Similarity measurement algorithm of REE distribution curve and its application for provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea
-
摘要:
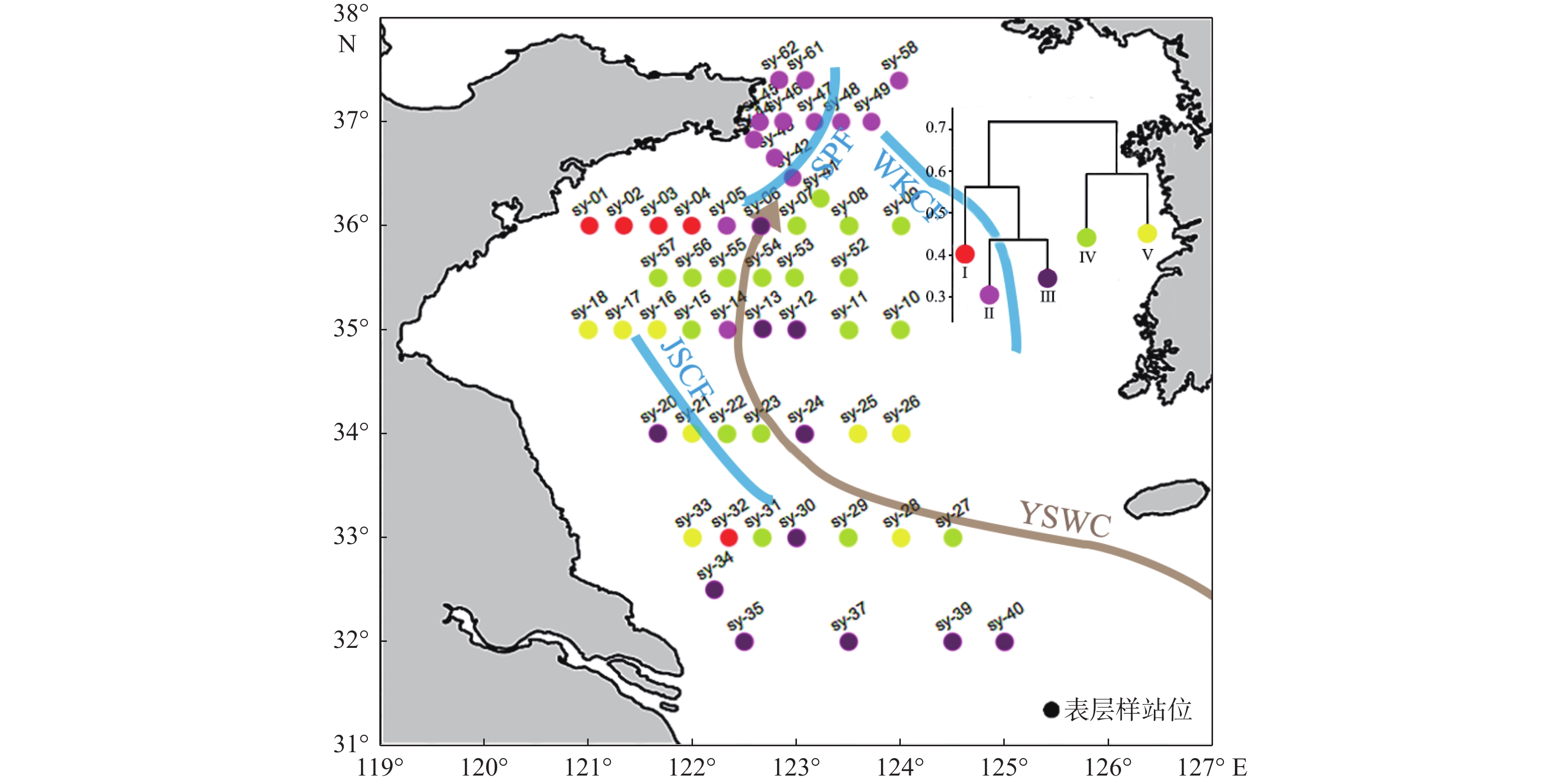
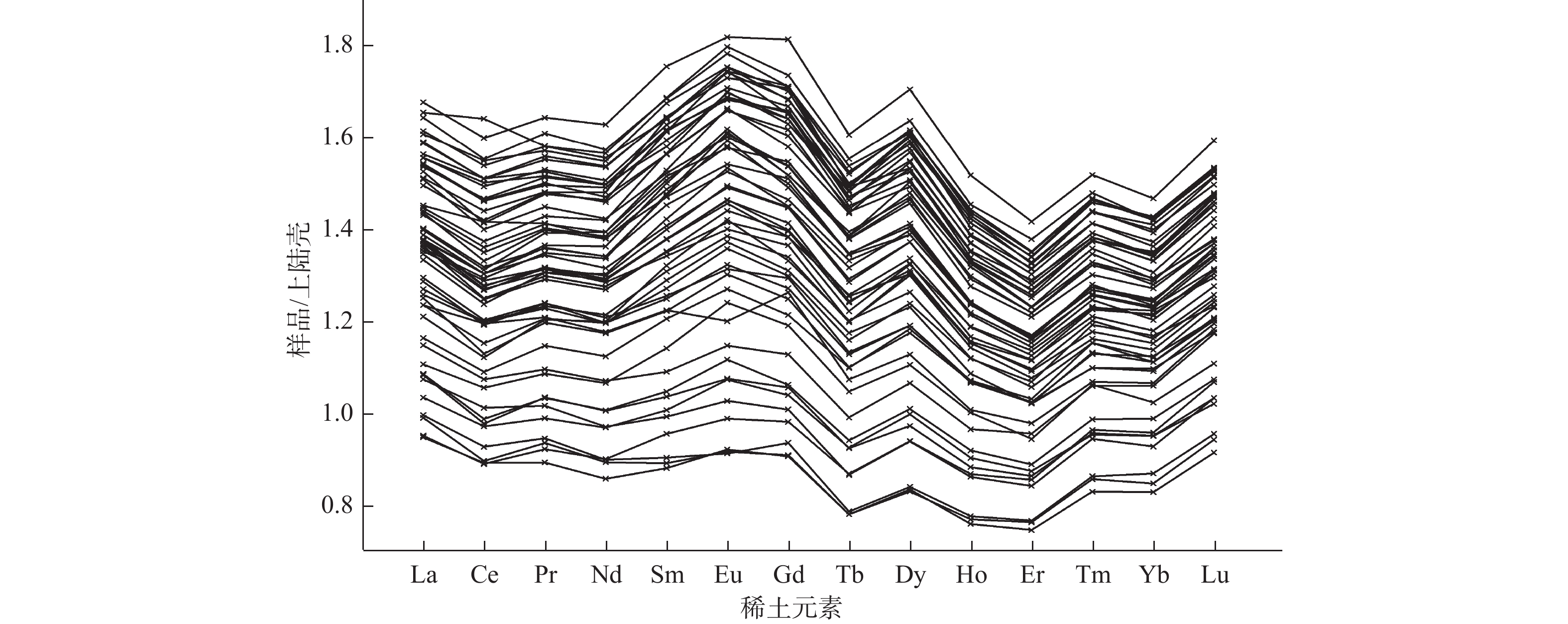
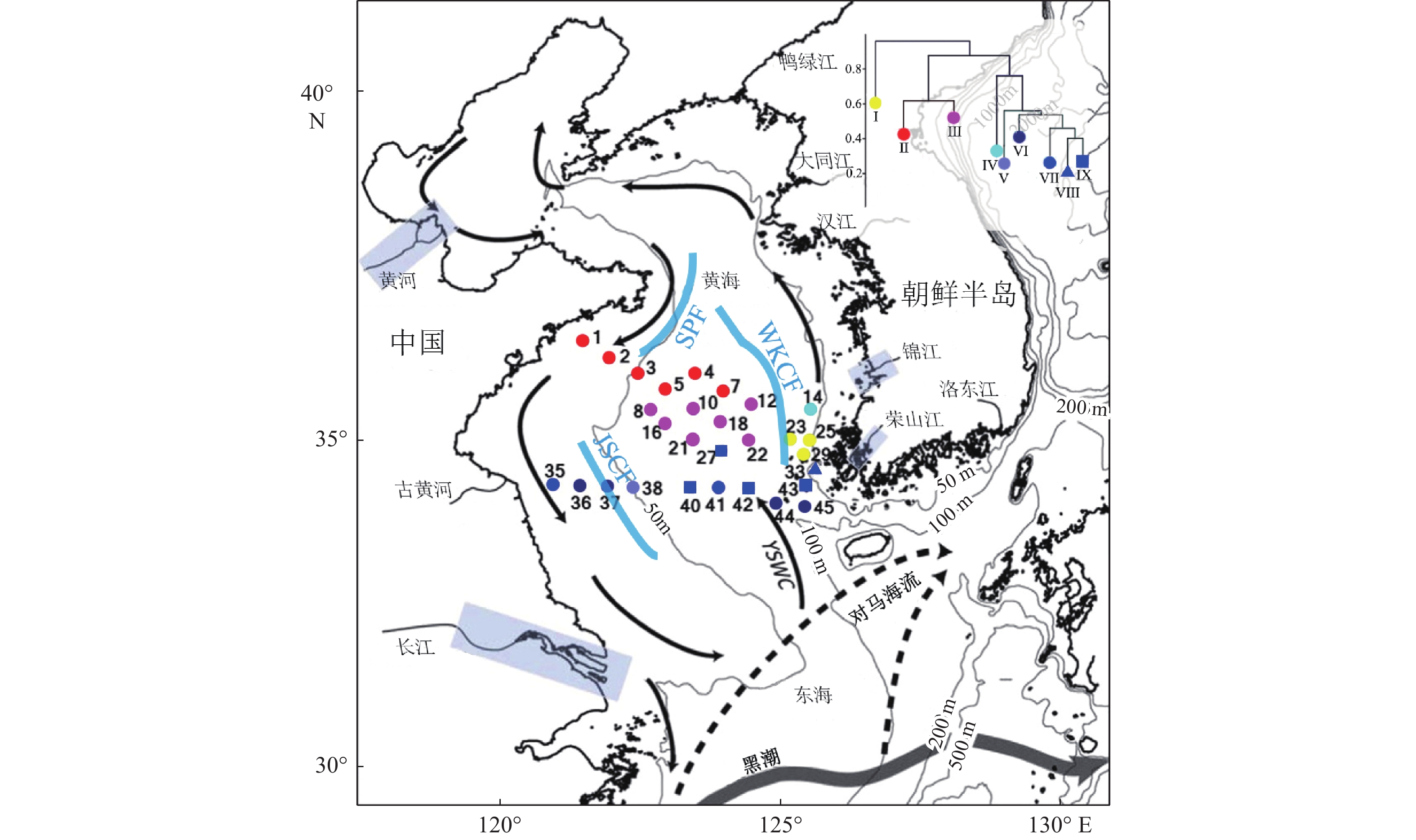
稀土元素配分曲线常被用于判别沉积物物源,相同物源沉积物的稀土元素配分曲线往往具有相似的形态特征。然而,当前稀土元素配分曲线相似性判别仍然采用人眼目视判别,主观性较强且无法实现定量判别,因此需要一种统一的度量手段实现稀土元素配分曲线的定量相似度计算,进而在此基础上开展聚类、分类等统计分析操作,充分挖掘稀土元素数据中的物源信息。本研究提出一种稀土元素配分曲线相似性度量算法,该算法不受稀土元素绝对丰度的影响,能够有效甄别稀土元素配分曲线之间形态上的差异。该算法的聚类结果显示,黄河和长江是南黄海中部泥质区的主要物质来源,黄河黏土粒级物质可以由沿岸流输运至黄海33°N处,长江黏土粒级物质被黄海暖流携带北上最远至黄海36°N附近,西朝鲜海洋锋面将朝鲜半岛河流的影响范围限制在了其东侧;东南黄海泥质区除了接收朝鲜半岛河流的供给外,其南部还接收了中国河流的细粒物质供应。
Abstract:Rare earth element (REE) distribution curves are often used to specify sediments provenance. The REE distribution curves of sediments from the same source are often similar in shape. However, currently, the similarity discrimination of REE distribution curves still relies on visual discrimination by the human eye, which is highly subjective and cannot achieve quantitative discrimination. Therefore, a unified measurement method is needed to realize the quantitative calculation of the similarity of REE distribution, based on which statistical analyses such as clustering and classification were carried out and the information of provenance in REE perspectives was fully explored. An algorithm for measuring the similarity was proposed, and it is independent of the absolute abundance of REE and can effectively map the differences in the shape of REE distribution curves. The clustering results based on this algorithm show that the Yellow River and the Yangtze River are the main provenances of the muddy area in the central part of the South Yellow Sea. The Yellow River clay fractions can be transported to 33 °N of the Yellow Sea by alongshore current, while the Yangtze River clay fractions be carried northward by the Yellow Sea Warm Current as far as to 36 °N of the Yellow Sea. The West Korea Coastwise Front limits the influence of the rivers in the Korean Peninsula to its east. In addition to receiving the supply from the rivers in the Korean Peninsula, the southeast Yellow Sea mud also receives the supply of fine-grained sediments from Chinese rivers.
-
Key words:
- rare earth element /
- REE distribution curve /
- provenance /
- similarity measurement /
- clustering
-

-
表 1 各河流沉积物稀土元素配分曲线的相似度
Table 1. The similarity of curves in REE distribution of sediments among different rivers
长江 黄河 鸭绿江 汉江 锦江 荣山江 长江 1.0 0.667 4 0.076 8 0.109 5 0.131 3 0.136 8 黄河 0.667 4 1.0 0.060 2 0.090 6 0.131 3 0.116 0 鸭绿江 0.076 8 0.060 2 1.0 0.101 4 0.174 2 0.154 5 汉江 0.109 5 0.090 6 0.101 4 1.0 0.524 1 0.475 9 锦江 0.131 3 0.116 2 0.174 2 0.524 1 1.0 0.611 5 荣山江 0.136 8 0.116 0 0.154 5 0.475 9 0.611 5 1.0 表 2 各河流沉积物稀土元素数据的欧式距离
Table 2. The Euclidean distance of REE data of sediments among different rivers
长江 黄河 鸭绿江 汉江 锦江 荣山江 长江 0 0.937 5 1.176 0 2.001 6 1.158 1 0.898 0 黄河 0.937 5 0 2.044 3 2.682 0 1.590 2 0.797 5 鸭绿江 1.176 0 2.044 3 0 1.543 0 1.476 9 1.769 5 汉江 2.001 6 2.682 0 1.543 0 0 1.201 3 2.032 1 锦江 1.158 1 1.590 2 1.769 5 1.201 3 0 0.882 9 荣山江 0.898 0 0.797 5 1.769 5 2.032 1 0.882 9 0 -
[1] 张宏飞, 高山. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012: 130.
[2] LIM D,JUNG H S,CHOI J Y. REE partitioning in riverine sediments around the Yellow Sea and its importance in shelf sediment provenance[J]. Marine Geology,2014,357:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.002
[3] JUNG H S,LIM D,CHOI J Y,et al. Rare earth element compositions of core sediments from the shelf of the South Sea,Korea:their controls and origins[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2012,48:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.08.008
[4] LIM D,CHOI J Y,SHIN H H,et al. Multielement geochemistry of offshore sediments in the southeastern Yellow Sea and implications for sediment origin and dispersal[J]. Quaternary International,2013,298:196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.01.004
[5] 王金土. 黄海表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学[J]. 地球化学,1990,19(1):44-53. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1990.01.005
[6] GUO Y L,YANG S Y,SU N,et al. Revisiting the effects of hydrodynamic sorting and sedimentary recycling on chemical weathering indices[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2018,227:48-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.02.015
[7] XU Z K,LI T G,CHANG F M,et al. Clay-sized sediment provenance change in the northern Okinawa Trough since 22 kyr BP and its paleoenvironmental implication[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2014,399:236-245.
[8] HU B Q,YANG Z S,QIAO S Q,et al. Holocene shifts in riverine fine-grained sediment supply to the East China Sea Distal Mud in response to climate change[J]. The Holocene,2014,24(10):1253-1268. doi: 10.1177/0959683614540963
[9] YANG S Y,JUNG H S,CHOI M S,et al. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow)River sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,201(2):407-419. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00715-X
[10] SONG Y,CHOI M S. REE geochemistry of fine-grained sediments from major rivers around the Yellow Sea[J]. Chemical Geology,2009,266(3/4):328-342.
[11] JUNG H,KIM J,LIM D,et al. REE fractionation and quantification of sediment source in the Yellow Sea mud deposits,Εast Αsian marginal sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2021,217:104374. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2021.104374
[12] ZHU Y T,BAO R,ZHU L H,et al. Investigating the provenances and transport mechanisms of surface sediments in the offshore muddy area of Shandong Peninsula:insights from REE analyses[J]. Journal of Marine Systems,2022,226:103671. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2021.103671
[13] LIU Y,CHENG Y,LIU J W,et al. Provenance discrimination of surface sediments using rare earth elements in the Yalu River estuary,China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2015,74(4):3507-3517. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4391-x
[14] 张晓波,张勇,孔祥淮,等. 山东半岛南部近岸海域表层沉积物稀土元素的物源指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014,34(3):57-66.
[15] 严杰,高建华,李军,等. 鸭绿江河口外海域柱状沉积物稀土元素的分布特征及物源指示[J]. 海洋通报,2013,32(6):601-609. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.06.001
[16] AI L N,HAN Z Z,WU X,et al. Geochemical and grain-sized implications for provenance variations of the central Yellow Sea muddy area since the Middle Holocene[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2020,19(3):577-588. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-4211-0
[17] SONG S,FENG X L,LI G G,et al. Change in sediment provenance near the current estuary of Yellow River since the Holocene transgression[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2018,17(3):535-544. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3377-1
[18] XU F J,LI A C,LI T G,et al. Rare earth element geochemistry in the inner shelf of the East China Sea and its implication to sediment provenances[J]. Journal of Rare Earths(English Edition),2011,29(7):702-709. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60526-1
[19] 李中,刘洋洋,张铁峰. 基于形态相似距离的时间序列相似度计算[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2016,37(3):679-683. doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2016.03.0023
[20] 张瑞,聂明龙,禚喜准. 稀土元素聚类分析方法在物源示踪方面的应用[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版),2017,36(1):28-31.
[21] 张霄宇,张富元,高爱根,等. 稀土元素在长江口及邻近陆架表层沉积物中的分布及物源示踪研究[J]. 中国稀土学报,2009,27(2):282-288. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2009.02.023
[22] 丁永伟,杨小虎,陈根才,等. 基于弧度距离的时间序列相似度量[J]. 电子与信息学报,2011,33(1):122-128.
[23] 张雪丽,牛强. 基于角点弯曲度的时间序列相似性搜索算法[J]. 计算机工程,2011,37(15):37-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2011.15.010
[24] 肖瑞,刘国华. 基于趋势的时间序列相似性度量和聚类研究[J]. 计算机应用研究,2014,31(9):2600-2605. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2014.09.009
[25] 张建业,潘泉,张鹏,等. 基于斜率表示的时间序列相似性度量方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2007,20(2):271-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2007.02.022
[26] 梁建海,张建业,杨峰,等. 基于斜率偏离的时间序列相似性搜索方法研究[J]. 计算机应用研究,2010,27(1):54-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2010.01.015
[27] 董晓莉,顾成奎,王正欧. 基于形态的时间序列相似性度量研究[J]. 电子与信息学报,2007,29(5):1228-1231.
[28] 王瑞,贾瑞玉. 基于形态模式的时间序列相似性度量算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2017,34(9):253-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2017.09.049
[29] 门连生,卫婧菲,李中. 基于形态相似距离的时间序列相似性度量[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2015,51(4):120-122. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1312-0107
[30] 王钊,汤子健. 基于涨落模式的时间序列相似性度量研究[J]. 计算机应用研究,2017,34(3):697-701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2017.03.013
[31] 张鹏,李学仁,张建业,等. 时间序列的夹角距离及相似性搜索[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2008,21(6):763-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2008.06.008
[32] 王达,荣冈. 时间序列的模式距离[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2004,38(7):2-5.
[33] 张海涛,李志华,孙雅,等. 新的时间序列相似性度量方法[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2014,35(4):1279-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2014.04.031
[34] YANG S,LI C,LEE C B,et al. REE geochemistry of suspended sediments from the rivers around the Yellow Sea and provenance indicators[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2003,48(11):1135-1139. doi: 10.1007/BF03185768
[35] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985.
[36] 郭炳火, 徐建平, 速记兰, 等. 中国近海环流[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 174-181.
[37] CRONAN D S,HODKINSON R A. Geochemistry of hydrothermal sediments from ODP Sites 834 and 835 in the Lau Basin,southwest Pacific[J]. Marine Geology,1997,141(1/4):237-268.
[38] LIM D I,JUNG H S,CHOI J Y,et al. Geochemical compositions of river and shelf sediments in the Yellow Sea:grain-size normalization and sediment provenance[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2006,26(1):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.10.001
[39] YANG Z S,LIU J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2007,240(1/4):169-176.
[40] LIU J,SAITO Y,KONG X,et al. Sedimentary record of environmental evolution off the Yangtze River estuary,East China Sea,during the last ~13,000 years,with special reference to the influence of the Yellow River on the Yangtze River delta during the last 600 years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews,2010,29(17/18):2424-2438.
[41] LI J,HU B,WEI H,et al. Provenance variations in the Holocene deposits from the southern Yellow Sea:clay mineralogy evidence[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2014,90:41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.05.001
[42] 蓝先洪,张宪军,赵广涛,等. 南黄海NT1孔沉积物稀土元素组成与物源判别[J]. 地球化学,2009,38(2):123-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2009.02.003
[43] LIM D,XU Z,CHOI J,et al. Holocene changes in detrital sediment supply to the eastern part of the central Yellow Sea and their forcing mechanisms[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2015,105:18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.032
[44] PARK S,LEE H,HAN H,et al. Evolution of late Quaternary mud deposits and recent sediment budget in the southeastern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology,2000,170(3/4):271-288.
[45] 秦蕴珊,李凡. 黄河入海泥沙对渤海和黄海沉积作用的影响[J]. 海洋科学集刊,1986,27:125-135.
[46] 蓝先洪,王红霞,李日辉,等. 南黄海沉积物常量元素组成及物源分析[J]. 地学前缘,2007,14(4):197-203. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.04.021
[47] 蓝先洪,张宪军,刘新波,等. 南黄海表层沉积物黏土矿物分布及物源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011,31(3):11-16.
[48] 蓝先洪,申顺喜. 南黄海中部沉积岩心的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋通报,2002,21(5):46-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.05.007
[49] 范德江,杨作升,孙效功,等. 东海陆架北部长江、黄河沉积物影响范围的定量估算[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2002,32(5):748-756.
[50] 边昌伟. 中国近岸泥沙在渤海、黄海和东海的输运[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
[51] CHOUGH S K,KIM J W,LEE S H,et al. High-resolution acoustic characteristics of epicontinental sea deposits,central–eastern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine geology,2002,188(3/4):317-331.
[52] LEE H J,CHU Y S. Origin of inner-shelf mud deposit in the southeastern Yellow Sea:Huksan Mud Belt[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research,2001,71(1):144-154. doi: 10.1306/040700710144
[53] YANG S Y,JUNG H S,LIM D I,et al. A review on the provenance discrimination of sediments in the Yellow Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2003,63(1/2):93-120.
[54] LIM D I,CHOI J Y,JUNG H S,et al. Recent sediment accumulation and origin of shelf mud deposits in the Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Progress in Oceanography,2007,73(2):145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2007.02.004
[55] XU Z K,LIM D,CHOI J Y,et al. Rare earth elements in bottom sediments of major rivers around the Yellow Sea:implications for sediment provenance[J]. Geo-Marine Letters,2009,29(5):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s00367-009-0142-x
[56] WAN S M,LI A C,CLIFT P D,et al. Increased contribution of terrigenous supply from Taiwan to the northern South China Sea since 3 Ma[J]. Marine Geology,2010,278(1/4):115-121.
[57] WANG J, LI A,XU K,et al. Clay mineral and grain size studies of sediment provenances and paleoenvironment evolution in the middle Okinawa Trough since 17 ka[J]. Marine Geology,2015,366:49-61.
[58] ZHAO Y F,ZOU X Q,LIU Q,et al. Clay mineralogy indicates the muddy sediment provenance in the estuarine-inner shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,152:69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.036
-




 下载:
下载: