Grain-size characteristics of surface sediment and sedimentary environment in Zhanjiang Bay
-
摘要:
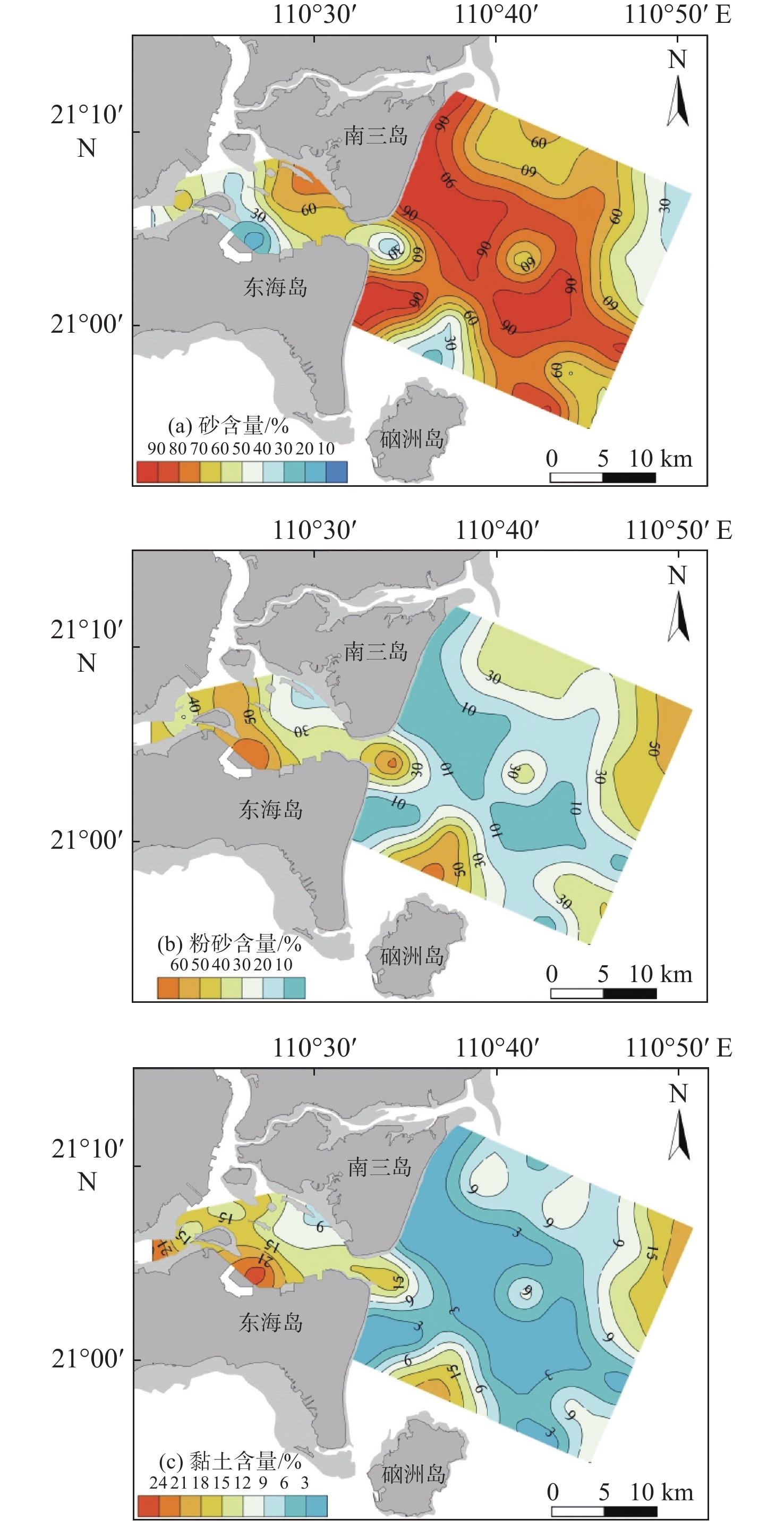
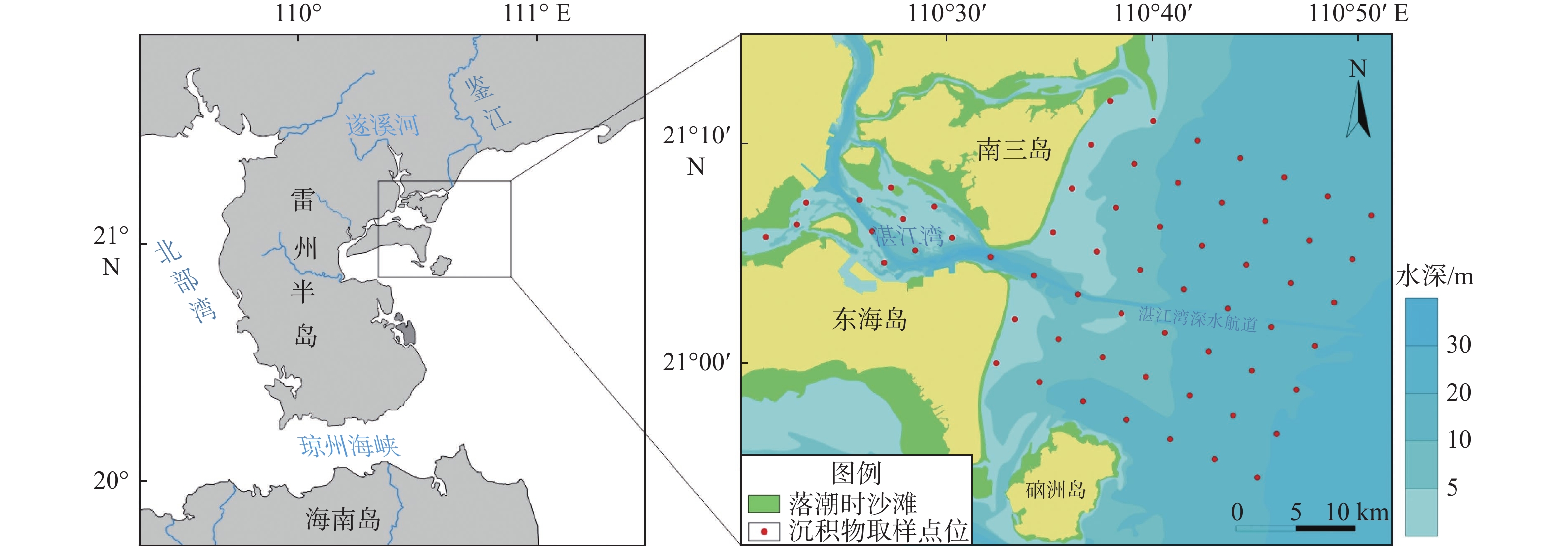
根据湛江湾海域2020年10月采集的61个表层沉积物样品粒度分析结果,对沉积物粒度参数进行了总结,划分了沉积物类型,结合Pejrup三角图解对湛江湾海域沉积动力环境进行了分区,运用Gao-Collins粒径趋势分析模型,探讨了沉积物运移趋势。结果表明,湛江湾海域表层沉积物类型共有5种,其中砂、粉砂质砂、砂质粉砂分布最广,粒度组成以细砂为主,平均粒径均值为3.93Φ,分选较差,粒度分布曲线以正偏、正态分布为主。沉积动力判别图解揭示湛江湾海域沉积水动力较强,整体表现为湾内比湾外弱、湾外向外海方向逐渐减弱的特征。粒径趋势分析反映出湛江湾内整体向南部潮流深槽方向运移,湾外围绕沉积中心整体呈逆时针方向运移。湛江湾海域表层沉积物的运移和分布主要受泥沙来源及潮流、波浪、沿岸流等沉积动力环境的共同作用,近年来,人类活动的影响愈加明显。
Abstract:Based on the results of particle size analysis of 61 surface sediment samples collected in October, 2020 in Zhanjiang Bay, Guangdong, China, the particle size parameters of sediments were summarized, and the sediment types were classified. The Pejrup triangle diagram was used to divide the sedimentary dynamic environment of Zhanjiang Bay. The Gao-Collins particle size trend analysis model was used to explore the sediment migration trend. Results show that there are five types of surface sediments in Zhanjiang Bay, among which sand, silty sand, and sandy silt are the most widely distributed. The particle size composition is mainly fine sand, and the average particle size is 3.93Φ. The sorting is poor. The particle size distribution curve is mainly positive and normal distribution. The discriminant diagram of sedimentary dynamics reveals that the sedimentary hydrodynamic force in Zhanjiang Bay is strong; and it is generally weaker inside the bay than outside the bay and gradually weakens oceanward. The particle size trend analysis shows that the whole water in Zhanjiang Bay moves to the tidal deep trough in the south, while water of outer bay flows counterclockwise around the sedimentary center. The movement and distribution of surface sediments in the bay are mainly affected by sediment sources and sedimentary dynamic environments such as tides, waves, and coastal current. In recent years, the influence of human activities has become more obvious.
-

-
[1] 张连杰,赵博,王鹏,等. 大连湾海域沉积动力环境与物质输运[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2019,35(6):12-19.
[2] 汤世凯,于剑峰,李金鹏,等. 丁字湾近岸海域表层沉积物粒度特征及沉积动力环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2019,39(2):70-78. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018022703
[3] 赵利,蔡观强,钟和贤,等. 海南岛东南浅海表层沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):64-74. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020051502
[4] 刘成,胡日军,朱海龙,等. 庙岛群岛海域沉积动力环境分区及沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(8):24-33. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.08004
[5] 吕纪轩,胡日军,李毅,等. 烟台北部近岸海域表层沉积物粒度分布及沉积动力环境特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(4):27-36. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.097
[6] 张际标,姚兼辉,陈春亮,等. 湛江东海岛潮间带表层沉积物粒度的分布及环境要素的相关性[J]. 应用海洋学学报,2015,34(1):49-56. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2015.01.007
[7] 陈碧珊,陈诗敏,何炽鹏,等. 雷州半岛红树林湿地表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):198-205. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.01.19
[8] 李拴虎. 湛江湾外航道二侧浅滩冲淤变化的成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2013,13(35):10595-10599.
[9] 贺松林,丁平兴,孔亚珍. 湛江湾沿岸工程冲淤影响的预测分析[J]. 海洋学报,1997,19(1):55-63.
[10] 张志飞,褚裕良,何杰. 多年围填海工程对湛江湾水动力环境的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2016(3):96-104.
[11] 林微,张乔民,赵焕庭. 湛江港潮汐汊道落潮三角洲动力场模拟和沉积动态分析[J]. 热带海洋,1995,14(1):54-61.
[12] 韩志远,谢华亮,李怀远,等. 湛江湾口外落潮三角洲演变特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(1):45-50. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2020.010
[13] 赵冲久. 湛江湾水文泥沙特性分析[J]. 水道港口,1999,20(4):16-21.
[14] FOLK R L,ANDEWS P B,LEWIS D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,1970,13(4):937-968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211
[15] PEJRUP M. The triangular diagram used for classification of estuarine sediments: a new approach[C]//P. L. de Boer et al. Tide-influenced Sedimentary Environments and Facies. Dordrecht: D. Reidel Publishing Company, 1988: 289-300.
[16] GAO S,COLLINS M. Net sediment transport patterns inferred from grain-size trends,based upon definition of “Transport Vectors”[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1992,81(1/2):47-60.
[17] 时翠,甘华阳,夏真,等. 珠江口内伶仃洋表层沉积物粒度特征及其运移趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(1):13-20.
[18] 高抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析:原理与应用软件[J]. 沉积学报,2009,27(5):826-836.
[19] 程鹏,高抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度特征和净输运趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2000,31(6):604-615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.06.004
[20] 李亮,何其江,龙根元,等. 南海宣德海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2017,37(6):140-148. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.06.015
[21] 刘志杰,公衍芬,周松望,等. 海洋沉积物粒度参数3种计算方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋学报,2013,35(3):179-188.
[22] 曹立,刘建国,何伟,等. 华南沿岸大型河流粘土矿物组合特征及对南海北部沉积物的贡献[J]. 地球科学,2018,43(2):192-202.
[23] 叶春池,黄方. 湛江港口门潮汐地貌体系的沉积环境和沉积作用[J]. 海洋通报,1994,13(1):51-58.
[24] 许冬,初凤友,李家彪,等. 粤西—琼东北近海沉积物的运移和沉积[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2014,44(3):905-917.
[25] 杨毅,徐艳东,王发云,等. 粤西沿岸流和物质输移模型研究及应用[J]. 科学技术与工程,2015,15(19):80-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.19.015
[26] 中国科学院南海海洋研究所. 湛江港30万吨级航道改扩建工程环境影响报告书[R]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 2018.
[27] 余科平,张琴. 湛江湾海砂开采对周边海域水动力特征的影响[J]. 人民珠江,2017,38(10):65-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2017.10.014
-



 下载:
下载: