Selection of parameters for simulation of net ecosystem carbon flux in Yancheng coastal wetland, Jiangsu
-
摘要:
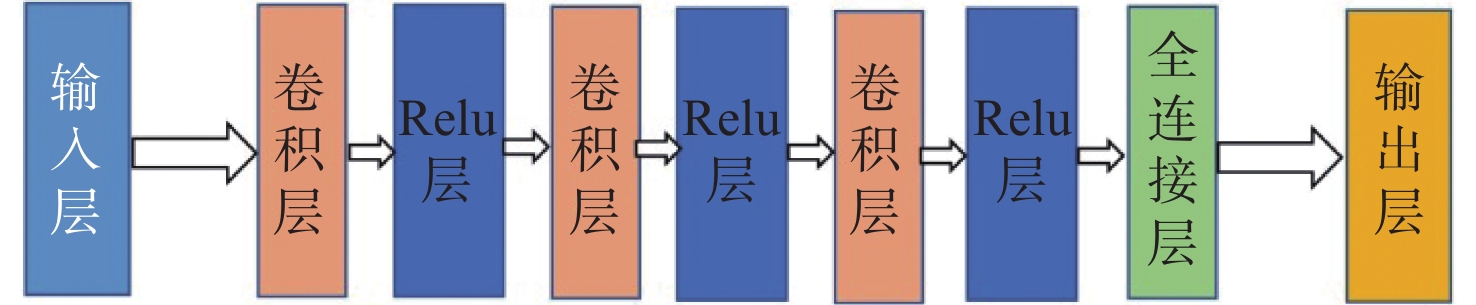
滨海湿地净生态系统碳交换量受到多种环境因素的影响,在进行滨海湿地净碳交换量估算建模时,参数的选择至关重要,如何合理地选择输入参数不仅对于估算结果的精度有影响,同时也会影响预测模型的适用性。本研究使用了Pearson、Spearman、距离相关系数、最大互信息相关系数4种相关系数来计算各个环境因素与净碳交换量之间的相关性,基于相关系数来选择最佳的输入参数组合。利用实际测得的江苏盐城盐沼湿地数据,依次选择各个相关性中最高的8个参数组合,基于卷积神经网络对江苏盐城滨海湿地NEE进行建模,得到了4个预测模型,并使用均方根误差和平均绝对值误差来进行模型精度的验证。研究表明,使用基于最大互信息系数得到的参数组合进行滨海湿地NEE建模时模型的精度最好,误差最小;净光合有效辐射,净辐射,地表辐射与NEE在4个相关系数中都属于强相关,表明这一类辐射类参数对滨海湿地NEE的影响要大于其他参数;各参数与NEE之间的关系既包含线性关系也包含非线性关系,传统的单一线性分析手段无法完整准确地反应各个环境参数与NEE之间的响应关系;基于卷积神经网络的滨海湿地NEE预测模型在精度上要优于其它同类型模型,这表明使用该模型在进行NEE预测建模时具有很好的适用性。
Abstract:The net ecosystem carbon exchange (NEE) of coastal wetland is affected by various environmental factors. The selection of parameters is very important for estimating and modeling the NEE of coastal wetland. How to reasonably select the input parameters affects not only the accuracy of the estimation results, but also the applicability of the prediction model. Four correlation coefficients were used, including the Pearson correlation coefficient, the Spearman correlation coefficient, the distance correlation coefficient, and the correlation coefficient of maximum mutual information, to calculate the correlation between various environmental factors and NEE, according to which the best combination of input parameters was chosen. Using the measurement data of the Yancheng salt marsh wetland in Jiangsu Province, eight parameter combinations with the highest correlation were selected, then eight factors were input into the convolutional neural network for model training, and finally four prediction models obtained. The root mean square error and mean absolute error were used to verify the accuracy of the model. After calculation, the root mean square errors of the four models were 0.0134, 0.0092, 0.0109, 0.0051, and the absolute errors were 0.064, 0.068, 0.0574, 0.0439, respectively. This study shows that: 1) to model the NEE of coastal wetland with the parameter combination based on the maximum mutual information coefficient, the photosynthetic effective radiation, surface radiation, net radiation, photosynthetic effective radiation, soil albedo, air temperature, relative humidity, surface temperature, and soil moisture content, the accuracy of the modeling is the best and the error is the smallest. 2) Among 15 parameters used, the net photosynthetic effective radiation, net radiation, surface radiation, and NEE are strongly correlated in the four correlation coefficients, which showed that radiation parameter had a greater impact on wetland carbon cycle than other parameters. 3) Relationship between each parameter and NEE included both linear and nonlinear relationships. The conventional single linear analysis method cannot completely and accurately reflect the response relationship between each environmental parameter and NEE. In the future works, we shall not only study the linear relationship among variables but also pay more attention to the nonlinear mutual relationship. 4) The accuracy of the coastal wetland NEE prediction model based on convolutional neural network was better than other similar models’, which shows that the model is applicate in NEE prediction modeling. This study provided a reference for NEE prediction modeling and analysis of coastal wetland in the future.
-
Key words:
- convolutional neural network /
- correlation coefficient /
- coastal wetland /
- NEE
-

-
表 1 观测参数符号及名称
Table 1. Symbols and names of the variables
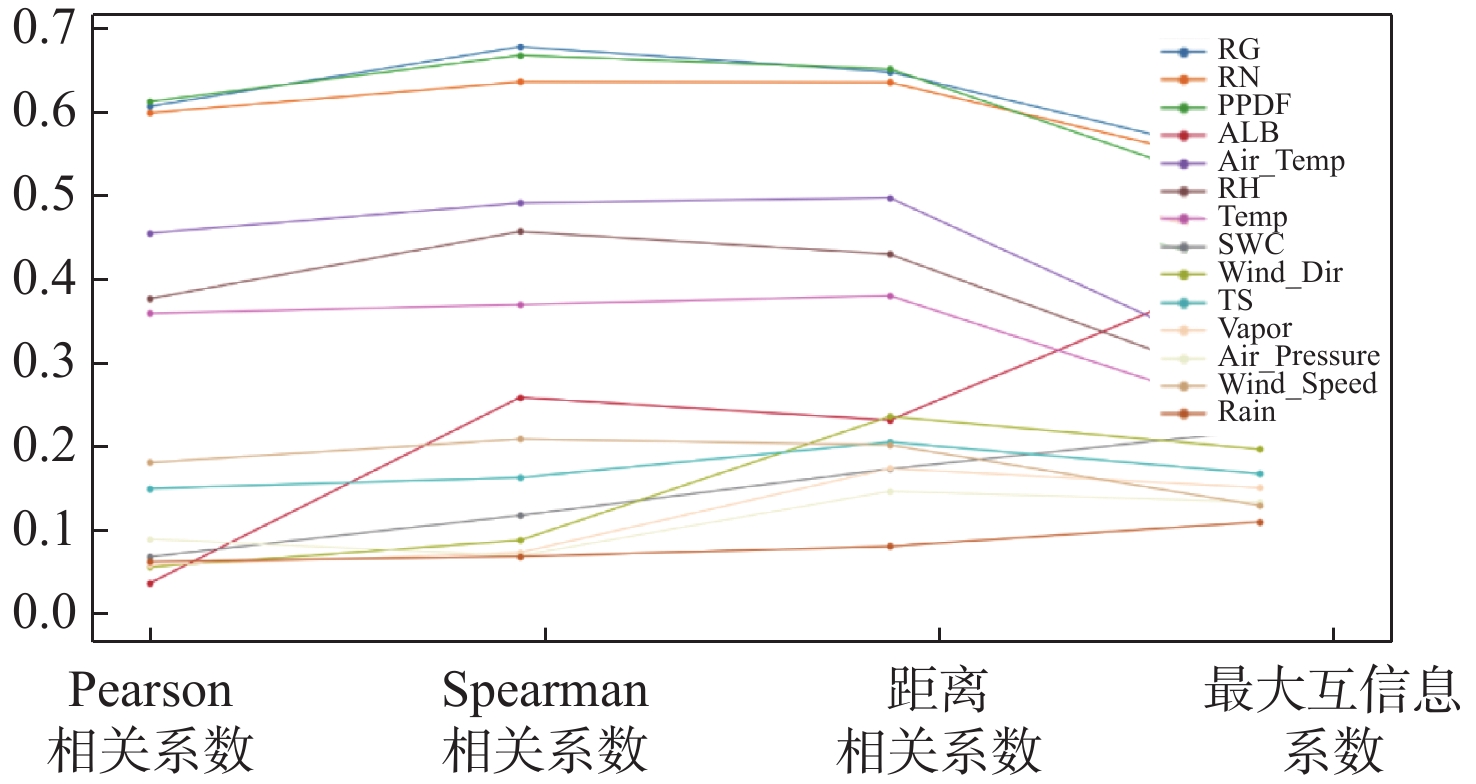
符号 参数名称 符号 参数名称 RG 地表辐射 WDir 风向 PPDF 光合有效辐射 APre 气压 RN 净辐射 Rain 降雨量 ATemp 气温 WSpee 风速 RH 相对湿度 Vapor 蒸汽压 TS 土壤温度 SWC 土壤含水量 Temp 地表温度 ALB 土壤反照率 NEE 净生态系统碳交换量 表 2 Pearson相关系数计算结果Table2 Pearson correlation coefficient calculation results
参数名称 Rp 参数名称 Rp RG 0.607 8 RN 0.599 3 PPDF 0.613 9 ALB 0.000 1 ATemp 0.446 1 RH 0.362 6 Temp 0.343 7 SWC 0.033 8 WDir 0.020 6 TS 0.120 6 Vapor 0.023 0 APre 0.056 1 WSpee 0.153 7 Rain 0.027 6 表 3 Spearman相关系数计算结果
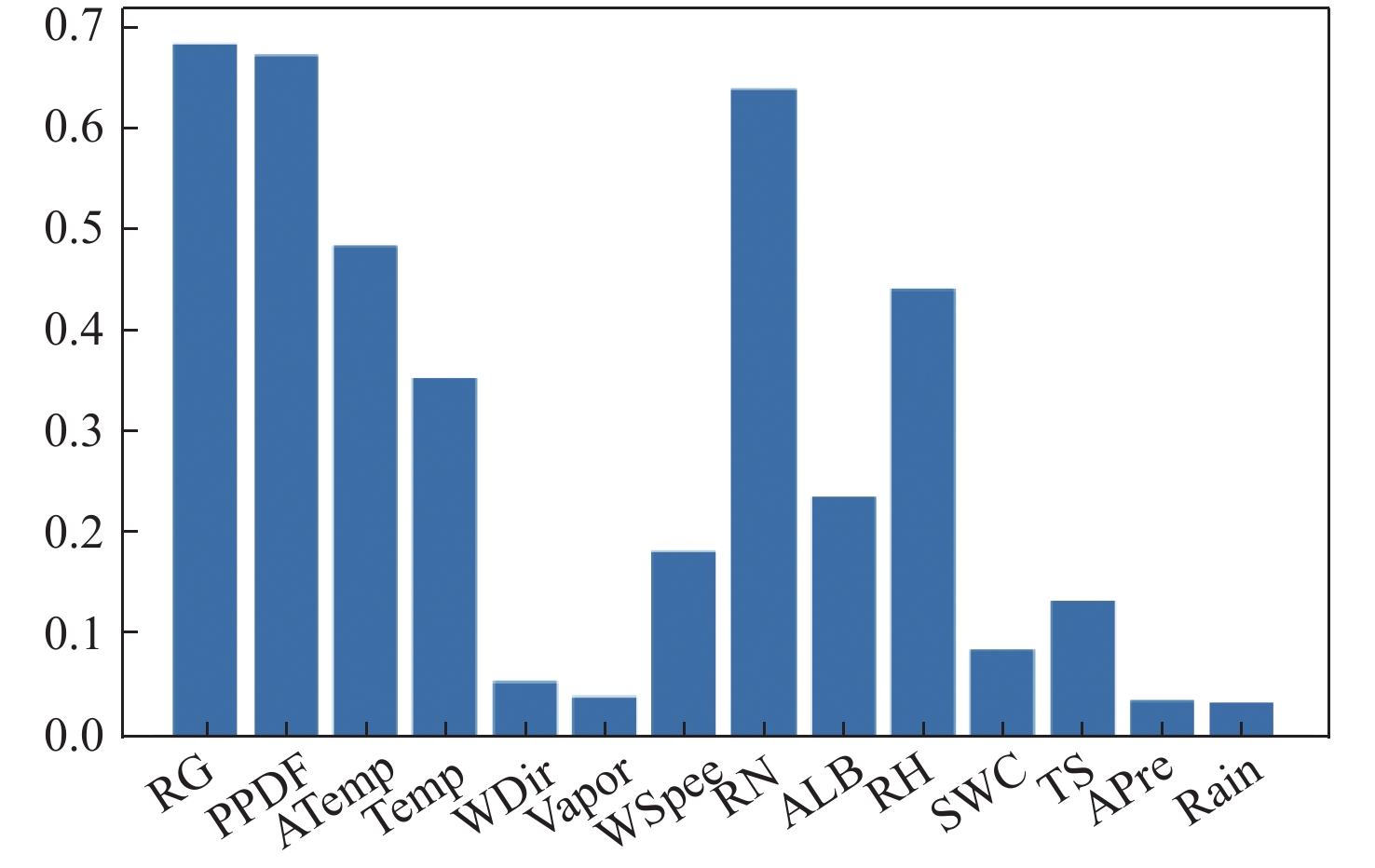
Table 3. Results of the Spearman coefficient calculation
参数名称 Rs 参数名称 Rs RG 0.683 5 RN 0.638 8 PPDF 0.672 6 ALB 0.236 7 ATemp 0.484 5 RH 0.442 1 Temp 0.355 0 SWC 0.086 3 WDir 0.054 5 TS 0.134 5 Vapor 0.039 0 APre 0.035 0 WSpee 0.183 6 Rain 0.034 1 表 4 距离相关系数计算结果
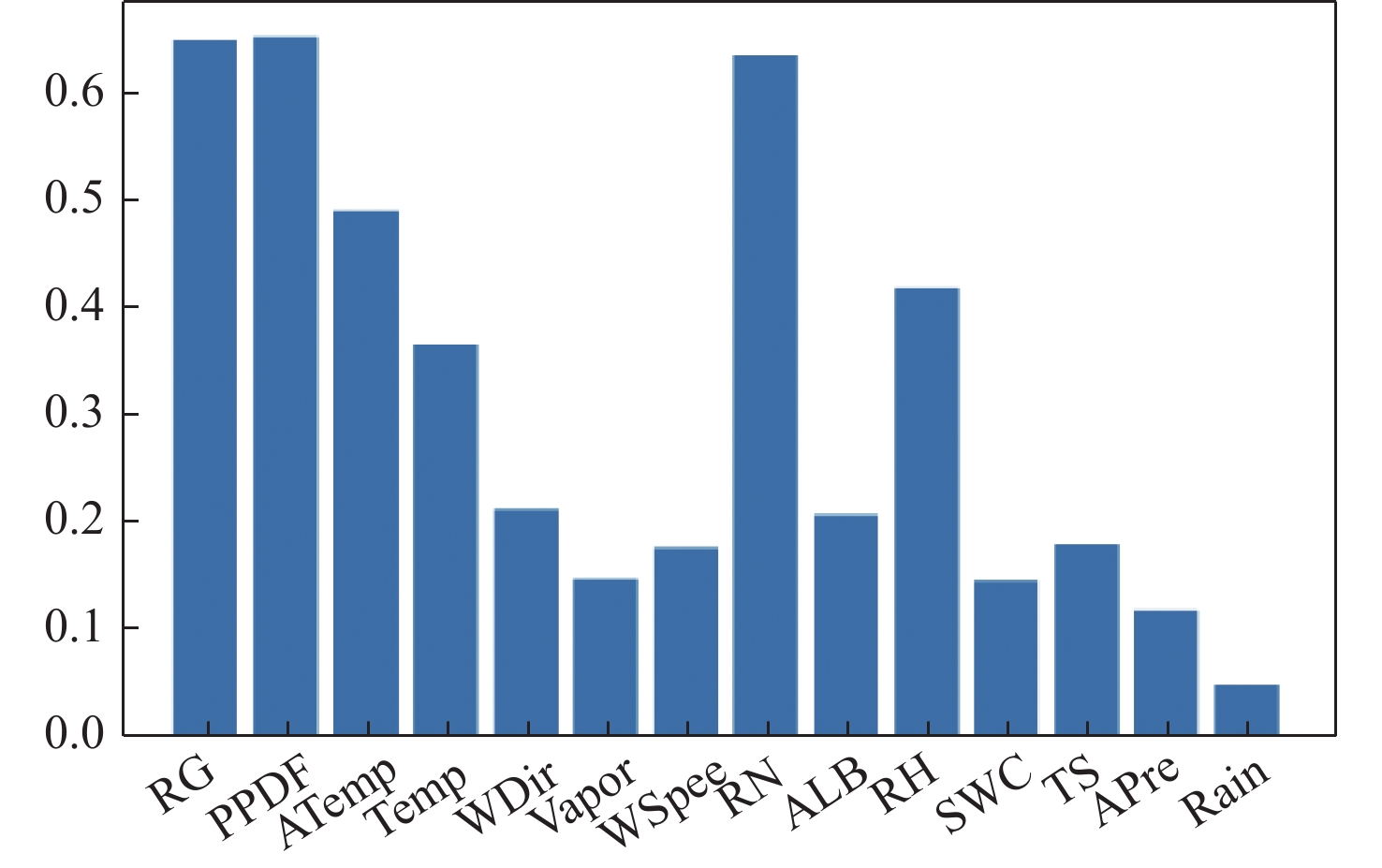
Table 4. Results of distance coefficient calculation
参数名称 dCor 参数名称 dCor RG 0.651 4 RN 0.638 2 PPDF 0.655 2 ALB 0.207 6 ATemp 0.491 0 RH 0.419 2 Temp 0.366 3 SWC 0.145 6 WDir 0.212 2 TS 0.179 9 Vapor 0.146 1 APre 0.117 2 WSpee 0.176 2 Rain 0.046 9 表 5 最大信息系数计算结果
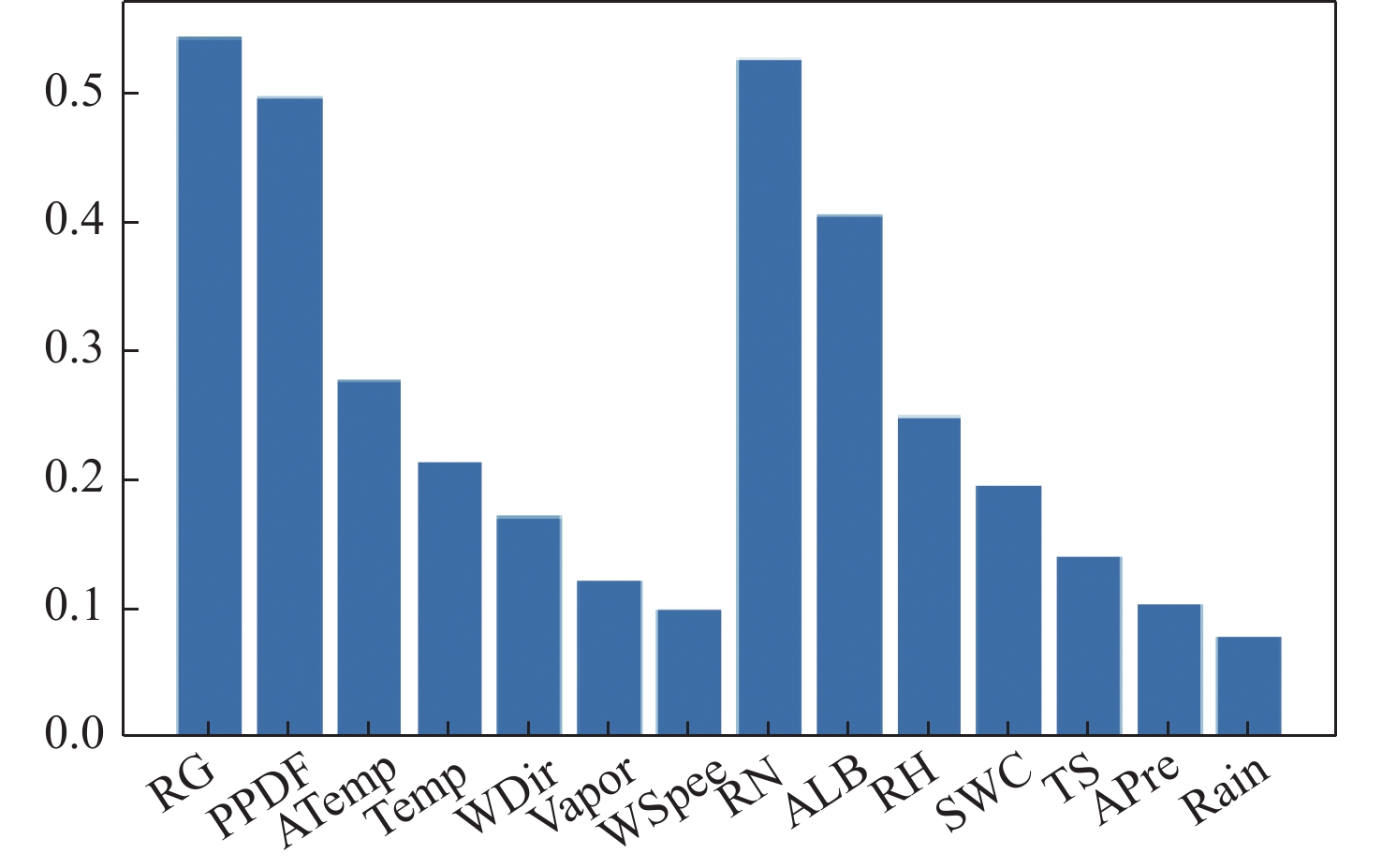
Table 5. Results of the maximal information coefficients calculation
参数名称 
参数名称 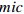
RG 0.539 6 RN 0.522 7 PPDF 0.494 7 ALB 0.403 6 ATemp 0.275 7 RH 0.247 4 Temp 0.213 4 SWC 0.195 0 WDir 0.170 8 TS 0.139 5 Vapor 0.121 6 APre 0.103 3 WSpee 0.099 0 Rain 0.078 1 表 6 参数组合
Table 6. Combination of the parameters
相关系数计算方法 参数组合 Pearson相关系数 光合有效辐射,地表辐射,净辐射,气温,
相对湿度,地表温度,风速,土壤温度Spearman相关系数 地表辐射,光合有效辐射,净辐射,气温,
相对湿度,地表温度,土壤反照率,风速距离相关系数 光合有效辐射,地表辐射,净辐射,气温,
相对湿度,地表温度,风向,土壤反照率最大信息系数 地表辐射,净辐射,光合有效辐射,土壤反照率,气温,相对湿度,地表温度,土壤含水率 表 7 误差计算结果
Table 7. Results of calculation error
均方根误差 绝对值误差 CNN_Model1 0.013 4 0.064 0 CNN_Model2 0.009 2 0.068 4 CNN_Model3 0.010 9 0.057 4 CNN_Model4 0.005 1 0.043 9 -
[1] 唐剑武,叶属峰,陈雪初,等. 海岸带蓝碳的科学概念、研究方法以及在生态恢复中的应用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2018,48(6):661-670.
[2] TANG J W,YE S F,CHEN X C, et al. Coastal blue carbon:concept,study method,and the application to ecological restoration[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences),2018,61(6):637-646.
[3] 吕亚香,戚智彦,刘伟,等. 早春和夏季氮磷添加对内蒙古典型草原退化群落碳交换的影响[J]. 植物生态学报,2021,45(4):11-13.
[4] MÜLLER C,LUCHT W. Robustness of terrestrial carbon and water cycle simulations against variations in spatial resolution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:atmospheres,2007,112(D6):19-26.
[5] DESAI,ANKUR R. Climatic and phenological controls on coherent regional interannual variability of carbon dioxide flux in a heterogeneous landscape[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research. Biogeosciences,2011,116(G3):G00J02-1-G00J02-13.
[6] GRANT R F,BALDOCCHI D D,MA S. Ecological controls on net ecosystem productivity of a seasonally dry annual grassland under current and future climates:modelling with Ecosys[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2012,152:189-200.
[7] DOU X,YANG Y. Estimating forest carbon fluxes using four different data-driven techniques based on long-term eddy covariance measurements:model comparison and evaluation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:78-94.
[8] CAI J , XU K , ZHU Y , et al. Prediction and analysis of net ecosystem carbon exchange based on gradient boosting regression and random forest[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 262: 1429-1442.
[9] AGO E E,AGBOSSOU E K,GALLE S,et al. Long term observations of carbon dioxide exchange over cultivated savanna under a Sudanian climate in Benin (West Africa)[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2014,197:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.06.005
[10] HAO L,ZHANG Z. Mining the intrinsic trends of CO2 solubility in blended solutions[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization,2018,26:496-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.06.008
[11] ZHANG Z,LI H,CHANG H et al. Machine learning predictive framework for CO2 thermodynamic properties in solution[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization,2018,26:152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jcou.2018.04.025
[12] WU J,ALBERT L P,LOPES A P et al. Leaf development and demography explain photosynthetic seasonality in Amazon evergreen forests[J]. Science,2016,351(6276):972-976. doi: 10.1126/science.aad5068
[13] VELPURI M N,SENAY G B,SINGH R K,et al. A comprehensive evaluation of two MODIS evapotranspiration products over the conterminous United States:using point and gridded FLUXNET and water balance ET[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment:An Interdisciplinary Journal,2013,139:35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.07.013
[14] CAI J,XU K,ZHU Y et al. Prediction and analysis of net ecosystem carbon exchange based on gradient boosting regression and random forest[J]. Applied Energy,2020,262:114566-114566. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114566
[15] WANG Y Y,XIE Z H,JIA B H,et al. Improving simulation of the terrestrial carbon cycle of China in Version 4.5 of the community land model using a revised V_(cmax) Scheme[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters,2015,8(2):88-94. doi: 10.1080/16742834.2015.11447243
[16] SCHAEFER K,SCHWALM C R,WILLIAMS C,et al. A model-data comparison of gross primary productivity:results from the north American carbon program site synthesis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Biogeosciences Research,2012,117(G3):G03010-1-G03010-15.
[17] CHE S, TAN X, XIANG C, et al. Stand basal area modelling for Chinese fir plantations using an artificial neural network model[J]. Journal of Forestry Research,2019,30(5):1641-1649.
[18] JUNG M,REICHSTEIN M,MARGOLIS H,et al. Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide,latent heat,and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance,satellite,and meteorological observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research. Biogeosciences,2011,116(G3):G00J07-1-G00J07-16.
[19] XIAO J F,ZHUANG Q L,BALDOCCHI D D,et al. Estimation of net ecosystem carbon exchange for the conterminous United States by combining MODIS and AmeriFlux data[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2008,148(11):1827-1847. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2008.06.015
[20] ROBERT J M,MAIER H R,DANDY J M,et al. Non-linear variable selection for artificial neural networks using partial mutual information[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software,2008,23(10/11):1312-1326.
[21] QUILTY J,ADAMOWSKI J,KHALIL B,et al. Bootstrap rank-ordered conditional mutual information (broCMI):a nonlinear input variable selection method for water resources modeling[J]. Water Resources Research,2016,52(3):2299-2326. doi: 10.1002/2015WR016959
[22] GALELLI S,HUMPHREY G B,MAIER H R, et al. An evaluation framework for input variable selection algorithms for environmental data-driven models[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software,2014,62:33-51.
[23] NOORI R,KARBASSI A R,MOGHADDAMNIA A, et al. Assessment of input variables determination on the SVM model performance using PCA,Gamma test,and forward selection techniques for monthly stream flow prediction[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2011,401(3/4):177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.02.021
[24] 李永强,董智,丁晨曦,等. 山东省暖性草丛生态系统碳库现状和碳通量季节变化特征[J]. 植物生态学报,2018,42(3):11-13.
[25] 王富强,刘扬李,杨欢,等. 寒区滨河湿地生态系统碳通量特征及影响因素[J]. 水电能源科学,2018,36(10):68-71.
[26] GJ SZÉKELY, RIZZO M L, BAKIROV N K. Measuring and testing dependence by correlation of distances [C]//ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software & Technology, 2007.
[27] ABRAHART R J,ANCTIL F,Coulibaly P,et al. Two decades of anarchy Emerging themes and outstanding challenges for neural network river forecasting[J]. Progress in Physical Geography,2012,36(4):480-513. doi: 10.1177/0309133312444943
[28] YADAV A K,CHANDEL S S. Solar radiation prediction using Artificial Neural Network techniques:a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2014:33-33.
[29] MELESSE A M,HANLEY R S. Artificial neural network application for multi-ecosystem carbon flux simulation[J]. Ecological Modelling,2005,189(3/4):305-314. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.03.014
[30] WEN X D,ZHAO Z H,DENG X W,et al. Applying an artificial neural network to simulate and predict Chinese Cross Mark fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantation carbon flux in subtropical China[J]. ECOL MODEL,2014,294(5):19-26.
[31] GU,JIUXIANG,WANG,ZHENHUA,KUEN,JASON,et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks[J]. Pattern Recognition:The Journal of the Pattern Recognition Society,2018:77354-377.
[32] HAMZEHIE M E, MAZINANI S, DAVARDOOST F, et al. Developing a feed forward multilayer neural network model for prediction of CO2 solubility in blended aqueous amine solutions[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2014,21:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2014.07.022
[33] BEIGZADEH R, RAHIMI M, SHABANIAN S R. Developing a feed forward neural network multilayer model for prediction of binary diffusion coefficient in liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria,2012,331:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.fluid.2012.06.025
[34] SLAVAKIS K,THEODORIDIS S,YAMADA I. Online Kernel-Based Classification Using Adaptive Projection Algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing:a publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society,2008,56(7):2781-2796.
[35] ZHANG K,ZHU G F,MA J Z,et al. Parameter analysis and estimates for the MODIS evapotranspiration algorithm and multiscale verification[J]. Water Resources Research,2019,55(3):2211-2231. doi: 10.1029/2018WR023485
[36] LIU Y L,ZHOU G M,DU H Q,et al. Response of carbon uptake to abiotic and biotic drivers in an intensively managed Lei bamboo forest[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2018,223:713-722.
[37] LIU H X,YI Y J,YUE Y S,et al. Reducing the likelihood of carbon loss from wetlands by improving the spatial connections between high carbon patches[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,267:121819.1-121819.12.
[38] 韩智献,仝川,刘白贵,等. 模拟海平面上升和氮负荷增加对河口感潮沼泽湿地CO2垂直交换的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(6):2421-2429.
[39] 陈小平,刘廷玺,王冠丽,等. 温度和水分对科尔沁草甸湿地净生态系统碳交换量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2018,29(5):1523-1534.
-



 下载:
下载: