Composition of minerals in surface sediments of the Yellow Sea and their provenance
-
摘要:
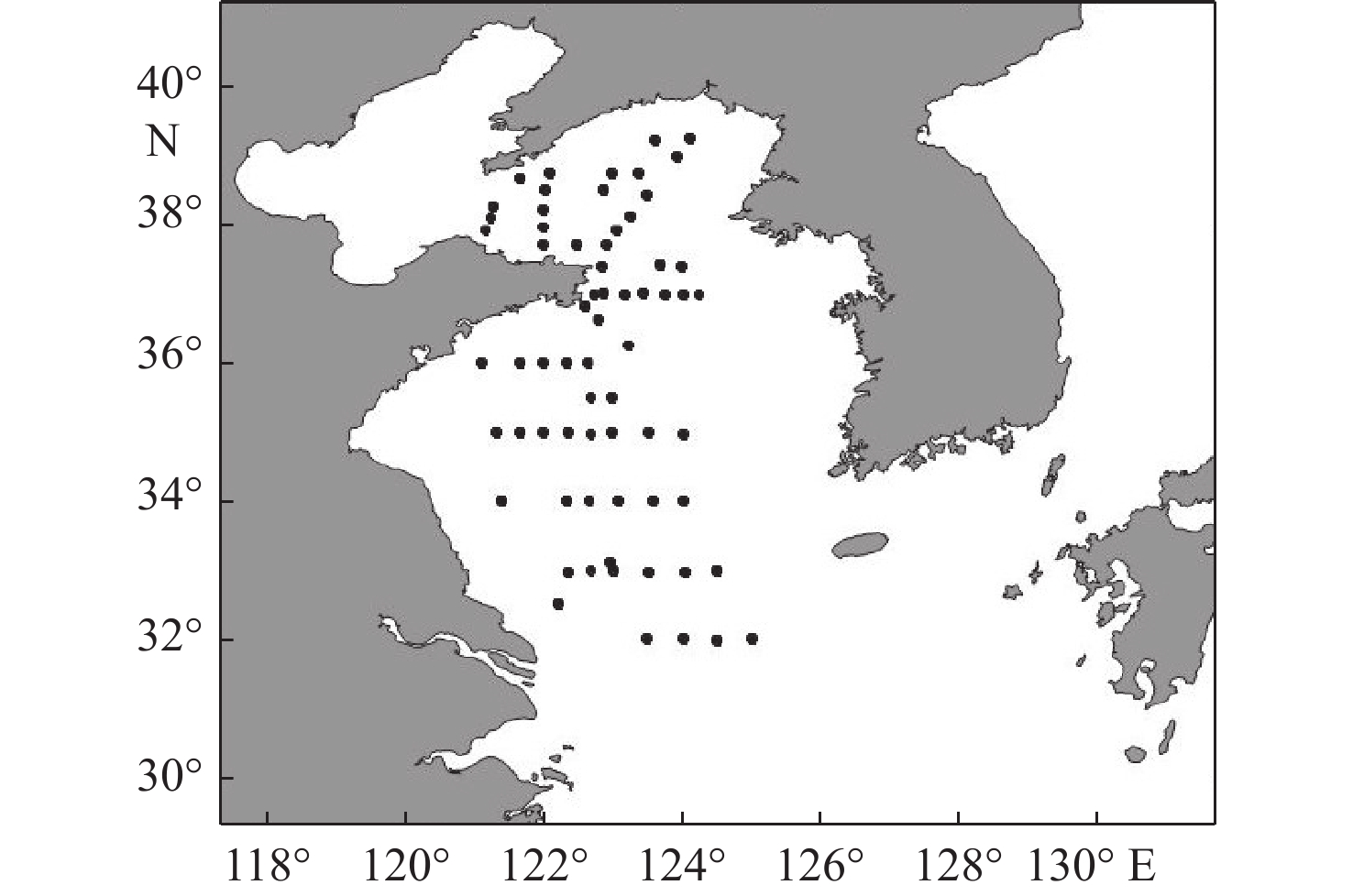
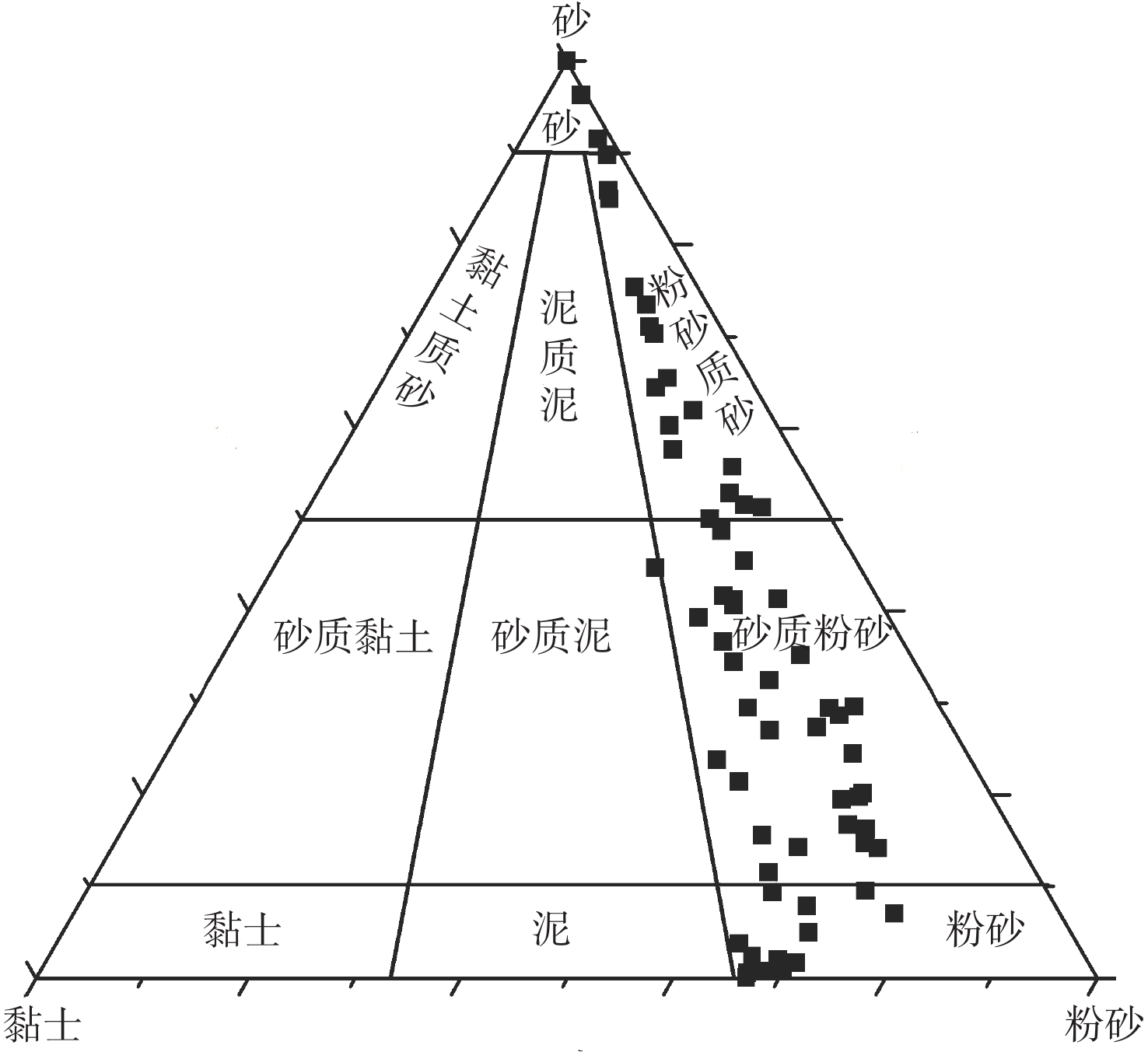
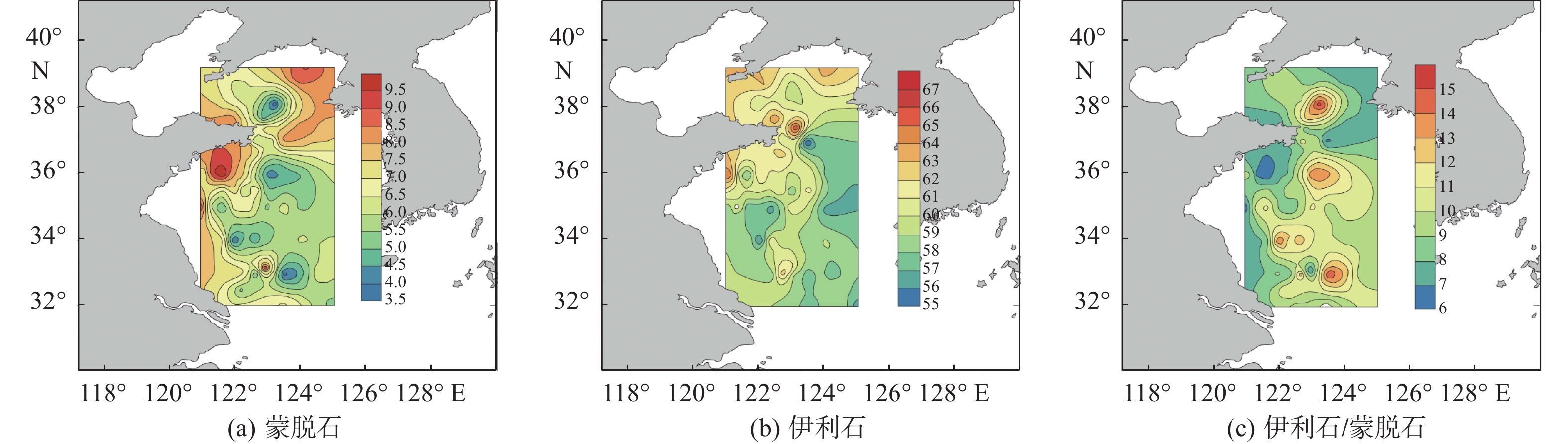
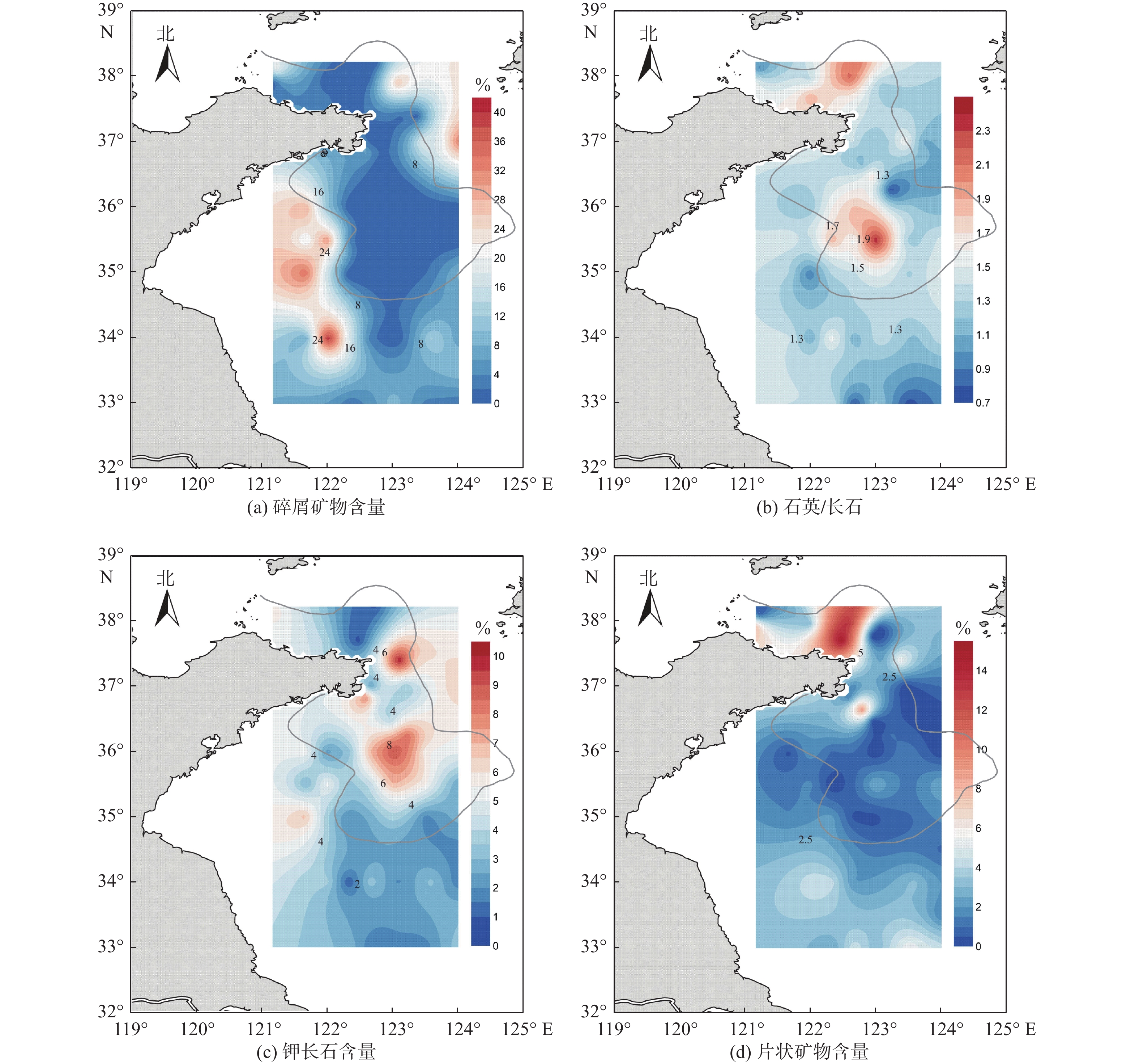
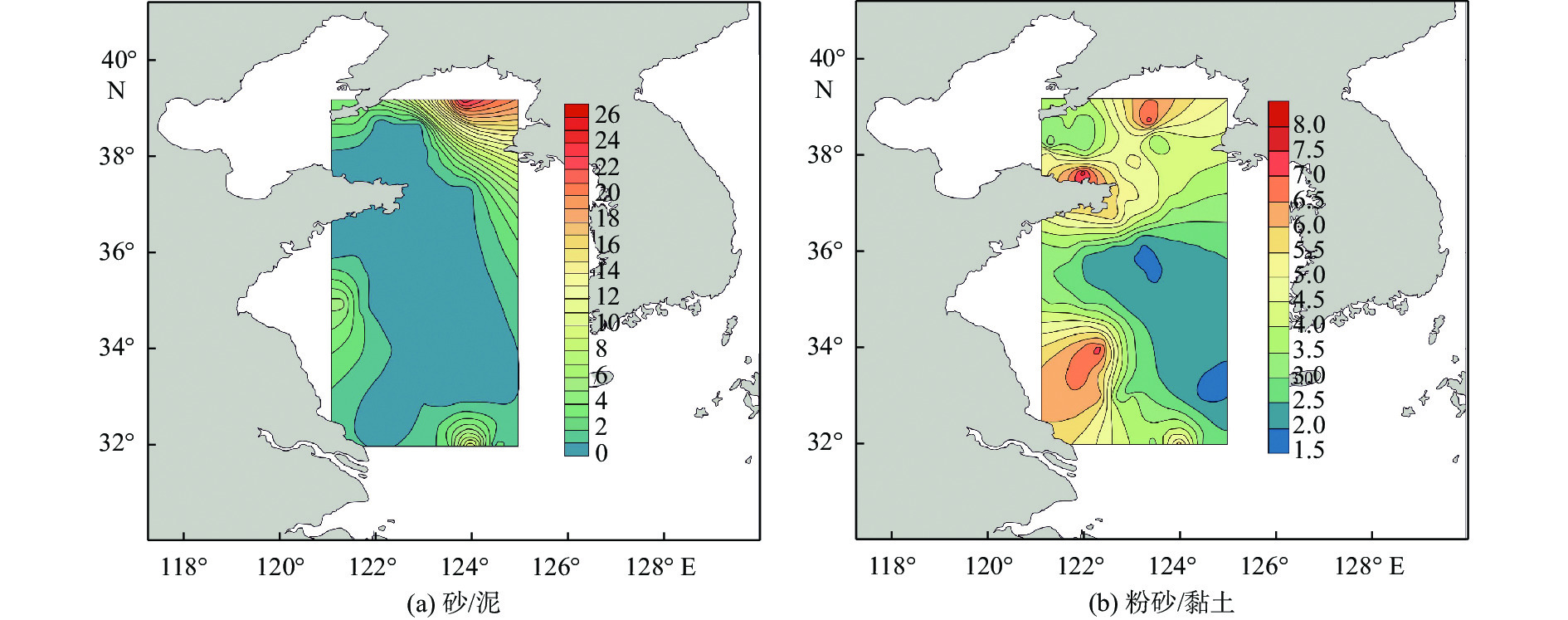
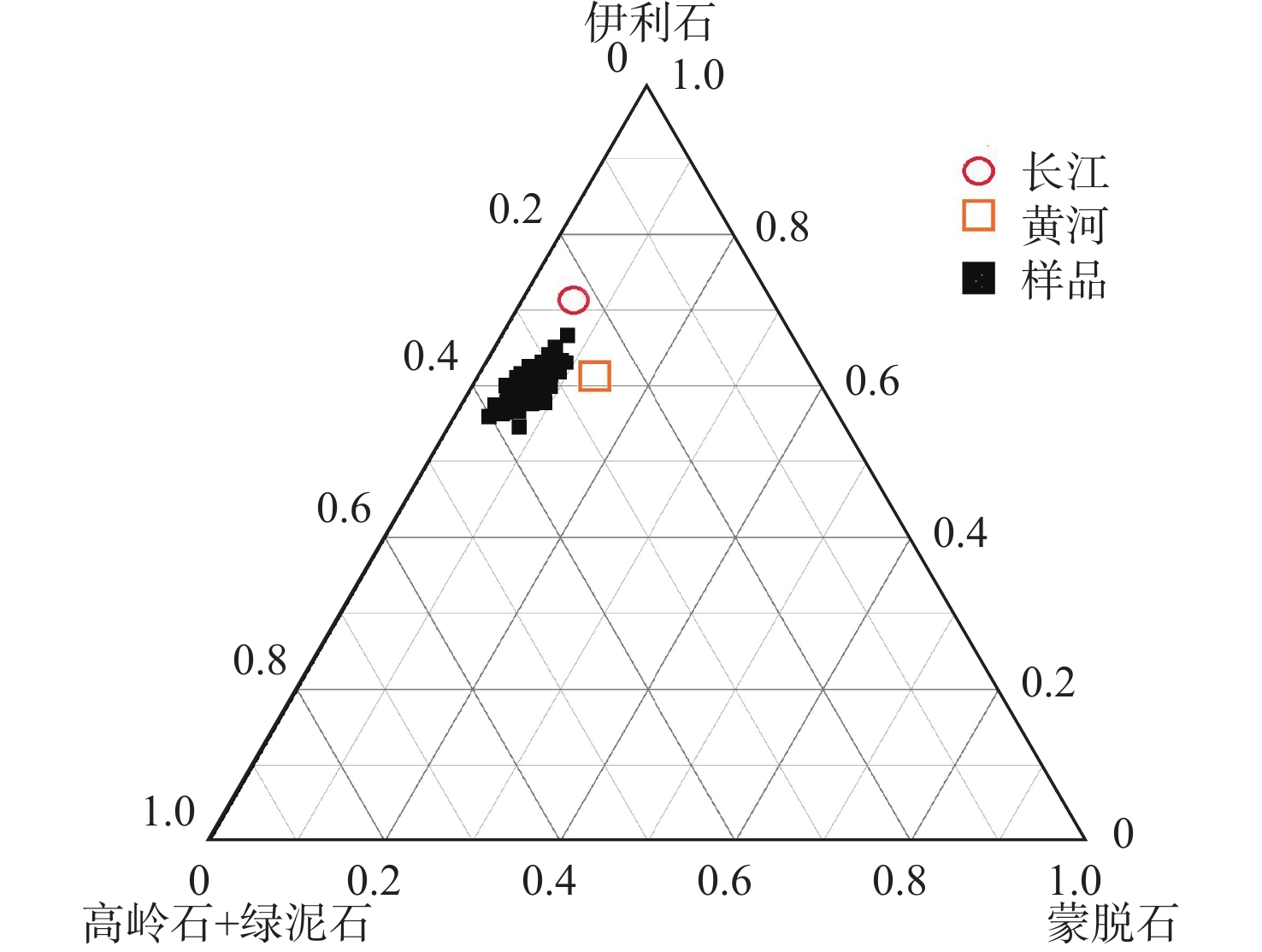
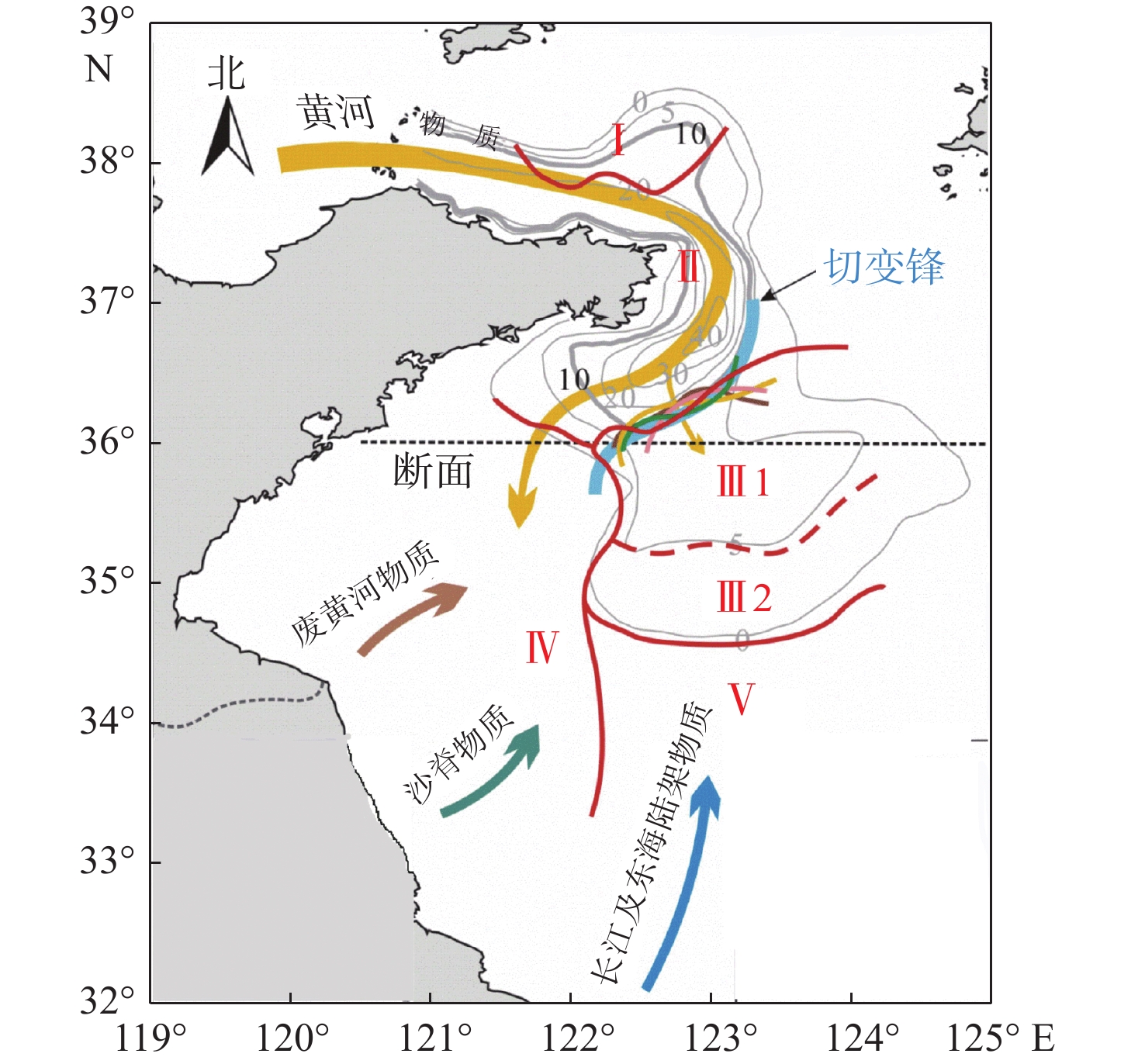
以黄海66个表层沉积物为研究对象,通过粒度、黏土矿物和碎屑矿物分析,研究了黄海表层沉积物的粒度分布与矿物组成特征,探讨了研究区沉积物的矿物组成特征对其物源、沉积环境的指示意义。黄海表层沉积物平均粒径为5.2Φ,分选较差;黏土矿物组合类型为伊利石-高岭石-蒙脱石-绿泥石,其中伊利石的含量最高,蒙脱石的含量最低;碎屑矿物(粒径为0.063~0.125 mm)平均含量为8.07%,标准偏差为4.03,分布趋势与平均粒径分布基本一致,轻矿物以石英和长石为主;重矿物以角闪石和绿帘石为主,其次是不透明矿物和片状矿物,重矿物主要集中分布于黄海南部。物源识别结果表明:黄海的东北部海域接受鸭绿江沉积物的供应;黄海北部主要为黄河源沉积物;南黄海西部沉积物主要为黄海沿岸流南下带来的现代黄河物质和再悬浮的老黄河沉积物;南黄海中部沉积物来源复杂以黄河沉积物为主,长江沉积物的供应较少。
Abstract:Based on the grain size, clay mineral and detrital mineral data of 66 surface sediment samples collected from the Yellow Sea, this paper is devoted to the grain size distribution and mineral composition characteristics of the samples with a detailed discussion on sediment provenance. The results suggest that the average grain size of surface sediments in the Yellow Sea is around 5.2Φ, with poor sorting. Clay minerals are characterized by the assemblage of illite-kaolinite-smectite-chlorite. Illite dominates and smectite is the lowest. The distribution of detrital minerals shows a similar pattern as the mean grain size. The light minerals mainly consist of quartz and feldspar. Heavy minerals mainly occur in the southern part of the Yellow Sea, dominated by hornblende and epidote. Study of material sources suggest that the sediments in the northeastern Yellow Sea are mainly from the Yalu River, while the provenance of the northern part is the modern Yellow River. In the western South Yellow Sea, sediments are mainly from the modern Yellow River either transported by coastal currents, or resuspended from the abandoned Yellow River delta in the northern Jiangsu Province. In the central South Yellow Sea, sediments are mainly from the Yellow River, followed by some supplement of sediments from the Yangtze River.
-
Key words:
- Yellow Sea /
- surface sediment /
- mineral composition /
- provenance analysis
-

-
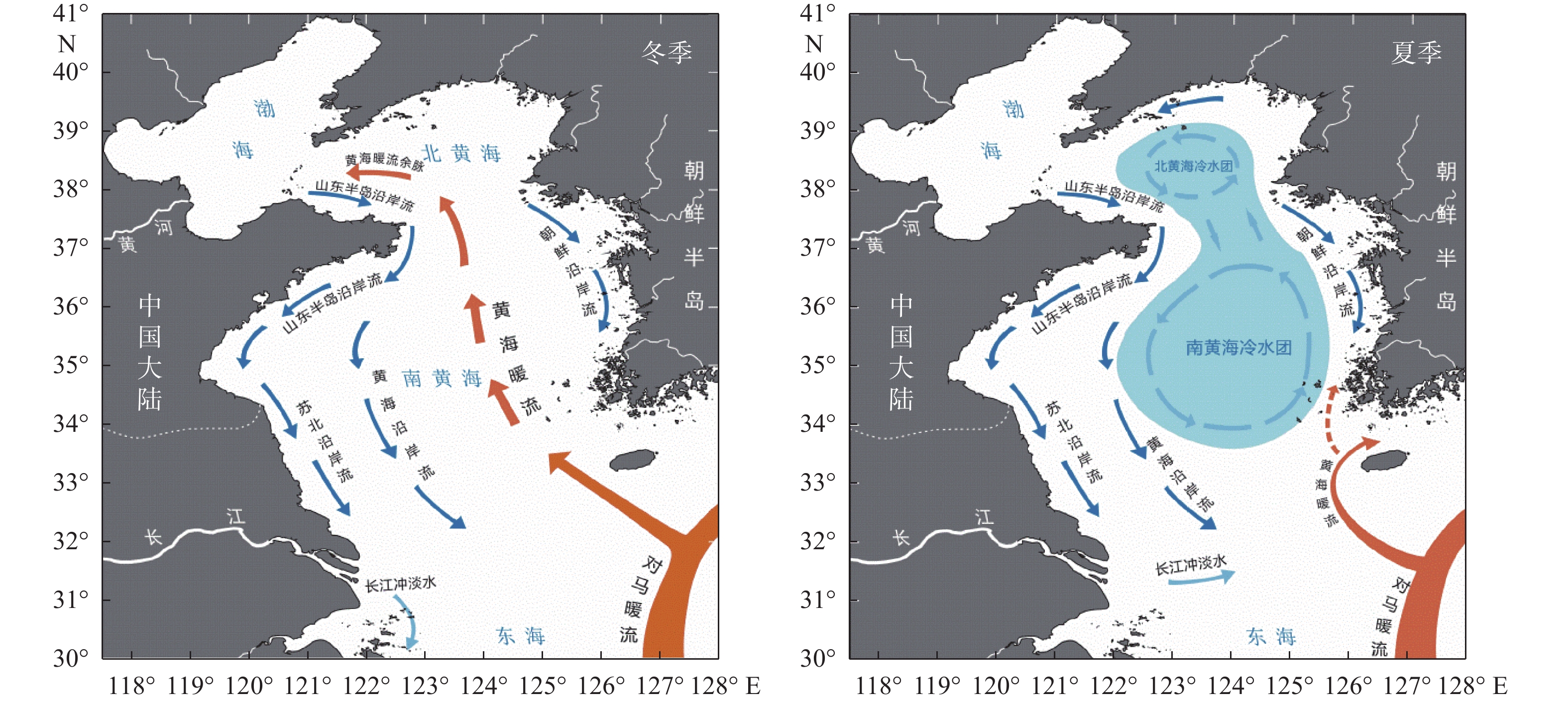
图 1 黄海冬、夏季环流体系[33]
Figure 1.
图 7 研究区表层沉积物重矿物含量成熟度 [38]
Figure 7.
表 1 表层沉积物样品中黏土矿物含量统计表
Table 1. Percentage contents of clay minerals of the surface sediment
表 2 研究区表层沉积物碎屑矿物含量
Table 2. Detrital mineral content in surface sediments of the Yellow Sea
矿物含量 平均值 最大值 最小值 标准偏差 变异系数/% 碎屑矿物/% 8.07 40.9 0.01 4.03 49.94 重矿物含量/% 5.84 29.6 0.63 5.92 101.37 闪石类/% 37.3 66.0 0.84 28.5 76.41 帘石类/% 16.8 27.6 0.28 13.7 81.55 不透明矿物/% 14.5 76.8 1.45 20.6 142.07 自生黄铁矿/% 4.21 42.5 0 7.31 173.63 片状重矿物/% 11.9 93.5 0 15.1 126.89 稳定矿物/% 6.34 27.0 0 4.98 78.55 辉石类/% 0.49 2.28 0 0.28 57.14 变质类/% 0.13 0.92 0 0.11 84.62 风化碎屑/% 2.40 7.06 0 1.93 80.42 ZTR含量/% 0.40 2.20 0 0.31 77.50 重矿物成熟度 11.3 42.4 0 10.8 95.58 石英/长石 1.38 2.40 0.74 0.31 22.46 钾长石/% 3.95 10.20 0.78 2.07 52.41 片状轻矿物/% 4.08 41.02 0.00 7.93 194.36 -
[1] MORTON A C. Geochemical studies of detrital heavy minerals and their application to provenance research[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications,1991,57(1):31-45. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1991.057.01.04
[2] 赵利. 长江、黄河入海沉积角闪石的矿物化学特征及对中国陆架泥质沉积的物源指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[3] LIM D I,CHOI J Y,JUNG H S,et al. Recent sediment accumulation and origin of shelf mud deposits in the Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Progress in Oceanography,2007,73(2):145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.02.004
[4] LIU Z X,XIA D X,BERNE S,et al. Tidal deposition systems of China's continental shelf,with special reference to the eastern Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1998,145(3/4):225-253.
[5] 王双. 黄渤海表层沉积物磁学特征及其环境指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[6] 申顺喜,陈丽蓉. 南黄海冷涡沉积和通道沉积的发现[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1993,24(6):563-570. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1993.06.001
[7] 蓝先洪,申顺喜. 南黄海中部沉积岩心的地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2000,20(2):33-38.
[8] 蓝先洪,申顺喜. 南黄海中部沉积岩心的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋通报,2002,21(5):46-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.05.007
[9] PARK Y A,KHIM B K. Clay minerals of the recent fine-grained sediments on the Korean continental shelves[J]. Continental Shelf Research,1990,10(12):1179-1191. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(90)90015-E
[10] PARK Y A,KHIM B K. Origin and dispersal of recent clay minerals in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1992,104(1/4):205-213.
[11] 魏建伟,石学法,辛春英,等. 南黄海黏土矿物分布特征及其指示意义[J]. 科学通报,2001,46(S1):30.
[12] 赵一阳,鄢明才,李安春,等. 中国近海沿岸泥的地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国地质,2002,29(2):181-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.02.014
[13] XIAO S,LI A C,LIU J P,et al. Coherence between solar activity and the East Asian winter monsoon variability in the past 8000 years from Yangtze River-derived mud in the East China Sea[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2005,237(2):293-304.
[14] WANG L,SARNTHEIN M,ERLENKEUSER H,et al. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene:high-resolution sediment records from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1999,156(1):245-284.
[15] 李真祥. 南黄海西部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其对沉积环境的指示[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2010.
[16] 程鹏,高抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度特征和净输运趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2000,31(6):604-615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.004
[17] HATHON E G,UNDERWOOD M B. Clay mineralogy and chemistry as indicators of hemipelagic sediment dispersal south of the Aleutian arc[J]. Marine Geology,1991,97(1/2):145-166.
[18] NAIDU A S,HAN M W,MOWATT T C,et al. Clay minerals as indicators of sources of terrigenous sediments,their transportation and deposition:Bering Basin,Russian-Alaskan Arctic[J]. Marine Geology,1995,127(1/4):87-104.
[19] UNDERWOOD M B,PICKERING K T. Clay-mineral provenance,sediment dispersal patterns,and mudrock diagenesis in the Nankai accretionary prism,Southwest Japan[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals,1996,44(3):339-356. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1996.0440304
[20] 蓝先洪,张训华,张志珣. 南黄海沉积物的物质来源及运移研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2005(4):53-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2005.04.008
[21] 陈忠,颜文. 海洋沉积黏土矿物与古气候、古环境演化响应的研究进展[J]. 海洋科学,2000,24(2):25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2000.02.009
[22] PETSCHICK R,KUHN G,GINGELE F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic:sources,transport,and relation to oceanography[J]. Marine Geology,1996,130(3/4):203-229.
[23] 杨作升. 黄河、长江、珠江沉积物中黏土的矿物组合、化学特征及其与物源区气候环境的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1988,19(4):38-48.
[24] 何良彪,刘秦玉. 黄河与长江沉积物中黏土矿物的化学特征[J]. 科学通报,1997,42(7):730-734.
[25] UDDIN A,LUNDBERG N. Unroofing history of the eastern Himalaya and the Indo-Burman ranges; heavy-mineral study of Cenozoic sediments from the Bengal Basin,Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1998,68(3):465-472. doi: 10.2110/jsr.68.465
[26] 宋友桂. 沉积矿物学在古环境恢复中的应用进展[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版),2009,32(4):17-27.
[27] 侯孟孜,衣华鹏,孙志高,等. 渤海北部海域碎屑矿物组成特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2017,31(4):118-123.
[28] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 黄海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989.
[29] 皮仲. 中全新世以来季风背景下黄海暖流的演化[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016.
[30] 薛春汀,张勇. 中国近岸海区沿岸流和海岸流对沉积物的搬运[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(1):1-7.
[31] 臧家业,汤毓祥,邹娥梅,等. 黄海环流的分析[J]. 科学通报,2001,46(S1):7.
[32] TEAGUE W J,JACOBS G A. Current observations on the development of the Yellow Sea Warm Current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2000,105(C2):3401-3411. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900301
[33] 王琳淼. 南黄海中部泥质区全新世以来古环境沉积记录及其对东亚季风的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[34] LEONARD B P. The ULTIMATE conservative difference scheme applied to unsteady one-dimensional advection[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,1991,88(1):17-74.
[35] 翁学传,张以恳,王从敏,等. 黄海冷水团的变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1988(4):368-379.
[36] 苏纪兰,黄大吉. 黄海冷水团的环流结构[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1995,26(S1):1-7.
[37] FOLK R L,ANDREWS P B,LEWIS D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13(4):937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[38] 张尧,韩宗珠,艾丽娜,等. 黄海全新世泥质体表层沉积物重矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(11):111-121.
[39] 何起祥,李绍全,刘健. 海洋碎屑沉积物的分类[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2002,22(1):118-124.
[40] 范德江,杨作升,毛登,等. 长江与黄河沉积物中黏土矿物及地化成分的组成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2001,21(4):7-12.
[41] YANG Z S,LIU J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,240(1/4):169-176.
[42] 申顺喜. 南黄海陆架沉积学研究[J]. 海洋科学,1993,17(5):24-28.
[43] 李凡,张秀荣,李永植,等. 南黄海埋藏古三角洲[J]. 地理学报,1998,65(3):238-243.
[44] 张宪军. 南黄海中西部全新世沉积特征及物源分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
[45] 王昆山,石学法,林振宏. 南黄海和东海北部陆架重矿物组合分区及来源[J]. 海洋科学进展,2003,21(1):31-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2003.01.004
[46] 刘金庆,张勇,印萍,等. 青岛近岸海域表层沉积物重矿物分布及物源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(1):69-78.
[47] 尹秀珍,刘万洙,蓝先洪,等. 南黄海表层沉积物的碎屑矿物、地球化学特征及物源分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2007,37(3):491-499.
[48] 王琦,曹立华,杨作升,等. 黄河水下三角洲的动力沉积特征[J]. 中国科学(B辑 化学 生命科学 地学),1991,21(6):659-665.
-



 下载:
下载: