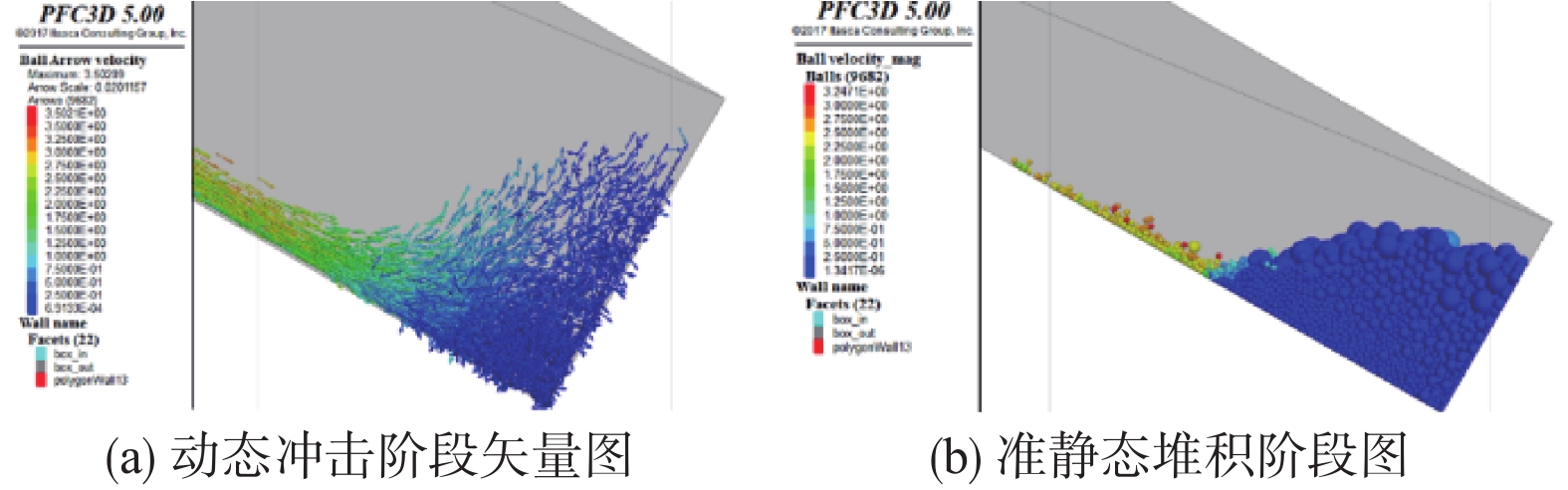
Particle sequence distribution and the effect of particle size on the impact effect in a fluidized landslide-debris flow
-
摘要:
滑体的运动速度、堆积形态、冲击力等因素决定了碎屑流的致灾程度。滑源区不同岩性特征和结构分布的差异导致了滑体粒序分布和颗粒粒径的差异。在运动过程中产生的碰撞、摩擦、跳跃,影响着滑坡碎屑流的致灾程度。在物理模型试验的基础上,运用三维离散元软件PFC3D,探究滑源区粒序分布及颗粒粒径对滑体运动速度、堆积形态、冲击力的影响。研究结果表明:碎屑流中各粒径颗粒的平均速度受颗粒粒径及滑源区初始粒序的共同影响,且初始粒序对各颗粒平均速度影响更大;在堆积形态方面,粒径大小对厚度方向上的粒序排布影响较大,而滑源区粒序分布对单种颗粒的堆积形态影响较大;在颗粒分选作用下,颗粒粒径成为控制峰值冲击力的主要因素,而滑源区粒序分布则通过决定滑体堆积形态控制了准静态堆积阶段碎屑流的冲击力。
Abstract:The severity of a landslide-debris flow is determined by such factors as the speed, deposition morphology and impact force of the sliding body. Differences in the lithological characteristics and structural distribution of the sliding source area lead to differences in the particle order distribution and particle size of the sliding body. During the movement, the collision, friction, and jumping between the particles affect the degree of hazard of the landslide-debris flow. Based on the physical model test, the dimensional discrete element software PFC3D is used to explore the influence of the particle order distribution and particle size on the speed, stacking morphology and impact force. The results show that the average velocity of particles in the debris flow is affected by both the particle size and the initial particle order in the slip source region, and the initial particle order has a greater effect on the average velocity of particles. The particle size has a greater effect on the particle order arrangement in the thickness direction, while the particle order distribution in the slip source area has a greater effect on the deposition morphology. Under the effect of particle-size segregation, the particle size becomes the main factor controlling the peak impact force and the slip source. The particle sequence distribution in the slip source area determines the accumulation morphology, which controls the impact force of the debris flow in the quasi-static accumulation stage.
-
Key words:
- landslide-debris flow /
- particle order distribution /
- particle-size /
- impact force /
- PFC3D
-

-
表 1 数值模拟中岩土样粒径分布
Table 1. Gradation composition of the samples in the numerical simulation
工况 粒径颗粒质量占比/% 初始粒序分布
(沿侧板自上而下)Large
10 mmMid
20 mmSmall
40 mmMIX Mixture(混杂粒序) LMS L-M-S LSM 33 33 34 L-S-M MLS M-L-S MSL M-S-L SLM S-L-M SML S-M-L 表 2 模拟参数
Table 2. Parameters used in the model
参数 颗粒 底板 挡板 密度/(kg·m−3) 1969 − − 泊松比 0.2 0.3 0.3 剪切模量/MPa 200 320 1000 摩擦系数 1.327 0.453 0.364 法向黏性阻尼 0.60 − − 切向黏性阻尼 0.07 − − 表 3 模型试验岩土样级配组成
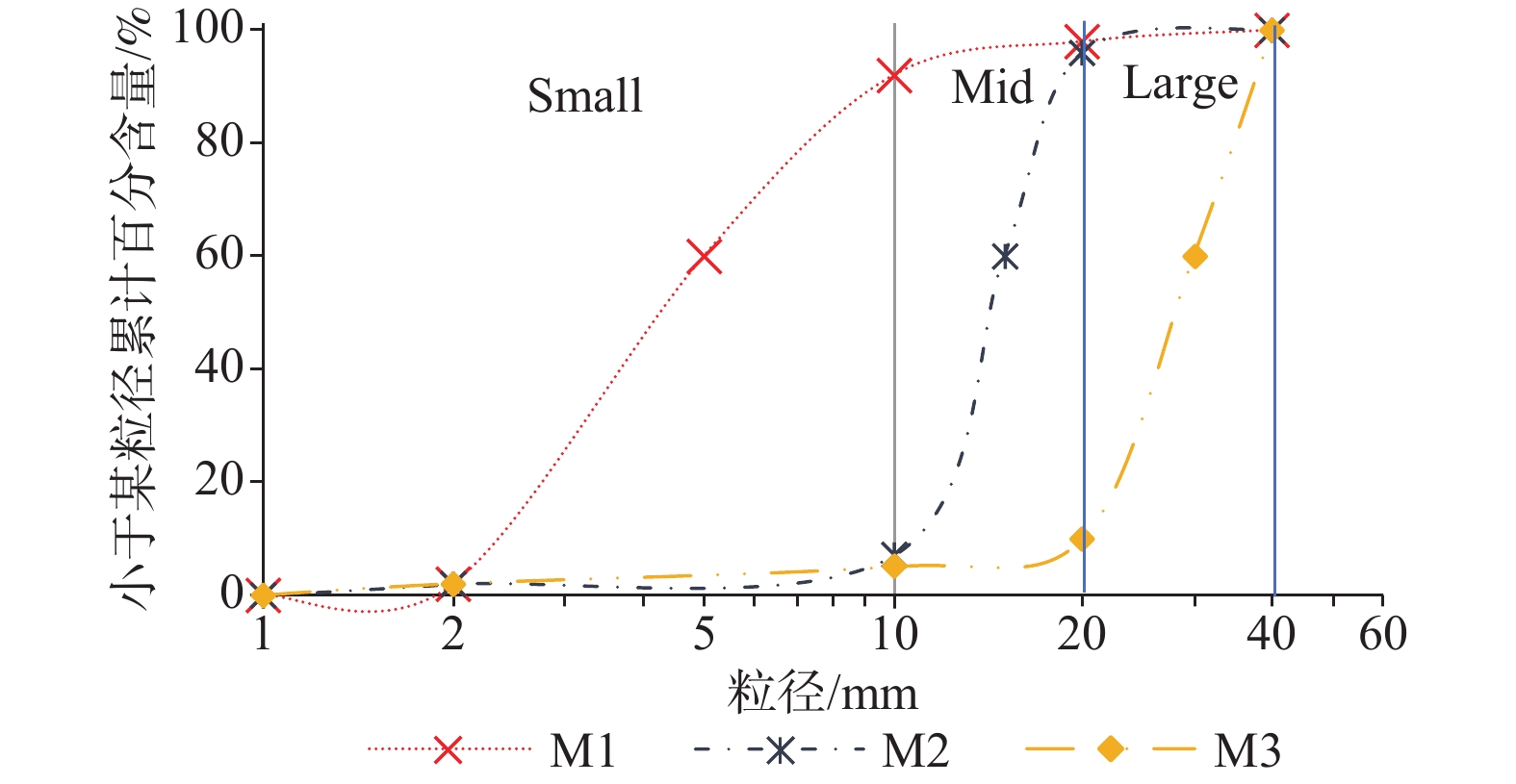
Table 3. Gradation compositions of the samples in the model test
滑体模型 颗粒粒径/mm 1~10 10~20 20~30 M1 90% 5% 5% M2 5% 90% 5% M3 5% 5% 90% 表 4 不同工况下的平均速度峰值
Table 4. Average maximum speed under different working conditions
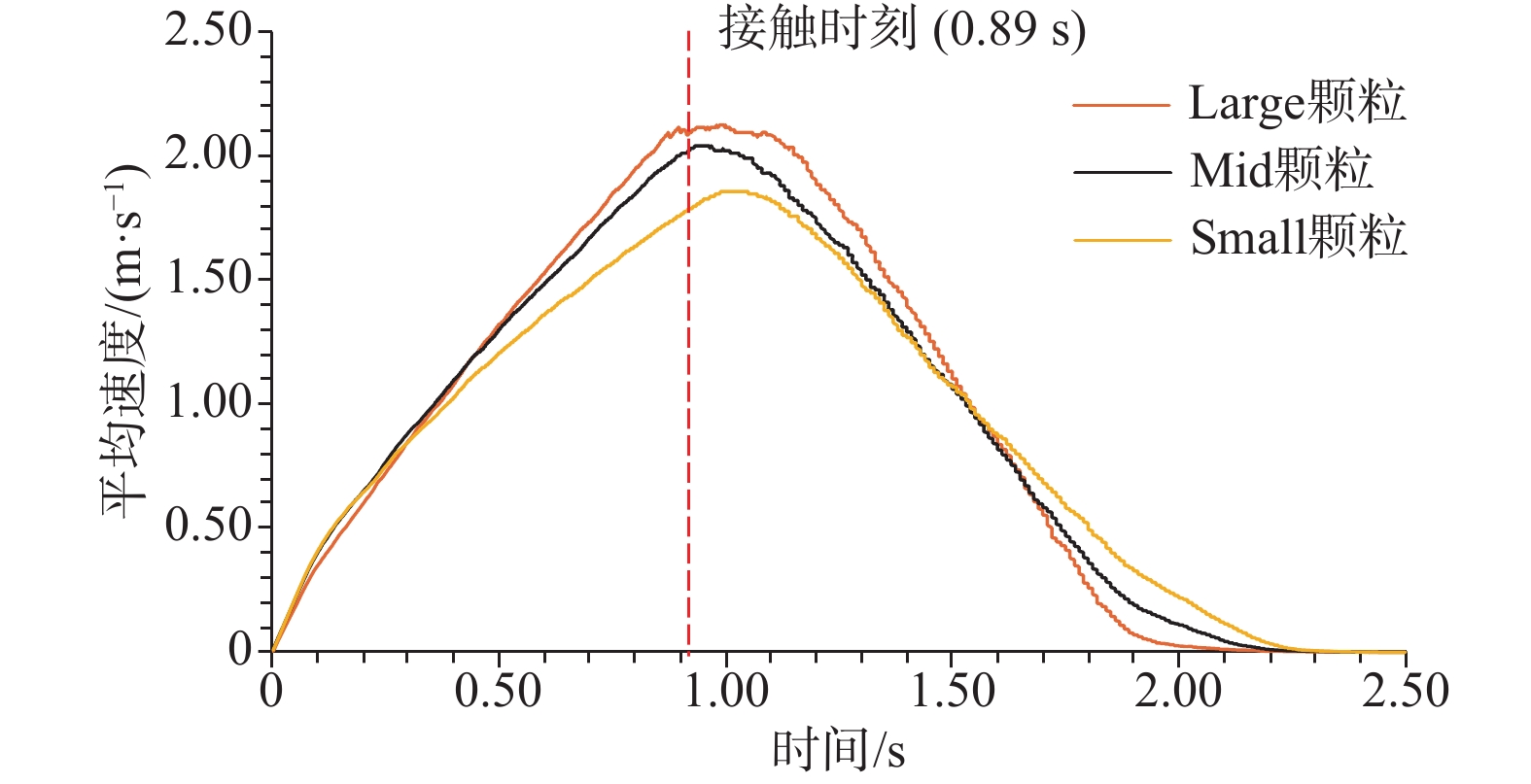
/(m·s−1) MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 2.12 2.40 2.37 2.14 2.11 2.13 1.88 Mid 2.04 2.04 1.60 2.33 2.42 1.71 1.85 Small 1.86 1.57 1.70 1.64 1.93 1.96 1.94 表 5 不同工况下平均速度峰值时刻
Table 5. Time of the average maximum speed under different working conditions
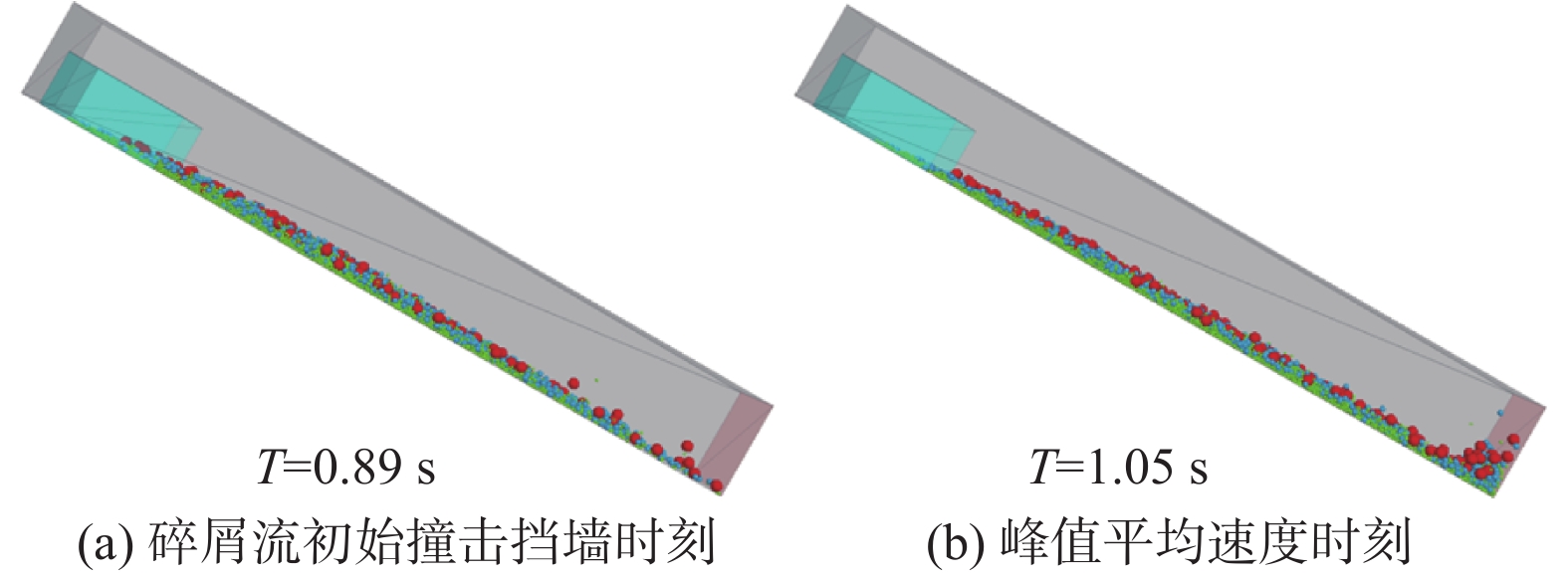
/s MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 0.91 0.90 0.90 0.92 0.97 0.92 1.15 Mid 0.94 0.98 1.26 0.97 0.96 1.27 1.13 Small 1.01 1.19 1.08 1.25 1.11 1.01 0.99 表 6 碎屑流冲击挡墙后的侧面堆积形态(侧视图)
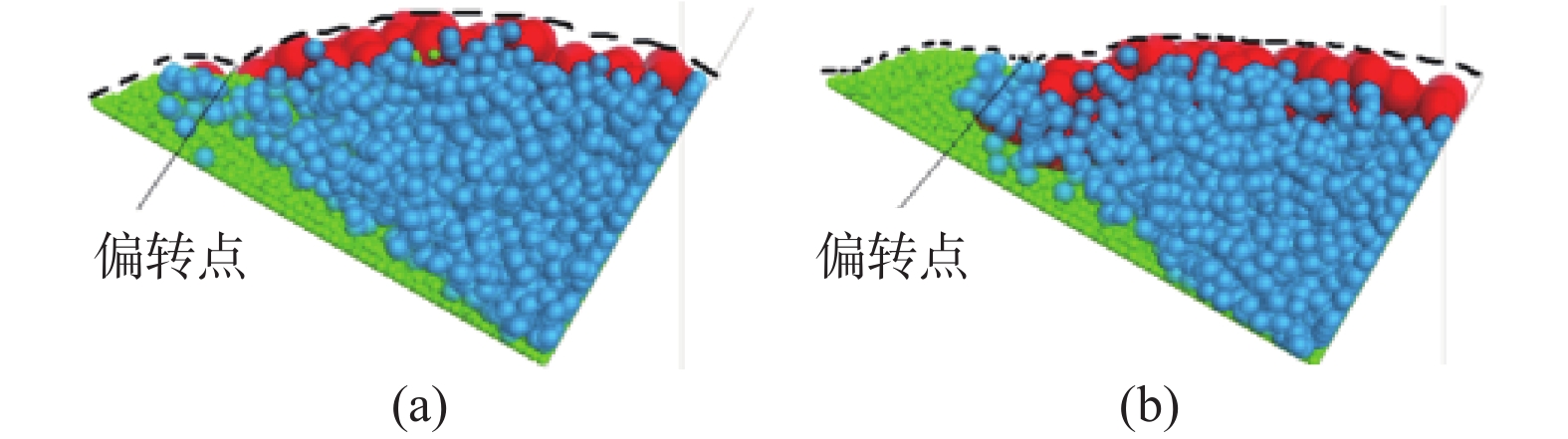
Table 6. Side deposit shape after the impact on the parapet by the fluidized landslide-debris flow (side view)
MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML 全部颗粒 Large颗粒 Mid颗粒 Small颗粒 表 7 3种颗粒的平均堆积长度
Table 7. Average deposit length of three kinds of particles
/m MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 0.214 0.180 0.167 0.210 0.219 0.205 0.231 Mid 0.193 0.184 0.266 0.150 0.160 0.253 0.202 Small 0.195 0.258 0.206 0.238 0.198 0.166 0.159 表 8 3种颗粒的平均堆积高度
Table 8. Average deposit height of three kind of particles
/m MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 0.148 0.147 0.135 0.144 0.146 0.147 0.142 Mid 0.101 0.087 0.081 0.098 0.118 0.080 0.103 Small 0.043 0.037 0.041 0.037 0.040 0.048 0.053 表 9 各颗粒的整体峰值冲击力
Table 9. The maximum impact force of each kind of particles
/N MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML 全部 276 216 425 161 370 383 229 Large 256 189 424 117 326 357 168 Mid 98 118 60 87 81 75 22 Small 84 55 75 32 65 121 107 表 10 各颗粒整体峰值冲击力作用时刻
Table 10. Time of the maximum impact force of each kind of particles
/s MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML 全部 0.8 0.97 0.88 1.02 0.93 0.92 0.91 Large 0.876 0.94 0.88 0.89 0.93 0.92 0.98 Mid 0.937 1.10 0.97 1.41 1.62 0.96 0.92 Small 1.69 0.92 1.31 1.21 1.61 0.96 1.89 表 11 3种颗粒峰值冲击力在滑体峰值冲击力中的占比
Table 11. The maximum impact force of three kinds of particles as a percentage of the maximum impact force of the sliding body
/% MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 92.7 63.8 99.76 53.35 88.35 93.21 73.29 Mid 4.75 27.0 0.00 31.86 2.56 1.24 9.11 Small 2.50 9.2 0.24 14.78 9.09 5.55 17.60 表 12 3种颗粒准静态冲击力
Table 12. Quasi-static impact force of three kinds of particles
/N MIX LMS LSM MLS MSL SLM SML Large 2.3 14.9 32.8 10.3 4.8 13.3 2.4 Mid 41.0 63.2 14.3 73.8 59.1 8.8 18.7 Small 75.9 28.7 56.7 22.2 55.0 92.2 95.7 -
[1] FAN Xiaoyi, TIAN Shujun, ZHANG Youyi. Mass-front velocity of dry granular flows influenced by the angle of the slope to the runout plane and particle size gradation[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2016,13(2):234 − 245. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3396-3
[2] YANG Qingqing, CAI Fei, UGAI Keizo, et al. Some factors affecting mass-front velocity of rapid dry granular flows in a large flume[J]. Engineering Geology,2011,122(3/4):249 − 260.
[3] 葛云峰, 周婷, 霍少磊, 等. 高速远程滑坡运动堆积过程中的能量传递机制[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(11):3939 − 3949. [GE Yunfeng, ZHOU Ting, HUO Shaolei, et al. Energy Transfer Mechanism during Movement and Accumulation of Rockslide Avalanche[J]. Chinese Journal of Earth Science,2019,44(11):3939 − 3949. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 姚鑫, 余凯, 张永双, 等. “1·11”镇雄灾难性滑坡滑动机制−高孔隙度土流态化启动与滑动液化[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2014,33(5):1047 − 1054. [YAO Xin, YU Kai, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Mechanisms of catastrophic landslide on January 11, 2013, in Zhenxiong County: fluidization initiation and movement liquefaction of high porosity soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2014,33(5):1047 − 1054. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, SHI Anwen, et al. Sedimentary deformation structures in the Nyixoi Chongco rock avalanche: implications on rock avalanche transport mechanisms[J]. Landslides,2019,16(3):523 − 532. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1117-7
[6] WANG Yufeng CHENG Qiangong, YUAN Yunqiang, et al. Emplacement mechanisms of the Tagarma rock avalanche on the Pamir-western Himalayan syntaxis of the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(3):527 − 542. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01298-1
[7] 张涛, 杨志华, 张永双, 等. 四川茂县新磨村高位滑坡铲刮作用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):138 − 145. [ZHANG Tao, YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. An analysis of the entrainment of the Xinmo high-position landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):138 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李天话. 不同颗粒级配滑坡岩土体运动分选机制及冲击作用研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2019.
LI Tianhua. Movement segregation mechanism and impact effect of landslide in different gradation grades[D]. Mianyang, China: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[9] 郑光, 许强, 彭双麒. 滑坡-碎屑流的堆积特征及机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(4):842 − 852. [ZHENG Guang, XU Qiang, PENG Shuangqi. Mechanism analysis of the accumulation characteristics of rock avalanche[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(4):842 − 852. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 周公旦, 孙其诚, 崔鹏. 泥石流颗粒物质分选机理和效应[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2013,45(1):28 − 36. [ZHOU Gongdan, SUN Qicheng, CUI Peng. Study on the mechanisms of solids segregation in granular debris flows[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2013,45(1):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李天话, 樊晓一, 姜元俊. 滑坡碎屑流颗粒分选效应的数值模拟[J]. 西南科技大学学报,2019,34(1):26 − 33. [LI Tianhua, FAN Xiaoyi, JIANG Yuanjun. Numerical simulation study of solids segregation in landslide debris flow[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology,2019,34(1):26 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8755.2019.01.005
[12] DI LUZIO E, BIANCHI-FASANI G, ESPOSITO C, et al. Massive rock-slope failure in the Central Apennines (Italy): the case of the Campo di Giove rock avalanche[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2004,63(1):1 − 12. doi: 10.1007/s10064-003-0212-7
[13] ZHOU Jiawen, CUI Peng, YANG Xingguo. Dynamic process analysis for the initiation and movement of the Donghekou landslide-debris flow triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,76:70 − 84. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.007
[14] JIANG Yuanjun TOWHATA Ikuo. Experimental study of dry granular flow and impact behavior against a rigid retaining wall[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2013,46(4):713 − 729. doi: 10.1007/s00603-012-0293-3
[15] MORIGUCHI S, BORJA R I, YASHIMA A, et al. Estimating the impact force generated by granular flow on a rigid obstruction[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2009,4(1):57 − 71. doi: 10.1007/s11440-009-0084-5
[16] 宋跃, 姜元俊, 王萌. 碎石垫层对碎屑流冲击棚洞的缓冲效应研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(10):2359 − 2369. [SONG Yue, JIANG Yuanjun, WANG Meng. Buffering effect of gravel cushion layer on the impact of dry granular flow against a rock shed[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(10):2359 − 2369. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 肖思友, 苏立君, 姜元俊. 碎屑流冲击柔性网的离散元仿真研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(3):526 − 533. [XIAO Siyou, SU Lijun, JIANG Yuanjun. Numerical investigation on flexible barriers impacted by dry granular flows using DEM modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,41(3):526 − 533. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张睿骁, 樊晓一, 姜元俊. 滑坡碎屑流冲击拦挡结构的离散元模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(1):148 − 155. [ZHANG Ruixiao, FAN Xiaoyi, JIANG Yuanjun. Discrete element simulation of the impact of landslide debris flow on resistive structures[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(1):148 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] BI Yuzhang, HE Siming LI Xinpo, et al. Effects of segregation in binary granular mixture avalanches down inclined chutes impinging on defending structures[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(3):263. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5076-1
[20] ALBABA A, LAMBERT S, NICOT F, et al. Relation between microstructure and loading applied by a granular flow to a rigid wall using DEM modeling[J]. Granular Matter,2015,17(5):603 − 616. doi: 10.1007/s10035-015-0579-8
[21] 王智德. 云南普宣高速公路顺层岩质边坡稳定性分析与开挖控制[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2015.
WANG Zhide Stability Analysis and Excavation Control of Bedding Rock Slope of Puli-Xuanwei Expressway in Yunnan Province[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 张玉明.水库运行条件下马家沟滑坡—抗滑桩体系多场特征与演化机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018.
ZHANG Yuming. Multi-field characteristics and evolution mechanism of Majiagou landslide-stablizing piles system under reservoir operations[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 岳建军. 缓倾外软硬互层型滑坡基本特征及失稳机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.
YUE Jianjun. Study on basic Characteristics and instability mechanism of the landslide with inter bedded soft and hard rock beddings of low dip angles [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: