Non-tidal bathymetry in the open sea with GNSS-PPP/INS tight combination mode
-
摘要:
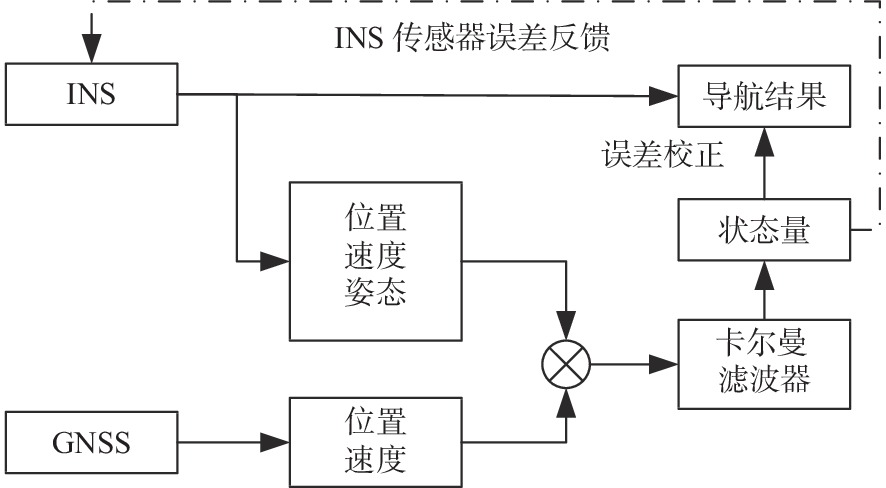
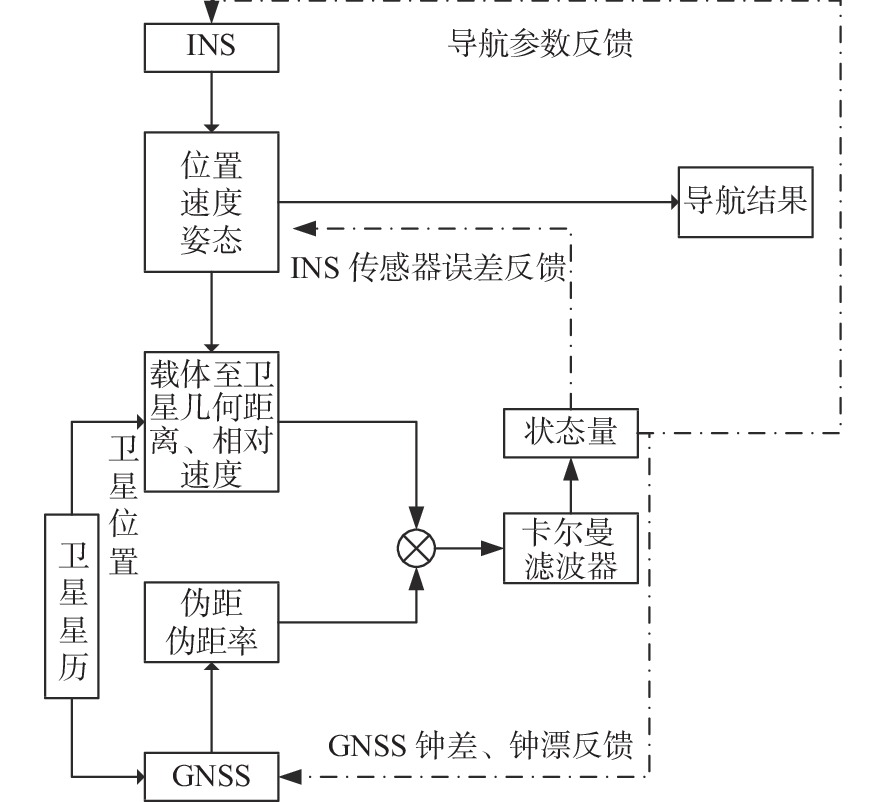
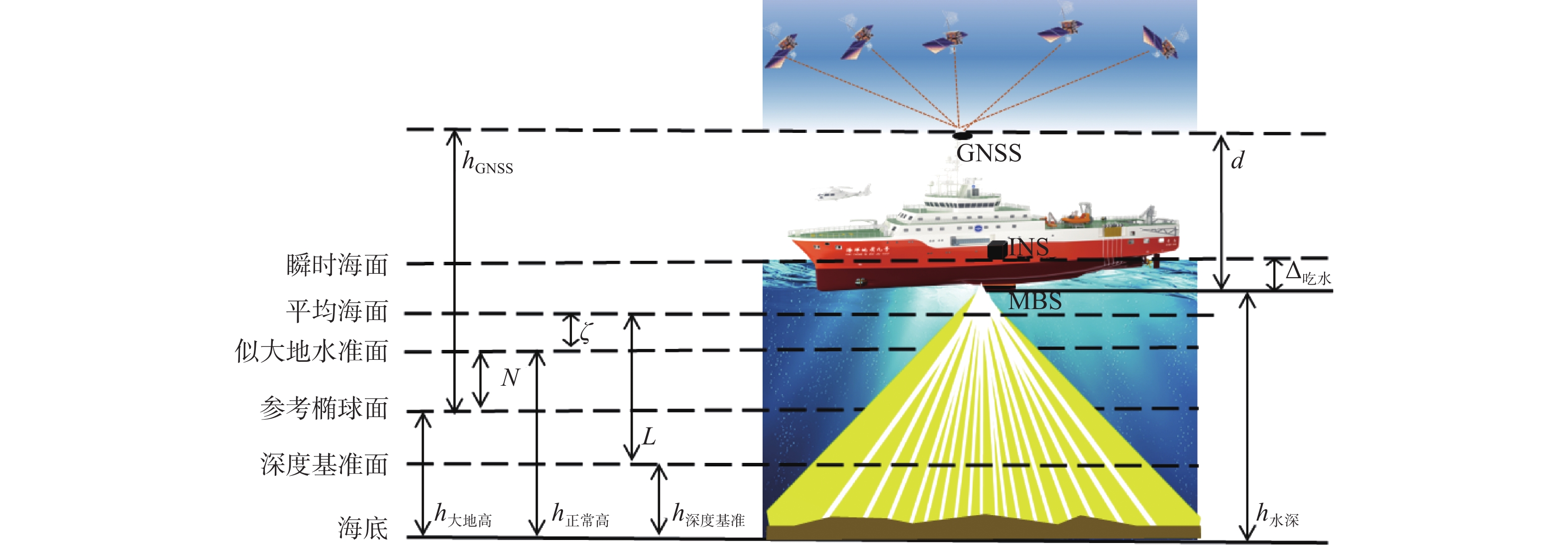
为实现高精度远海水深测量潮位改正,基于GNSS/INS组合系统开展了远海多波束无验潮水深测量方法研究,并给出了无验潮水深测量基本原理及实施技术流程。结合GNSS/INS组合形式及滤波原理,分别探讨了在GNSS有效和失效状态下PPP/INS松组合与紧组合的性能差异。以PPP/INS紧组合解算结果为基础进行无验潮水深测量改正,并与传统预报潮位改正方法进行了对比,经试验验证,基于PPP/INS紧组合模式下的远海无验潮水深测量准确度可达0.14 m,并有效消除了动态吃水影响,在典型水深断面处的水深测量准确度明显优于预报潮位改正模式。
-
关键词:
- 全球导航卫星系统 /
- 惯性导航系统 /
- PPP/INS紧组合 /
- 无验潮水深测量
Abstract:To realize tidal correction for ocean bathymetry, an ocean multibeam non-tidal bathymetry method was applied based on a combined system of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and Inertial Navigation System (INS), and the basic principles and procedures of the non-tidal bathymetry are presented. Considering the form and filtering principle of the GNSS/INS system, differences in performance between PPP/INS loose combination and tight combination under valid or invalid state of GNSS were discussed. The outcome of the PPP/INS tight combination were used to correct the non-tidal bathymetry and compared with that of the traditional tidal correction method. It was verified that the accuracy of the non-tidal bathymetry in the PPP/INS tight combination mode could reach 0.14 m, and the influence of dynamic draft could be effectively eliminated, which improved the accuracy in open sea multibeam bathymetry and in bathymetric survey at the typical water depth section, performing obviously better than the predicted tide correction model.
-

-
表 1 相关性统计表
Table 1. Statistics of correlation coefficient
统计方案 相关系数 松组合-PPP 0.986 紧组合-PPP 0.997 松组合-紧组合 0.988 表 2 GNSS失效时松/紧组合高程精度统计
Table 2. Statistics in elevation accuracy between loose and tight combination in case of GNSS failure
/m 对比方案 绝对值最大值 均值 标准差 松组合-PPP 2.97 −0.02 0.20 紧组合-PPP 0.38 0.02 0.13 表 3 典型水深断面重合点水深不符情况统计
Table 3. Statistics in inconsistent water depth at coincidence points of typical water depth section
/m 对比方案 中误差 绝对值最大值 原始水深 1.25 2.06 预报潮位改正 0.13 0.43 无验潮模式 0.08 0.26 表 4 重叠区内重合点水深不符情况统计
Table 4. Statistics in the inconsistent water depth at coincidence points in the overlapping area
对比方案 统计项 水深不符值范围/m 合计 中误差/m 0~0.5 0.5~1.0 >1.0 预报潮位改正 个数 9 336 192 2 9 530 0.15 百分比 97.96% 2.02% 0.02% 100% 无验潮模式 个数 9 366 164 0 9 530 0.14 百分比 98.28% 1.72% 0 100% -
[1] 罗小峰,黄海龙,路川藤,等. 基于数学模型的长江口海域潮位推算方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2020,53(9):761-765.
[2] 黄辰虎,陆秀平,欧阳永忠,等. 远海航渡式水深测量水位改正方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘,2013,33(5):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2013.05.003
[3] 许军,桑金,刘雷. 中国近海及邻近海域精密潮汐模型的构建[J]. 海洋测绘,2017,37(6):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2017.06.004
[4] 阳凡林,康志忠,独知行,等. 海洋导航定位技术及其应用与展望[J]. 海洋测绘,2006,26(1):71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2006.01.022
[5] 赵建虎,陆振波,王爱学. 海洋测绘技术发展现状[J]. 测绘地理信息,2017,42(6):1-10.
[6] 魏荣灏,陈佳兵,徐达. 基于PPK无验潮的水下地形测量技术研究[J]. 海洋技术学报,2021,40(1):57-62.
[7] 高兴国,田梓文,麻德明,等. GNSS支持下的无验潮测深模式优化[J]. 测绘通报,2018,11(4):7-10.
[8] 冯国正,曹磊,马耀昌,等. EGM 2008模型的无验潮测深技术[J]. 测绘科学,2018,43(1):26-30.
[9] 刘文勇,郑晖. GPS-RTK无验潮测深精度影响因素分析[J]. 测绘科学,2015,40(11):7-12.
[10] 吴敬文,付五洲,薛剑锋. 沿岸多模式GNSS三维水深测量方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘,2019,39(3):41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.03.009
[11] 赵建虎,董江,柯灝,等. 远距离高精度GPS潮汐观测及垂直基准转换研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2015,40(6):761-766.
[12] 赵建虎,王胜平,张红梅. 基于GPSPPK/PPP的长距离潮位测量[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2008,33(9):910-913.
[13] 张小红,李星星,李盼. GNSS精密单点定位技术及应用进展[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1399-1407. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170327
[14] 杨元喜. 弹性PNT基本框架[J]. 测绘学报,2018,47(7):893-898. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20180149
[15] 杨元喜. 综合PNT体系及其关键技术[J]. 测绘学报,2016,45(5):505-510. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2016.20160127
[16] 梁健,韩彦岭,于文浩,等. 低成本GNSS/INS组合导航系统探讨[J]. 导航定位学报,2019,7(4):110-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2019.04.020
[17] 付心如,徐爱功,孙伟. 抗差自适应UKF的INS/GNSS组合导航算法[J]. 导航定位学报,2017,5(2):111-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2017.02.020
[18] 王浩源,孙付平,肖凯. PPP/INS组合系统研究进展与展望[J]. 全球定位系统,2017,42(5):53-58.
[19] 牛小骥,班亚龙,张提升,等. GNSS/INS深组合技术研究进展与展望[J]. 航空学报,2016,37(10):2895-2908.
[20] 樊云鹏,杨锁昌. GNSS/INS深组合导航关键技术研究[J]. 飞航导弹,2017(10):22-25,48.
[21] 伍蔡伦, 智奇楠. 高精度GNSS/INS组合定位及测姿技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2021: 78-88.
[22] 高周正. 多模GNSS PPP/INS组合系统算法与应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2016.
-



 下载:
下载: