Application and uncertainty analysis of beachrock to Mid-late Holocene sea-level reconstruction in the northern South China Sea
-
摘要:
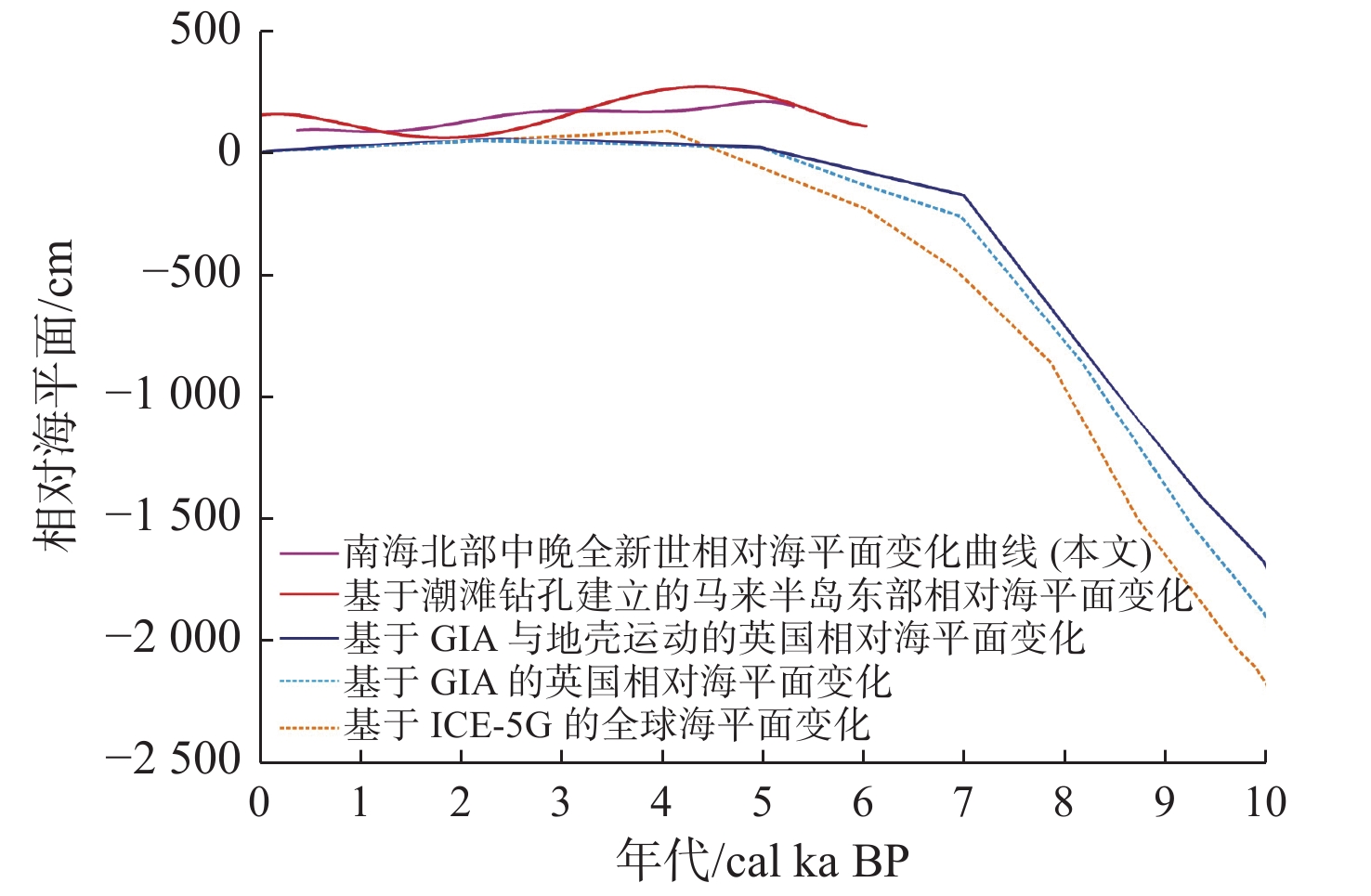
过去海平面变化特征对认识现代海平面变化过程和预估未来情景具有重要科学和现实意义。海滩岩作为热带和亚热带地区海岸潮间带特有的沉积岩,是海岸变迁和古海平面高程的重要标志物。然而,由于存在海滩岩形成后动力条件发生变化、采用的测年方法不同以及海平面高程估算和分析误差等问题,基于海滩岩的过去海平面重建结果依然存在较大争议和不确定性。我们分析和总结了南海北部中晚全新世海滩岩重建海平面的进展,以及在海平面研究中存在的问题和潜在机遇,从海滩岩的形成年代与海滩岩形成后高程产生变化等方面进一步量化研究海滩岩重建海平面变化的不确定性。同时,通过对南海北部海南岛东部沿岸的3块原生珊瑚礁(1块大型块状滨珊瑚和2块滨珊瑚微环礁)进行高精度高程测量和铀系测年,共获得6个海平面数据,结合冰川均衡调整模型(Glacial Isostatic Adjustment,GIA)和ICE-5G模型结果,对基于海滩岩重建的南海北部中晚全新世海平面的可靠性进行比较和评估。以上不确定性分析和研究结果表明,通过年代与高程校正后,海平面重建结果准确性进一步提高。研究结果可为以其他海平面标志物重建的过去海平面的不确定性分析和可靠性分析提供参考和借鉴。
Abstract:The characteristics of the past sea-level change have important scientific and practical significance for understanding the process of the modern sea-level change, and predicting future scenarios. Beachrock, as a unique sedimentary rock in coastal intertidal zones in tropical and subtropical regions, is an important indicator of coastal change and the past sea-level elevation. However, due to the change of dynamic conditions after the formation of beachrock, the different dating methods, the estimation of indicative range represented by beachrock and error analysis, the results of past sea-level reconstruction based on beachrock are still controversial and uncertain. Therefore, we analyze and summarize the progress of sea-level reconstruction of Mid-late Holocene based on beachrocks in the northern South China Sea, as well as the existing problems and potential opportunities in sea-level research. The uncertainty of sea-level reconstruction based on beachrock is further quantitatively studied from the aspects of the formation age of beachrock and the elevation change after the formation of beachrock . At the same time, the high-precision elevation measurement and U-Th dating of three in-situ coral reefs (one large massive Porites and two Porites microatolls) along the east coast of Hainan Island in the northern South China Sea were conducted, and six new sea-level data are obtained. In conjunction with Glacial Isostatic Adjustment (GIA) and ICE-5G model results, they were applied to the reliability analysis and comparison of the reconstructed Mid-late Holocene sea level in the north of the South China Sea based on beachrocks. The uncertainty analysis and results indicate that the accuracy of sea-level reconstruction result is further improved after the correction of age and elevation, which can provide reference for the uncertainty and reliability analysis of the reconstructed sea-level based on other sea-level indicators.
-
Key words:
- northern South China Sea /
- beachrock /
- Mid-late Holocene /
- sea-level change /
- uncertainty analysis
-
0. 引言
滑坡易发性评价(landslide susceptibility assessment)主要基于区域孕灾地质条件对滑坡发生的可能性进行评估[1-2],经历了从早期定性评价(基于专家先验知识)至目前定量评价(数据驱动)的过程[2-3],随着信息化技术在地质灾害评价中的深入应用,数据获取越来越便利,大量滑坡易发性定量评价模型不断涌现并开展广泛应用,包括二元统计分析模型,如信息量模型[4-6]、确定性系数模型[7-8]、证据权模型[9-11]、频率比模型[12]等,多元统计分析模型,如逻辑回归模型[13-15]、随机森林模型[16-17]、判别分析模型[18-19]等。二元统计模型通过独立比较各孕灾因子与滑坡分布的关系计算因子分级对应权重值,但各孕灾因子之间对于滑坡相对重要性并不明确;相反,多元统计模型则可以有效评估因变量(滑坡分布)与一组自变量(孕灾因子)的相互关系。国内外学者在针对滑坡易发性评价中已开展了大量单一模型及耦合模型的应用与对比研究[20-25],总体上,统计型数据驱动模型较定性模型评价结果更客观且重复性更强,多元统计模型较二元统计模型通常具有更好的评价结果[26-28],通过二元统计模型与多元统计模型的耦合,综合两者的优势,评价结果具有更高的预测精度。
四川省凉山州普格县地处云贵高原之横断山脉、地质构造复杂,地质灾害发育。历史灾害统计表明,区内地质灾害主要以滑坡为主,共发育195处,远超泥石流(80处)及崩塌(18处)灾害数量,对当地居民的生命、财产安全和县内重要设施构成巨大威胁。通过开展普格县滑坡孕灾地质条件分析及灾害分布规律研究,本文利用信息量模型、确定性系数模型、证据权模型、频率比模型分别与逻辑回归模型进行耦合对普格县滑坡易发性开展评价,对比分析了各耦合模型评价的有效性和准确率,精准预测区内滑坡地质灾害的发生,为当地政府和人民开展防灾减灾工作部署提供重要指导,同时也为川西南县域滑坡易发性定量评估模型与防灾减灾工作提供理论指导和技术支持。
1. 数据来源及方法
1.1 研究区概况
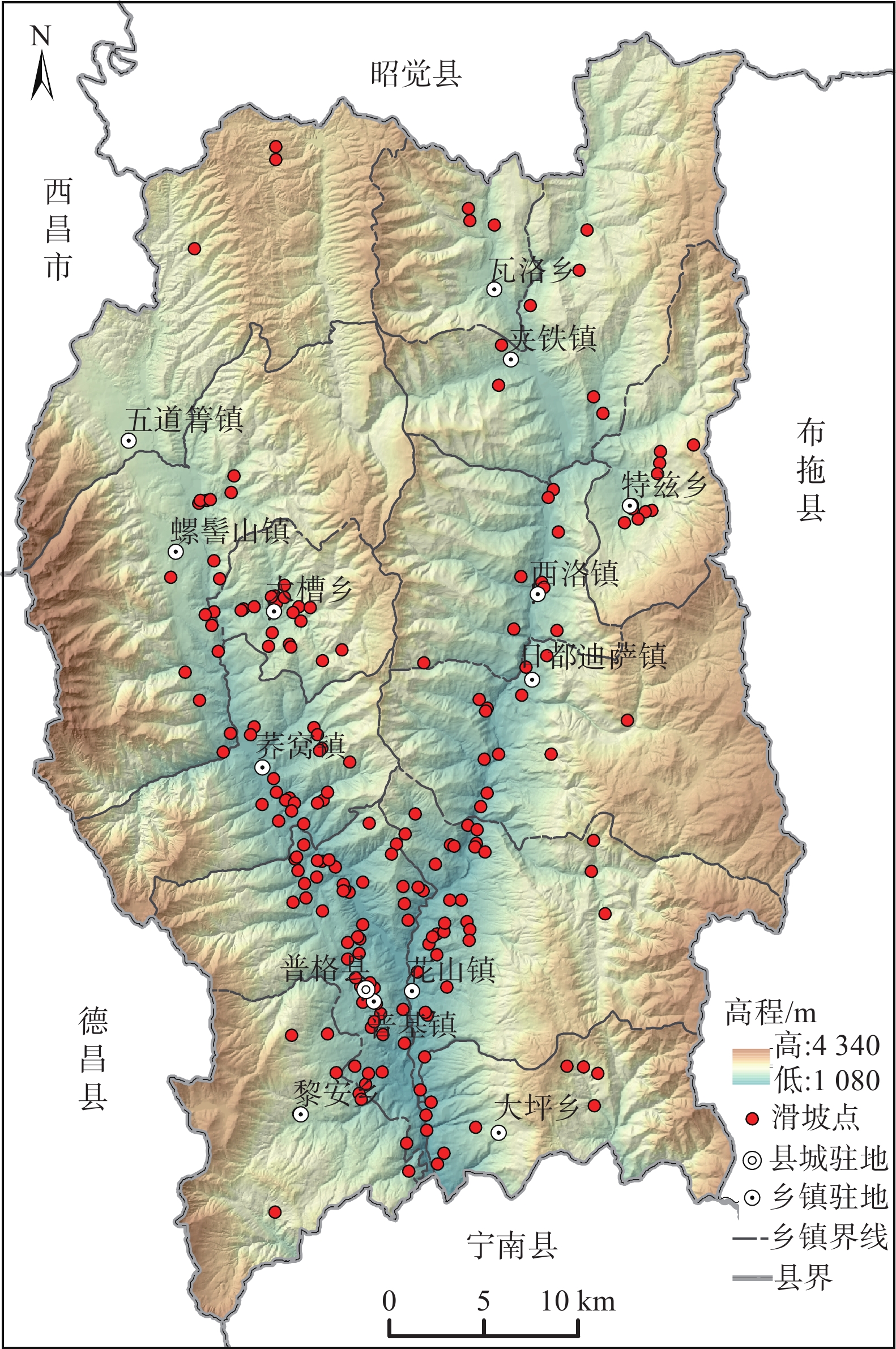
普格县地处四川省西南部,隶属凉山彝族自治州,南北长68 km,东西宽41 km,面积1905.41 km2(图1)。地貌形态主要包括侵蚀堆积河谷平原、山间盆地,以及侵蚀、剥蚀构造中高山区,地形表现为三山夹两谷,为典型云贵高原横断山区地貌,海拔介于1080~4340 m。
普格县地处则木河断裂和黑水河断裂交汇处,发育一系列近南北向褶皱、断裂构造。县域内地层以侏罗系和白垩系红层分布最广,缺失石炭系和泥盆系。岩性包括砾岩、砂岩、泥岩、页岩等碎屑岩,灰岩、泥灰岩、白云岩等碳酸盐岩,以及玄武岩火山岩等,则木河、西洛河及其支流沿岸分布第四系松散堆积物。
滑坡是区内发育数量最多的一种地质灾害,共发育195处,占地质灾害总数的67%,其中小型滑坡141处,中型滑坡45处,大型滑坡9处,主要以小型为主。县域中南部地区是滑坡灾害的高发区,包括普基镇、花山镇、荞窝镇、大槽乡等一带。
1.2 数据来源
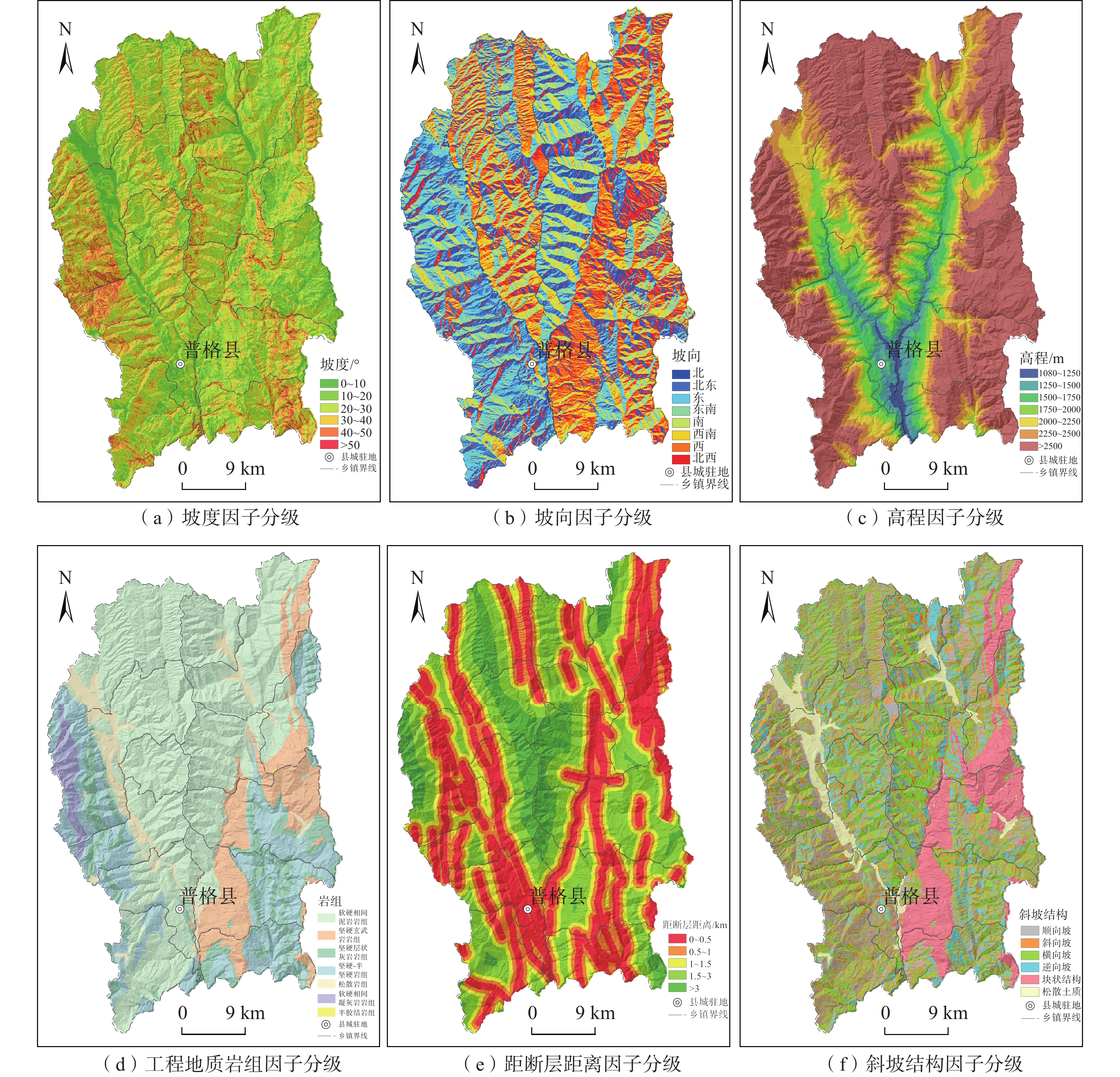
文中用于滑坡易发性评价的灾点数据和基础地理与地质数据主要包括:(1)历史滑坡数据:来自2005年以来历年灾害调查、汛期排查、2015年地灾详查以及2021年县域地灾风险评价野外资料[29];(2)数值高程模型(DEM):来自县域1∶5万地形图,空间分辨率为20 m×20 m,通过DEM提取了研究区坡度、坡向、高程等数据;(3)工程地质岩组、断层及斜坡结构数据:源自1∶20万西昌幅地质图;(4)行政区划等基础地理数据:来源于三调数据。
1.3 评价模型
文中采用栅格单元法进行评价(20 m×20 m),通过信息量模型、确定性系数模型、证据权模型、频率比模型等分别与逻辑回归模型进行耦合计算,前者可以很好地刻画评价因子不同特征值对易发性的敏感程度,而后者可以较客观的确定影响因子之间的权重大小。选取各评价因子分级的信息量值、确定性系数值、证据权值以及归一化频率比值作为耦合模型自变量,通过逻辑回归模型的回归运算得到各逻辑回归系数(β),再计算滑坡概率,最终得到普格县4种耦合模型下滑坡易发性评价图。
(1)信息量模型(Information,I)
地质灾害的形成受多种因素影响,信息量模型[4]主要原理为特定评价单元内致灾因素作用下地质灾害发生与区域地质灾害发生频率的函数比,反映一定地质环境下致灾因素及其分级区间的组合。信息量计算公式:
Iij=lnNj/NSj/S (1) 式中:Iij——致灾因素i在j状态下地质灾害发生的信息 量值;
Nj——对应因素在j状态下地质灾害分布的单元数;
N——调查区已有地质灾害分布的单元总数;
Sj——对应因素在j状态分布的单元数;
S——调查区单元总数。
(2)确定性系数模型(Certainty Factor,CF)
确定性系数模型也是一种常用的滑坡易发性评价模型[6],基于滑坡发生的概率函数,计算评价因子的确定性系数,其公式如下:
CF={PPa−PPsPPs(1−PPa)(PPa<PPs)PPa−PPsPPa(1−PPs)(PPa⩾PPs) (2) 式中:CF——滑坡发生的确定性系数;
PPa——因子分级类别a中的滑坡数与a的面积比 值,表示滑坡在因子分级类别a中发生的 条件概率;
PPs—研究区滑坡总数与研究区总面积之比, 表示滑坡在整个研究区中发生的先验 概率。
CF的区间为[−1,1],正值表示滑坡发生的确定性增加,越接近1越易于发生滑坡;负值表示滑坡发生的确定性降低,越接近−1越不易于发生滑坡;值为0代表条件概率与先验概率相同,不确定是否会发生滑坡[6]。
(3)证据权模型(Weights-of-Evidence,WE)
证据权模型是一种以贝叶斯概率统计为基础的二元统计模型,因该方法较直观、透明且符合地质问题解决的常规思路而得到广泛应用[10]。其计算公式如下:
W+=ln((A+i/B+)/(A−i/B−)) (3) W−=ln((a+i/B+)/(a−i/B−)) (4) Wf=W+−W− (5) 式中:
W+ 、W− ——分别表示影响因子分布区的正相关和 负相关权重值;Wf——综合权重,指示特定因子等级对滑坡变形失 稳的权重;
A+i 、A−i ——分别表示特定因子等级中发生和未发生 滑坡的栅格数;a+i 、a−i ——分别表示其他因子等级中发生和未发 生滑坡的栅格数;B+、B−——分别表示所有发生和未发生滑坡的栅 格数。
(4)频率比模型(Frequency Ratio,FR)
该模型按照一定的规则分析滑坡分布与其影响因子状态之间的空间关系 [12]。通过计算不同影响因子(F)分级区间(j)内滑坡面积(L),频率比FjR(Frequency Ratio)表示为:
FjR=P(LFj)P(Fj)=ALFj/ALAFjA=ALFj/AFjAL/A=P(L|Fj)P(L) (6) 式中:P(LFj)——滑坡分级区间j内滑坡的频率;
P(Fj)——研究区中各因子分级j的频率;
ALFj——因子分级区间j内滑坡的面积;
AL——滑坡总面积;
AFj——因子分级区间j的总面积;
A——研究区总面积。
(5)逻辑回归模型(Logistic Regression,LR)
该模型能通过简单的线性回归描述滑坡各致灾因子之间复杂的非线性关系[13]。利用Logit变换,对滑坡发生的概率P和不发生的概率1-P的比值取自然对数,建立线性回归方程:
Z=ln(P/(1−P))=β0+β1X1+β2X2+⋯+βnXn (7) P=1/(1+e−z) (8) 式中:P——地质灾害发生概率;
Z——地质灾害发生概率的目标函数;
X1、X2、⋯、Xn ——滑坡影响因子指标值;β0——常数项;
β1、β2、⋯、βn ——逻辑回归系数。2. 评价因子选取及分级
普格县滑坡地质灾害普遍发育于具有一定地形坡度、断层破碎带影响范围内易崩易滑工程地质岩组区,如区内则木河断裂破碎带、黑水河断裂破碎带以及侏罗系-白垩系红层发育区等。通过分析区内滑坡地质灾害分布特征、孕灾规律、形成条件和演化过程,结合高精度DEM数据和遥感影像,建立了滑坡易发性指标体系,提取高程、坡度、坡向、地势起伏度、曲率、斜坡结构、工程地质岩组、距断层距离、距水系距离、距道路距离等主要孕灾因子,根据各因子与滑坡发育关系、各因子相关性,排除具有较大相关性因子,最终选取坡度、坡向、高程、工程地质岩组、距断层距离和斜坡结构等6个因子开展普格县滑坡易发性评价,各因子分级如表1和图2所示。
表 1. 评价因子分级及I值、CF值、WF值和NFR值Table 1. Calculation results of I, CF, WF and NFR values for classification level of each evaluation factor评价因子 分级 分级面积/km2 滑坡点/个 信息量值(I) 确定性系数值(CF) 证据权值(WF) 归一化评率比值(NFR) 坡度/(°) 0~10 190.90 17 −0.2634 −0.2316 −0.2888 0.1837 10~20 497.15 78 0.3889 0.3222 0.5724 0.3527 20~30 620.30 77 0.2321 0.2071 0.3667 0.3015 30~40 438.61 20 −0.6898 −0.4983 −0.8286 0.1199 40~50 138.49 3 −1.7342 −0.8235 −1.7967 0.0422 >50 21.54 0 −1.7342 −1.0000 −1.6118 0.0000 坡向 北 237.61 17 −0.7700 −0.5370 −0.8436 0.0582 北东 229.75 17 −0.2255 −0.2019 −0.2528 0.1003 东 264.22 29 −0.0776 −0.0747 −0.0895 0.1163 东南 223.00 23 0.0920 0.0879 0.1048 0.1378 南 213.81 23 0.0828 0.0795 0.0938 0.1365 西南 228.02 22 0.1185 0.1118 0.1358 0.1415 西 269.04 42 0.4051 0.3331 0.4907 0.1885 北西 241.54 22 −0.0392 −0.0384 −0.0447 0.1209 高程/m 1080~1250 18.04 8 1.5566 0.7892 1.5932 0.2481 1250~1500 73.97 60 2.0284 0.8685 2.3385 0.3977 1500~1750 127.88 39 1.0536 0.6513 1.1978 0.1500 1750~2000 181.76 38 0.7973 0.5495 0.9348 0.1161 2 000~2250 260.21 31 0.2378 0.2116 0.2812 0.0664 2250~2500 277.74 10 −1.0438 −0.6479 −1.1486 0.0184 >2500 967.41 9 −2.7618 −0.9368 −3.4370 0.0033 工程地质岩组 软硬相间砂泥岩岩组 1012.50 137 0.2928 0.2538 0.7790 0.2852 坚硬玄武岩岩组 244.86 20 −0.2247 −0.2012 −0.2538 0.1700 坚硬层状灰岩岩组岩、白云质灰岩岩组 195.97 8 −0.6951 −0.5010 −0.7509 0.1062 坚硬−半坚硬砂岩组 324.87 14 −1.2006 −0.6990 −1.3347 0.0641 松软岩组 90.32 16 0.5650 0.4316 0.6035 0.3745 软硬相间凝灰岩 38.21 0 −1.2006 −1.0000 −0.9848 0.0000 半胶结岩组 0.27 0 −1.2006 −1.0000 −0.9848 0.0000 距断层距离/km 0~0.5 577.04 108 0.5763 0.4381 0.9892 0.4092 0.5~1 372.13 44 0.1105 0.1047 0.1393 0.2568 1~1.5 272.36 20 −0.2133 −0.1921 −0.2448 0.1858 1.5~3 476.60 19 −0.8907 −0.5896 −1.0700 0.0944 >3 208.88 4 −1.4520 −0.7659 −1.5421 0.0538 斜坡结构 顺向坡 284.78 49 0.4893 0.3870 0.6068 0.2398 斜向坡 513.76 46 −0.1274 −0.1196 −0.1706 0.1294 横向坡 521.17 43 −0.1973 −0.1791 −0.2624 0.1207 逆向坡 252.00 22 −0.1356 −0.1268 −0.1547 0.1284 块状结构斜坡 240.57 16 −0.4146 −0.3394 −0.4625 0.0971 松散土质斜坡 94.72 19 0.6605 0.4834 0.7107 0.2846 (1)坡度
对滑坡而言,斜坡坡度是极为重要的影响因素。利用调查区20 m分辨率DEM数据提取坡度数据,得到各滑坡灾害点坡度信息,统计表明:大部分滑坡发育在坡度40°内的斜坡,随着斜坡坡度的增加,滑坡发育的数量呈现出先增后减的趋势,在10°~30°间的发育的滑坡数量最多(155处),占总数的79.49%。
(2)坡向
斜坡的不同坡向代表了不同的日照辐射强度,影响着坡体表面地下水的蒸发并导致植被覆盖率的差异,这些差异进一步影响着斜坡岩土体物理力学性质,不同程度地影响着区内滑坡的易发性。基于ArcGIS坡向分析工具,将斜坡坡向分为北、北东、东、东南、南、西南、西以及北西等8个方向。
(3)高程
普格县地处云贵高原横断山区,全县最高点位于西北边界的螺髻山,海拔4340 m;最低点位于南部的黑水河河谷一带,海拔1080 m,最大相对高差达3260 m。海拔高程差异影响着坡体内含水量、坡内应力大小,同时不同高差人口密度、人类工程活动的强弱、坡体表面的植被分布情况也不尽相同。
区内高程1080~1700 m范围主要为河谷及两侧斜坡人类工程活动强烈区域,河谷地貌演化的应力最大释放区,这一高程区间内岩体更为破碎,应力更为集中,所以相应地更易发育滑坡。
(4)工程地质岩组
工程地质岩组对滑坡的发育有着极为重要的影响,区内工程地质岩组主要包括软硬相间砂泥岩岩组、坚硬玄武岩岩组、坚硬层状灰岩岩组、坚硬-半坚硬砂岩岩组、第四系松散岩组、软硬相间凝灰岩岩组、半胶结岩组等7大岩组。统计表明:区内软硬相间砂泥岩岩组发育的滑坡数量最多,如区内侏罗系和白垩系砂岩、泥岩及页岩地层,发育滑坡137处,占总数的70.25%,其次坚硬玄武岩岩组内发育滑坡20处,约占总数的10.26%。从滑坡灾害密度分布来看,也是软硬相间砂泥岩岩组、坚硬玄武岩岩组及第四系松散岩组分布密度最大。
(5)距断层距离
断裂是内动力地质作用的表现,普格县南北向呈“Y”字形分布则木河和黑水河两条主断裂带,其次级断层极为发育。控制着县域地层分布、河流展布和地貌演化。断裂带及其影响区岩体普遍较破碎,在具备良好地形条件下滑坡灾害发生概率明显增大。
区域强活动性发震大断裂影响范围可达20 km以上,活动性弱、规模较小的断层及主要褶皱其影响范围仅1 km。为从宏观上揭示地质构造内生动力地质作用对滑坡的影响,在普格县现有地质构造的基础上,创建断裂的多环缓冲区,统计离断层不同距离内的滑坡发育特征。其缓冲距离可分为:0~0.5 km、0.5~1 km、1.5~3 km及>3 km。随着距断裂带距离的增大,滑坡的发育数量和发育密度均逐渐减少。
(6)斜坡结构
斜坡岩土体结构类型往往影响着滑坡、崩塌等主要地质灾害的失稳破坏方式,理论和实践均表明,岩土体类型与成灾模式之间存在着强烈的成生联系。通常,对于滑坡灾害来说,顺向斜坡最易发生基岩顺层滑动,逆向坡及横向坡发生失稳滑动的可能性较低。统计结果表明,区内顺向坡发育的滑坡数量最多,而松散土质斜坡发育的滑坡点密度是最多的,斜向坡次之,块状结构坡最低。
3. 评价结果与讨论
3.1 易发性评价结果
随机抽取普格县滑坡总数的80%与相同数量的随机非灾害点作为训练样本数据,共计312个样本点。通过各单一模型与逻辑回归模型耦合开展滑坡易发性评价,样本赋值“1”表示滑坡点,“0”表示非滑坡点,作为逻辑回归模型的因变量,自变量为坡度、坡向、高程、工程地质岩组、距断层距离和斜坡结构等6项评价因子的信息量值(I)、确定性系数值(CF)、证据权值(WF)和归一化频率比值(NFR)。利用SPSS软件开展二元逻辑回归分析,为确保各因子具有数理统计意义,其显著性水平均小于0.05。基于逻辑回归计算各因子系数值后可得耦合模型滑坡易发性评价公式分布如下:
PI−LR=1/1+exp[−(−0.101+0.686I1j+1.355I2j+0.874I3j+0.154I4j+0.586I5j+0.303I6j)]; (9) PCF−LR=1/1+exp[−(−0.405+1.055CF1j+1.722CF2j+1.890CF3j+0.354CF4j+0.994CF5j+0.464CF6j)]; (10) PWF−LR=1/1+exp[−(−0.287+0.558WF1j+1.198WF2j+0.722WF3j+0.27WF4j+0.507WF5j+0.25WF6j)]; (11) PNFR−LR=1/1+exp[−(−5.588+4.320NFR1j+10.762NFR2j+10.188NFR3j+4.301NFR4j+3.564NFR5j−0.612NFR6j)]; (12) 式中:PI−LR、PCF−LR、PWF−LR、PNFR−LR——I-LR模型、CF- LR模型、WF- LR模型、NFR- LR模型下滑坡 发生的概率值;
I1j−I6j、CF1j−CF6j、WF1j−WF6j、NFR1j−NFR6j— 坡度、坡向、高程、工程地质岩组、距断层距离和 斜坡结构的I、CF、WF和NFR值。
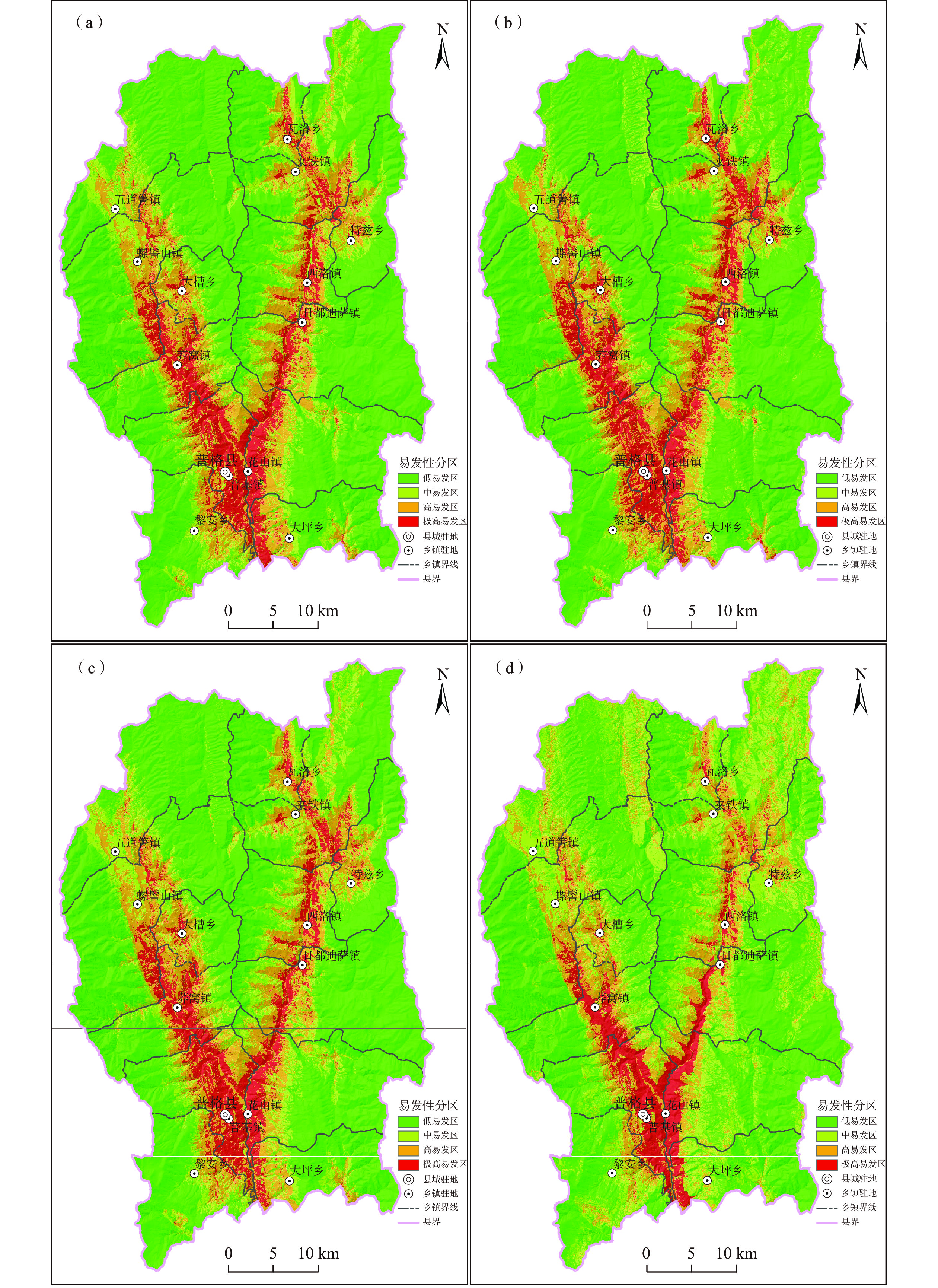
根据上述滑坡概率模型,通过GIS分析得到研究区滑坡概率分布,将滑坡易发性划分为:低易发(P:0~0.25)、中易发(P:0.25~0.5)、高易发(P:0.5~0.75)和极高易发(P:0.75~1),研究区各耦合模型滑坡易发性评价分区如图3。统计各易发等级内训练集滑坡点数量、占比及密度(表2),各耦合模型主要灾害点近半数落入极高易发区,其中I-LR、CF-LR和WF-LR耦合模型极高易发区滑坡数量占比分别达51.28%、51.28%和50%,NFR-LR耦合模型为43.59%;落入中易发以上的滑坡占比介于94.87%~96.15%;滑坡灾害点密度自极高易发区至低易发区呈现明显降低的趋势。同时,四种耦合模型低易发区面积均超过50%,达到52.92%~63.22%,极高易发区面积占比均低于10%。绝大部分滑坡灾害点集中发育在面积较小的极高-高易发区,而中-低易发区滑坡数量显著减小,与县域实际滑坡灾害点分布情况较吻合,表明四种耦合模型均有效评价了普格县滑坡易发性。
表 2. 普格县滑坡易发性不同模型评价结果对比(训练集)Table 2. Comparison of landslide susceptibility evaluation results of different models评价模型 易发性等级 面积/km2 面积占比/% 训练集滑坡点(156个) 滑坡数量/个 占比/% 点密度/个/km2 I-LR 极高易发 169.89 8.91 80 51.28 0.47 高易发 303.28 15.90 50 32.05 0.16 中易发 269.10 14.11 20 12.82 0.07 低易发 1164.73 61.08 6 3.85 0.01 CF-LR 极高易发 183.43 9.62 80 51.28 0.44 高易发 284.62 14.92 47 30.13 0.17 中易发 233.42 12.24 21 13.46 0.09 低易发 1205.53 63.22 8 5.13 0.01 WF-LR 极高易发 168.77 8.85 78 50.00 0.46 高易发 302.78 15.88 51 32.69 0.17 中易发 278.71 14.62 21 13.46 0.08 低易发 1156.74 60.66 6 3.85 0.01 NFR-LR 极高易发 129.04 6.77 68 43.59 0.53 高易发 248.98 13.06 50 32.05 0.20 中易发 519.76 27.26 31 19.87 0.06 低易发 1009.23 52.92 7 4.49 0.01 从滑坡易发性评价分区图可以看出(图3),四种耦合模型计算结果具有一定的相似性,结合区域孕灾地质条件与滑坡灾害点发育分布规律分析,四种耦合模型滑坡易发性评价分区图具有以下特点:
(1)县域内滑坡极高、高易发区主要发育于则木河和黑水河河谷一带,多种有利因素使得滑坡在该带较为发育,包括水对河岸斜坡带的冲刷、软化和动水压力,可大幅降低坡岸岩土体强度,同时山区河谷两岸是人类活动最为活跃区,建房修路切坡较普遍,人为扰动进一步增加了滑坡的易发性。
(2)普格县城周边是滑坡极高、高易发主要集中区,区内则木河断裂带与黑水河断裂带在此汇聚,岩土体受众多断层切割、挤压拉裂作用,变得松散破碎,力学强度显著降低,在河岸斜坡的有利地形条件下,滑坡易发性较其他区域明显增大。
(3)中低易发区多位于远离河谷的高海拔地区,此外在五道箐镇等局部较为平坦的河谷区也有发育。
3.2 评价精度对比分析
为了检验评价结果精确性和合理性,有必要针对四种耦合模型开展评价精度对比分析,首先统计分析了未参与评价的测试样本滑坡点在各易发性分级下的灾害点数量占比情况,其次,通过常用的受试者特征曲线法(Receiver Operating Characteristic curve,ROC)[30]、Sridevi Jadi经验概率法[31]等对模型评价的精度进行多维度检验。
(1)合理性检验
为了检验模型稳定性,选择没有参与模型训练的39个灾害点(占滑坡总样本数的20%,详见表1),测试灾害点在各易发等级内的分布状况,同时可以评估地质灾害易发程度区划结果的合理性。
从检验结果可以看出(表3),测试灾害点在各易发区的分布与训练集样本分布特征较相似,各模型测试组灾害点落在极高易发区的百分比均最大,其中WF-LR耦合模型极高易发区灾害点占比甚至达到51.28%。计算测试样本落在各等级区的比例(Gei)与各等级区面积百分比(Sai)的比值(Rei),各耦合模型均满足Rei值自极高易发区至低易发区急剧降低的趋势,说明各耦合模型地质灾害易发性评价及易发程度区划均是合理的。
表 3. 普格县滑坡易发性评价模型结果对比(测试样本)Table 3. Comparison of landslide susceptibility evaluation results of different models评价模型 易发性等级 面积/km 面积占比Sai/% 测试样本滑坡点(39个) Rei=Gei/Sai 滑坡数量/个 占比Gei/% I-LR 极高易发 169.89 8.91 19 48.72 5.47 高易发 303.28 15.90 12 30.77 1.93 中易发 269.10 14.11 3 7.69 0.55 低易发 1164.73 61.08 5 12.82 0.21 CF-LR 极高易发 183.43 9.62 19 48.72 5.06 高易发 284.62 14.92 13 33.33 2.23 中易发 233.42 12.24 2 5.13 0.42 低易发 1205.53 63.22 5 12.82 0.20 WF-LR 极高易发 168.77 8.85 20 51.28 5.79 高易发 302.78 15.88 12 30.77 1.94 中易发 278.71 14.62 2 5.13 0.35 低易发 1156.74 60.66 5 12.82 0.21 NFR-LR 极高易发 129.04 6.77 19 48.72 7.20 高易发 248.98 13.06 10 25.64 1.96 中易发 519.76 27.26 5 12.82 0.47 低易发 1009.23 52.92 5 12.82 0.24 (2)精度对比
采用Sridevi Jadi经验概率法[31]评估各模型滑坡易发性预测的准确性,其表达式为:
P=KsS(1−(K−Ks)/(N−S))1/3 (13) 式中:P——预测精度值;
N——评价单元总数;
S——存在滑坡的单元总数;
K——滑坡易发性为中、高和极高的单元总数;
Ks——存在滑坡的中、高、极高易发性单元总数。
评价计算结果显示,4种耦合模型的预测精度P值分别为80%(I-LR)、80%(CF-LR)、80%(WF-LR)、76%(NFR-LR),前三种耦合模型预测精度几乎相同,NFR-LR耦合模型预测精度稍差。
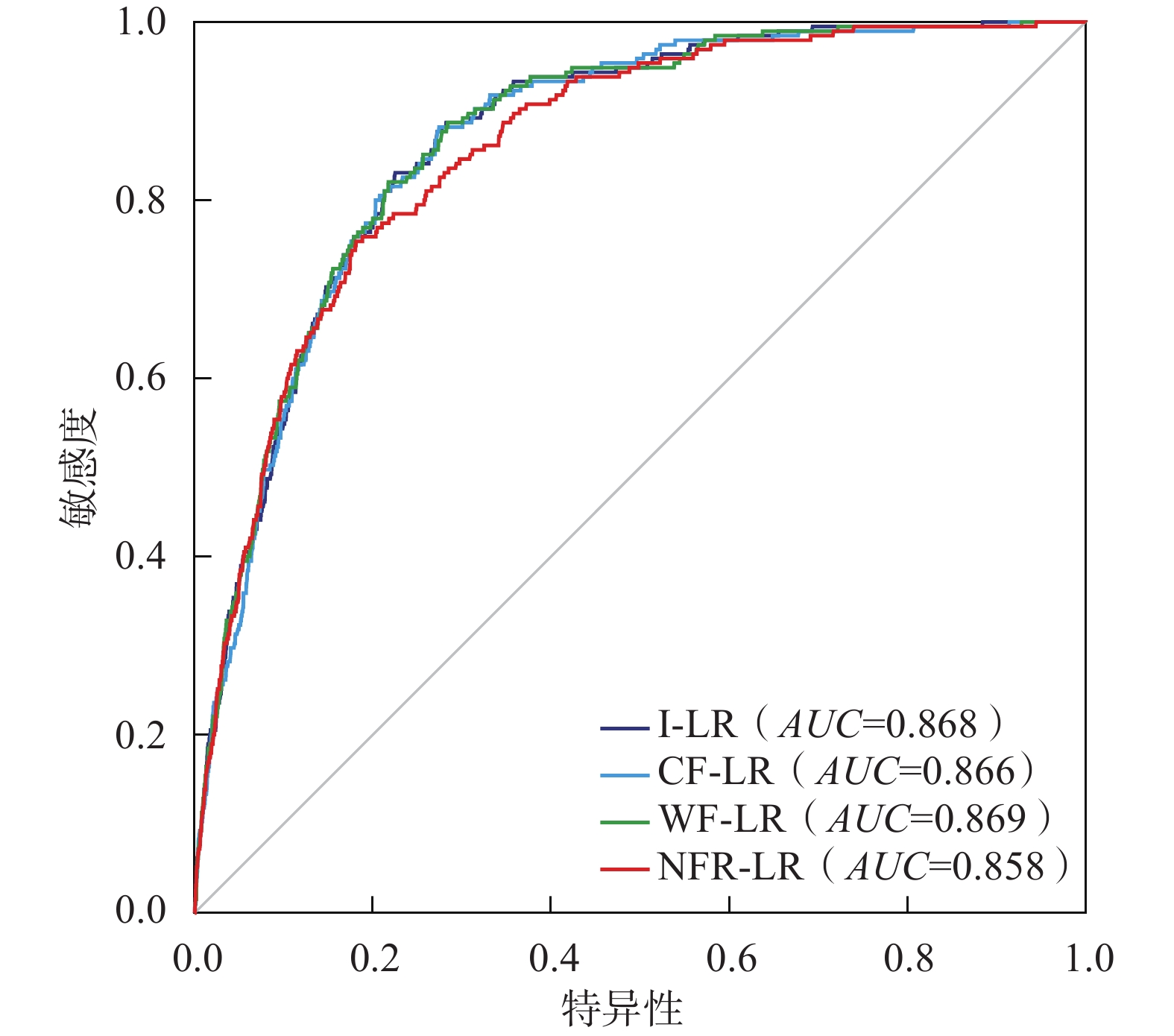
此外,ROC曲线也是目前检验滑坡易发性评价准确性最常用的手段之一[30],其作为一种二元分类模型,通过计算样本真阳性率(灵敏度)和假阳性率(1-特异度)并分别作为纵坐标和横坐标绘制ROC曲线。ROC曲线下的面积(Area Under Curve,AUC),作为数值可以直观的呈现评价结果的精准度,具有很好的客观性和有效性,其值越大,预测精度越高。
各耦合模型ROC曲线AUC值总体差异不大(图4),均大于0.85,表明4种耦合模型均能够客观准确的对普格县滑坡灾害易发性进行分级评价,且预测结果准确率由高到低依次为WF-LR模型(AUC=0.869)>I-LR模型(AUC=0.868)>CF-LR模型(AUC=0.866)>NFR-LR模型(AUC=0.858)。
4. 结论
(1)基于信息量模型(I)、确定性系数模型(CF)、证据权模型(WF)、频率比模型(FR)分别与逻辑回归模型(LR)进行耦合,选取坡度、坡向、高程、工程地质岩组、距断层距离和斜坡结构等6项孕灾因子,开展普格县滑坡易发性评价,各耦合模型获取的极高易发区面积(占比)分别为169.89 km2(8.9%,I-LR)、183.43 km2(9.62%,CF-LR)、168.77 km2(8.85%,WF-LR)和129.04 km2(6.77%,NFR-LR),4种耦合模型评价结果和易发程度区划均是合理的。
(2)普格县滑坡发育的极高、高易发区主要位于则木河和黑水河河谷区,尤其是普格县城-普基镇-花山镇一带,滑坡主要分布在坡度10°~30°,坡向西、西南,海拔1250~1500 m,软硬相间碎屑岩岩组,距断层距离1 km内,斜坡结构为顺向坡和松散土质斜坡等因子类别内。
(3)4种耦合模型均能够客观准确的对普格县滑坡易发性进行分级评价,预测结果准确率由高到低依次为WF-LR模型(AUC=0.869)>I-LR模型(AUC=0.868)>CF-LR模型(AUC=0.866)>NFR-LR模型(AUC=0.858)。
-
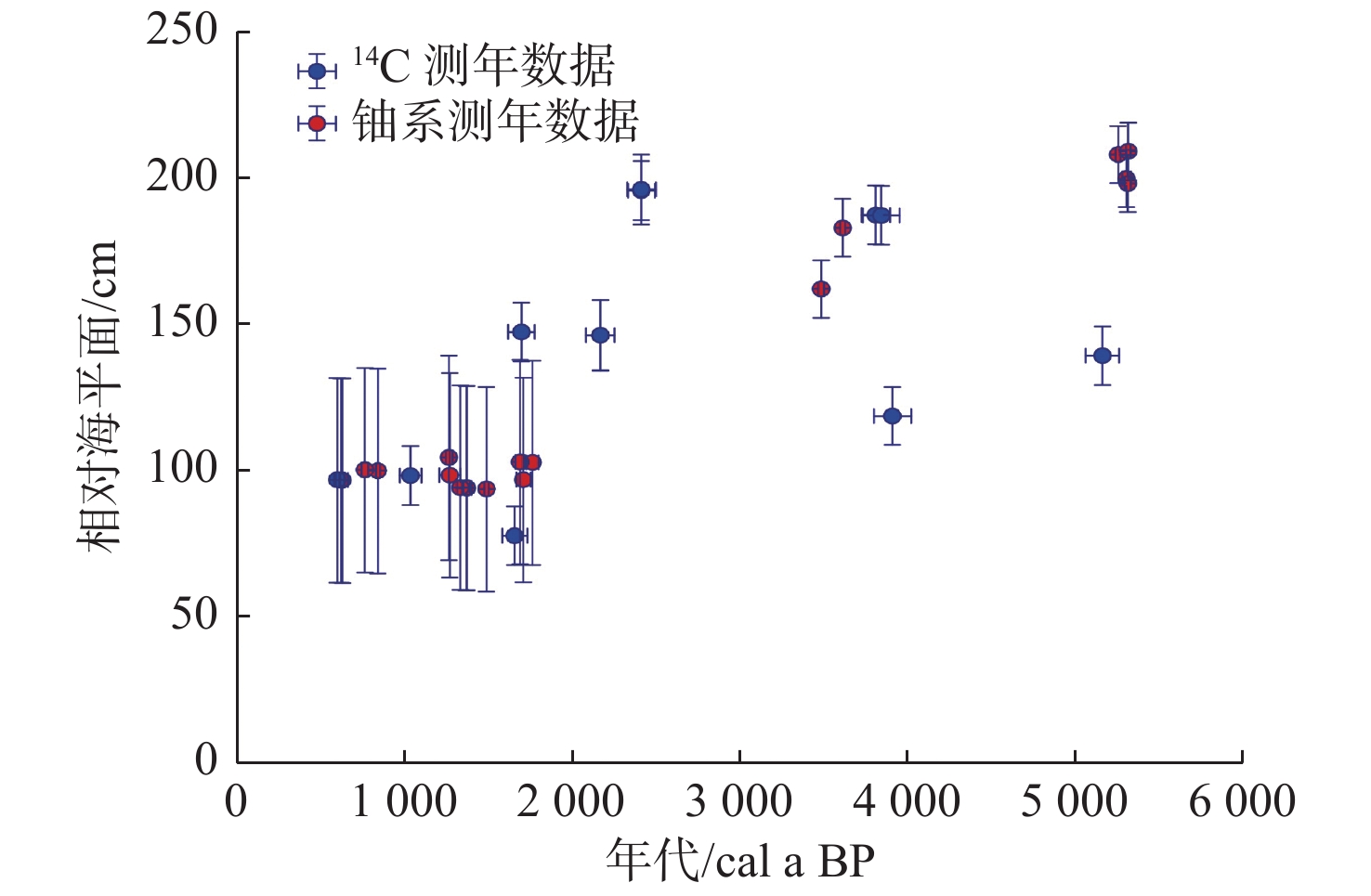
表 1 南海北部海南岛东部沿岸珊瑚样品的同位素数据和铀系年龄[31]
Table 1. The isotopic data and U-series ages of the coral samples from the eastern coast of Hainan Island, the northern South China Sea [31]
样本编号 U /
(μg/g)±2σ 232Th /
(ng/g)±2σ 230Th/ 232Th ±2σ 230Th/238U ±2σ 234U/ 238U ±2σ 年龄/
a BP±2σ 年龄/
cal a BP±2σ 校正后234U/ 238U值 ±2σ δ 234U/‰ ±2σ TGLC-001 3.151 6 0.002 8 5.825 6 0.006 1 91.39 0.16 0.055 68 0.000 09 1.146 5 0.001 6 5423 12 5375 27 1.148 8 0.001 6 148.8 1.6 TGLC-002 3.167 7 0.002 3 3.12 0.004 1 170.77 0.44 0.055 43 0.000 13 1.144 9 0.001 1 5406 14 5381 19 1.147 2 0.001 1 147.2 1.1 TGLC-003 3.013 0.002 3 2.314 7 0.002 8 151.47 0.43 0.038 35 0.000 1 1.147 6 0.001 6 3704 11 3684 15 1.149 1 0.001 6 149.1 1.6 TGLC-004 2.921 8 0.002 3.154 5 0.003 5 104.53 0.23 0.037 19 0.000 08 1.149 7 0.001 3 3584 9 3556 16 1.151 2 0.001 3 151.2 1.3 QGC-001 2.912 6 0.001 3 2.150 5 0.002 3 225.62 0.46 0.054 9 0.000 1 1.147 1 0.001 1 5343 11 5324 15 1.149 3 0.001 1 149.3 1.1 QGC-002 2.820 7 0.002 2 1.022 1 0.001 3 464.19 1.05 0.055 43 0.000 11 1.1475 0.0013 5394 13 5385 14 1.149 8 0.001 3 149.8 1.3 注:表内数据源自文献[31]。 表 2 南海北部海滩岩记录的过去海平面变化信息(14C测年)[22, 25, 59-68]
Table 2. The past sea-level change recorded by beachrock in the northern South China Sea (14C dating) [22, 25, 59-68]
区域 点位 样品编号 纬度/(N) 经度/(E) 未校正年龄/
a BP±2σ 误差 海平面高程/cm 校正后年龄a/
cal a BP构造抬升高程b/cm 校正后的海平面高程c/cm 数据来源 下限年龄 上限年龄 中值年龄 珠三角 深圳西冲 西冲砂堤 25°07' 104°06' 2 179 85 250 1 357 1 617 1 497 3.29 246.71 [64] 珠三角 惠州碧甲 亚妈庙沙堤 25°11' 119°16' 2 415 80 200 1 627 1 905 1 771 3.90 196.10 [64] 粤东 汕头大屿山 贝澳湾内沙堤 23°02'—23°38' 116°14'—117°19' 2 820 95 170 2 104 2 431 2 271 4.54 165.46 [64] 粤东 汕头大屿山 贝澳湾内沙堤 23°02'—23°38' 116°14'—117°19' 2 380 90 50 1 578 1 870 1 729 3.46 46.54 [64] 粤东 汕头大屿山 贝澳湾内沙堤 23°02'—23°38' 116°14'—117°19' 1 700 80 −4 889 1 136 1 004 2.01 −6.01 [64] 粤东 汕头大屿山 贝澳湾内沙堤 23°02'—23°38' 116°14'—117°19' 1 660 75 80 833 1 078 962 1.92 78.08 [64] 粤东 汕头大屿山 长沙湾海滩 23°02'—23°38' 116°14'—117°19' 1 300 60 0 524 693 617 1.23 −1.23 [64] 粤西 茂名电白 茂名电白 21°29' 110°53' 5 520 130 100 5 351 5 721 5 545 11.09 88.91 [60] 粤东 潮州饶平 潮州饶平 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 5 160 100 150 4 950 5 304 5 129 10.26 139.74 [60] 北部湾 广西涠洲岛 涠洲岛 21°02' 109°06' 6 000 100 600 5 909 6 216 6 064 12.13 587.87 [60] 海南岛 乐东莺歌海 莺歌海 19°11' 110°57' 5 995 95 0 5 908 6 207 6 059 21.21 −21.21 [60] 粤东 汕头河浦 KWG-310 23°26' 116°60' 3 320 100 500 2 734 3 033 2 889 5.78 494.22 [66] 粤东 汕头澄海 KWG-440 23°46' 116°75' 2 485 70 250 1 721 1 981 1 855 3.71 246.29 [66] 粤东 惠州惠东 平海岭头 22°98' 114°72' 2 415 85 200 1 623 1 910 1 771 3.54 196.46 [66] 珠三角 深圳西冲 KWG-209 25°07' 104°06' 2 170 85 150 1 350 1 607 1 488 3.27 146.73 [66] 粤东 汕头南澳 KWG-307 23°42' 117°02' 1 990 80 350 1 171 1 411 1 299 2.60 347.40 [66] 粤东 汕头南澳 2-① 23°42' 117°02' 3 230 100 251 2 631 2 946 2 781 5.56 245.44 [63] 粤东 汕头南澳 2-② 23°42' 117°02' 3 460 100 254 2 884 3 206 3 052 6.10 247.90 [63] 粤东 潮州饶平 1-⑤ 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 3 050 100 88 2 407 2 711 2 555 5.11 82.89 [63] 粤东 潮州饶平 1-④ 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 3 260 95 69 2 680 2 973 2 818 5.64 63.36 [63] 粤东 潮州饶平 1-③ 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 3 500 100 15 2 935 3 259 3 100 6.20 8.80 [63] 粤东 潮州饶平 1-② 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 3 670 105 −28 3 144 3 466 3 306 6.61 −34.61 [63] 粤东 潮州饶平 1-① 23°28'—24°14' 116°35'—117°11' 3 880 120 −104 3 382 3 739 3 569 7.14 −111.14 [63] 珠三角 江门台山 海晏公角 22°15' 112°48' 3 910 110 127 3 434 3 774 3 605 7.93 119.07 [63] 珠三角 江门台山 海晏公角 22°15' 112°48' 3 600 100 52 3 063 3 378 3 221 7.09 44.91 [63] 珠三角 江门台山 海晏公角 22°15' 112°48' 2 560 95 360 1 793 2 105 1 949 4.29 355.71 [63] 珠三角 深圳西冲 深圳大鹏西冲 25°07' 104°06' 2 485 85 250 1 707 1 992 1 856 4.08 245.92 [63] 雷州半岛 雷州半岛南部 雷州半岛南部 20°91' 110°09' 1 040 65 100 306 492 398 1.39 98.61 [63] 海南岛 三亚大东海 三亚大东海 18°19' 109°28' 5 450 190 60 5 230 5 726 5 462 19.12 40.88 [22] 海南岛 乐东莺歌海 乐东莺歌海 19°11' 110°57' 4 365 85 100 4 051 4 368 4 197 14.69 85.31 [22] 海南岛 三亚鹿回头 鹿回头水尾岭 18°21' 109°49' 4 345 210 200 3 863 4 453 4 169 14.59 185.41 [22] 海南岛 三亚东瑁岛 东瑁岛东岸 18°09'—18°37' 108°56'—109°48' 3 865 85 230 3 398 3 685 3 548 12.42 217.58 [22] 海南岛 三亚东瑁岛 东瑁岛西岸 18°09'—18°37' 108°56'—109°48' 3 810 85 200 3 342 3 625 3 482 12.19 187.81 [22] 海南岛 三亚鹿回头 鹿回头水尾岭 18°21' 109°49' 3 630 190 400 2 989 3 499 3 257 11.40 388.60 [22] 粤东 揭阳惠来 惠来龙江新开河 22°53'—23°46' 115°36'—116°37' 3 290 110 0 2 700 3 021 2 854 6.28 −6.28 [22] 海南岛 三亚马岭 三亚马岭 18°09'—18°37' 108°56'—109°48' 2 630 75 0 1 886 2 169 2 036 7.13 −7.13 [22] 海南岛 临高美夏 临高美夏 19°34'—20°20' 109°03'—109°53' 2 160 90 0 1 339 1 602 1 478 5.17 −5.17 [22] 海南岛 文昌烟墩 烟墩二公滩 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 1 890 90 300 1 062 1 309 1 192 4.17 295.83 [22] 粤西 阳江海陵 海陵劳元 21°28'—22°41' 111°16'—112°21' 1 650 70 220 826 1063 951 2.09 217.91 [22] 海南岛 三亚小东海 三亚小东海 18°09'—18°37' 108°56'—109°48' 1 190 70 0 449 630 531 1.86 −1.86 [22] 海南岛 东方八所 东方八所 18°43'—19°38' 108°36'—109°07' 1 020 90 0 277 496 378 1.32 −1.32 [22] 海南岛 乐东九所 乐东九所 18°43'—19°38' 108°36'—109°07' 1 020 90 0 277 496 378 1.32 −1.32 [22] 海南岛 三亚鹿回头 31 18°21' 109°49' 3 750 190 300 3 154 3 673 3 409 11.93 288.07 [65] 海南岛 文昌烟墩 45 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 2 054 109 100 1 235 1 519 1 369 4.79 95.21 [65] 海南岛 文昌烟墩 58 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 1 020 80 400 284 489 380 1.33 398.67 [65] 海南岛 三亚海头 9 18°09'—18°37' 108°56'—109°48' 4 439 132 0 4 087 4 499 4 292 15.02 −15.02 [67] 海南岛 三亚天涯海角 13 18°29' 109°34' 4 170 140 60 3 715 4 146 3 940 13.79 46.21 [67] 海南岛 三亚天涯海角 17 18°29' 109°34' 3 844 109 200 3 358 3 687 3 525 12.34 187.66 [67] 海南岛 三亚天涯海角 29 18°29' 109°34' 3 333 114 0 2 736 3 063 2 906 10.17 −10.17 [67] 海南岛 三亚大东海 51 18°19' 109°28' 2 360 90 50 1 550 1 840 1 705 5.97 44.03 [67] 海南岛 三亚大东海 54 18°19' 109°28' 2 325 75 0 1 530 1 790 1 662 5.82 −5.82 [67] 海南岛 文昌烟墩 55 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 2 212 132 50 1 359 1 700 1 540 5.39 44.61 [67] 海南岛 临高龙豪 57 19°34'—20°20' 109°03'—109°53' 2 141 81 0 1 325 1 570 1 457 5.10 −5.10 [67] 海南岛 儋州排浦 67 19°63' 109°16' 1 087 86 0 321 535 438 1.53 −1.53 [67] 珠三角 香港贝澳 香港贝澳 22°32' 114°17' 1 700 80 150 889 1 136 1 004 2.21 147.79 [61] 海南岛 西沙东岛 西沙东岛 16°33' 112°02' 3 630 150 - 3 040 3 460 3 256 - - [22] 海南岛 西沙东岛 西沙东岛 16°33' 112°02' 3 250 120 - 2 637 2 994 2 806 - - [22] 海南岛 西沙群岛 永兴岛西北 16°50' 112°20' 2 760 90 - 2 040 2 338 2 195 - - [63] 粤东 汕头广澳 汕头广澳 23°22' 116°78' 1 725 125 - 881 1 192 1 028 - - [59] 粤东 汕头广澳 汕头广澳 23°22' 116°78' 2 725 125 - 1 966 2 334 2 154 - - [59] 粤东 汕头广澳 汕头广澳 23°22' 116°78' 3 225 125 - 2 590 2 965 2 773 - - [59] 粤东 潮州海山岛 潮州海山岛 23°41' 116°59' 1 725 125 - 881 1 192 1 028 - - [59] 粤东 潮州海山岛 潮州海山岛 23°41' 116°59' 2 725 125 - 1 966 2 334 2 154 - - [59] 粤东 潮州海山岛 潮州海山岛 23°41' 116°59' 3 225 125 - 2 590 2 965 2 773 - - [59] 粤东 潮州海山岛 潮州海山岛 23°41' 116°59' 3 725 125 - 3192 3560 3 376 - - [59] 珠三角 香港贝澳 香港贝澳 22°32' 114°17' 1 610 70 - 785 1 018 907 - - [61] 海南岛 西沙东岛 7 16°33' 112°02' 4 856 200 - 4 547 5 111 4 830 - - [67] 海南岛 西沙东岛 26 16°33' 112°02' 3 417 136 - 2 803 3 183 3 004 - - [67] 海南岛 西沙东岛 27 16°33' 112°02' 3 378 133 - 2 765 3 133 2 959 - - [67] 海南岛 海南抱虎港 碎屑上层 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 3 340 30 - 2 782 2 993 2 902 - - [62] 海南岛 海南抱虎港 粗砂层 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 3 400 30 - 2 855 3 080 2 975 - - [62] 海南岛 海南抱虎港 碎屑下层 19°20'—20°10' 108°21'—111°03' 3 510 30 - 2 997 3 225 3 114 - - [62] 海南岛 西沙群岛
广金岛GJ 16°27' 111°42' 1 850 30 - 1 070 1 251 1 156 - - [25] 海南岛 西沙群岛
永兴岛YX 16°50' 112°20' 1 250 30 - 509 646 578 - - [25] 海南岛 三亚鹿回头 LH 18°21' 109°49' 3 160 30 - 2 588 2 799 2 695 - - [25] 粤东 潮州海山岛 Bed-12 23°41' 116°59' 2 910 30 - 2 284 2 514 2 395 - - [68] 粤东 潮州海山岛 Bed-10 23°41' 116°59' 3 530 30 - 3 024 3 252 3 140 - - [68] 粤东 潮州海山岛 Bed-5 23°41' 116°59' 3 720 30 - 3 259 3 464 3 370 - - [68] a:对表2中的原始数据(即未校正的数据),使用最新的CALIB 8.0重新校正。使用海洋校正曲线Marine 20,并考虑北半球碳库效应与区域海洋碳库校正值。5000 a BP之前的区域海洋碳库效应年龄偏差δR为(151±85) a,之后的为(89±59) a。b:考虑南海北部构造作用的影响,本文以平均速率0.035 mm/a计算雷琼区域海平面受构造抬升运动的影响,珠江三角洲的构造抬升速率为0.022 mm/a,北部湾及其他地区的构造抬升速率为0.020 mm/a。c:RSL=A-TUE, A为原海平面高程,TUE为平均构造抬升高程,RSL为校正后海平面高程。 表 3 南海北部海滩岩和新增珊瑚样品记录的过去海平面变化信息(铀系测年)[31, 51]
Table 3. The past sea-level change recorded by beachrock and the newly added coral samples in the northern South China Sea (U-series dating) [31, 51]
区域 点位 样品编号 标志物 纬度/
(°N)经度/
(°E)校正后234U/ 238U值 ±2σ δ 234U/
‰±2σ 未校正年龄/
a BP±2σ 校正后年龄/
cal a BP±2σ 日历年龄
(距1950年年龄)/
cal a BP±2σ 海平面高程/cm 误差 数据来源 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 7th layer of BG 海滩岩 21°04' 109°06' 1.147 2 0.6 147.2 0.6 928 10 913 12 845 12 100.3 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 6th layer of BG 海滩岩 21°04' 109°06' 1.147 1 0.6 147.1 0.6 866 13 836 20 768 20 100.6 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of BG 海滩岩 21°04' 109°06' 1.148 4 1.5 148.4 1.5 1457 22 1342 62 1274 62 98.8 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of BG 海滩岩 21°04' 109°06' 1.144 1.5 144.0 1.5 1844 26 1780 42 1712 42 97.3 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of GSB 海滩岩 21°03' 109°08' 1.146 8 1.6 146.8 1.6 1880 26 1834 35 1766 35 103.1 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of GSB 海滩岩 21°03' 109°08' 1.146 5 1.7 146.5 1.7 1771 25 1760 26 1692 26 103.3 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of GSB 海滩岩 21°03' 109°08' 1.1456 1.3 145.6 1.3 1358 19 1337 21 1269 21 104.8 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of HL-I 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.146 1 0.8 146.1 0.8 1490 15 1443 28 1375 28 94.4 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of HL-I 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.146 0.7 146.0 0.7 1572 13 1561 14 1493 14 94.0 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of HL-II 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.147 3 0.8 147.3 0.8 706 13 701 13 633 13 97.0 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 3th layer of HL-II 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.146 0.7 146.0 0.7 1468 14 1441 19 1373 19 94.4 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of HL-II 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.146 0.7 146.0 0.7 1411 19 1405 19 1337 19 94.6 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of HL-III 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.147 2 0,8 147.2 0,8 774 12 694 41 626 41 97.1 35 [51] 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 3th layer of HL-III 海滩岩 21°02' 109°08' 1.147 6 0.7 147.6 0.7 683 8 672 10 604 10 97.1 35 [51] 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-001 珊瑚 19°63' 111°02' 1.148 8 1.6 148.8 1.6 5423 12 5375 27 5304 27 200.2 9.8 [31] 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-002 珊瑚 19°63' 111°02' 1.1472 1.1 147.2 1.1 5406 14 5381 19 5310 19 198.5 9.8 [31] 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-003 珊瑚 19°64' 111°01' 1.149 1 1.6 149.1 1.6 3704 11 3684 15 3613 15 183.4 9.8 [31] 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-004 珊瑚 19°64' 111°01' 1.151 2 1.3 151.2 1.3 3584 19 3556 16 3485 16 162.5 9.8 [31] 海南岛 青葛 QGC-001 珊瑚 19°31' 110°66' 1.149 3 1.1 149.3 1.1 5343 11 5324 15 5253 15 208.4 9.8 [31] 海南岛 青葛 QGC-002 珊瑚 19°31' 110°66' 1.149 8 1.3 149.8 1.3 5394 13 5385 14 5314 14 209.5 9.8 [31] 表 4 选取的指示南海北部过去海平面的海滩岩和珊瑚礁数据(校正前)
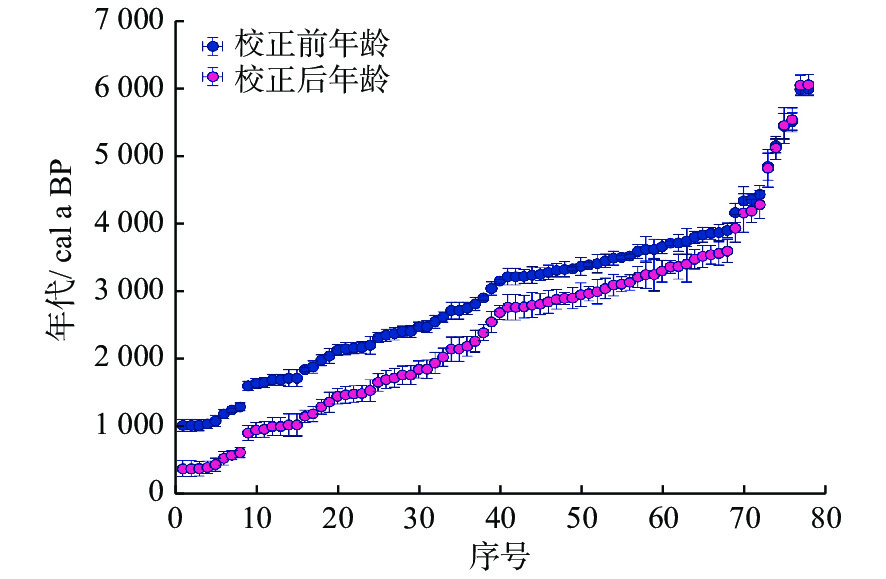
Table 4. Selected beachrocks and corals indicating the ancient sea-level in the northern South China Sea(before correction)
序号 区域 点位 样品编号 测年方法 未校正年龄
/a BP±2σ 误差 海平面高程
/cm误差 1 珠三角 惠州碧甲 亚妈庙沙堤 14C测年 2 415 80 196.10 10.0 2 粤东 汕头大屿山 贝澳湾内沙堤 14C测年 1 660 75 78.08 10.0 3 粤东 潮州饶平 潮州饶平 14C测年 5 160 100 139.74 10.0 4 粤东 惠州惠东 平海岭头 14C测年 2 415 85 196.46 12.0 5 珠三角 深圳西冲 KWG-209 14C测年 2 170 85 146.73 12.0 6 珠三角 江门台山 海晏公角 14C测年 3 910 110 119.07 10.0 7 雷州半岛 雷州半岛南部 雷州半岛南部 14C测年 1 040 65 98.61 10.0 8 海南岛 三亚东瑁岛 东瑁岛西岸 14C测年 3 810 85 187.81 10.0 9 海南岛 三亚天涯海角 17 14C测年 3 844 109 187.66 10.0 10 珠三角 香港贝澳 香港贝澳 14C测年 1 700 80 147.79 10.0 11 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 7th layer of BG 铀系测年 845 12 100.3 35.0 12 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 6th layer of BG 铀系测年 768 20 100.6 35.0 13 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of BG 铀系测年 1 274 62 98.8 35.0 14 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of BG 铀系测年 1 712 42 97.3 35.0 15 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of GSB 铀系测年 1 766 35 103.1 35.0 17 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of GSB 铀系测年 1 692 26 103.3 35.0 18 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of GSB 铀系测年 1 269 21 104.8 35.0 19 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of HL-I 铀系测年 1 375 28 94.4 35.0 20 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 1th layer of HL-I 铀系测年 1493 14 94.0 35.0 21 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of HL-II 铀系测年 633 13 97.0 35.0 22 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 3th layer of HL-II 铀系测年 1 373 19 94.4 35.0 23 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 2th layer of HL-II 铀系测年 1 337 19 94.6 35.0 24 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 4th layer of HL-III 铀系测年 626 41 97.1 35.0 25 北部湾 涠洲岛 The 3th layer of HL-III 铀系测年 604 10 97.1 35.0 26 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-001 铀系测年 5 304 27 200.2 9.8 27 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-002 铀系测年 5 310 19 198.5 9.8 28 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-003 铀系测年 3 613 15 183.4 9.8 29 海南岛 铜鼓岭 TGLC-004 铀系测年 3 485 16 162.5 9.8 30 海南岛 青葛 QGC-001 铀系测年 5 253 15 208.4 9.8 31 海南岛 青葛 QGC-002 铀系测年 5 314 14 209.5 9.8 -
[1] KOPP R E,KEMP A C,BITTERMANN K,et al. Temperature-driven global sea-level variability in the Common Era[J]. PNAS,2016,113(11):E1434.
[2] WEBSTER J M,GEORGE N P J,BEAMAN R J,et al. Submarine landslides on the Great Barrier Reef shelf edge and upper slope:a mechanism for generating tsunamis on the north-east Australian coast?[J]. Marine Geology,2015,371(1):120-129.
[3] ZHANG Y Z,XIE J Z,LIU L. Investigating sea-level change and its impact on Hong Kong's coastal environment[J]. Geographic Information Sciences,2011,17(2):105-112.
[4] FREDERIKSE T, LANDERER F,CARON L,et al. The causes of sea-level rise since 1900[J]. Nature,2020,584(7821):393-397. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2591-3
[5] LIU W C,HUANG W C. Influences of sea level rise on tides and storm surges around the Taiwan coast[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2018,173:9-13.
[6] WILES E,GREEN A N,COOPER J A G. Rapid beachrock cementation on a South African beach:linking morphodynamics and cement style[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2018,378(10):13-18.
[7] BONADUCE A,PINARDI N,ODDO P,et al. Sea-level variability in the Mediterranean Sea from altimetry and tide gauges[J]. Climate Dynamics,2016,47(9/10):1-16.
[8] CHEN X Y,ZHANG X B,CHURCH J A,et al. The increasing rate of global mean sea-level rise during 1993–2014[J]. Nature Climate Change,2017,7(7):492-495. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3325
[9] CHURCH J A,WHITE N J. Sea-level rise from the late 19th to the early 21st Century[J]. Surveys in Geophysics,2011,32(4):585-602.
[10] DEAN R G,HOUSTON J R. Recent sea level trends and accelerations:comparison of tide gauge and satellite results[J]. Coastal Engineering,2013,75(5):4-9.
[11] 刘振夏. 中国现代海平面变化及影响[J]. 海洋开发与管理,1991,8(3):17-20.
[12] 胡志博,郭金运,谭争光,等. 由TOPEX/Poseidon和验潮站监测香港海平面变化[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2014,34(4):56-59.
[13] 李大炜,李建成,团文征. 利用卫星测高与验潮站数据监测越南近海海平面变化[J]. 测绘通报,2017,1(6):1-4.
[14] 陆青,左军成,吴灵君. 热带太平洋海平面低频变化[J]. 海洋学报,2017,39(7):43-52.
[15] 汤超莲,游大伟,陈特固,等. 1986―2008年广东沿海海平面变化趋势[J]. 热带地理,2009,29(5):423-428.
[16] 余克服,陈特固. 南海北部晚全新世高海平面及其波动的海滩沉积证据[J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(6):138-145.
[17] ZONG Y Q. Mid-Holocene sea-level highstand along the Southeast Coast of China[J]. Quaternary International,2004,117(1):55-67. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00116-2
[18] XIONG H X,ZONG Y Q,PENG Q. Holocene sea-level history of the northern coast of South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2018,194(15):12-26.
[19] 乐远福,唐立超,余克服. 北大西洋沿岸过去2 000年海平面变化的若干重要特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2022,38(6):1-15.
[20] 乐远福. 南海北部全新世以来海平面变化特征及未来趋势预测[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2023,39(2):1-16.
[21] 黄金森,朱袁智,沙庆安. 西沙群岛现代海滩岩岩石学初见[J]. 地质科学,1978,13(4):358-364.
[22] 李平日. 华南全新世海滩岩及其古地理意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1988,1(4):25-33.
[23] 王绍鸿. 福建全新世海滩岩及其地质意义[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版),1995,1(4):106-112.
[24] 赵希涛,沙庆安,冯文科. 海南岛全新世海滩岩[J]. 地质科学,1978,1(2):67-77,98,103-105.
[25] 朱长歧,周斌,刘海峰. 南海海滩岩的细观结构及其基本物理力学性质研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(4):683-693.
[26] DARYONO L R,NAKASHIMA K,KAWASAKI S,et al. Sediment characteristics of beachrock:a baseline investigation based on microbial induced carbonate precipitation at Krakal-Sadranan Beach,Yogyakarta,Indonesia[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(2):520. doi: 10.3390/app10020520
[27] FALKENROTH M,SCHNEIDER B,HOFFMANN G. Beachrock as sea-level indicator:a case study at the coastline of Oman (Indian Ocean)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2019,206(15):81-98.
[28] GASSE F,FONTES J C,CAMPO E V,et al. Holocene environmental changes in Bangong Co Basin (Western Tibet). Part 4:Discussion and conclusions[J]. Palaeogeography,1996,120(1/2):79-92.
[29] 孙金龙,徐辉龙. 中国的海滩岩研究与进展[J]. 热带海洋学报,2009,1(2):103-108.
[30] 詹文欢,刘以宣. 粤东沿海全新世海滩岩的特征及其所反映的海平面变化[J]. 热带海洋学报,1998,17(2):24-31.
[31] YUE Y F, TANG L C, YU K F, et al. Coral reef records of sea-level highstand and climate events in northern South China Sea during the Mid-Holocene [J]. Unpublished.
[32] 张乔民,隋淑珍. 中国红树林湿地资源及其保护[J]. 自然资源学报,2001,16(1):28-36.
[33] 曾丽丽,施平,王东晓,等. 南海蒸发和净淡水通量的季节和年际变化[J]. 地球物理学报,2009,52(4):929-938.
[34] WANG Y J,CHENG H,Edwards R L. The Holocene Asian monsoon:links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science,2007,308(5723):854-857.
[35] 刘秦玉,李薇,徐启春. 东北季风与南海海洋环流的相互作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼,1997,28(5):493-502.
[36] XIAN L Z,FAN Q Y,ZENG G,et al. The variation of the low-level cross-equatorial flow over the South China Sea and its association with the East Asian summer monsoon in midsummer[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology,2018,34(3):339-346.
[37] YUE Y F,YU K F,TAO S C,et al. 3500-year western Pacific storm record warns of additional storm activity in a warming warm pool[J]. Palaeogeography,2019,521:57-71. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.02.009
[38] 杨庆轩,梁鑫峰,田纪伟,等. 南海北部海流观测结果及其谱分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼,2008,39(6):561-568.
[39] QI H E,WEI Z,WANG Y. Study on the sea currents in the northern shelf and slope of the South China Sea based on the observation[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2012,34(1):17-28.
[40] 郭忠信,杨天鸿,仇德忠. 冬季南海暖流及其右侧的西南向海流[J]. 热带海洋学报,1985,1(1):3-11.
[41] 毕福志,袁义申,尹云鹏. 广东海山岛晚全新世"海滩岩田"的沉积相及其海岸升降特征的研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1987,2(2):47-59.
[42] 毕福志,袁又申. 山东乳山海滩岩及其重要科学意义[J]. 现代地质,1991,1(2):85-91.
[43] 张明书. 关于海滩岩几个问题的初步研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1985,1(2):107-114.
[44] 王国忠. 南海珊瑚礁区沉积学 [M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2001: 1-336.
[45] 王雪木,陈万利,薛玉龙,等. 西沙群岛宣德环礁晚第四纪灰砂岛沉积地层[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(6):37-45.
[46] 孙志鹏,许红,王振峰,等. 西沙群岛海滩岩类型及其油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质动态,2010,26(7):1-6.
[47] YU K F,HUA Q,ZHAO J X,et al. Holocene marine C-14 reservoir age variability:evidence from Th-230-dated corals in the South China Sea[J]. Paleoceanography,2010,25(2):25-40.
[48] FANG X Q,HOU G L. Synthetically reconstructed Holocene temperature change in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2011,31(4):385-393.
[49] STOULOS S,SAMARTZIDOU E,MANIATIS Y,et al. U-series geochronology using the spectrometry method cooperated with C-14 dating results[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry,2018,318(3):1837-1843. doi: 10.1007/s10967-018-6054-3
[50] 刘文会,余克服,王瑞,等. 涠洲岛北港海滩岩的铀系年代及其海平面指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2020,40(3):764-774.
[51] YAN T L, YU K F, WANG R,et al. Records of sea-level highstand over the Meghalayan age/late Holocene from uranium-series ages of beachrock in Weizhou Island,northern South China Sea[J]. Holocene,2021,11/12(31):1745-1760.
[52] 梁文,黎广钊. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁分布特征与环境保护的初步研究[J]. 环境科学研究,2002,15(6):5-17.
[53] 杨红强,余克服. 微环礁的高分辨率海平面指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究,2015,35(2):354-362.
[54] 时小军,余克服,陈特固,等. 中—晚全新世高海平面的琼海珊瑚礁记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(5):1-9.
[55] 聂宝符,陈特固. 雷州半岛珊瑚礁与全新世高海面[J]. 科学通报,1997,42(5):511-514.
[56] ENGELHART S E,HORTON B P,KEMP A C. Holocene sea-level changes along the United States' Atlantic Coast[J]. Oceanography,2011,24(2):70-79. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2011.28
[57] FRANCA A. Encyclopedia of modern coral reefs:structure,form and process[J]. Reference reviews,2011,25(8):39-40. doi: 10.1108/09504121111184480
[58] SHENNAN I,PELTIER W R,DRUMMOND R,et al. Global to local scale parameters determining relative sea-level changes and the post-glacial isostatic adjustment of Great Britain[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2002,21(1-3):397-408. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00091-9
[59] 毕福志,林耀光. 中国全新世海平面变化周期与世界未来海平面变化规律[J]. 第四纪研究,1991,11(1):43-54,99-100.
[60] 孙桂华,朱本铎. 南海及其周缘地区全新世海平面遗迹的构造含义[J]. 海洋学报,2009,31(5):58-68.
[61] 王为. 香港贝澳湾全新世海滩岩的发现及意义[J]. 科学通报,1993,38(3):258-260.
[62] 徐笑梅,高抒,周亮,等. 海南岛东北部海岸极端波浪事件沉积记录[J]. 海洋学报,2019,41(6):52-67.
[63] 詹文欢,刘以宣. 从广东沿海海滩岩探讨历史时期海平面变化[J]. 南海研究与开发,1996,1(4):30-25.
[64] 张崧,孙现领,王为,等. 广东深圳大鹏半岛海岸地貌特征[J]. 热带地理,2013,33(6):647-658.
[65] 张仲英,刘瑞华. 海南岛沿海的全新世[J]. 地理科学,1987,2:129-138,197.
[66] 宗永强,李平日. 粤东全新世海滩岩形成条件初步分析[J]. 热带地理,1984,4:15-22.
[67] 王建华. 华南沿海全新世海滩岩的特征及其意义[J]. 中山大学学报论丛,1992,1(1):111-122.
[68] SHEN J W, LONG J P, PEDOJA K,et al. Holocene coquina beachrock from Haishan Island,east coast of Guangdong Province,China[J]. Quaternary International,2013,310(15):199-212.
[69] STUIVIER M, REIMER P J. CALIB rev. 8. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35, 215-230.
[70] HEATON T J,KHLER P,BUTZIN M,et al. Marine20—the marine radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55,000 cal BP)[J]. Radiocarbon,2020,62(4):779-820. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2020.68
[71] YAO Y T, ZHAN W H, SUN J L,et al. Emerged fossil corals on the coast of northwestern Hainan Island,China:implications for mid-Holocene sea level change and tectonic uplift[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(23):2869-2876. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5692-7
[72] ZONG Y Q, YIM W S, YU F, et al. Late Quaternary environmental changes in the Pearl River Mouth region,China[J]. Quaternary International,2009,206(1/2):35-45.
[73] ZONG Y Q,INNES J B,WANG Z,et al. Mid-Holocene coastal hydrology and salinity changes in the east Taihu area of the lower Yangtze wetlands,China[J]. Quaternary Research,2011,76(1):69-82. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2011.03.005
[74] CHEN J H, EDWARDS R L, WASSERBURG G J. 238U,234U and 232Th in seawater[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters,1986,80(3/4):241-251.
[75] STIRLING C H,ESAT T M,MCCULLOCH M T,et al. High-precision U-series dating of corals from Western Australia and implications for the timing and duration of the Last Interglacial[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters,1995,135(1/4):115-130.
[76] 朱照宇,邱燕,周厚云,等. 南海全球变化研究进展[J]. 地质力学学报,2002,8(4):315-322,324.
[77] CHEN Y G, LIU T K. Sea Level Changes in the last several thousand years,Penghu Islands,Taiwan Strait[J]. Quaternary Research,1996,45(3):254-262. doi: 10.1006/qres.1996.0026
[78] BAKER J L,LACHNIET M S,CHERVYATSOVA O,et al. Holocene warming in western continental Eurasia driven by glacial retreat and greenhouse forcing[J]. Nature Geoscience,2017,10(6):430-435. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2953
[79] XIONG H X,ZONG Y Q, HUANG G Q,et al. Sedimentary responses to Holocene sea-level change in a shallow marine environment of southern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,166(10):95-106.
[80] XIONG H X,ZONG Y Q,LI T,et al. Coastal GIA processes revealed by the early to middle Holocene sea-level history of East China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2020,233(1):106249.
[81] 陈俊仁,陈欣树. 全新世海南省鹿回头海平面变化之研究[J]. 南海地质研究,1991,3:77-86.
[82] BAKER R G V,HAWORTH R J. Smooth or oscillating late Holocene sea-level curve? Evidence from cross-regional statistical regressions of fixed biological indicators[J]. Marine Geology,2000,163(1):353-365.
[83] 刘嘉麒,倪云燕,储国强. 第四纪的主要气候事件[J]. 第四纪研究,2001,21(3):239-248.
[84] RAJSHEKHAR C,REDDY P P. Late Quaternary beach rock formations of Andaman-Nicobar Islands,Bay of Bengal[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India,2003,62(5):595-604.
[85] CALDAS L,STATTEGGER K,VITAL H. Holocene sea-level history:evidence from coastal sediments of the northern Rio Grande do Norte coast,NE Brazil[J]. Marine Geology,2006,228(1/4):39-53.
[86] BLAAUM M. Methods and code for "classical" age-modeling of radiocarbon sequences[J]. Quaternary Geochronology,2010,5(5):512-518. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.01.002
[87] CRAIG H. Carbon 13 in Plants and the relationships between carbon 13 and carbon 14 variations in nature[J]. Journal of Geology,1954,62(2):115-149. doi: 10.1086/626141
[88] MARTIN C W. Radiocarbon dating:recent applications and future potential[J]. Geoarchaeology-an International Journal,2010,14(4):371-373.
[89] HALL B L,HENDERSON G M. Use of uranium-thorium dating to determine past 14C reservoir effects in lakes:examples from Antarctica[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2001,193(3/4):565-577.
[90] 姜帆,刘俊文,黄志炯,等. 黑碳气溶胶的稳定和放射性碳同位素研究进展[J]. 科学通报,2020,65(35):109-120.
[91] BLAAUW M, CHRISTEN J A. Flexible paleoclimate age-depth models using an autoregressive gamma process[J]. Bayesian Analysis,2011,6(3):657-674.
[92] 刘志杰,余佳,孙晓燕,等. 海洋沉积物14C测年数据整合与校正问题探讨[J]. 第四纪研究,2016,36(2):492-502.
[93] 余克服,赵建新,施祺,等. 永暑礁西南礁镯生物地貌与沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2003,23(4):1-7.
[94] 陈以健,POLACH H. 沉积物中碳酸盐14C年龄的可靠性[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,1987,2:133-141.
[95] 邓文峰,韦刚健,李献华. 有孔虫的高精度Mg/Ca比值的ICP-AES分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2005,25(2):147-151.
[96] 樊耘畅,丁旋,樊加恩,等. 东海陆架浙闽沿岸泥质区不同属种底栖有孔虫对14C测年的影响及其原因初探[J]. 第四纪研究,2018,38(3):792-798.
[97] 李建芬,苏盛伟,商志文,等. 渤海湾巨葛庄贝壳堤与下伏泥层有孔虫组合的海面变化意义[J]. 地质通报,2016,35(10):1584-1589.
[98] STIRLING C H,ANDERSEN M B. Uranium-series dating of fossil coral reefs:extending the sea-level record beyond the Last Glacial cycle[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters,2009,284(3/4):269-283.
[99] ZHAO J X ,YU K F ,FENG Y X. High-precision 238U-234U-230Th disequilibrium dating of the recent past:a review[J]. Quaternary Geochronology,2009,4(5):423-433. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2009.01.012
[100] BARD E,ARNOLD M,FAIRBANKS R G,et al. 230Th-234U and 14C ages obtained by mass spectrometry on corals[J]. Radiocarbon,1993,35:191-199. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200013886
[101] EISENHAUER A,WASSERBURG G J,CHEN J H,et al. Holocene sea-level determination relative to the Australian continent:U/Th (TIMS) and 14C (AMS) dating of coral cores from the Abrolhos Islands[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1993,114:529-547. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(93)90081-J
[102] INGRAM B L,SOUTHON J R. Reservoir ages in eastern Pacific coastal and estuarine waters[J]. Radiocarbon,1996,38:573-582. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200030101
[103] HUA Q,ULW S,Yu K F,et al. Temporal variability in the Holocene marine radiocarbon reservoir effect for the Tropical and South Pacific[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2020,249:106613. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106613
[104] ZHAO J X, YU K F. Timing of Holocene sea-level highstands by mass spectrometric U-series ages of a coral reef from Leizhou Peninsula,South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2002,47(4):348-352.
[105] 张培震,王琪,马宗晋. 中国大陆现今构造运动的GPS速度场与活动地块[J]. 地学前缘,2022,9(2):12.
[106] ZHANG P,XIA H,XIA L. Thermal Ionization Mass Spec trometry (TIMS)-U-Series ages of corals from the South China Sea and Holocene high sea level[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemisty,2003,22(2):133-139. doi: 10.1007/BF02831522
[107] MA Z B,XIAO J,ZHAO X T,et al. Precise U-series dating of coral reefs from the South China Sea and the high sea level during the Holocene[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2003,19(2):296-303.
[108] HO K S, CHEN J C, JUANG W. Geochronology and geochemistry of late Cenozoic basalts from the Leiqiong area,southern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2000,18(3):307-324. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00059-0
[109] LU R. Study on the modern crustal vertical movement in Guangdong coast[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,1997,17(1):25-33.
[110] 滕建彬,沈建伟,PEDOJA K. 深圳西冲湾的海蚀地貌与海滩沉积研究[J]. 现代地质,2007,21(3):511-517.
[111] YU K F,LIU D S. High-frequency climatic oscillations recorded in a Holocene coral reef at Leizhou Peninsula,South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,2002,45(12):1057-1067. doi: 10.1360/02yd9103
[112] 詹文欢,朱照宇,姚衍桃,等. 南海西北部珊瑚礁记录所反映的新构造运动[J]. 第四纪研究,2006,26(1):77-84.
[113] GISCHLER E,LOMANDO A J. Holocene cemented beach deposits in Belize[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1997,110(3):277-297.
[114] KINDLER P,BAIN R J. Submerged upper Holocene beachrock on San Salvador Island,Bahamas:implications for recent sea-level history[J]. Geologische Rundschau,1993,82(2):241-247.
[115] BOEYINGA J,DUSSELJEE D W,POOL A D G. The effect of beach rock formation on the morphological evolution of a beach. the case study of an eastern Mediterranean Beach:Ammoudara,Greece[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2013,69(1):65-69.
[116] 何耀堂. 福建泉州湾全新世海滩岩特征及物源环境分析[J]. 福建地质,2014,33(2):112-118.
[117] 马克俭,冯应俊. 浙江沿海全新世海滩岩的沉积相及其意义[J]. 地震地质,1993,15(3):269-276.
[118] 孙奕映,WU P,黄光庆,等. 广东全新世海平面重建与冰川均衡调整模型结果的比较[J]. 第四纪研究,2015,35(2):281-290.
[119] 聂宝符,陈特固. 雷州半岛珊瑚礁与全新世高海面[J]. 科学通报,1997,42(5):1-7.
[120] ZHANG Y,ZONG Y,XIONG H,et al. The middle-to-late Holocene relative sea-level history,highstand and levering effect on the east coast of Malay Peninsula[J]. Global and Planetary Change 2021,196,1033:69.
[121] LAMBECK K,ROUBY H,PURCELL A,et al. Inaugural article by a recently elected academy member:sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2014,111(43):211-216.
[122] 汪汉胜,贾路路,PATRICK W,等. 末次冰期冰盖消融对东亚历史相对海平面的影响及意义[J]. 地球物理学报,2012,55(4):1144-1153.
[123] BRADLEY S L,MILNE G A,TEFERLE F N,et al. Glacial isostatic adjustment of the British Isles:new constraints from GPS measurements of crustal motion[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2009,178:14-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.04033.x
[124] BRADLEY S L,MILNE G A,SHENNAN I,et al. An improved glacial isostatic adjustment model for the British Isles[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science,2011,26(5):541-552. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1481
[125] PELTIER W R. Global glacial isostasy and the surface of the ice-age earth:the ice-5g (vm2) model and grace[J]. Annual Review of Earth Planetary Sciences,2004,20(32):111-149.
[126] TURCOTTE D L,BURKE K. Global sea-level changes and the thermal structure of the earth[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters,1978,41(3):341-346. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90188-7
[127] 杨学祥. 地壳均衡与海平面变化[J]. 地球科学进展,1992,7(5):22-30.
[128] WANG L. East Asian monsoon climate during the Late Pleistocene:high-resolution sediment records from the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology,1999,156(1/4):245-284.
[129] PELTIER W R,WU P,YUEN D. The Viscosities of the Earth's Mantle[J]. American Geophysical Union,2013,4:1-16.
[130] ZONG Y,YANG Z,XIONG H,et al. The middle-to-late Holocene relative sea-level history,highstand and levering effect on the east coast of Malay Peninsula[J]. Global Planetary Change,2020,196:103369.
[131] 时小军,余克服,陈特固. 南海周边中全新世以来的海平面变化研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2007,27(5):121-132.
-




 下载:
下载: