Temporal and spatial variations of erosion and accumulation off the Qingshuigou mouth of the Yellow River
-
摘要:
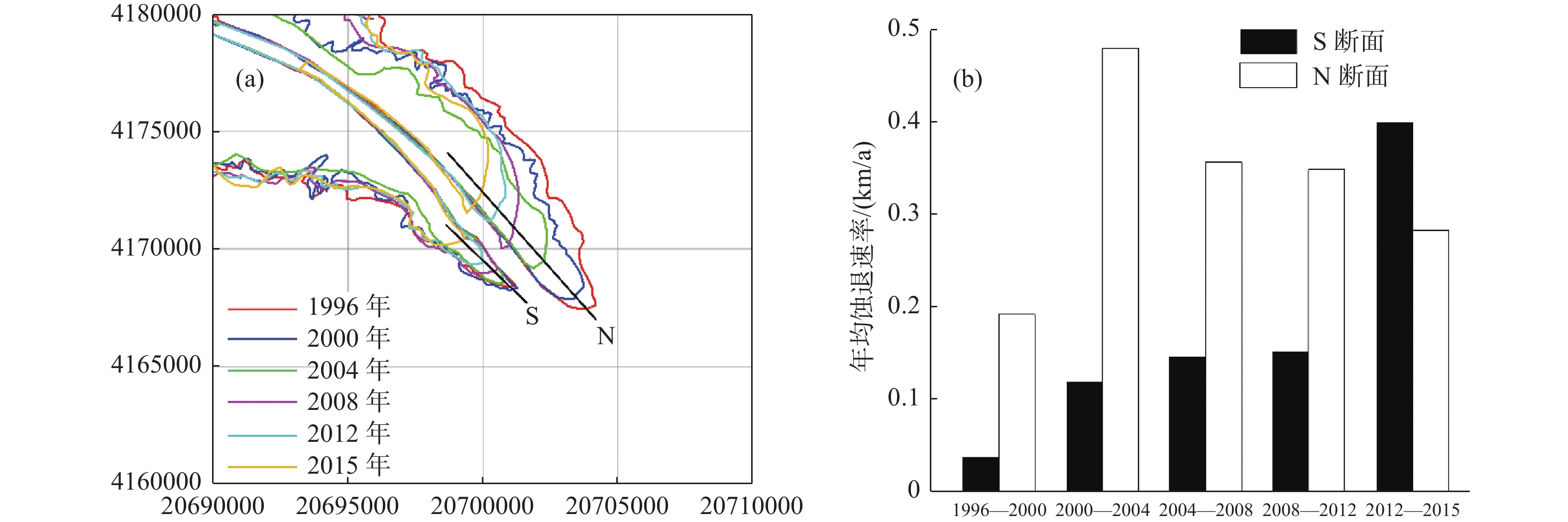
黄河于1996年人工改汊至清8入海是导致清水沟废弃河口岸线蚀退和海底侵蚀冲刷的主要诱因。但目前有关清水沟废弃河口海底冲淤演化对黄河人工改道的响应的认识尚有不足。因此,利用现代黄河三角洲毗邻海域多年的水深资料和Landsat卫星遥感影像,综合分析了清水沟(废弃)河口在1996—2015年的岸线变化及冲淤时空变化。结果表明:黄河清水沟废弃河口沙嘴两侧蚀退速率的变化存在明显的时空差异性。黄河改道初期(1996—2002年),研究区海底冲刷速率较快,年均冲刷速率约为0.03~0.05 km3/a;2002—2007年,研究区海底冲刷速率大幅降低至约0.02 km3/a;2007—2010年,随着黄河口位置再次向北迁移,研究区海底年均冲刷速率增大至约0.026 km3/a;2010—2015年,研究区海底年均冲刷速率减缓至约0.01 km3/a,远小于1996—2002年黄河改道初期时的水平。同时,基于Delft3D模式构建了黄河三角洲高分辨率三维水动力模型,定量研究了清水沟废弃河口潮流与冬季波浪变化对海底冲淤变化的影响,结果表明波浪和潮流在河口侵蚀过程中扮演着不同的角色。一方面,潮流与波浪在三角洲前缘斜坡处形成的高底剪切应力区是使得该区域形成侵蚀中心的主要原因。清水沟废弃河口岸线不断向陆方向蚀退以及侵蚀冲刷所造成的研究区整体水深增加使得潮流与波浪对海底的侵蚀冲刷作用逐渐减弱,最终使得近年来研究区海底冲刷速率不断减缓。另外,波浪在河口近岸区形成的高底剪切应力是造成河嘴两侧叶瓣差异侵蚀和近岸区形成侵蚀中心的主要动力机制。同时,潮流、波浪与海底冲淤变化间的相互作用对于该区域冲淤演化模式有着重要影响。
Abstract:The deltaic river course of the Yellow River was diverted artificially northward at the Qing8 of the Qingshuigou channel to the current channel. The channel shift resulted in a decrease or cutoff in the sediment supply from the river. However, the response of the tempo-spatial variation in erosion and accumulation off the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth to the channel shift has not been well studied. Based on multi-years bathymetric data and Landsat satellite remote sensing images off the Yellow River Delta, the tempo-spatial variations of erosion-accumulation off the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth were analyzed comprehensively. In the early stage of the Yellow River diversion (1996—2002), the seafloor erosion rate in the study area was relatively fast, and the average annual seafloor erosion rate was about 0.03-0.05 km3/a. From 2002 to 2007, the value was significantly reduced to about 0.02 km3/a. During 2007—2010, as the Yellow River mouth diverted northward again in 2007, the average annual seafloor erosion increased to about 0.26 km3/a. In the years of 2010—2015, the value reduced to about 0.01 km3/a again, which was much lower than the level at the initial stage of the Yellow River artificial diversion in 1996. Meanwhile, the tidal regime changes and its response to tempo-spatial variation of erosion-accumulation off the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth were simulated using the Delft-3D model. The results indicated that waves and currents played significant but different roles in the erosion and accumulation of seabed in the study area. On one hand, The high bed shear stress area formed by the tidal current and wave on the slope of the delta front caused the area to be severely eroded after the Yellow River rerouted. In addition, as the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth gradually eroded landward and water depth at the slope continuously increased, the influence of tidal current and wave to seafloor decreased gradually. Finally, the erosion rate of seabed continuously decreased in the study area in recent years. The wave-induced high-bottom shear stress zone mostly resulted in the different erosion on both sides of the mouth and the formation of erosion center in the nearshore area. Meanwhile, the interactions between hydrodynamics and delta erosion played an important role in the erosion-accumulation evolution pattern of the subaqueous delta off the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth of the Yellow River.
-

-
表 1 Landsat卫星遥感影像详细信息
Table 1. The detailed information of satellite images
日期 影像类型 空间分辨率/m 1996-09-20 TM 30 2000-05-02 TM 30 2004-05-13 TM 30 2008-10-31 ETM+ 30 2012-08-15 ETM+ 30 2015-05-10 ETM+ 30 表 2 1996—2015年清水沟废弃河口海底冲刷量及年均冲刷速率阶段性变化
Table 2. Phase changes in erosion volumes and rate off the abandoned Qingshuigou mouth in 1996—2005
时间段/年 冲刷量/km3 冲刷速率/(km3/a) 1996—2000 0.14 0.03 2000—2002 0.12 0.05 2002—2007 0.10 0.02 2007—2010 0.08 0.026 2010—2015 0.05 0.01 -
[1] SYVITSKI J P,SATIO Y. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean[J]. Science,2007,308:376-380.
[2] WRIGHT L D. Sediment transport and deposition at river mouths:a synthesis[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin,1977,88:857-868. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1977)88<857:STADAR>2.0.CO;2
[3] SYVITSKI J P,SAITO Y. Morphodynamics of deltas under the influence of humans[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2006,57(3):261-282.
[4] WOODROFFE C D,NICHOLLS R J,SAITO Y,et al. Landscape variability and the response of Asian megadeltas to environmental change[J]. Global Change and Integrated Coastal Management,2006,5:277-314.
[5] NILSSON C,REIDY C A,DYNESIUS M,et al. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world' s large river systems[J]. Science,2005,308:405-408. doi: 10.1126/science.1107887
[6] VöRöSMARTY C J,MEYBECK M,FEKETE B,et al. Anthropogenic sediment retention:Major global impact from registered river impoundments[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2003,39(1):169-190.
[7] WANG H J,YANG Z S,SAITO Y,et al. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years:connections to impacts from Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2006,50:212-225. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.01.005
[8] WANG H J,YANG Z S,SAITO Y,et al. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950—2005):impacts of climate change and human activities[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2007,57:331-354. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003
[9] WANG S,FU B,PIAO S,et al. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes[J]. Nature Geoscience,2016,9(1):38-41. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2602
[10] YANG S L, LI M, DAI S B, et al. Drastic decrease in sediment supply from the Yangtze River and its challenge to coastal wetland management[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(6).
[11] SYVITSKI J P,KETTNER A J,OVEREEM I,et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities[J]. Nature. Geoscience,2009,2(10):681-686. doi: 10.1038/ngeo629
[12] TESSLER Z D,VöRöSMARTY C J,GROSSBERG M,et al. Profiling risk and sustainability in coastal deltas of the world[J]. Science,2015,349(6248):638-643. doi: 10.1126/science.aab3574
[13] GAO J H,SHI Y,SHENG H,et al. Rapid response of the Changjiang (Yangtze) River and East China Sea source to sink conveying system to human induced catchment perturbations[J]. Marine Geology,2019,414:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.05.003
[14] SCHMIDT F,HINRICHS K,ELVERT M. Sources,transport,and partitioning of organic matter at a highly dynamic continental margin[J]. Marine Chemistry,2009,118(1):37-55.
[15] VONK J E,SÁNCHEZ GARCÍA L,VAN DONGEN B E,et al. Activation of old carbon by erosion of coastal and subsea permafrost in Arctic Siberia[J]. Nature,2012,489(7414):137. doi: 10.1038/nature11392
[16] BI N S,WANG H J,YANG Z S. Recent changes in the erosion–accretion patterns of the active Huanghe (Yellow River) delta lobe caused by human activities[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,90:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.02.014
[17] EDMONDS D A,SLINGERLAND R L. Significant effect of sediment cohesion on delta morphology[J]. Nature Geoscience,2009,3(2):105-109.
[18] NITTROUER J A,BEST J L,BRANTLEY C,et al. Mitigating land loss in coastal Louisiana by controlled diversion of Mississippi River sand[J]. Nature Geoscience,2012,5(8):534-537. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1525
[19] NITTROUER J A,VIPARELLI E. Sand as a stable and sustainable resource for nourishing the Mississippi River delta[J]. Nature Geoscience,2014,7(5):350-354. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2142
[20] TEMMERMAN B S,KIRWAN M L,KATRINA H. Building land with a rising sea[J]. Science,2015,349(6248):9-11.
[21] MARGINS OFFICE[Z]. NSF margins program science plans, 2003.
[22] LOICZ IPO[Z]. Land-ocean interactions in the coastal zone: Science plan and implementation strategy, 2005.
[23] FUTURE EARTH COASTS IPO[Z]. Strategy for research 2018–2028, 2018.
[24] MILLIMAN J D,MEADE R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology,1983,91(1):1-21. doi: 10.1086/628741
[25] 中国河流泥沙公报2011[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2011.
[26] 胡小雷,陈沈良,刘小喜,等. 2012年调水调沙期间黄河口水沙扩散途径及范围[J]. 泥沙研究,2014(3):49-56.
[27] JIANG C,PAN S Q,CHEN S L. Recent morphological changes of the Yellow River (Huanghe) submerged delta:causes and environmental implications[J]. Geomorphology,2017,293:93-107. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.04.036
[28] LI G X,YUE S H,ZHAO D B,et al. Rapid deposition and dynamic processes in the modern Yellow River Mouth[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology,2004,24(3):29-36.
[29] XING G,WANG H J,YANG Z,et al. Spatial and temporal variation in erosion and accumulation of the subaqueous Yellow River Delta (1976—2004)[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2016,SI74:32-47.
[30] CUI B L,LI X Y. Coastline change of the Yellow River Mouth and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976~2005)[J]. Geomorphology,2011,127(1/2):20-40.
[31] BI N S,YANG X S,WANG H J,et al. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2010,86(3):352-362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.005
[32] 刘付程,陈沈良,彭俊,等. 基于FCM方法的黄河水下三角洲沉积动力环境分区[J]. 海洋学报,2016,38(9):89-99.
[33] 王柯萌. 调水调沙影响下的黄河入海水沙运输机制[D]. 青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 2018.
[34] FU Y T,CHEN S L,JI H Y,et al. The modern Yellow River Delta in transition:causes and implications[J]. Marine Geology,2021,436:106-476.
[35] WU X,WANG H J,BI N S,et al. Evolution of a tide-dominated abandoned channel:a case of the abandoned Qingshuigou course,Yellow River[J]. Marine Geology,2020,422:106-116.
[36] 裘祥海. 基于DEM的河床冲淤量计算与评价[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014.
[37] ALESHEIKH A A,GHORBANALI A,NOURI N. Coastline change detection using remote sensing[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2007,4(1):61-66.
[38] 凡姚申. 黄河三角洲近岸海床侵蚀过程及其动力机制[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019.
[39] 刘猛. 黄河现行三角洲叶瓣蚀积演化的动力机制研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2018.
[40] WANG H J,YANG Z S,LI G,et al. Wave climate modeling on the abandoned Huanghe (Yellow River) Delta lobe and related deltaic erosion[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2006,224:906-918.
[41] YANG Z S,JI Y,BI N S,et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2011,93(3):173-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005
-




 下载:
下载: