Application of gas chimney-type gas cloud recognition method based on attribute optimization in the eastern Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要:
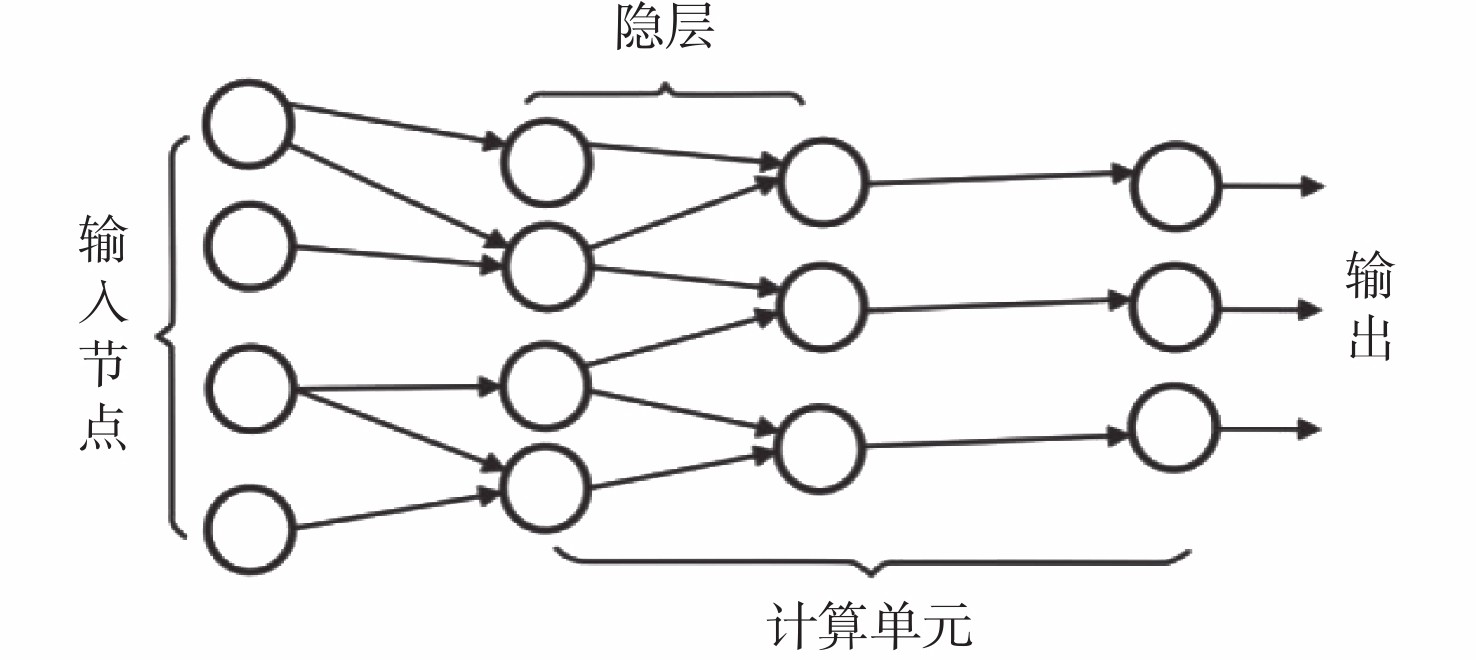
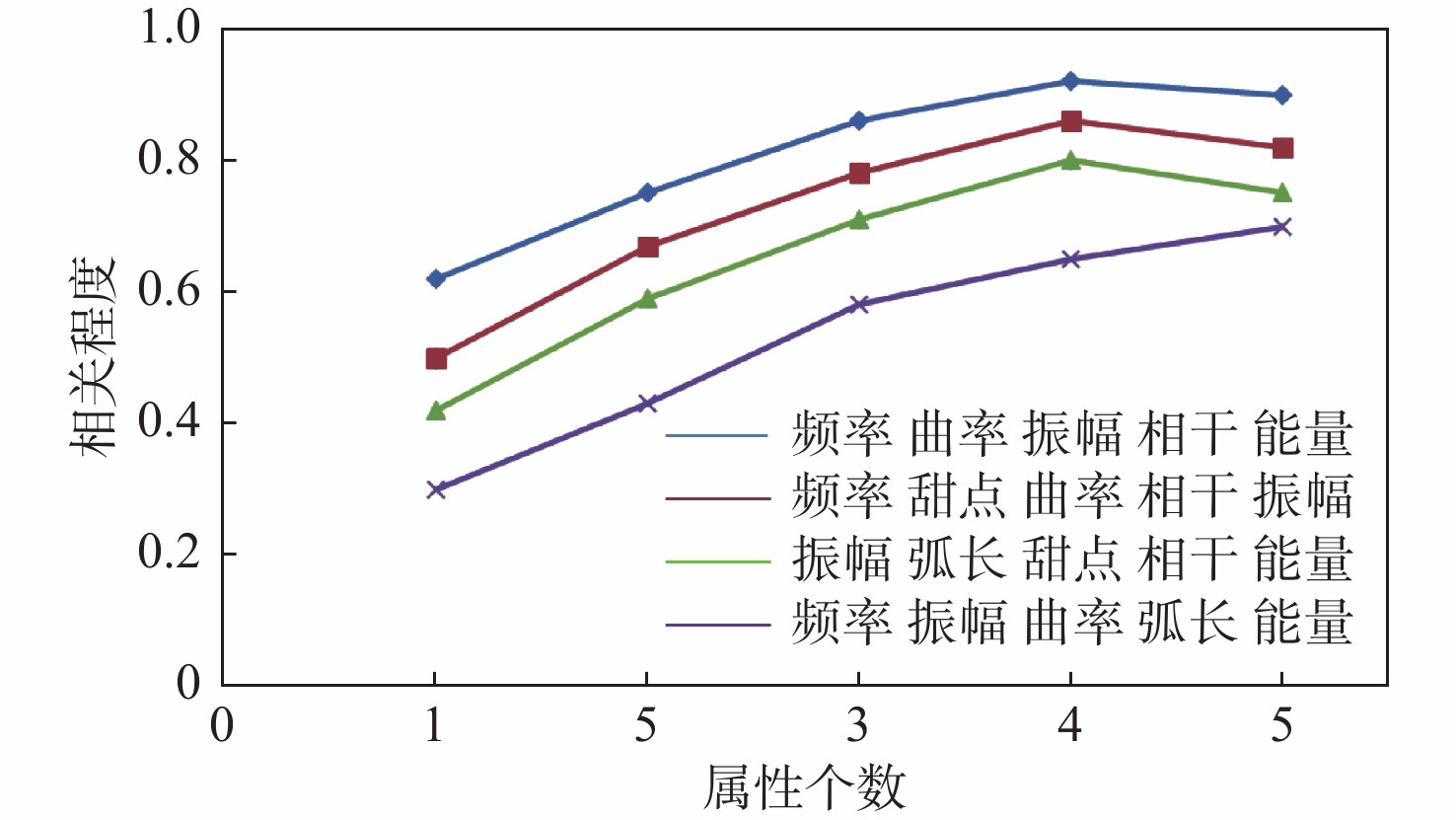
渤海地区气云表现形式多样,目前还没有系统的分类。根据不同气云带的分布范围,将渤海地区的气云从深至浅划分为气烟囱型、亮点型和麻坑型3类,并分析其成因机理。针对气烟囱型气云,利用单一地震属性进行气云识别和预测,具有一定局限性,且神经网络方法就是一个“黑匣子”,无法判断属性在计算过程中发挥的作用。文中提出利用具有 “多属性融合神经网络”技术体系,对不同的属性组合进行分类,突出对气云敏感的属性,从而对气云准确识别,精细刻画气云的空间分布范围。该方法在渤东地区蓬莱A油田取到较好的应用效果,为下一步寻找大中型油气藏提供了依据。
Abstract:Gas cloud in the eastern Bohai Bay Basin shows various forms and there is no systematic classification at present. According to the distribution of different gas clouds in vertical direction, gas cloud of Bohai Sea could be classified into three types from deep to shallow: gas chimney type, bright spot type, and flax pit type; and their formation mechanism were analyzed. For the gas chimney type, conventional methods use a single seismic attribute to identify and predict the gas cloud, which have certain limitations, and previous neural network method is a "black box", unable to judge the effect of attributes in the calculation process. We developed a "multi-attribute fusion neural network" technology system to classify different attribute combinations, highlight the sensitive attributes of gas cloud, to accurately identify the gas cloud and finely determine the spatial distribution range of gas cloud. This method has been successfully applied in Penglai A Oilfield in the eastern Bohai Bay Basin, which provides a basis for further exploration of large and medium-sized reservoirs.
-

-
表 1 气云带成因、分类及特征
Table 1. Origin, classification and characteristics of gas clouds
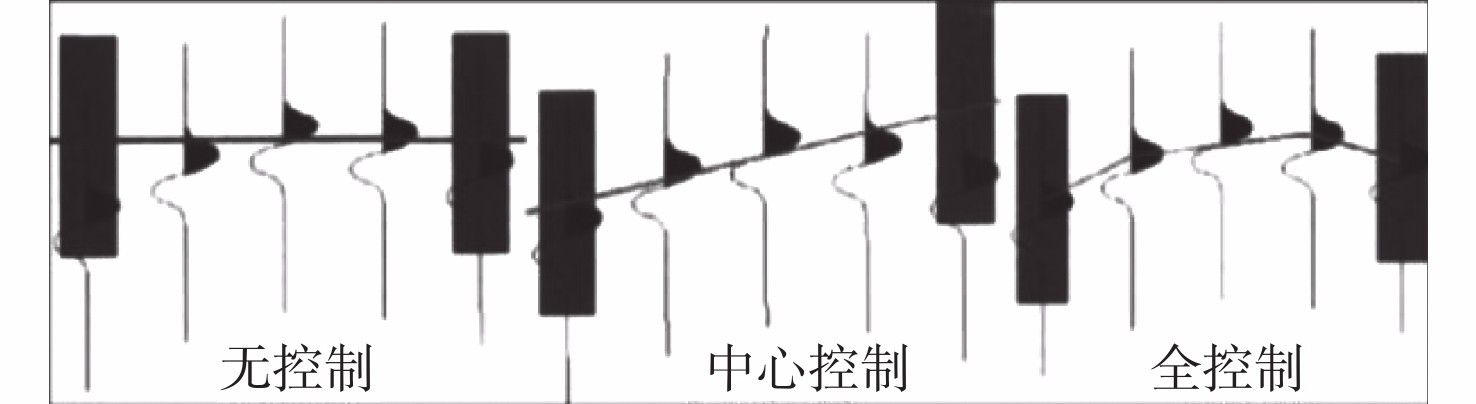
气云类型 特征 成因 扩散机理 模式图 分布位置 气烟囱型 弱振幅,反射波杂乱,频率低、相干值低、速度低 断涌式 垂向断裂和侧向运移 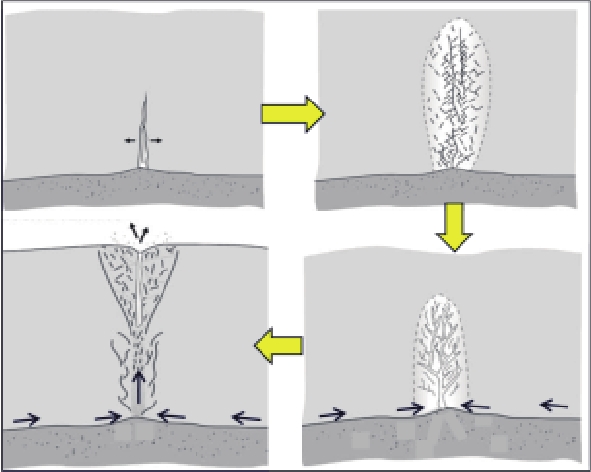
油气充注能力强的高凸起之上 亮点型 强振幅、低频阴影、偶极相位、极性反转 断渗式 断层相关,排放至浅层或地表 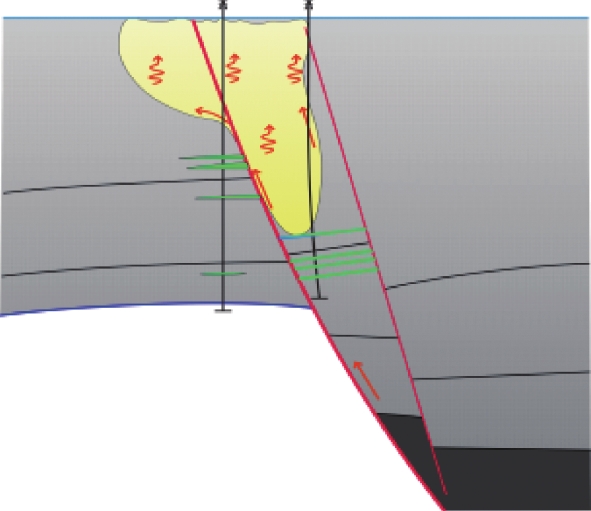
凸起周边,断裂发育区尤为发育 麻坑型 强振幅、速度低 缝渗式 扩散或裂缝 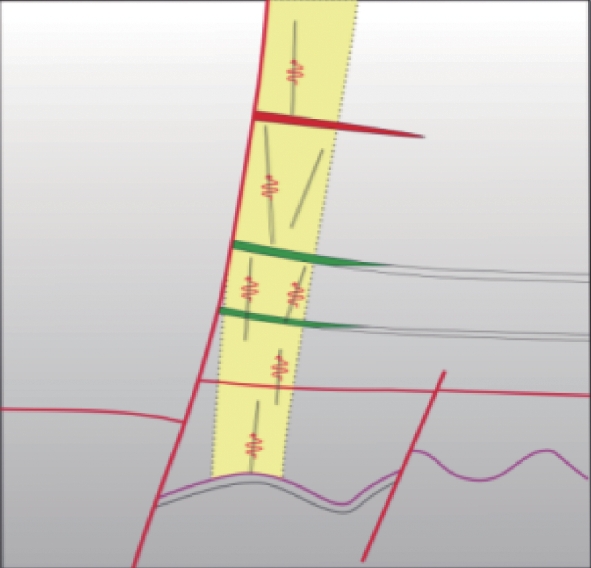
渤海海域广泛分布 -
[1] 张为民,李继亮,钟嘉猷,等. 气烟囱的形成机理及其与油气的关系探讨[J]. 地质科学,2000,35(4):449-455. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.04.008
[2] 邸鹏飞,黄华谷,黄保家,等. 莺歌海盆地海底麻坑的形成与泥底辟发育和流体活动的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报,2012,31(5):26-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.05.005
[3] 姜正龙,张为民,肖毓祥. 东海陆架盆地台北坳陷烟囱构造特征[J]. 石油学报,2006,27(1):34-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.01.007
[4] 顾兆峰,张志殉,刘怀山. 海底浅层圈闭与浅层气地震反射特征对比[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(3):115-122.
[5] 汪云家,王兴谋,韩文功. 济阳坳陷三维地震资料中亮点气藏的特征及识别方法[J]. 石油物探,1995,34(4):66-72.
[6] 杨涛涛,吕福亮,王彬,等. 琼东南盆地南部深水区气烟囱地球物理特征及成因分析[J]. 地球物理学进展,2013,28(5):2634-2641. doi: 10.6038/pg20130544
[7] 马明侠,王始波,张海燕,等. 松辽盆地北部浅层气的地震“亮点低频”识别[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2008,27(5):117-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3754.2008.05.031
[8] 马明侠. 松辽盆地北部浅层生物气形成条件及其资源潜力评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.
[9] 李彦鹏, 孙鹏远, 魏庚雨, 等. 利用陆上三分量数据改善气云区构造成像[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2009, 44(4) : 417-424
[10] 许翠霞, 边海光, 马朋善, 等. 气烟囱的地球物理响应特征及油气勘探[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(4): 1831-1836.
[11] 尹 川, 张金淼, 骆宗强, 等. 气烟囱模式识别技术在油气运移通道检测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 19(3): 1343-1349.
[12] 刘伟, 陈学华, 贺振华, 等. 基于倾角数据体的神经网络气烟囱识别[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(6): 937-944
[13] 杨瑞召,李洋,庞海玲,等. 倾角导向体控制的气烟囱识别技术及其在海拉尔盆地贝尔凹陷中的应用[J]. 现代地质,2013,27(1):223-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.01.026
[14] ALVARADO1 J M, AMINZADEH F, CONNOLLY D L. Application of gas chimney technology in the Lamprea area, offshore GOM [J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1999, 1949-4645.
[15] AMINZADEH F,BERG T. Determining migration path from a seismically derived gas chimney:a south Africa case history[J]. Society of Exploration Geophysicists and American Assocation of Petroleum Geologists,2013:231-236. doi: 10.1190/1.9781560803119.ch15
[16] HEGGLAND R,MELDAHL P ,STATOIL,et al. Detection of seismic chimneys by neural networks,a new prospect evalutation tool[J]. EAGE 62nd Conference and Technical Exhibition,2000:283-289. doi: 10.3997/2214-4609-pdb.28.A6
[17] CONNOLLY D L,BROUWER F,WALRAVEN D. Detecting fault-related hydrocarbon migration pathways in seismicdata:implications for fault-seal,pressure,and charge prediction[J]. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans,2008(58):191-203.
[18] MELDAHL P,HEGGLAND R,BRIL B,et al. Identifying fault and gas chimneys using multi-attributes and neural networks[J]. Geophysics,2001,20(5):474-482.
[19] MELDAHL P,HEGGLAND R,GROOT P D,et al. The chimney cube,an example of semi-automated detectionof seismic objects by directive attributes and neural networks[J]. Society of Exploration Geophysicists Extended Abstracts,1999:935-937.
-




 下载:
下载: