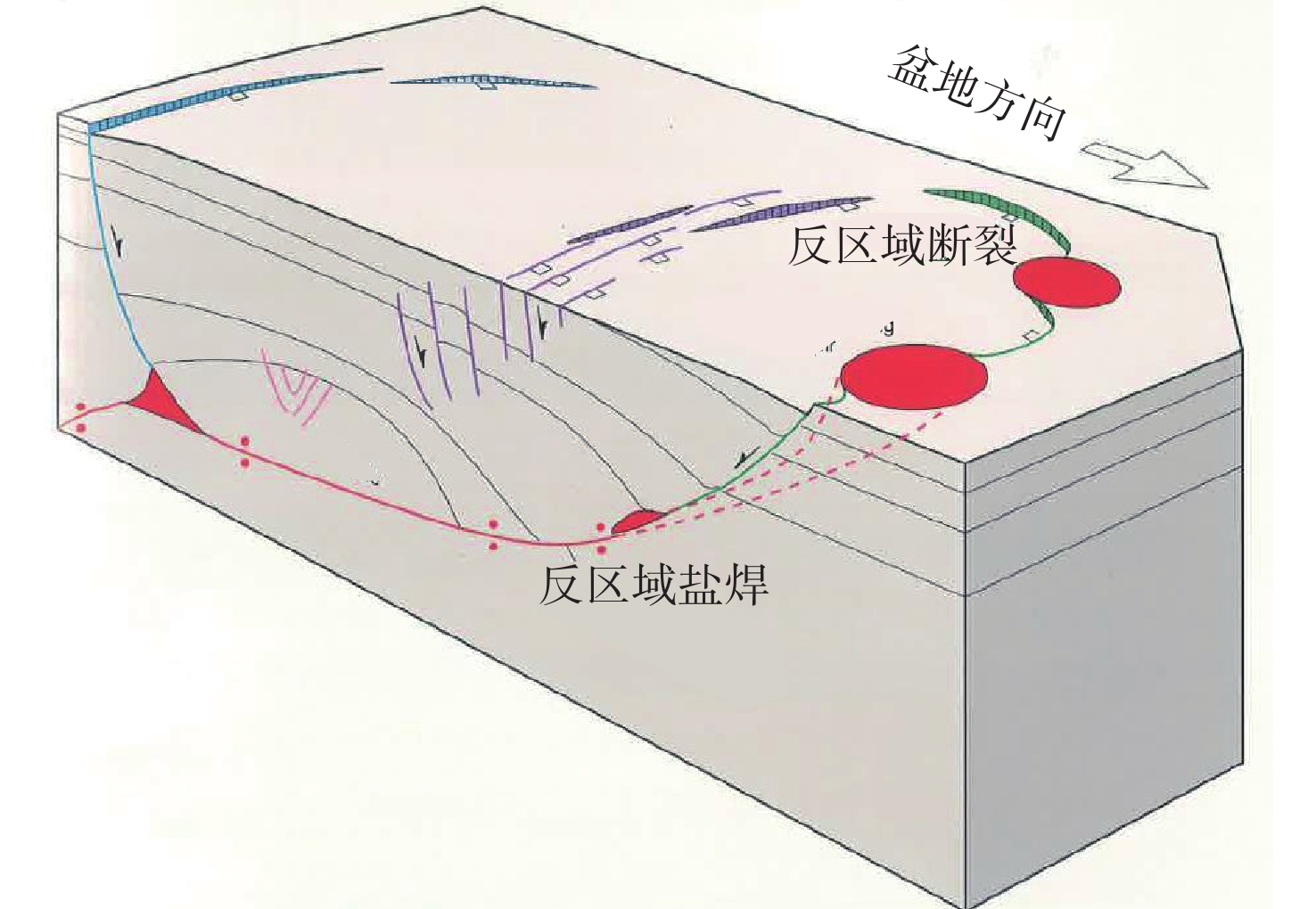
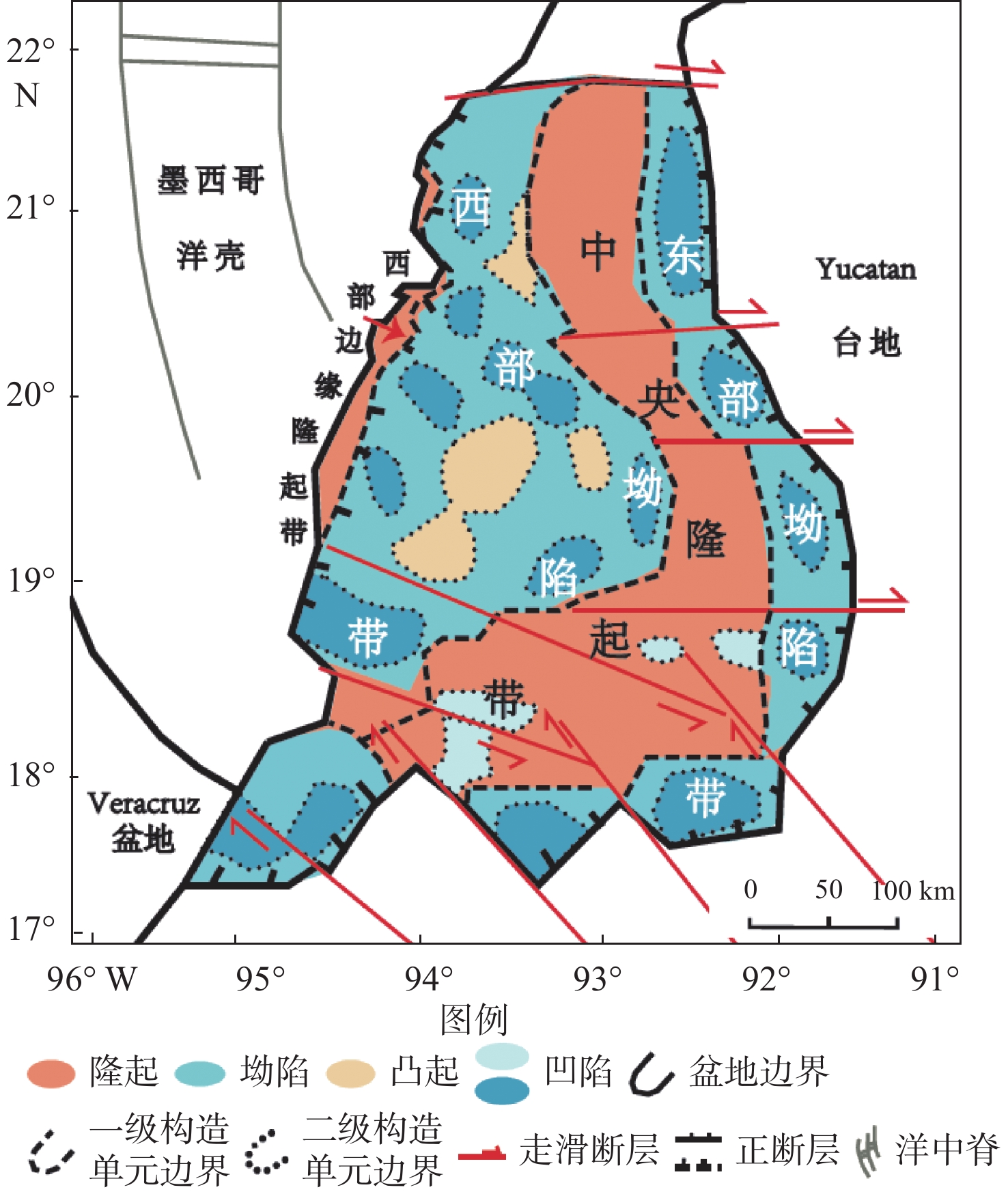
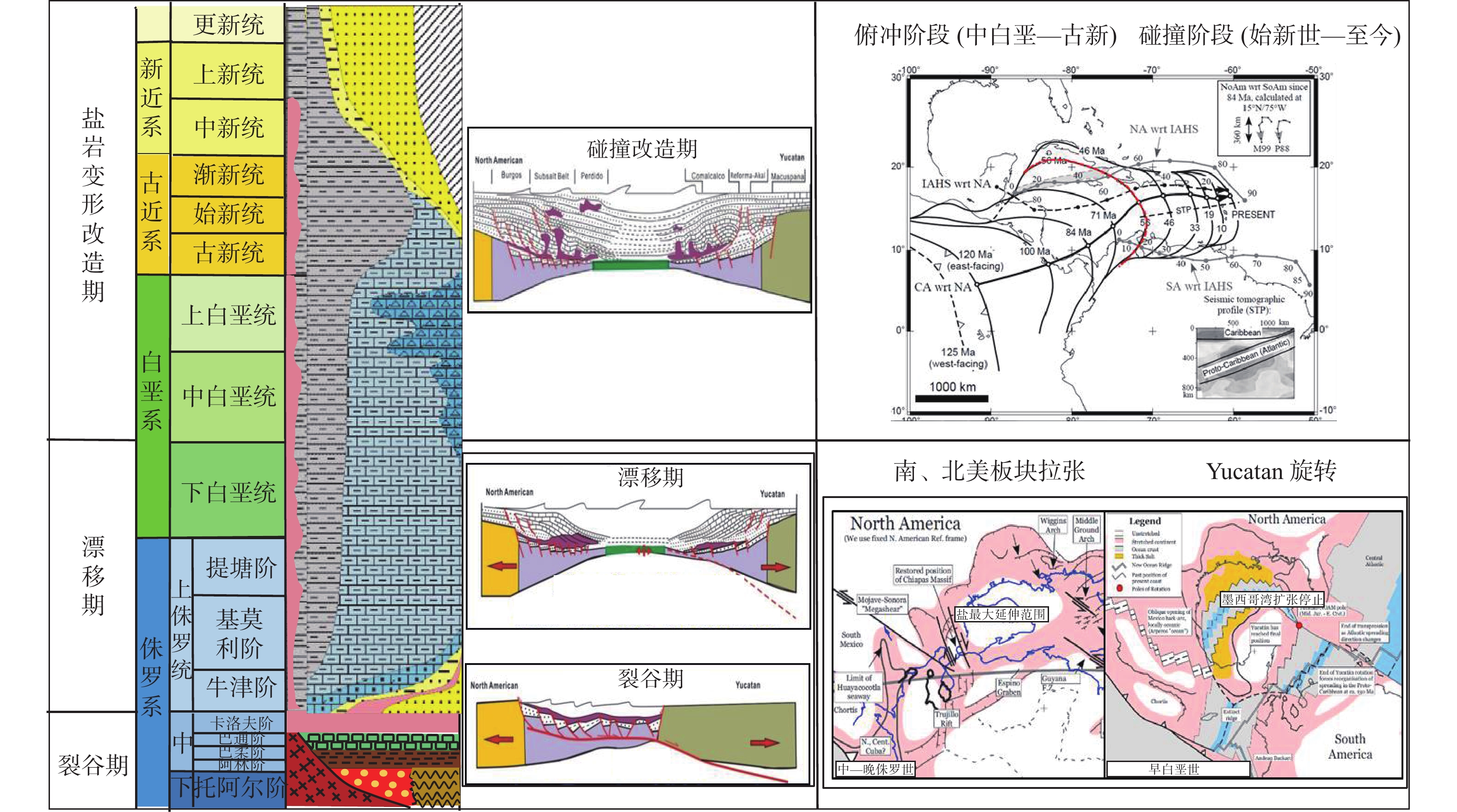
墨西哥Sureste盆地是墨西哥最具油气潜力的盆地,但与北部相比,勘探程度不高。自招标以来,受资料品质以及含盐岩的影响,尽管陆续有油气发现,但盆地构造演化与构造单元划分仍没有明确的定论。基于地震、重力、磁力资料,结合区域地质特征,通过2D Move软件,采用地球物理与地质相结合研究,确定了Sureste盆地构造演化特征,明确了Sureste盆地断裂特征、盐下、盐上构造单元划分以及构造样式,总结了各单元构造形成时间。研究认为,盆地断裂大致呈NE—SW、NW—SE以及近EW向3个方向展布。受早期基底形态控制,盐下构造具有“两坳一隆”特点。板块构造演化影响下的盐相关构造的形成受控于重力滑脱影响,盐上构造具有“南北分带,东西分异”,形成时间具有“东早西晚”的特点。该研究为后续Sureste盆地构造分析以及勘探研究指明了方向,对国内边缘海盆地的构造研究具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:The Sureste Basin in Mexico bears great potential of oil and gas resources. However, comparing to the north of the country, the exploration level of the Sureste Basin is not so high as expected since bidding, due to the influence of data quality and the salty cover, although there have found many oil and gas discoveries. No clear conclusions have been acquired so far with regard to the tectonic evolution and structural unit division of the basin. In this paper, based on the seismic, gravity, magnetic and geological research data and using 2D Move software, tectonic evolution characteristics, subsalt and suprasalt structural unit divisions as well as structural styles of the basin were clarified and revealed. Faults are mainly developed in three directions in the basin, i.e., NE, NW and EW directions. Controlled by the earlier basement morphology, the subsalt structures are characterized by "two depressions and one uplift" in cross shape. While the formation of supersalt structures is mainly controlled by gravity slipping which is earlier in the east and later in the west in time, and with the characteristics of "south-north zoning and east-west differentiation". This study has provided not only a reference for future directions of oil and gas exploration in the Sureste Basin, but also a reference case for structural research of marginal basins in China.
-
Key words:
- salt movement /
- fracture /
- structural unit /
- structural style /
- Sureste Basin
-

-
[1] 任建业,何先云,张俊霞. 中国大陆东部晚中生代构造活化及其演化过程[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1988,22(2):90-96.
[2] 田世存,张国庆,孙东方,等. 墨西哥油气资源概况及第一轮油气招标简介[J]. 国际石油经济,2014,22(12):28-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7298.2014.12.006
[3] 赵阳,卢景美,刘 学考,等. 墨西哥湾深水油气勘探研究特点与发展趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2014,30(6):27-32.
[4] 李双林,张生银. 墨西哥及墨西哥湾盆地构造单元及其演化[J]. 海洋地质动态,2010,26(3):14-21.
[5] MENESES-ROCHA J J. Tectonic evolution of the Ixtapa graben,an example of a stake-slip basin of southeastern Mexico:implications for regional petroleum systems[J]. AAPG Memoir,2001,75:183-216.
[6] GIUNTA G,MARRONI M,PADOA E,et al. Geological Constraints for the geodynamic evolution of the southern margin of the Caribbean Plate[J]. AAPG Memoir 79,2003:104-125.
[7] PINDELL J L,KENNAN L. Tectonic evolution of the Gulf of Mexico,Caribbean and northern South America in the mantle reference frame:an update[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications,2009,328(1):1-55. doi: 10.1144/SP328.1
[8] GARCIAMOLINA G. Structural evolution of the SE Mexico offshore and onshore[D]. Houston, Texas: A Bell & Howell Information Company, 1994.
[9] AQUINO-LÓPEZ J A. Sureste Basin México and associated sub-basins: an update and future potential[R]. Mexico: AAPG International Conference, 2004.
[10] JACKSON M, HUDEC M. Salt tectonics: priciples and practice[M]. UK, Cambridge University Press, 2017.
[11] CRUZMERCADO M A, FLORESZAMORA J C. Salt provinces in the Mexican portion of the Gulf of Mexico: structural characterization and evolutionary model[M]. Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies Transactions, 2011: 93-104.
[12] MITRA S,GONZALEZ J,GARCIA J H,et al. Ek-Balam field:a structure related to multiple stages of salt tectonics and extension[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2007,91(11):1619-1636. doi: 10.1306/06260706112
[13] 孔国英, 卢景美, 周浩玮, 等. 墨西哥Sureste盆地盐相关圈闭发育特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(3): 33-39.
[14] MARTÍNEZ G B. Petroleum Prospectivity at the Salina del Bravo Province, Western Gulf of Mexico. Gulf Coast Association of Geologucal Societues [N]. 2012: 539-542.
[15] 关利群,屈红军,张功成,等. 世界主要深水盆地圈闭特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(4):209-214.
-



 下载:
下载: