Research progress and countermeasures on geological hazards induced by extreme storms in the Yellow River Delta
-
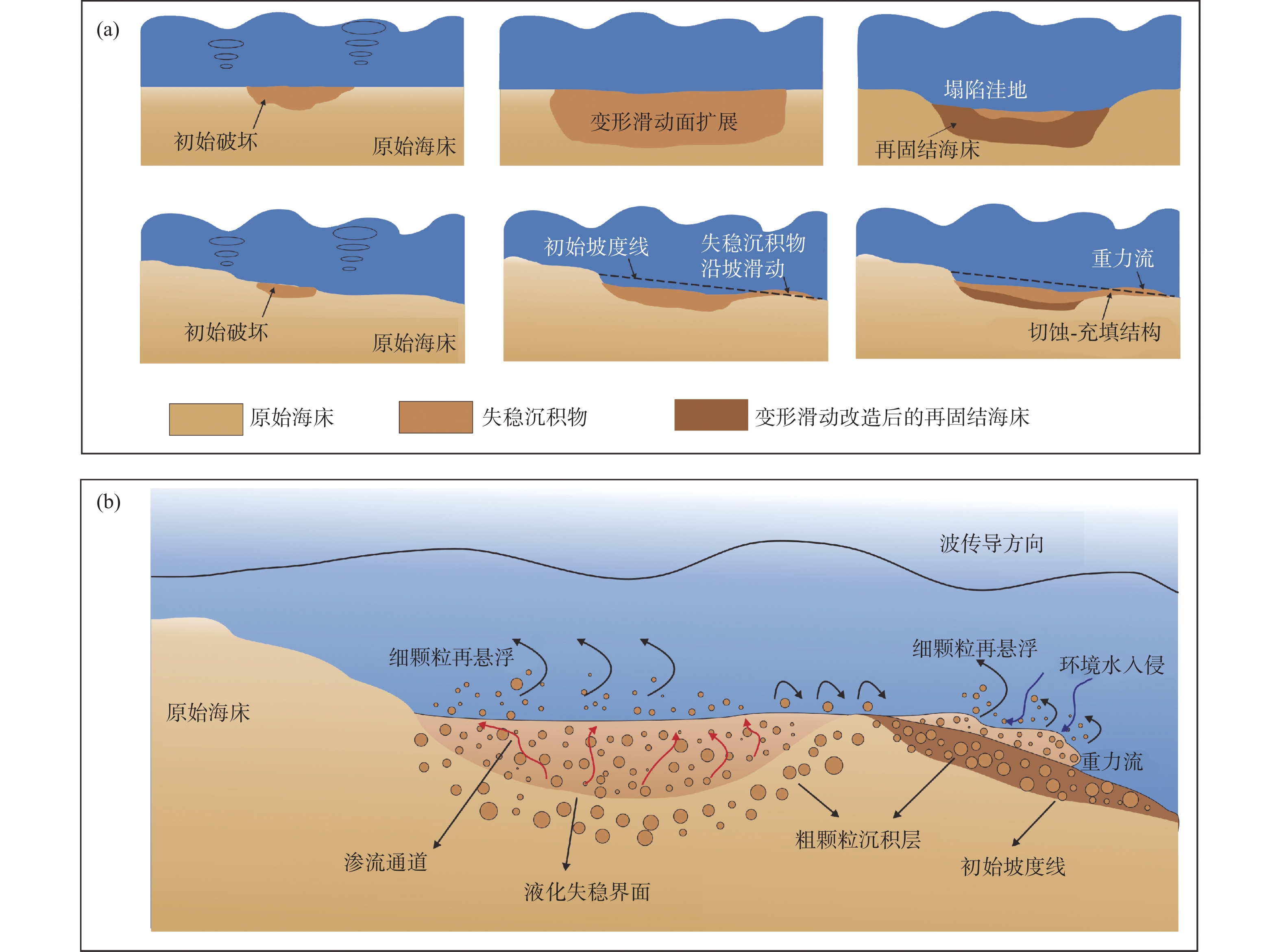
摘要:
受全球气候变化影响,河口三角洲及沿海地区极端风暴事件发生频率及其危害性不断加剧。风暴事件中海底沉积物在波浪荷载作用下产生压密固结、液化流变等动态响应,并伴随粒度成分、力学强度、结构分层等一系列海床工程地质性质的变化,诱发侵蚀、滑坡等海洋地质灾害,严重影响海洋资源开发工程及生态环境安全。黄河三角洲特殊的地理位置、气候特点和沉积特性,决定了其成为我国海洋地质灾害最多发的地区之一,是开展极端风暴事件下地质灾害机理与防控研究的理想试验场。近年来,海洋工程地质领域围绕风暴水动力-海底沉积物相互作用与致灾机理开展了大量研究,特别在极端风暴诱发海床液化、侵蚀冲刷、变形滑动的灾害特征、机制与定量评价方面取得了重要创新性成果,为全球气候背景下的海洋工程地质评价和防灾减灾提供了理论指导。今后应进一步加强多学科交叉与产学研联合攻关,在海洋地质灾害链生机制、灾害综合监测预警技术、海洋工程灾害防控技术等方面力争突破,不断提升我国海洋地质灾害应对能力。
Abstract:Under the influence of global climate change, the frequency and harmfulness level of extreme storm events in estuarine deltaic and coastal areas are increasing. In storm events, seabed sediments produce dynamic responses including pressure consolidation, liquefaction, and fluidization under wave stress, resulting in a series of impact on engineering geological properties, such as particle size composition, mechanical strength, and hierarchical structure. These dynamic responses induce marine geological disasters such as erosion and landslide, which seriously affect the stability of marine engineering construction and the safety of ecological environment. The special geographical location, climatic features, and sedimentary characteristics of the Yellow River Delta make it one of the areas where marine geological disasters happen most frequently in China. Thus it is an ideal background and unique testing ground for the study of geological disaster mechanism and its prevention and control under extreme storm events. In recent years, in the field of marine engineering geology, many studies have been carried out on the interaction between storm hydrodynamic force and seabed sediment, and on the mechanism of disaster. In particular, important innovative achievements have been made in characterization and mechanism of disaster development, quantitative evaluation on seabed liquefaction, erosion, deformation and sliding induced by extreme storms. It provides theoretical guidance for marine engineering geological evaluation and disaster prevention and/or mitigation under the global climate background. In the future, we should further strengthen the interdisciplinary and industry-university-institute cooperation, strive for breakthroughs in the chain-generation mechanism of marine geological disaster, comprehensive disaster monitoring and early warning technology, and marine engineering disaster prevention and control technology, and improve persistently China's ability of marine geological disaster response.
-

-
[1] 刘红军,李洪江. 黄河三角洲海上风机新型吸力锚基础型式分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2014,44(7):71-76.
[2] 刘昀, 刘敏. 风暴潮对黄河三角洲生态湿地的危害及应对措施[C]// 2020(第八届)中国水生态大会论文集, 2020: 552-556.
[3] 李东旭. 基于层次分析法的我国大河三角洲脆弱性评价模型研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2012.
[4] 孙永福, 宋玉鹏, 胡光海. 埕岛油田灾害地质研究成果报告[R]. 青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 2006.
[5] 杜逢超. 胜利油田作业三号修井平台倾覆地质原因分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.
[6] WANG H,LIU H J. Evaluation of storm wave-induced silty seabed instability and geo-hazards:a case study in the Yellow River delta[J]. Applied Ocean Research,2016,58:135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2016.03.013
[7] WRIGHT L D,WISEMAN W J,BORNHOLD B D,et al. Marine dispersal and deposition of Yellow River silts by gravity-driven underflows[J]. Nature,1988,332:629-632. doi: 10.1038/332629a0
[8] MORTON R A. Subaerial storm deposits formed on barrier flats by wind-driven currents[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1979,24(1/2):105-122.
[9] PRIOR D B, COLEMAN J M. Active slides and flows in underconsolidated marine sediments on the slopes of the Mississippi Delta[C]//Saxov S, Nieuwenhuis J K . Marine slides and other mass movements. NATO Conference Series. Boston, MA: Springer, 1982: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3362-3_3
[10] MORTON R A,SALLENGER A H. Morphological impacts of extreme storms on sandy beaches and barriers[J]. Journal of Coastal Research,2003,19(3):560-573.
[11] WANG H J,YANG Z S,LI Y H et al. Dispersal pattern of suspended sediment in the shear frontal zone off the Huanghe (Yellow River) Mouth[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2007,27(6):854-871. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.12.002
[12] WANG H J,WANG A M,BI N S,et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended sediment in the Bohai Sea,China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,90:17-32. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.006
[13] XIE W M,WANG X Y,GUO L C et al. Impacts of a storm on the erosion process of a tidal wetland in the Yellow River Delta[J]. CATENA,2021,205:105461. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105461
[14] GAO W, LI G X, CAO L H et al. Formation mechanism of seafloor instability in the modern Yellow River Delta[C]//Proceedings of the Twenty-fourth International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. Busan: ISOPE, 2014: 289–29.
[15] LIM D I,JUNG H S,CHOI J Y et al. Geochemical compositions of river and shelf sediments in the Yellow Sea:Grain-size normalization and sediment provenance[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2006,26(1):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.10.001
[16] 杨秀娟,贾永刚,刘红军,等. 黄河三角洲沉积物超固结特征及其成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009,29(5):29-34.
[17] SYVITSKI J P M,KETTNER A J,OVEREEM I et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities[J]. Nature Geoscience,2009,2(10):681-686. doi: 10.1038/ngeo629
[18] 许小峰, 顾建峰, 李永平. 海洋气象灾害[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2016.
[19] National Distater Risk Reduction and Management Council. SitRep No. 108, Effect of Typhoon “Yolanda” (Haiyan)[R]. Philippines: NDRRMC. 2014
[20] 王硕. 杭州湾沿岸平原新石器遗址海侵地层及极端风暴事件的数值模拟[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2021.
[21] CHILLARIGE A R V,MORGENSTERN N R,ROBERTSON P K et al. Seabed instability due to flow liquefaction in the Fraser River delta[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1997,34(4):520-533. doi: 10.1139/T97-019
[22] PRIOR D B,SUHAYDA J N,LU N Z et al. Storm wave reactivation of a submarine landslide[J]. Nature (London),1989,341(6237):47-50. doi: 10.1038/341047a0
[23] LIU X L,LU Y,YU H et al. In-Situ observation of storm-induced wave-supported fluid mud occurrence in the subaqueous Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2022,127(7):e2021JC018190.
[24] ALBATAL A,WADMAN H,STARK N et al. Investigation of spatial and short-term temporal nearshore sandy sediment strength using a portable free fall penetrometer[J]. Coastal Engineering,2019,143:21-37. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2018.10.013
[25] MOLINA J M,ALFARO P,MORETTI M et al. Soft-sediment deformation structures induced by cyclic stress of storm waves in tempestites (Miocene,Guadalquivir Basin,Spain)[J]. Terra nova (Oxford,England),1998,10(3):145-150. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.1998.00183.x
[26] KREISA R D. Storm-generated sedimentary structures in subtidal marine facies with examples from the Middle and Upper Ordovician of southwestern Virginia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,1981,51(3):823-848.
[27] BLUM M D,ROBERTS H H. Drowning of the Mississippi Delta due to insufficient sediment supply and global sea-level rise[J]. Nature Geoscience,2009,2(7):488-491. doi: 10.1038/ngeo553
[28] ERICSON J,VOROSMARTY C,DINGMAN S et al. Effective sea-level rise and deltas:causes of change and human dimension implications[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2006,50(1/2):63-82.
[29] 丁一汇, 杜祥琬. 气候变化对我国重大工程的影响与对策研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
[30] WALSH J P,CORBETT R,MALLINSON D et al. Mississippi delta mudflow activity and 2005 Gulf hurricanes[J]. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union,2006,87(44):477-478.
[31] WANG D W,MITCHELL D A,TEAGUE W J et al. Extreme waves under Hurricane Ivan[J]. Science,2005,309(5736):896. doi: 10.1126/science.1112509
[32] BEVER A J,MCNINCH J E,HARRIS C K. Hydrodynamics and sediment-transport in the nearshore of Poverty Bay,New Zealand:observations of nearshore sediment segregation and oceanic storms[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2011,31(6):507-526. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2010.12.007
[33] SHYNU R,RAO V P,SAMIKSHA S V et al. Suspended matter and fluid mud off Alleppey,southwest coast of India[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2017,185:31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.11.023
[34] TRAYKOVSKI P,GEYER W R,IRISH J D et al. The role of wave-induced density-driven fluid mud flows for cross-shelf transport on the Eel River continental shelf[J]. Continental shelf research,2000,20(16):2113-2140. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(00)00071-6
[35] GARRISON L E. The SEASWAB experiment[J]. Marine Geotechnology,1977,2(1/4):117-122.
[36] HERMAN P M J,MIDDELBURG J J,HEIP C H R. Benthic community structure and sediment processes on an intertidal flat:results from the ECOFLAT project[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2001,21(18):2055-2071.
[37] RIDENTE D,SPOSATO A,CHIOCCI F. Large-scale mapping of submarine geohazard-related features:example from the Italian Project MAGIC (Marine Geohazards along the Italian Coasts)[J]. Geophysical Research Abstracts,2010,12:5045.
[38] ZHANG H,LIU X L,JIA Y G et al. Rapid consolidation characteristics of Yellow River-derived sediment:Geotechnical characterization and its implications for the deltaic geomorphic evolution[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,270:105578. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105578
[39] LIU X L,ZHANG M S,ZHANG H et al. Physical and mechanical properties of loess discharged from the Yellow River into the Bohai Sea,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,227:4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.019
[40] PRIOR D B,YANG Z S,BORNHOLD B D et al. The subaqueous delta of the modern Huanghe (Yellow River)[J]. Geo-marine letters,1986,6(2):67-75. doi: 10.1007/BF02281642
[41] XU G H,LIU Z Q,SUN Y F et al. Experimental characterization of storm liquefaction deposits sequences[J]. Marine Geology,2016,382:191-199. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.10.015
[42] CHIEN L K,OH Y N,CHANG C H. Effects of fines content on liquefaction strength and dynamic settlement of reclaimed soil[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2002,39(1):254-265. doi: 10.1139/t01-083
[43] PRAKASH S,SANDOVAL J A. Liquefaction of low plasticity silts[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,1992,11(7):373-379. doi: 10.1016/0267-7261(92)90001-T
[44] GUO T Q, PRAKASH. Liquefaction of silts and silt-clay mixtures[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1999, 125 (8): 706–710.
[45] 曾长女,刘汉龙,丰土根,等. 饱和粉土孔隙水压力性状试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2005,26(12):1963-1966. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2005.12.020
[46] 曾长女,刘汉龙,陈育民. 细粒含量对粉土动孔压发展模式影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(8):2193-2198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.08.032
[47] 常方强,贾永刚,郭秀军,等. 黄河口粉土液化过程的现场振动试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(4):609-616. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.04.019
[48] 常方强,贾永刚. 黄河口粉质土海床液化过程的现场试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2012,45(1):121-126. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.01.002
[49] 刘晓磊,贾永刚,郑杰文. 波浪导致黄河口海床沉积物超孔压响应现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(11):3055-3062. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.11.003
[50] LIU X L,ZHANG S Y,ZHENG J W et al. Experimental dynamic sediment behavior under storm waves with a 50 year recurrence interval in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Anthropocene Coasts,2019,2(1):229-243. doi: 10.1139/anc-2018-0018
[51] DU X, SUN Y F, SONG Y P et al. Wave-induced liquefaction hazard assessment and liquefaction depth distribution: a case study in the Yellow River Estuary, China[C]//IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 569: 12011.
[52] 常方强,贾永刚. 波浪作用下埕岛海域粉质土海床的累积液化[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版),2013,34(4):434-438. doi: 10.11830/ISSN.1000-5013.2013.04.0434
[53] LIU X L,JIA Y G,ZHENG J W et al. Experimental evidence of wave-induced inhomogeneity in the strength of silty seabed sediments:Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Ocean Engineering,2013,59:120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.12.003
[54] LIU X L,JIA Y G,ZHENG J W et al. An experimental investigation of wave-induced sediment responses in a natural silty seabed:new insights into seabed stratification[J]. Sedimentology,2017,64(2):508-529. doi: 10.1111/sed.12312
[55] 贾永刚,陈天,李培英,等. 海洋地质灾害原位监测技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):1-14.
[56] LIU T,LI S P,KOU H L et al. Excess pore pressure observation in marine sediment based on fiber bragg grating pressure sensor[J]. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology,2019,37(7/8):775-782.
[57] LIU T,WEI G L,KOU H L et al. Pore pressure observation:pressure response of probe penetration and tides[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2019,38(7):107-113. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1462-4
[58] JIA Y G, LIU X L, ZHANG S T et al. Wave-forced sediment erosion and resuspension in Yellow River Delta[M]. New York: Springer, 2020.
[59] 赵东波. 黄河三角洲刁口叶瓣海岸的侵蚀研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004.
[60] ZHENG J W,JIA Y G,LIU X L et al. Sediment characteristics as a function of variable hydrodynamics in a tidal flat of the Yellow River Delta,China[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering,2014,136(1):011104. doi: 10.1115/1.4025547
[61] TEISSON C,OCKENDEN M,LE HIR P et al. Cohesive sediment transport processes[J]. Coastal Engineering,1993,21(1):129-162.
[62] WANG Y H. The intertidal erosion rate of cohesive sediment:a case study from Long Island Sound[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2003,56(5/6):891-896.
[63] 单红仙,张建民,贾永刚,等. 黄河口快速沉积海床土固结过程研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006(8):1676-1682. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.08.024
[64] 单红仙,郑杰文,贾永刚,等. 黄河口粉质土沉积物侵蚀性动态变化试验研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版),2009,31(4):112-119. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.04.013
[65] 孟祥梅,贾永刚,杨忠年,等. 现代黄河三角洲潮滩沉积物抗侵蚀性原位试验[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(3):39-45.
[66] ZHENG J W,JIA Y G,LIU X L et al. Experimental study of the variation of sediment erodibility under wave-loading conditions[J]. Ocean Engineering,2013,68:14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2013.04.010
[67] 郑杰文. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物波浪动力响应过程对其再悬浮控制作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.
[68] WOLANSKI E,SPAGNOL S. Dynamics of the turbidity maximum in King Sound,tropical Western Australia[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2003,56(5/6):877-890.
[69] TZANG S,OU S,HSU T. Laboratory flume studies on monochromatic wave-fine sandy bed interactions Part 2. Sediment suspensions[J]. Coastal Engineering,2009,56(3):230-243. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2008.07.005
[70] ZHANG S T,JIA Y G,WANG Z H et al. Wave flume experiments on the contribution of seabed fluidization to sediment resuspension[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2018,37(3):80-87. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1143-2
[71] ZHANG S T,JIA Y G,ZHANG Y Q, et al. Influence of seepage flows on the erodibility of fluidized silty sediments:parameterization and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2018,123(5):3307-3321.
[72] 单红仙,刘涛,陈友媛,等. 波浪载荷导致黄河口潮坪沉积物垂向运移现场观测研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2008(2):216-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.02.013
[73] LIU X L,ZHANG H,ZHENG J W,et al. Critical role of wave–seabed interactions in the extensive erosion of Yellow River estuarine sediments[J]. Marine Geology,2020,426:106208. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106208
[74] JIA Y G,ZHANG L P,ZHENG J W,et al. Effects of wave-induced seabed liquefaction on sediment re-suspension in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Ocean Engineering,2014,89:146-156. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.08.004
[75] LIU J P,MILLIMAN J D,GAO S,et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2004,209(1/4):45-67.
[76] ZHANG S T,JIA Y G,ZHANG Y Q et al. In situ observations of wave pumping of sediments in the Yellow River Delta with a newly developed benthic chamber[J]. Marine Geophysical Research,2018,39(4):463-474. doi: 10.1007/s11001-018-9344-9
[77] 朱超祁,贾永刚,刘晓磊,等. 海底滑坡分类及成因机制研究进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2015,35(6):153-163. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2015.06.016
[78] 贾永刚. 黄河口沉积物动力学与地质灾害[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.
[79] RAHMAN M S. Instability and Movement of Oceanfloor Sediments:a review[J]. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering,1994,7:589-599.
[80] ZHANG M,HUANG Y,BAO Y J. The mechanism of shallow submarine landslides triggered by storm surge[J]. Natural Hazards,2016,81(2):1373-1383. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-2112-0
[81] RAHMAN M S. Wave-induced instability of seabed:Mechanism and conditions[J]. Marine Geotechnology,1991,10(3/4):277-299.
[82] JENG D S. Mechanism of the wave-induced seabed instability in the vicinity of a breakwater:a review[J]. Ocean engineering,2001,28(5):537-570. doi: 10.1016/S0029-8018(00)00013-5
[83] WANG Z H,SUN Y F,JIA Y G et al. Wave-induced seafloor instabilities in the subaqueous Yellow River Delta—initiation and process of sediment failure[J]. Landslides,2020,17(8):1849-1862. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01399-2
[84] DIMITROVA R S,YANFUL E K. Factors affecting the shear strength of mine tailings/clay mixtures with varying clay content and clay mineralogy[J]. Engineering Geology,2012,125:11-25. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.10.013
[85] REN Y P,XU G H,XU X B et al. The initial wave induced failure of silty seabed:liquefaction or shear failure[J]. Ocean Engineering,2020,200:106990. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.106990
[86] 王虎,刘红军,张民生. 低应力条件下海洋粉土的不排水强度特性及其在海底浅层滑坡分析中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(4):849-856.
[87] XU G H,SUN Y F,WANG X et al. Wave-induced shallow slides and their features on the subaqueous Yellow River delta[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2009,46(12):1406-1417. doi: 10.1139/T09-068
[88] COLEMAN J M,GARRISON L E. Geological aspects of marine slope stability,northwestern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Marine Geotechnology,1977,2(1/4):9-44.
[89] PUIG P,OGSTON A S,MULLENBACH B L et al. Storm-induced sediment gravity flows at the head of the Eel submarine canyon,northern California margin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,2004,109:C03019.
[90] GEE M J R,GAWTHORPE R L,FRIEDMANN J S. Giant striations at the base of a submarine landslide[J]. Marine Geology,2005,214(1/3):287-294.
[91] YU H Y,LIU X L,LU Y et al. Characteristics of the sediment gravity flow triggered by wave-induced liquefaction on a sloping silty seabed:an experimental investigation[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022,10:909605. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.909605
[92] ERCILLA G,CASAS D,ALONSO B et al. Offshore geological hazards:charting the course of progress and future directions[J]. Oceans,2021,2(2):393-428. doi: 10.3390/oceans2020023
[93] HEIDRUN K, CHIOCCI F L, Christian Berndt, et al. Marine geohazards: Safeguarding society and the blue economy from a hidden threat[R]. Belgium: European Marine Board Publishing, 2021.
[94] 荆少东,梁晓勇,徐帅陵,等. 埕岛油田海上自升式平台反复插拔桩对地层的影响[J]. 油气田地面工程,2021,40(4):21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6896.2021.04.004
[95] 张宗峰,丁红岩,刘锦昆. 混凝土联锁排应用于海底管线冲刷防护试验研究[J]. 海洋工程,2015,33(2):77-83. doi: 10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2015.02.009
[96] KAZEMIAN S,HUAT B,PRASAD A et al. A review of stabilization of soft soils by injection of chemical grouting[J]. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences,2010,4:5862-5868.
[97] PAKIR F,MARTO A,MOHD YUNUS N Z et al. Effect of sodium silicate as liquid based stabilizer on shear strength of marine clay[J]. Jurnal Teknologi,2015,76:45-50.
[98] WANG C J,GUO C C,DU X M et al. Reinforcement of silty soil with permeable polyurethane by penetration injection[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,310:124829. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124829
[99] FANG H Y,ZHAO P,ZHANG C et al. A cleaner polyurethane elastomer grouting material with high hardening strain for the fundamental rehabilitation:the comprehensive mechanical properties study[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,318:125951. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125951
-




 下载:
下载: