Gravity, magnetic anomalies, and tectonic features of the Aegir Ridge and adjacent areas
-
摘要:
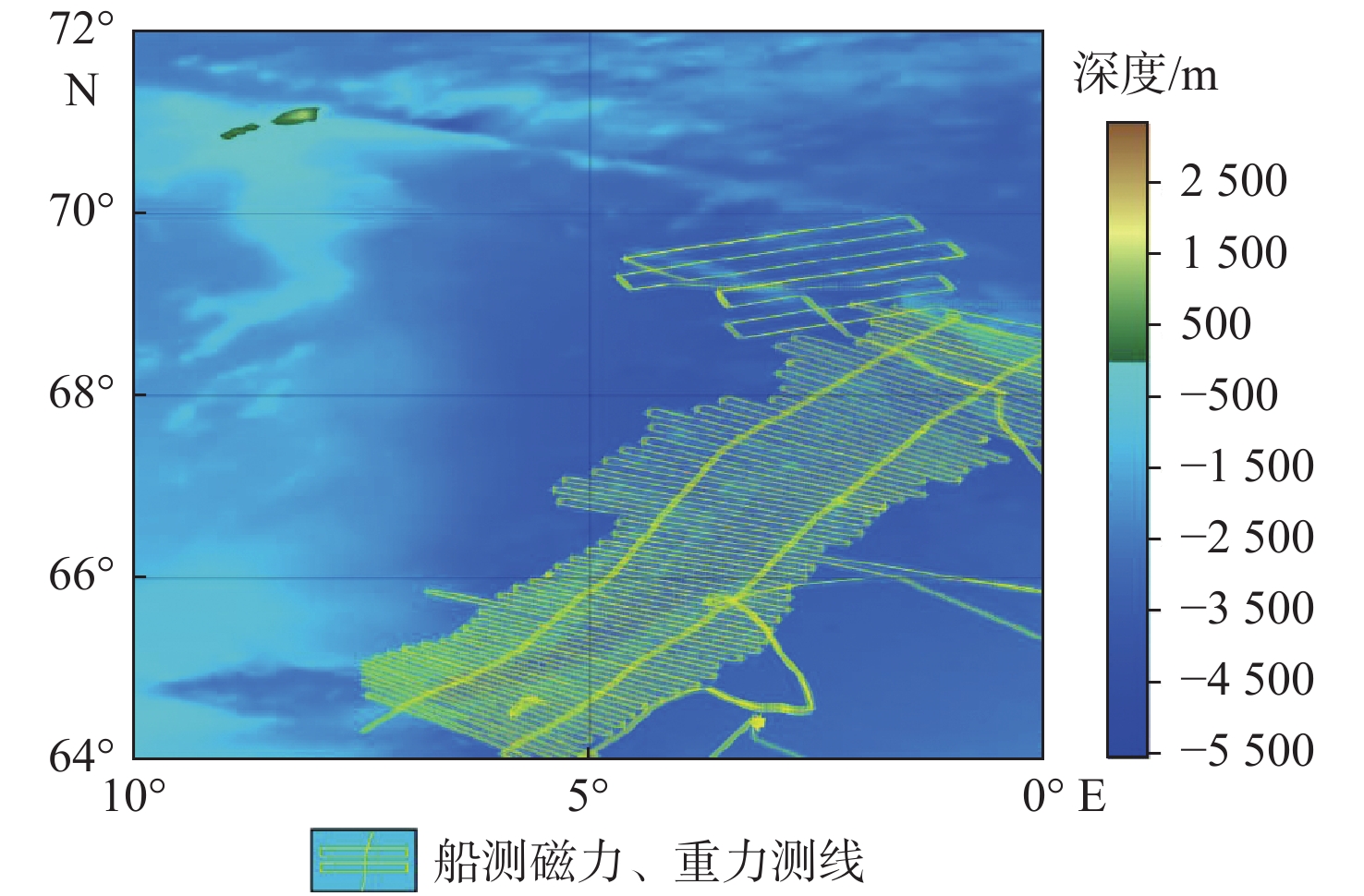
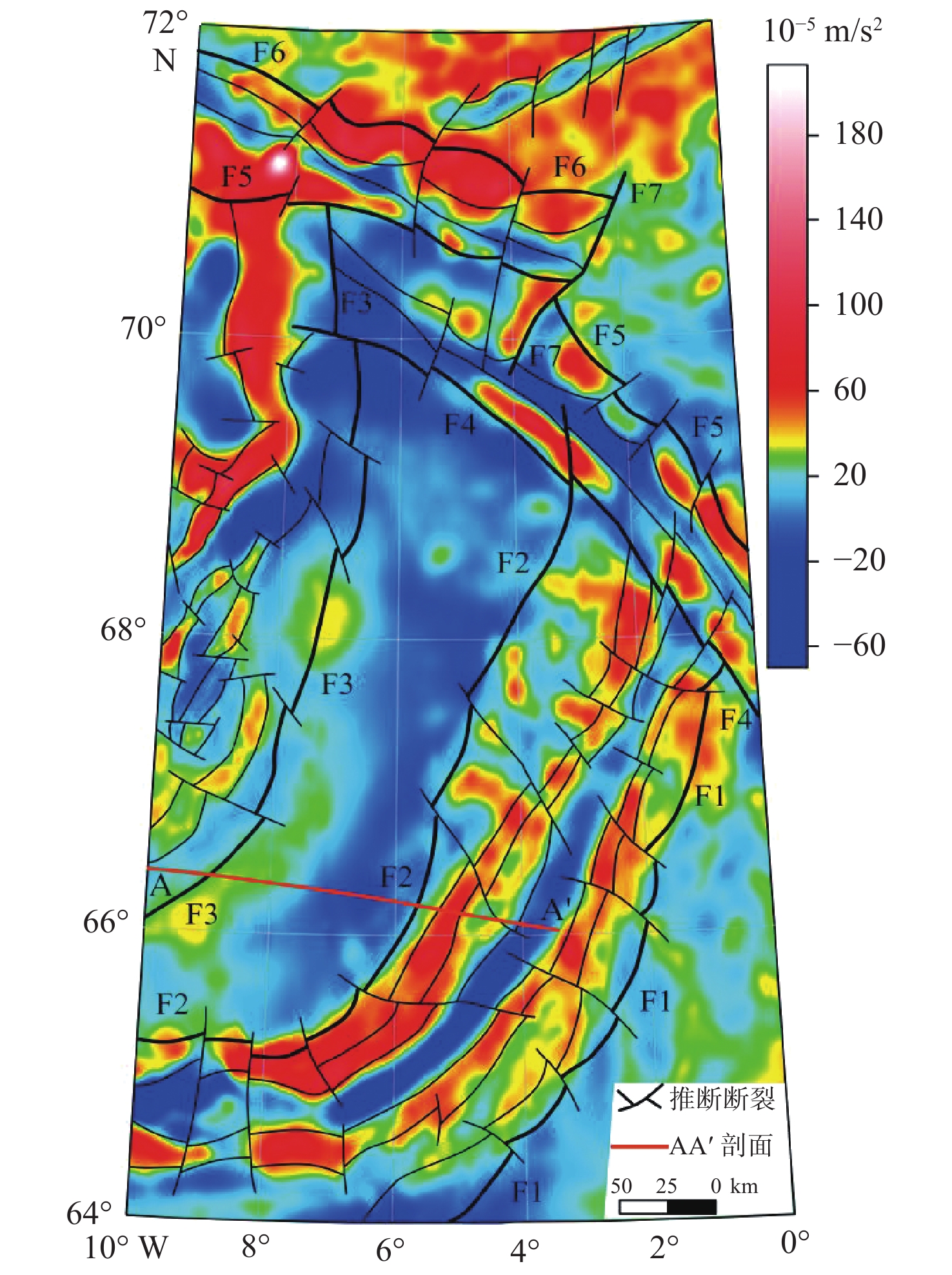
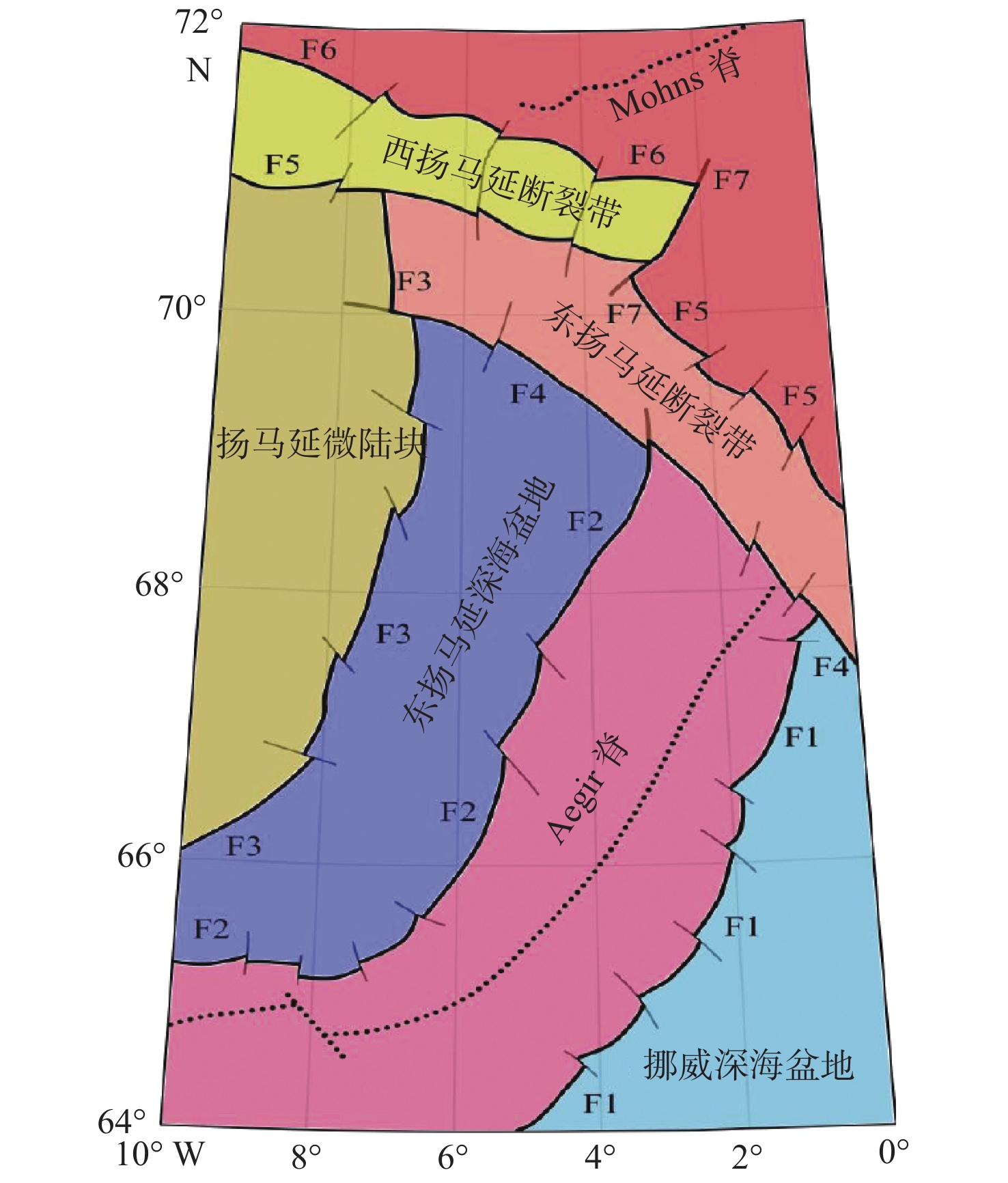
为研究北极地区挪威海内Aegir脊及邻区断裂构造特征,为北极地区油气勘探提供方向,在斯克里普斯海洋研究所发布的研究区重力数据(网格数据)基础上填充最新船测数据,对已有重磁资料进行异常分离、滑动平均和重磁场边界识别。目前,研究区的特征断裂和构造单元划分尚不清楚。根据异常极值带、异常带走向、异常梯度带变化程度等,对研究区进行了断裂识别和构造单元划分。研究表明:重磁异常特征呈NNE—NW—NE向展布,重力异常呈现高低分带,反映出该区基底隆坳相间的格架。根据重磁异常与断裂对应关系,识别出4个构造走向和7条主要断裂,划分出Mohns脊、扬马延微陆块、东扬马延断裂带、西扬马延断裂带、Aegir脊、东扬马延深海盆地和挪威深海盆地等7个构造单元。
Abstract:To study the characteristics of faults in the Aegir Ridge and its adjacent in the Norwegian Sea in the Arctic and provide direction for oil and gas exploration in the region, fill in the latest ship-borne survey data based on the gravity data (grid data) released by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. The available and the new gravity and magnetic data were analyzed by anomaly separation, sliding average, and magneto-gravity field boundary identification. At present, the division of characteristic faults and tectonic units in the study area remain unclear. According to the abnormal extreme-value, the trend of the abnormal zone, the variation scale of the abnormal gradient zone were clarified and the fault identification and structural unit division were performed. Results show that the magneto-gravity and the anomalies feature an NNE-NW-NE distribution. The gravity anomaly shows high-and-low zonation, reflecting the uplift-and-depression framework of the basement in this area. According to the corresponding relationship between magneto-gravity anomalies and faulting, 4 structural strikes and 7 regional faults were recognized. Finally, seven tectonic units were divided, i.e. Mohns Ridge, Jan Mayen Microcontinent, East Jan Mayen Fault Zone, West Jan Mayen Fault Zone, Aegir Ridge, East Jan Mayen Deep Sea Basin, and Norway Deep Sea Basin.
-
Key words:
- tectonic units /
- fault /
- gravity and magnetic data /
- Aegir Ridge /
- Arctic region
-

-
[1] 姜烨,刘琼,张英德. 扬马延微陆块构造特征及火山型被动陆缘远端带构造演化模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(5):112-122.
[2] 李进波,张文,赵亮,等. 扬马延微陆块中部重力场及构造特征[J]. 地球物理学进展,2018,33(2):467-472.
[3] JUNG W Y,VOGT P R. A gravity and magnetic anomaly study of the extinct Aegir Ridge,Norwegian Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1997,102(3):5065-5089. doi: 10.1029/96JB03915
[4] UENZELMANN‐NEBEN G,JOKAT W,MILLER H,et al. The Aegir Ridge:structure of an extinct spreading axis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1992,9/7(6):9203-9218.
[5] BREIVIK A J,MJELDE R,FALEIDE J I,et al. Rates of continental breakup magmatism and seafloor spreading in the Norway Basin-Iceland plume interaction[J]. Journalof Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2006,111(7):B07102. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004004
[6] BRANDSDOTTIR B,HOOFT E E E,MJELDE R,et al. Origin and evolution of the Kolbeinsey Ridge and Iceland Plateau,N-Atlantic[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2015,16(3):612-634.
[7] GREENHALGH E E,KUSZNIR N J. Evidence for thin oceanic crust on the extinct Aegir Ridge,Norwegian Basin,NE Atlantic derived from satellite gravity inversion[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(6):L06305. doi: 10.1029/2007GL029440
[8] BREIVIK A J,FALEIDE J I,MJELDE R. Neogene magmatism northeast of the Aegir and Kolbeinsey ridges,NE Atlantic:spreading ridge-mantle plume interaction?[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2008,9(2):Q02004. doi: 10.1029/2007GC001750
[9] KOPTEV A,CLOETINGH S,BUROV E,et al. Long-distance impact of Iceland plume on Norway's rifted margin[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x
[10] PERON-PINVIDIC G,GERNIGON L,GAINA C,et al. Insights from the Jan Mayen system in the Norwegian-Greenland sea:I. Mapping of a microcontinent[J]. Geophysical Journal International,2012,191(2):385-412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05639.x
[11] KANDILAROV A,MJELDE R,PEDERSEN R B,et al. The northern boundary of the Jan Mayen microcontinent,North Atlantic determined from ocean bottom seismic,multichannel seismic,and gravity data[J]. Marine Geophysical Research,2012,33(1):55-76. doi: 10.1007/s11001-012-9146-4
[12] HOVIKOSKI J,FYHN M B W,NØHR-HANSEN H,et al. Paleocene-Eocene volcanic segmentation of the Norwegian-Greenland seaway reorganized high-latitude ocean circulation[J]. Communications Earth & Environment,2021,2(1):1-10.
[13] RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ Q,OTTEMÖLLER L. Source study of the Jan Mayen transform fault strike-slip earthquakes[J]. Tectonophysics,2014(628):71-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.04.035
[14] KHARIN G S,EROSHENKO D V. Magmatism:the Jan Mayen hotspot,Arctic Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Seismology,2014,8(2):108-124. doi: 10.1134/S074204631402002X
[15] GREVEMEYER I,WEIGEL W,DEHGHANI G A,et al. The Aegir Rift:crustal structure of an extinct spreading axis[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches,1997,19(1):1-23. doi: 10.1023/A:1004288815129
[16] MEYER B,CHULLIAT A,SALTUS R. Derivation and error analysis of the earth magnetic anomaly grid at 2 arc min resolution version 3 (EMAG2v3)[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2017,18(12):4522-4537.
[17] BLISCHKE A,STOKER M S,BRANDSDÓTTIR B,et al. The Jan Mayen microcontinent's Cenozoic stratigraphic succession and structural evolution within the NE-Atlantic[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2019(103):702-737. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.02.008
[18] 邢锦程,袁炳强,张春灌,等. 特立尼达盆地重力场特征及油气远景[J]. 物探与化探,2021,45(6):1606-1616.
[19] 张明华, 乔计花, 黄金明, 等. 重磁电数据处理解释软件RGIS[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
[20] 韩梅,张春灌,李想,等. 利用重磁资料研究楚科奇边缘地构造特征[J]. 地球物理学进展,2022,37(3):945-951.
[21] KODAIRA S,NO T,NAKAMURA Y,et al. Coseismic fault rupture at the trench axis during the 2011 Tohokuoki earthquake[J]. Nature Geoscience,2012,5(9):646-650. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1547
[22] 陈青,袁炳强,董云鹏,等. 断裂识别新方法及其在肯尼亚Tana凹陷中的应用[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2013,43(4):599-605.
[23] 许文强,袁炳强,刘必良,等. 多种重磁位场边缘识别方法及在南黄海北部断裂构造识别中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探,2020,44(4):962-974.
[24] 张春灌,袁炳强,李玉宏. 吐鲁番中南部地区航磁异常特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(5):1811-1817.
[25] KODAIRA S,MJELDE R,GUNNARSSON K,et al. Structure of the Jan Mayen microcontinent and implications for its evolution[J]. Geophysical Journal International,1998,132(2):383-400. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.1998.00444.x
[26] 杜文波,邱燕,汪俊,等. 西南次海盆及邻区CFT测线重磁震联合反演及其应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2021,37(12):38-48.
[27] BLISCHKE A,GAINA C,HOPPER J R,et al. The Jan Mayen microcontinent:an update of its architecture,structural development and role during the transition from the Aegir Ridge to the mid-oceanic Kolbeinsey Ridge[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications,2017,447(1):299-337. doi: 10.1144/SP447.5
[28] VOGT P R,JUNG W Y. Treitel Ridge:a unique inside corner hogback on the west flank of extinct Aegir spreading ridge,Norway Basin[J]. Marine Geology,2009,267(1/2):86-100. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.09.006
-




 下载:
下载: