The characteristics of topography and surface sediment distributionnear Heishi Island, Shandong Peninsula
-
摘要:
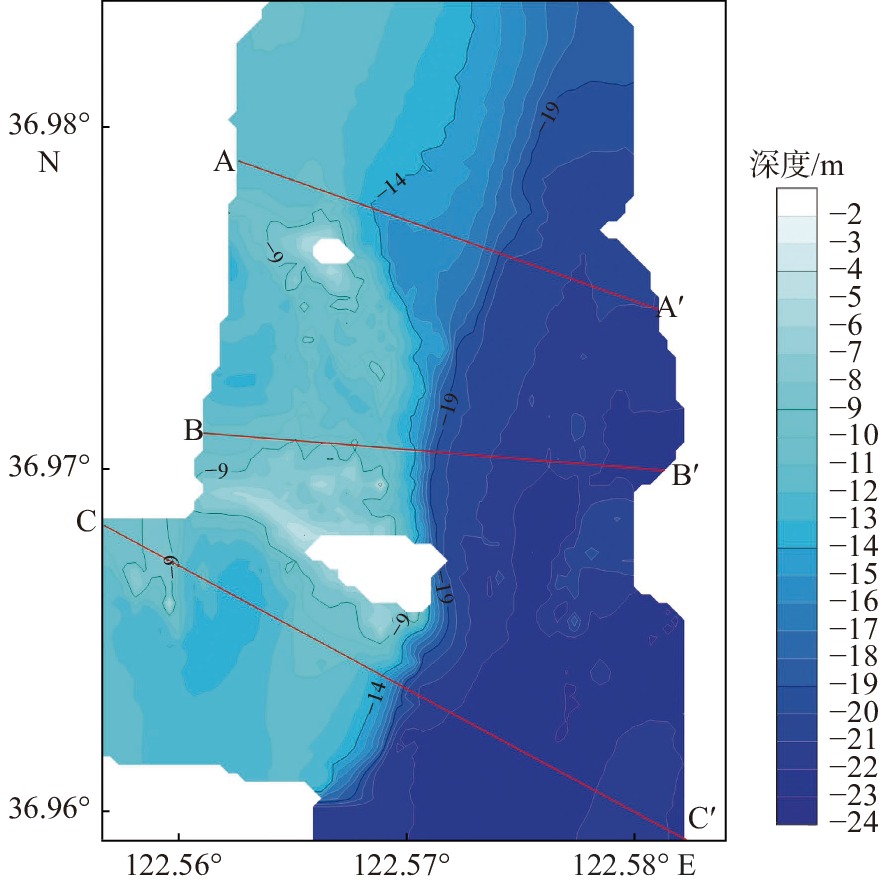
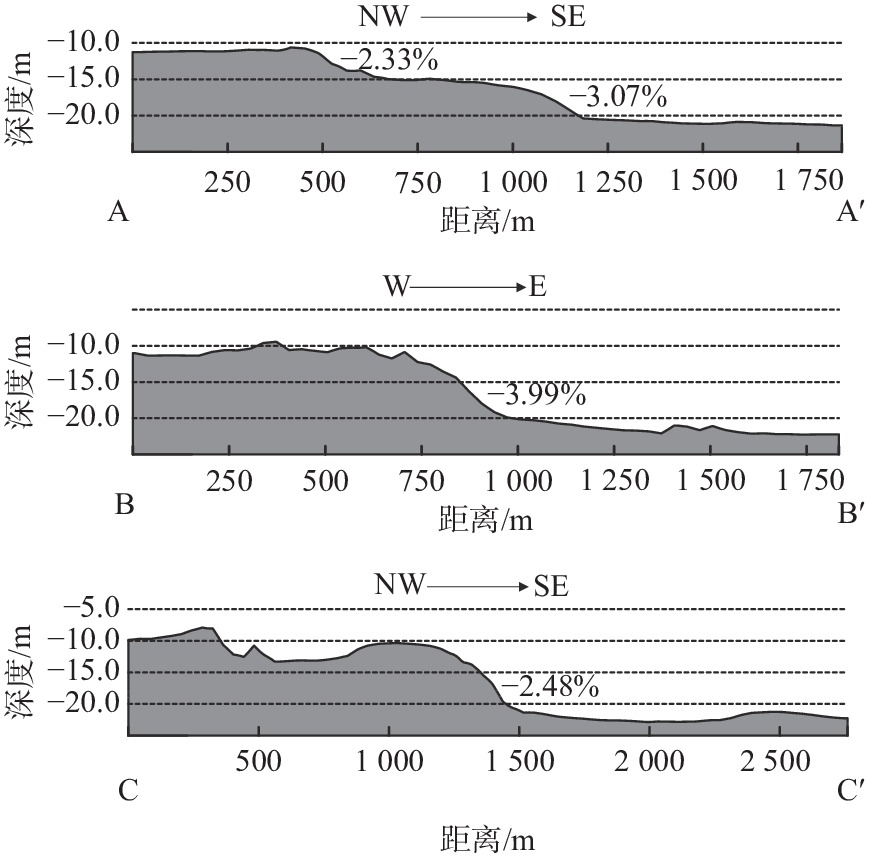
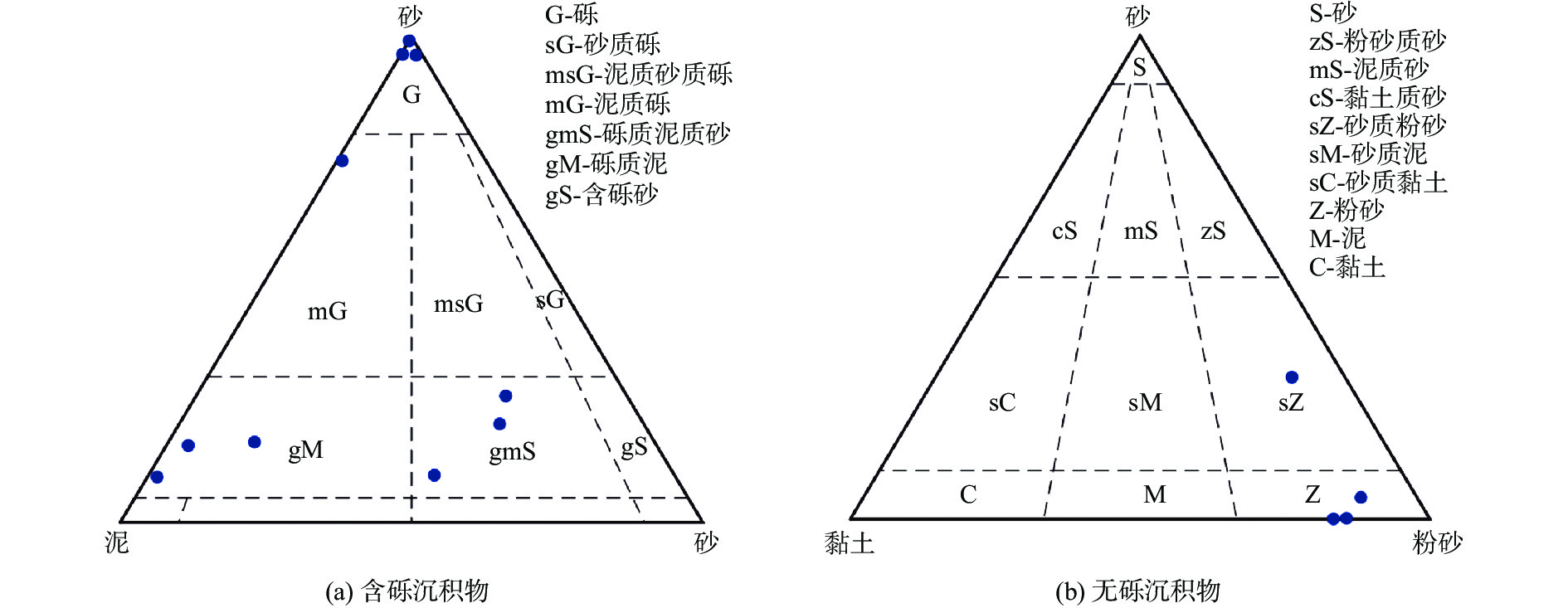
黑石岛附近海域位于山东威海黑泥湾东部,沉积环境复杂多变,多种因素控制表层沉积物分布,形成多种发育演化模式。利用单波束测深系统、浅地层剖面系统、表层沉积物取样、海流观测和实验室沉积物粒度测试、资料综合解释等方法,于2021年9—11月对研究海域开展综合地质环境调查。通过调查数据分析研究区水深地形特征、浅地层结构特征以及表层沉积物分布特征,并从多个角度揭示该海域沉积物分布特征的控制因素和成因。研究发现:目标海域水深介于3~24 m,平均水深约14 m,西部浅、东部深,存在陡坡,随着水深的增加坡度逐渐变缓,地貌类型主要以水下侵蚀岸坡为主;海底浅地层声学反射界面清晰,可全局跟踪,淤积厚度为0.5~2 m,沉积层厚度东西存在差异但相对稳定;表层沉积物类型多样,大致围绕黑石岛呈环带状分布,离岛方向上依次为粉砂、砾石、泥质砾;自西向东表层沉积物粒度逐渐减小,分选性变好。研究区表层沉积物分布受区域地形地貌和水动力条件的共同影响。
Abstract:The sea areas near Heishi Island are located in the east of Heini Bay, Weihai, Shandong Peninsular, East China. The sedimentary environment is complex and variable, and many factors control the distribution of surface sediments, forming a variety of developmental and evolutionary patterns. A comprehensive geological environment survey of the study area was carried out in Sep.–Nov., 2021 by using acoustic detection, surface sediment sampling, ocean current observation, laboratory sediment grain size testing, and comprehensive interpretation of data, based on which the characteristics of water depth topography, sub-bottom profile structure, and surface sediment distribution in the study area were analyzed and the controlling factors and causes of sediment distribution in the area were revealed from multiple perspectives. Results show that the water depth of the target area was between 3 m and 24 m, on average of about 14 m, shallower in the west and deeper in the east in a steep slope. With the increase of water depth, the slope gradually decreased, and the main landform type was underwater erosion bank slope. The acoustic reflection interface of seabed sub-bottom profile was clear and co be tracked globally. The siltation thickness was 0.5–2 m, and the thickness of sediment layer varied from east to west but relatively stable. The types of surface sediments varied, forming zones around the island, including silty sand, gravel, and muddy gravel away from the island. From west to east, the grain size of surface sediments decreased gradually and the sorting became better. It is concluded that the distribution of surface sediments in the study area is affected by regional topography and hydrodynamic conditions.
-
Key words:
- Heishi Island /
- submarine topography /
- surface sediment /
- distribution characteristic /
- influence factor
-

-
表 1 调查所采用的设备和软件
Table 1. The equipment and software used in the survey
声学探测设备及后处理软件 定位系统 美国Trimble差分GPS定位系统 潮汐仪 日本ALEC潮汐仪 导航系统 HYPACK 2020导航系统 声速剖面仪 加拿大AML声速剖面仪 单波束测深系统 无锡海鹰HY1601单波束回声测深系统 浅地层剖面系统 德国Innomar SES-2000参量阵浅地层剖面系统 后处理软件 CARIS HIPS 11.2、Surfer、Global Mapper、Sonarwiz 7.0 海流观测设备 海流计 挪威阔龙海流计 声学多普勒流速剖面仪 美国RDI-300K声学多普勒流速剖面仪 沉积物取样、分析设备 取样器 自制锚式取样器 激光粒度仪 法国CILAS 960L激光粒度分析仪 表 2 研究区表层沉积物组分含量及命名
Table 2. Analysis results of the content and grain size of surface sediment composition in the study area
区域 站位编号 纬度/N 经度/E 砾石/% 黏土/% 粉砂/% 砂/% 命名 黑石岛 HS01 36°05′02″ 122°34′11″ 0.00 14.32 85.50 0.18 粉砂 HS02 36°05′04″ 122°34′01″ 0.00 16.63 83.31 0.07 粉砂 HS03 36°05′10″ 122°34′04″ 80.35 0.12 0.68 18.84 砾石 HS04 36°05′07″ 122°34′15″ 60.32 2.81 21.86 15.01 泥质砾 HS05 36°05′45″ 122°34′01″ 80.66 0.05 0.37 18.91 砾石 老铁石岛 LT01 36°05′04″ 122°33′57″ 21.08 1.77 19.03 58.12 砾质泥质砂 LT02 36°05′48″ 122°33′57″ 0.00 9.14 61.49 29.36 砂质粉砂 LT03 36°05′51″ 122°34′01″ 12.82 8.77 71.67 6.75 砾质泥 LT04 36°05′39″ 122°33′04″ 7.86 2.76 38.48 50.91 砾质泥质砂 LT05 36°05′53″ 122°33′04″ 16.39 1.24 23.50 58.87 砾质泥质砂 LT06 36°05′00″ 122°33′57″ 13.38 10.37 58.34 17.91 砾质泥 LT07 36°05′52″ 122°34′11″ 0.00 9.68 85.84 4.48 粉砂 LT08 36°05′32″ 122°34′01″ 80.66 0.05 0.37 18.91 砾石 深水区 RP01 36°05′58″ 122°35′02″ 7.55 17.06 71.96 3.43 砾质泥 -
[1] 严立文. 浅海区海带养殖的沉积环境效应及动力机制[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2008.
[2] 张泽华,黄海军,刘艳霞,等. 浅海筏式养殖对周边海域潮流和悬浮体特征影响研究[J]. 海洋科学进展,2016,34(1):37-49.
[3] 刘艳霞,黄海军,樊建勇,等. 黑泥湾近岸悬沙分布与扩散变化监测[J]. 海洋科学,2009,33(1):25-29.
[4] 马立杰,李新正,毕海波,等. 山东黑泥湾潮间带沉积物重金属分布及其环境效应[J]. 海洋环境科学,2011,30(1):44-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2011.01.010
[5] 严立文,黄海军,刘艳霞. 基于GIS空间分析的海底表层沉积物粒度分布特征插值研究[J]. 海洋科学,2010,34(1):58-64.
[6] LIU Y X,HUANG H J,YAN L W,et al. Influence of suspended kelp culture on seabed sediment composition in Heini Bay,China[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2016,181:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.07.017
[7] 严立文,黄海军,陈纪涛,等. 黑泥湾海带养殖区沉积物重金属分布特征与富集机制[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2010,18(3):398-407.
[8] YAN L W,HUANG H J,LIU Y X. GIS-based analysis of spatial interpolations of sediments grain size in Heini Bay[J]. Marine Sciences,2010,34(1):58-64.
[9] 马立杰,崔迎春,王海荣. 运用因子分析评价山东黑泥湾沉积物重金属污染来源[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2012,28(4):57-61.
[10] LIU Y X,HUANG H J,LIU X,et al. Response of seafloor sediment composition to a strong storm event in the inner -shelf of Heini Bay,China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2019,175:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2019.01.010
[11] ZHANG Z H,HUANG H J,LIU Y X,et al. Numerical study of hydrodynamic conditions and sedimentary environments of the suspended kelp aquaculture area in Heini Bay[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2020,232(5):1-13.
[12] 刘晓. 黑泥湾海域沉降颗粒物通量及其影响因子研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2012.
[13] 王中波,何起祥,杨守业,等. 谢帕德和福克碎屑沉积物分类方法在南黄海表层沉积物编图中的应用与比较[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(1):1-8.
[14] 王建锋,邱桔斐,赵建丽,等. MATLAB CFTool在图解沉积物粒度参数计算中的应用[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2018,163(4):115-118.
[15] 张炳炎. 我国海洋调查船的现状与未来[J]. 世界科技研究与发展,1998,20(4):36-43. doi: 10.16507/j.issn.1006-6055.1998.04.014
[16] 种衍飞,郝义. 日照海岸带沙滩侵蚀现状及沉积物粒度特征分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(1):19-29.
[17] 赵东波. 常用沉积物粒度分类命名方法探讨[J]. 海洋地质动态,2009,25(8):41-44,46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2009.08.009
[18] 吕纪轩,胡日军,李毅,等. 烟台北部近岸海域表层沉积物粒度分布及沉积动力环境特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2020,36(4):27-36. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2019.097
[19] MILLIMAN J D,MEADE R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. Journal of Geology,1983,91:1-21.
[20] MACDONALD D D,INGERSOLL C G,BERGER T A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems.[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2000,39(1):20-31. doi: 10.1007/s002440010075
[21] SCHROTTKE K,BECKER M,BARTHOLOM A,et al. Fluid mud dynamics in the Weser estuary turbidity zone tracked by high-resolution side-scan sonar and parametric sub-bottom profiler[J]. Geo-Marine Letters,2006,26(3):185-198. doi: 10.1007/s00367-006-0027-1
[22] 杨慧良,尉佳,李攀峰,等. 九州-帕劳海脊两侧深海盆地浅部地层结构特征与分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(1):14-21. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2020072202
[23] MEILIANDA E,ALFIAN D,HUHN K. Sediment grain-size distribution analysis at the shallow sandy shelf of the North Sea using multivariate geostatistics[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences,2011,7(1):317-322.
[24] MOORE M,WILKIN J. Variability in the South Pacific Deep Western Boundary Current from current meter observations and a high-resolution global model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1998,103:5439-5457. doi: 10.1029/97JC03207
[25] 修日晨. 关于陆架海区潮流运动方向旋转的研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,1984(4):8-17.
[26] 金玉休,曹志敏,吴建政,等. 辽东浅滩潮流运动特征与沉积物输运[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(6):33-40. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2015.06.004
[27] GONI M A,MONACCI N,GISEWHITE R,et al. Terrigenous organic matter in sediments from the Fly River delta-clinoform system (Papua New Guinea)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,2008,113:1-27.
[28] ARNDTA S,JØRGENSENC B,LAROWED D E,et al. Quantifying the degradation of organic matter in marine sediments:a review and synthesis[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2013,123(4):53-86.
[29] JOHNSON M D,HUANG W,WEBER W J. A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments 13. Simulated diagenesis of natural sediment organic matter and its impact on sorption/desorption equilibria.[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2001,35(8):1680-1687.
[30] 尹超. 随机波浪作用下黑泥湾冲淤演变的数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2013.
[31] BURDIGE D J. Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: controls,mechanisms,and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets?[J]. Chemical Reviews,2007,107:467-485.
-




 下载:
下载: