End-member characteristics of sediment grain size of modern Yellow River Delta sediments and their response to channel shifts and human activities
-
摘要:
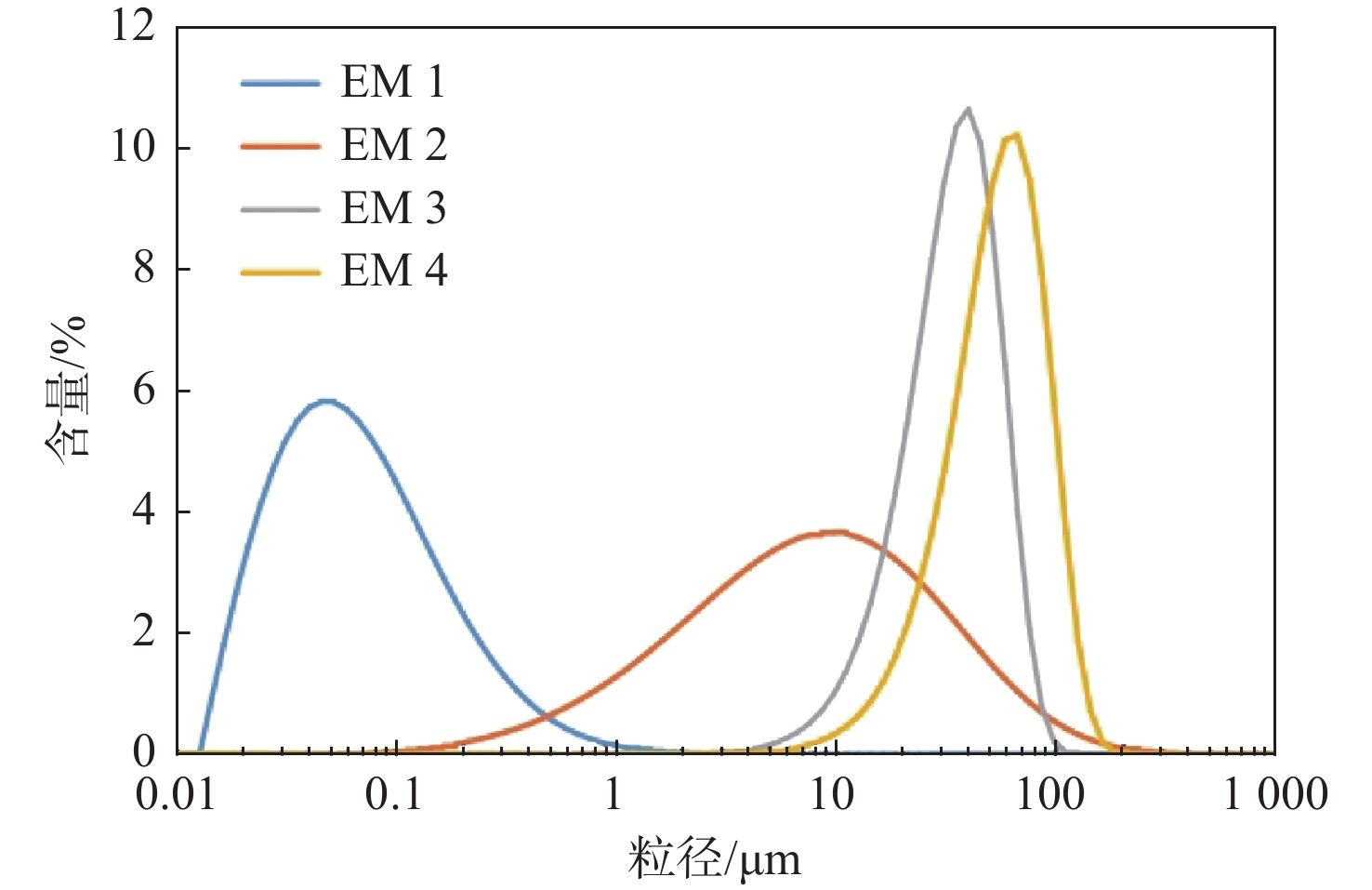
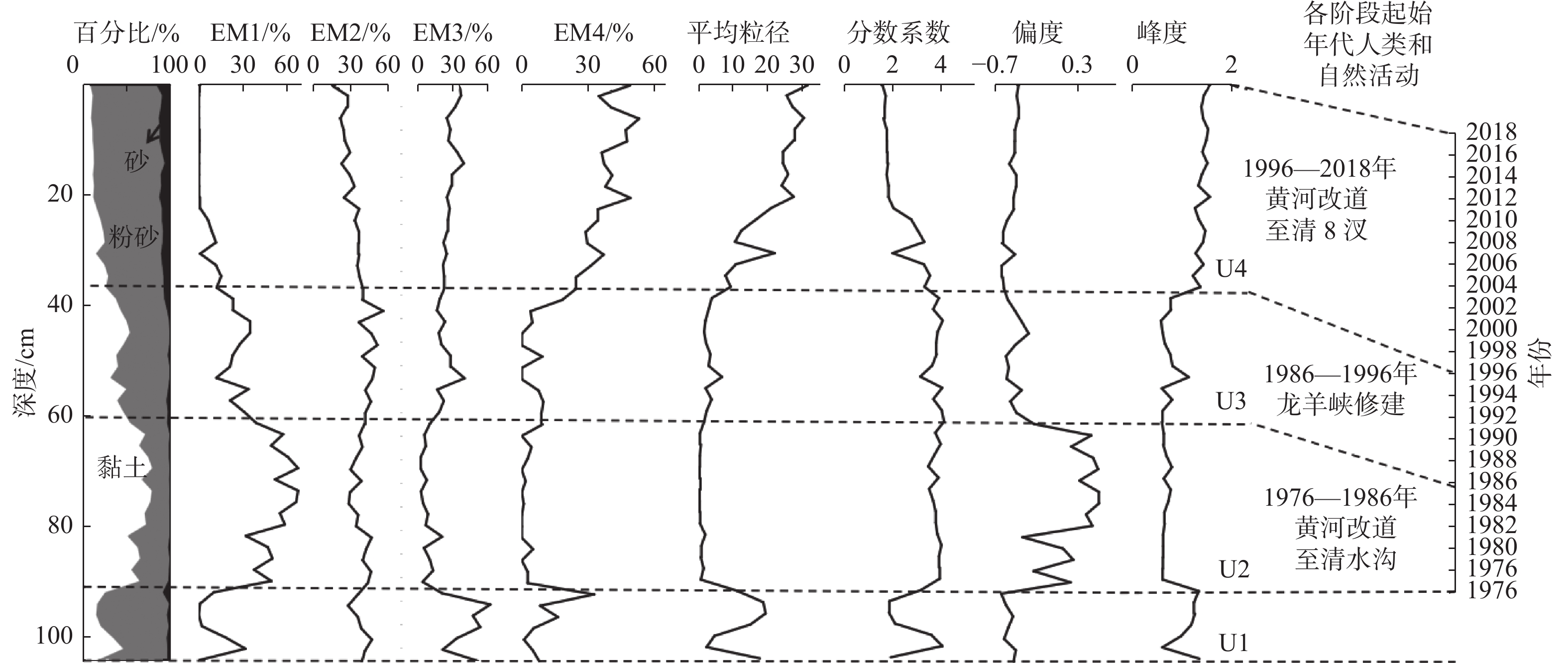
黄河三角洲沉积物记录了长时间尺度黄河流域环境变化,对流域河流改道和水库建设等自然和人类活动响应敏感。本研究以黄河1976年以来入海口附近陆上三角洲YDC钻孔为研究对象,采用参数化端元(EM)分析模型对YDC钻孔的粒度数据进行分析,结果表明:①EM1和EM2由粒径较细的黏土和细粉砂组成,为黄河长距离搬运弱水动力条件下沉积,EM3和EM4为粗粉砂组分,为较强动力条件下波浪和潮流作用沉积;②对比河道变迁和人类活动等资料,结合前人黄河口沉积速率研究数据,表明YDC钻孔粒度特征变化显著的界面可以作为黄河口沉积物定年的参考点;③YDC钻孔粒度参数和端元数据敏感地响应于1976年以来黄河改道清水沟入海、龙羊峡水库建设、黄河改道清8汊入海等自然和人类活动。研究结果对黄河三角洲河口治理和沿岸工程建设具有重要现实意义,并可为黄河流域生态保护与高质量发展提供科学依据。
Abstract:Yellow River Delta sediments record environmental changes in the Yellow River basin at long time scales, and respond sensitively to natural and human activities such as river diversions and reservoir construction in the basin. We analyzed the grain size distribution of core YDC from onshore delta since 1976 near the river mouth were analyzed using a parametric end-member analysis model. Results show that EM1 and EM2 are composed of fine-grained clay and fine powder sand, deposited under weak hydrodynamic conditions for long distance transport in the Yellow River, while EM3 and EM4 are coarse powder sand fractions, deposited by wave and tidal action under stronger dynamic conditions. By comparing the data on channel alteration and human activities, and combining data from previous studies on sedimentation rates in the Yellow River estuary, we found that significant changes in grain size characteristics could be used as reference points for sediment age determination. The grain size parameters and end element data reflect the natural and human activities since 1976, such as the diversion of the Yellow River from Qingshuigou to the sea, the construction of the Longyangxia Reservoir, and the diversion of the Yellow River from Qingbacha to the sea. This study provide a reference for the management of the Yellow River Delta estuary and coastal engineering construction, and a scientific basis for ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River basin.
-

-
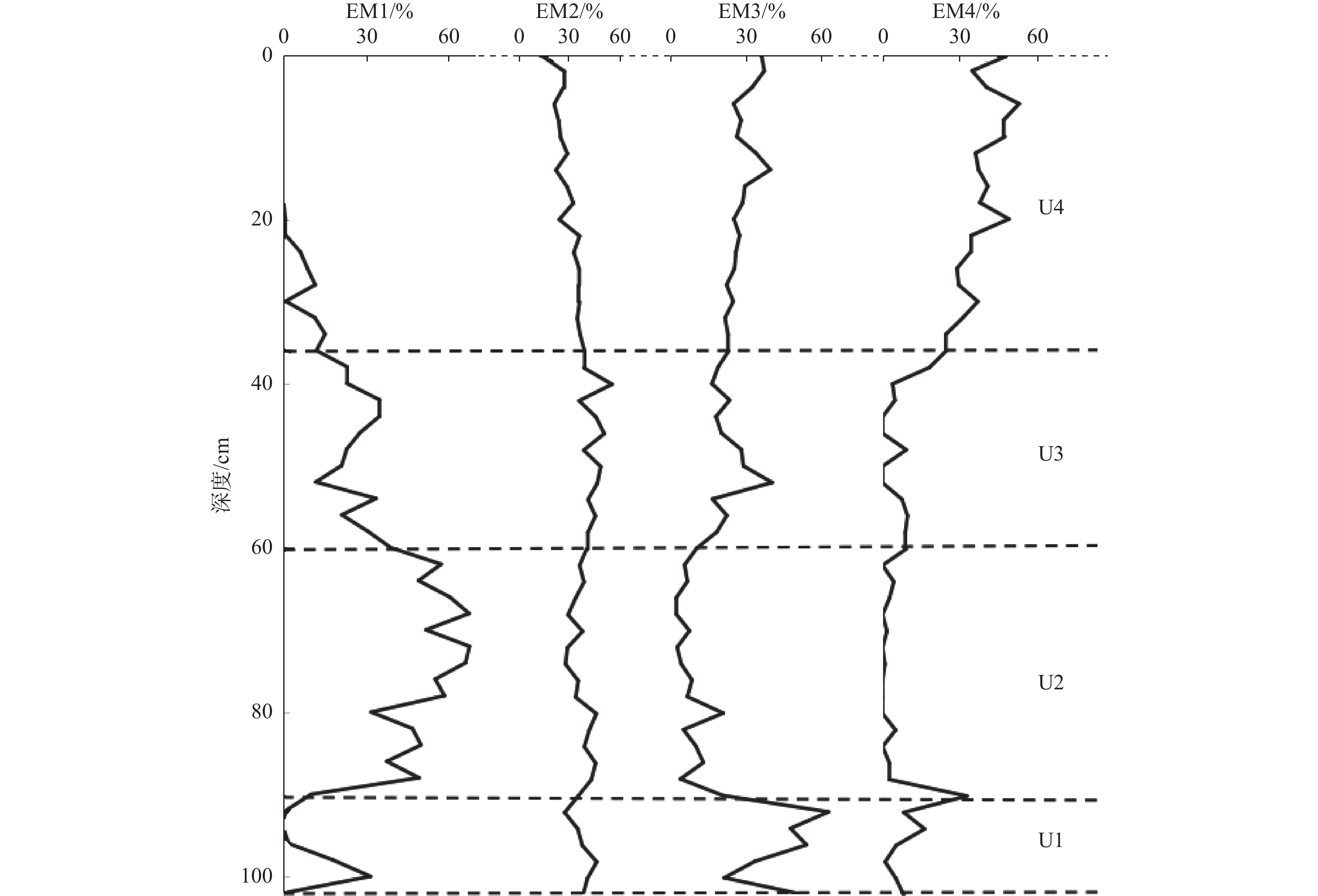
表 1 各地层粒度参数特征
Table 1. Characteristics of grain size parameters for each stratum
地层单元 U1(90~
102 cm)U2(60~
90 cm)U3(36~
60 cm)U4(0~
36 cm)平均粒径/μm 21.87 8.24 14.88 31 中值粒径 (Md) 17.77 2.03 6.69 26.87 分选系数(σ) 2.56 3.76 3.81 2.23 偏度(Sk) −0.52 0.23 −0.44 −0.5 峰度(Kg) 1.1 0.7 0.71 1.41 表 2 各粒度端元与粒度组分、参数的相关性分析
Table 2. Correlation in grain size of each end member with the grain size components and the parameters
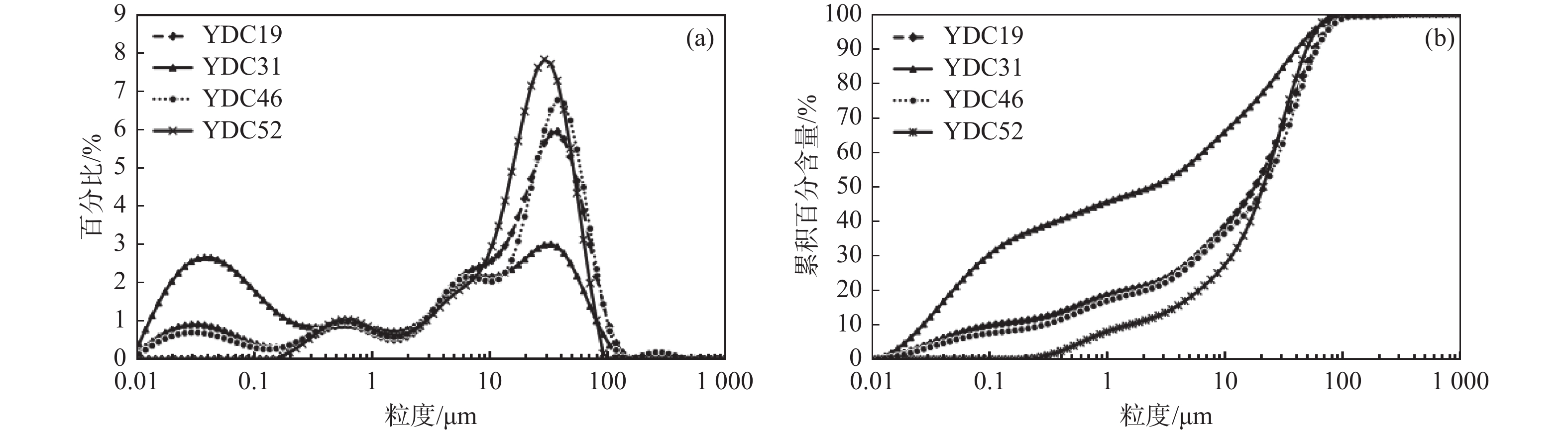
黏土 粉砂 砂 EM 1 EM 2 EM 3 EM 4 平均粒径 分选系数 偏度 峰度 黏粒 1 粉砂 −0.99 1 砂 −0.8 0.71 1 EM 1 0.99 −0.99 −0.74 1 EM 2 0.39 −0.32 −0.61 0.29 1 EM 3 −0.8 0.9 0.33 −0.83 −0.21 1 EM 4 −0.82 0.74 0.97 −0.75 −0.68 0.36 1 平均粒径 −0.88 0.85 0.85 −0.84 −0.70 0.64 0.90 1 分选系数 0.83 −0.81 −0.72 0.78 0.68 −0.69 −0.78 −0.96 1 偏度 0.83 −0.85 −0.52 0.87 −0.06 −0.72 −0.50 −0.50 0.47 1 峰度 −0.88 0.84 0.83 −0.84 −0.61 0.63 0.86 0.89 −0.87 −0.57 1 -
[1] WANG H J,BI N S,SAITO Y,et al. Recent changes in sediment delivery by the Huanghe (Yellow River) to the sea:Causes and environmental implications in its estuary[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2010,391(3/4):302-313.
[2] MILLIMAN J D,MEADE R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. Journal of Geology,1983,91(1):1-21.
[3] 胡刚,张勇,孔祥淮,等. 全新世中国大河三角洲沉积演化模式转化及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(5):77-89.
[4] 吴晓,范勇勇,王厚杰,等. 三角洲废弃河道演化过程及受控机制:以黄河刁口废弃河道为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(2):22-29.
[5] 韩广轩,栗云召,于君宝,等. 黄河改道以来黄河三角洲演变过程及其驱动机制[J]. 应用生态学报,2011,22(2):467-472.
[6] ZHOU L Y,LIU J,SAITO Y,et al. Modern sediment characteristics and accumulation rates from the delta front to prodelta of the Yellow River (Huanghe)[J]. Geo-Marine Letters,2016,36(4):247-258.
[7] DETHIER E N,RENSHAW C E,MAGILLIGAN F J. Rapid changes to global river suspended sediment flux by humans[J]. Science,2022,376(6600):1447-1452.
[8] JIANG C,CHEN S L,PAN S Q,et al. Geomorphic evolution of the Yellow River Delta:Quantification of basin-scale natural and anthropogenic impacts[J]. Catena,2018,163:361-377.
[9] XU J X. Grain-size characteristics of suspended sediment in the Yellow River,China[J]. Catena,2000,38(3):243-263.
[10] 王兆夺,黄春长,杨红瑾,等. 六盘山东麓晚更新世以来黄土粒度指示的物源特征及演变[J]. 地理科学,2018,38(5):818-826.
[11] VARGA G,UJVARI G,KOVACS J. Interpretation of sedimentary (sub)populations extracted from grain size distributions of central European loess-paleosol series[J]. Quaternary International,2019,502:60-70.
[12] CHEN J,YANG T B,QIANG M R,et al. Interpretation of sedimentary subpopulations extracted from grain size distributions in loess deposits at the Sea of Azov,Russia[J]. Aeolian Research,2020,45:100597.
[13] WEN Y L,WU Y Q,TAN L H,et al. End-member modeling of the grain size record of loess in the Mu Us Desert and implications for dust sources[J]. Quaternary International,2019,532:87-97.
[14] WANG H J,WU X,Bi N S,et al. Impacts of the dam-orientated water-sediment regulation scheme on the lower reaches and delta of the Yellow River (Huanghe):a review[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2017,157:93-113.
[15] WU X,BI N S,et al. Stepwise morphological evolution of the active Yellow River (Huanghe) delta lobe (1976—2013):dominant roles of riverine discharge and sediment grain size[J]. Geomorphology Amsterdam,2017,292:115-127.
[16] 朱纹君,韩美,孔祥伦,等. 1990-2018年黄河三角洲人类活动强度时空格局演变及其驱动因素[J]. 水土保持研究,2021,28(5):287-292.
[17] 李越,宋友桂,宗秀兰,等. 伊犁盆地北部山麓黄土粒度端元指示的粉尘堆积过程[J]. 地理学报,2019,74(1):162-177.
[18] 刘蓉,岳大鹏,赵景波,等. 陕西横山L_2以来风沙/黄土沉积序列的粒度端元特征及其环境意义[J]. 干旱区地理,2021,44(5):1328-1338.
[19] 张晓东,翟世奎,许淑梅. 端元分析模型在长江口邻近海域沉积物粒度数据反演方面的应用[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2006(4):159-166.
[20] 林镇坤,王爱军,叶翔. 南流江河口水下三角洲表层沉积物端元分析及其沉积动力环境意义[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(1):124-134.
[21] 解锡豪,曹向明,李志忠,等. 闽江口地区不同砂质沉积的粒度端元特征及其环境指示[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报,2021,16(2):38-46.
[22] 李松,王厚杰,张勇,等. 黄河在调水调沙影响下的入海泥沙通量和粒度的变化趋势[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2015,31(7):20-27.
[23] PATERSON GA,HESLOP D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J]. Geochemistry,2015,16(12):4494-4506.
[24] 袁杰,曹广超,鄂崇毅,等. 环青海湖表层土壤沉积物粒度分布特征及其指示意义[J]. 水土保持研究,2015,22(3):150-154.
[25] 任寒寒. 黄河三角洲高分辨沉积记录及其对河道变迁和重大人类活动的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.
[26] 秦小光,蔡炳贵,穆燕,等. 黄土粉尘搬运过程的动力学物理模型[J]. 第四纪研究,2009,29(6):1154-1161.
[27] 刘梦慧,李徐生,韩志勇,等. 下蜀黄土参数化粒度端元分析及其物源示踪[J]. 地球环境学报,2021,12(5):510-525.
[28] 王兆夺,于东生,汪卫国,等. 泉州湾表层沉积物粒度指示的沉积动力端元解析[J]. 热带地理,2021,41(5):975-986.
[29] 陈艇,刘青松,郑一. 黄河水下三角洲钻孔沉积物磁学记录及其年代学意义[J]. 科学通报,2021,66(30):3902-3915.
[30] 宋莎莎. 现代黄河三角洲潮滩的沉积物粒度、核素分布及其环境意义[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2020.
[31] HU N J,HUANG P,LIU J H,et al. Tracking lead origin in the Yellow River estuary and nearby Bohai Sea based on its isotopic composition[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science,2015,163:99-107.
[32] 王琬璋,周良勇,段宗奇,等. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物磁性地层年代框架及环境磁学研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2019,62(5):1772-1788.
[33] 薛春汀,叶思源,高茂生,等. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物沉积年代的确定[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2009,31(1):117-124.
[34] 李栓科. 近代黄河三角洲的沉积特征[J]. 地理研究,1989,8(4):45-55.
[35] 李谷祺,陈沈良,彭俊,等. 黄河三角洲YDZ1孔沉积环境分析[J]. 海洋科学进展,2013,31(2):205-212.
[36] 张金萍,肖宏林,张鑫. 龙羊峡水库对下游水沙条件变化的影响分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2020,1:83-87.
[37] 胡春宏,张晓明,赵阳. 黄河泥沙百年演变特征与近期波动变化成因解析[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(5):725-733.
[38] WU X,WANG H J,Bi N S,et al. Evolution of a tide-dominated abandoned channel:a case of the abandoned Qingshuigou course,Yellow River[J]. Marine Geology,2020,422(7/26):106116.
[39] 袁萍,毕乃双,吴晓,等. 现代黄河三角洲表层沉积物的空间分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2016,36(2):49-57.
[40] 师长兴. 黄河口不同粒度泥沙沉积与扩散分析[J]. 地理研究,2021,40(4):1125-1133.
[41] 王兆夺. 黄河中游—淮河上游全新世黄土土壤粒度与物源关系分析[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2018.
[42] PYE K,ZHOU L P. Pleistocene and Holocene aeolian dust deposition in North China and the Northwest Pacific Ocean[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,1989,73(1/2):11-23.
-




 下载:
下载: