Discrete element simulation of the influence of anisotropy on the mechanical properties of soft soil
-
摘要:
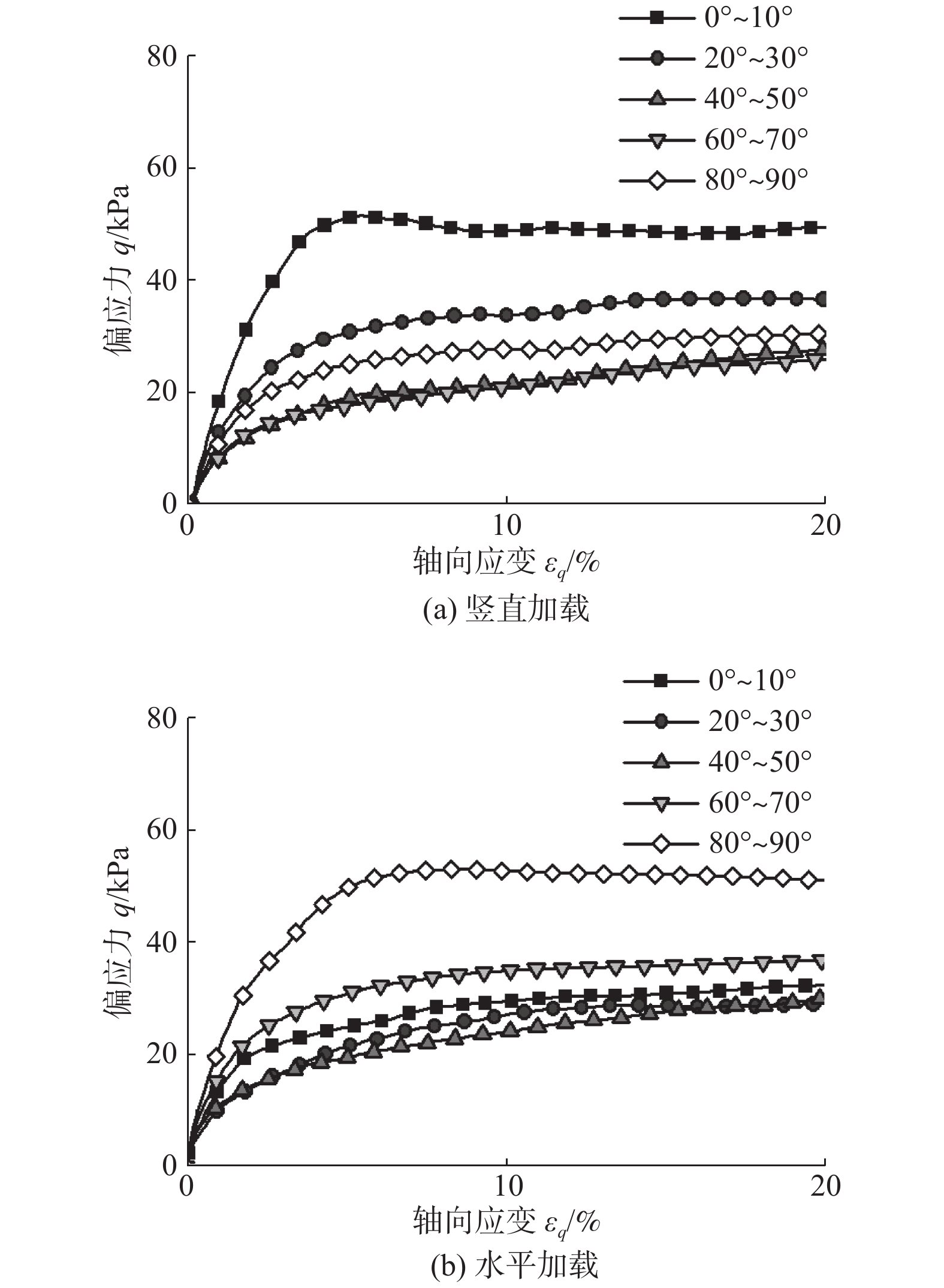
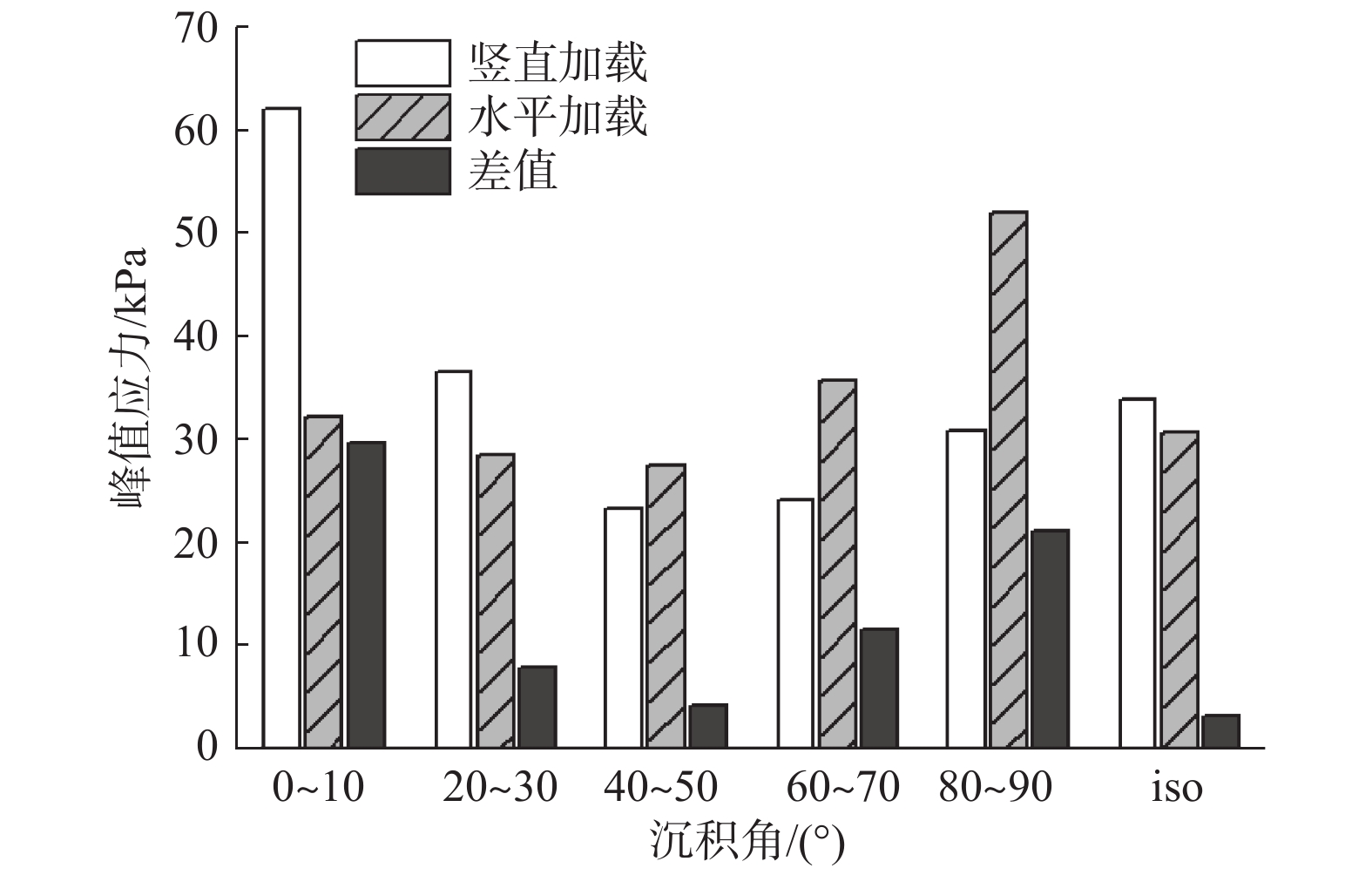
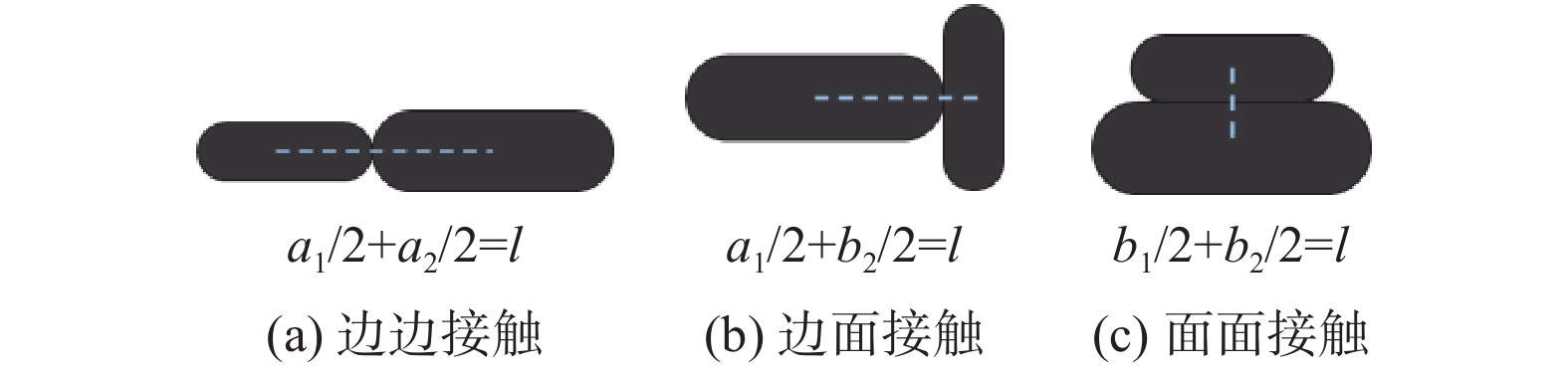
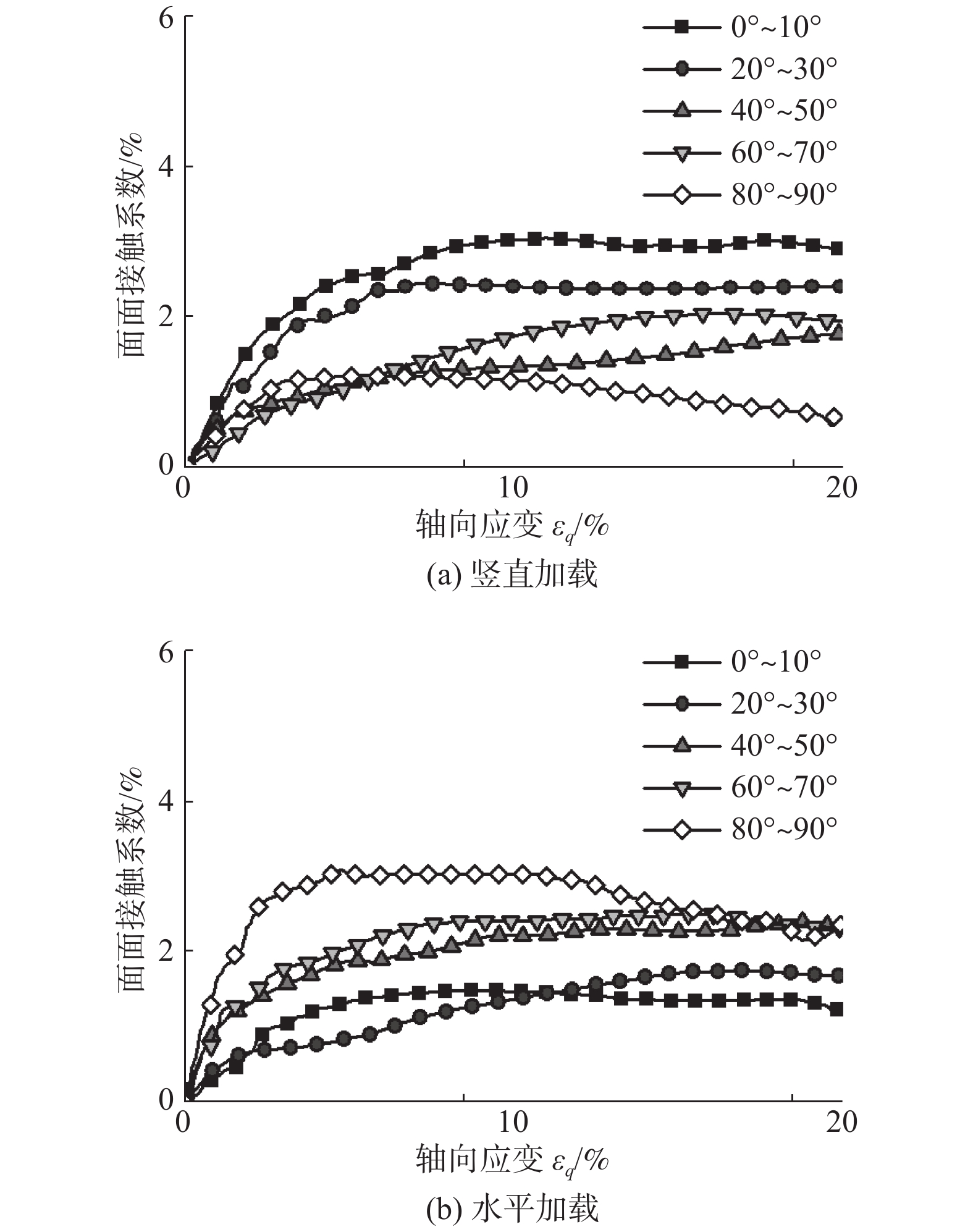
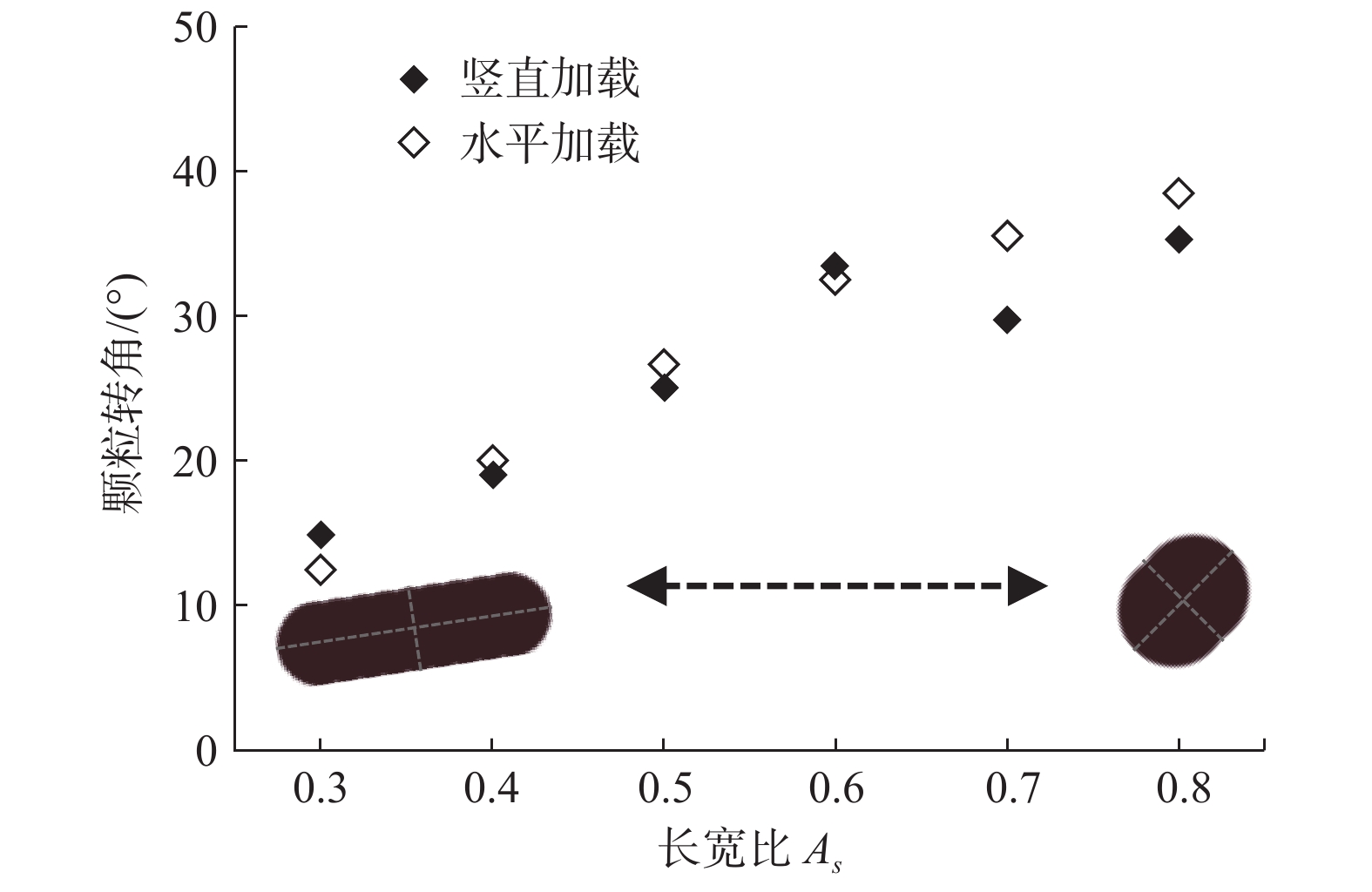
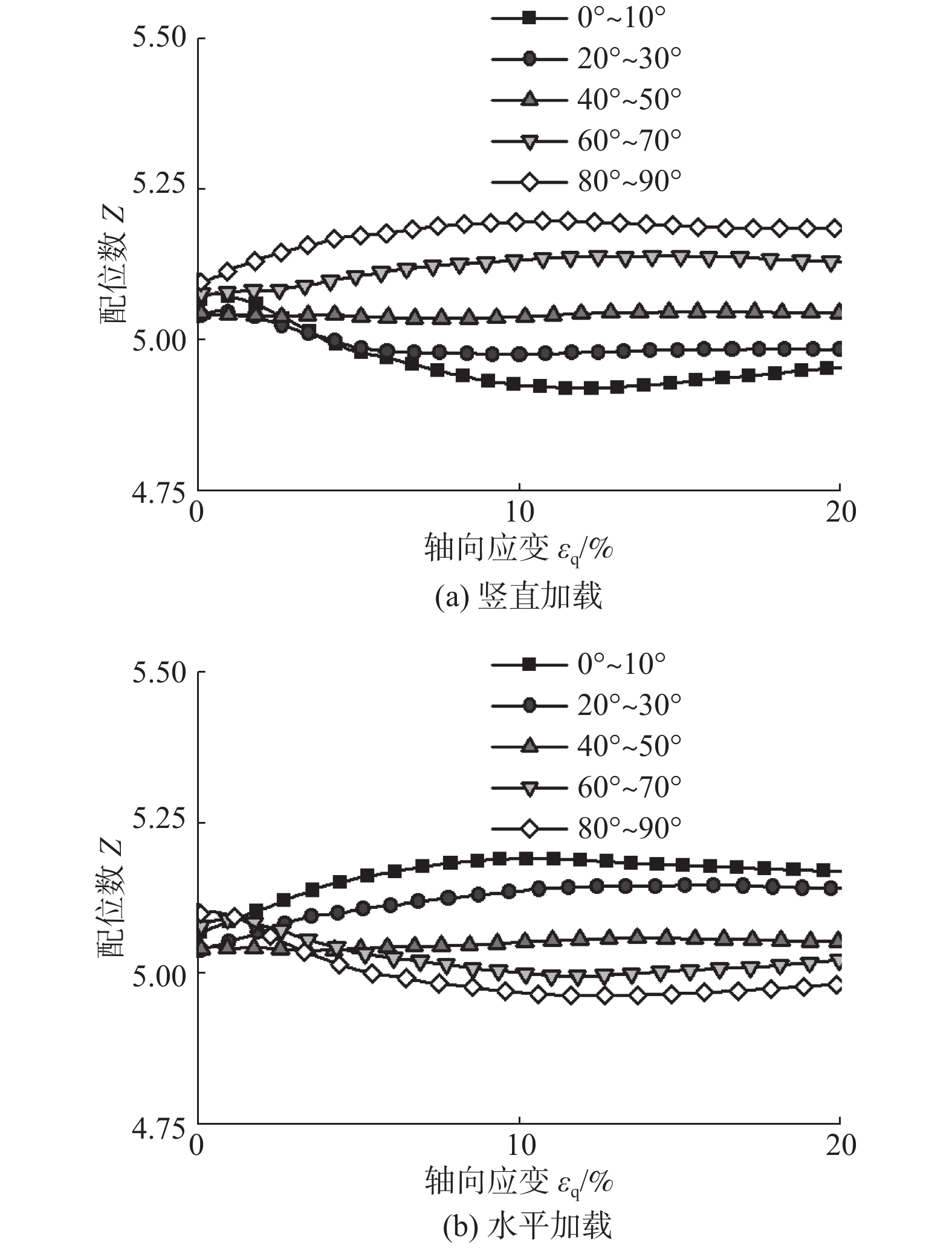
软土预压工程中,初始和诱发各向异性对软土力学性质的影响十分显著,而现有研究缺乏对初始和诱发各向异性的统一研究方法。采用离散单元法,以颗粒长宽比作为定量评价指标,构建真实形态的颗粒模型,生成5组不同沉积角的初始各向异性试样,并进行竖直和水平两方向加载的双轴模拟实验,研究了初始各向异性和诱发各向异性对软土力学特性影响;在细观层面,以颗粒为对象研究了颗粒接触形式和转动角度的变化规律,以接触为对象研究了配位数和接触法向各向异性的发展趋势,在此基础上探究抗剪强度指标与各向异性关系。结果表明:初始和诱发各向异性共同影响试样力学性质,当加载方向和软土沉积方向垂直时,土体有最大的峰值强度。颗粒接触形式中面面接触的比例随加载的进行逐渐增大,并影响着试样初始模量和抗剪强度,配位数和接触法向各向异性受颗粒接触形式的影响有不同的演化规律,并在加载后期趋于稳定;同时,初始各向异性试样相较各向同性试样有更大的黏聚力,诱发各向异性主要影响试样内摩擦角,进而影响试样抗剪强度。
Abstract:The initial and induced anisotropy has a significant effect on the mechanical properties of soft soil in preloading engineering. However, there is a lack of unified research methods for the initial and induced anisotropy. Discrete element method is adopted in this study, and the length-width ratio of particles is used as the quantitative evaluation index. Five types of initial anisotropy samples with different deposition angles are generated. The effects of initial anisotropy and induced anisotropy on the mechanical properties of soft soil are studied by vertical and horizontal loading. At the micro level, the contact form and rotation angle of particles are examined from the point of view of particles, and the development trend of coordination number and contact normal to anisotropy is studied from the point of view of contact. The relationship between shear strength index and anisotropy is explored. The results show that initial and induced anisotropy influences the mechanical properties of the samples. When the loading direction is perpendicular to the soft soil deposition direction, the soil mass has the maximum peak strength. In the particle contact form, the proportion of surface contact gradually increases with loading. The initial modulus and shear strength are influenced. The coordination number and contact normal anisotropy have different evolutions under the influence of particle contact form, and tend to be stable at the later loading stage. In terms of shear strength parameters, the initial anisotropy will increase the cohesion of the sample, and the induced anisotropy will mainly change the internal friction angle, which is consistent with the law of shear strength.
-
Key words:
- soft soil /
- anisotropy /
- peak stress /
- shear strength index /
- mesoscopic and macroscopic characteristics
-

-
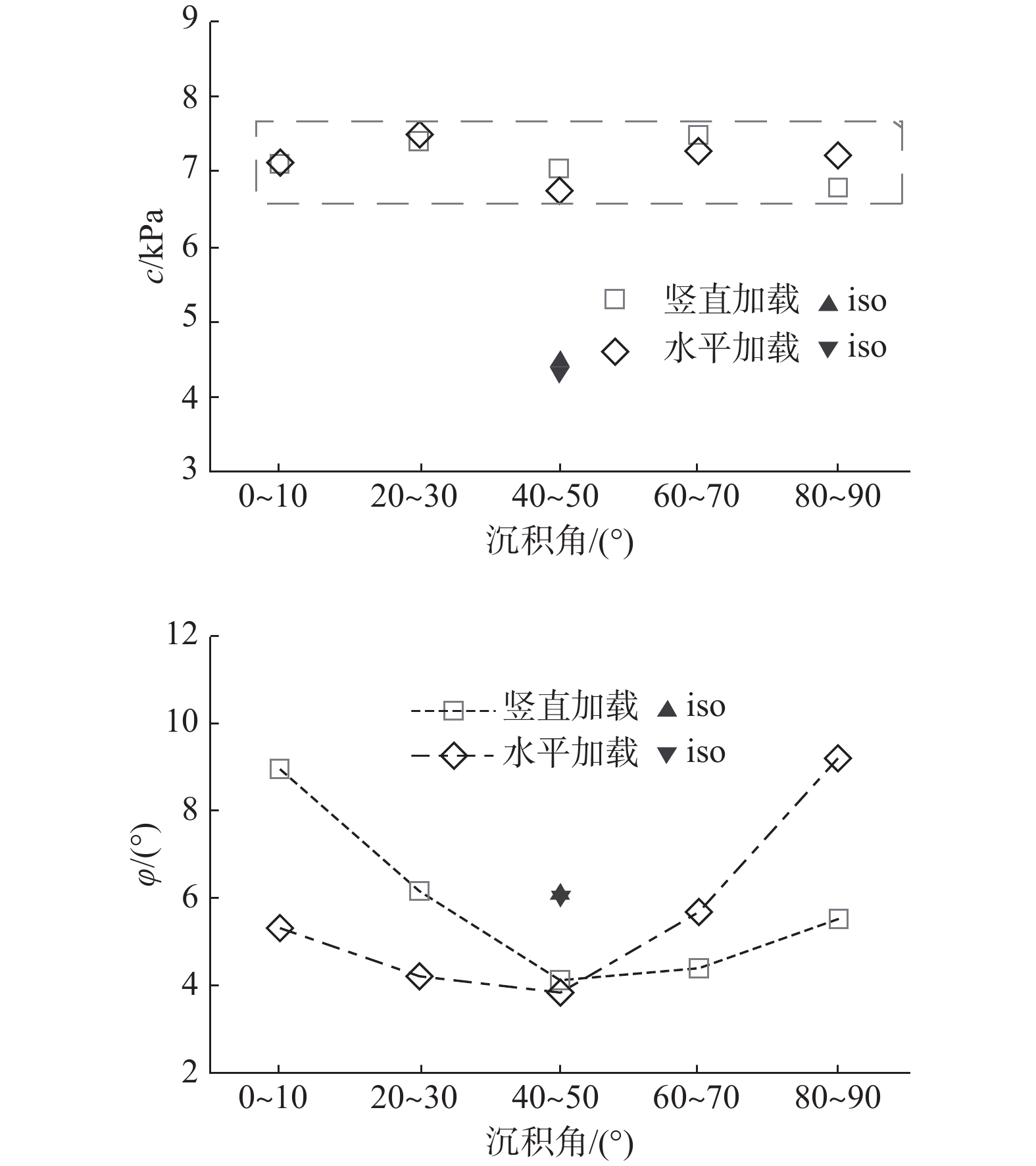
表 1 数值模型参数
Table 1. Parameters used in the numerical model
有效模量E/MPa 刚度比k 摩擦系数μ 阻尼系数 颗粒密度ρ/(kg·m−3) 1 1 0.03 0.7 2700 表 2 不同沉积角试样的抗剪强度指标
Table 2. Shear strength indices of the samples with different deposition angles
沉积角/° 竖直加载 水平加载 c/kPa  /(°)
/(°)
c/kPa  /(°)
/(°)
0~10 7.10 8.95 7.12 5.31 20~30 7.40 6.13 7.50 4.21 40~50 7.03 4.11 6.74 3.82 60~70 7.47 4.36 7.28 5.69 80~90 6.78 5.50 7.21 9.22 iso 4.47 6.09 4.33 6.01 -
[1] 张坤勇, 殷宗泽, 梅国雄. 土体两种各向异性的区别与联系[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(9):1599 − 1604. [ZHANG Kunyong, YIN Zongze, MEI Guoxiong. Difference and connection of two kinds of anisotropy of soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(9):1599 − 1604. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.022
[2] ODA M, KOISHIKAWA I, HIGUCHI T. Experimental study of anisotropic shear strength of sand by plane strain test[J]. Soils Foundation,1978,18(4):25 − 38.
[3] SIDDIQUEE M S A, TATSUOKA F, TANAKA T, et al. Model tests and FEM simulation of some factors affecting the bearing capacity of a footing on sand[J]. Soils and Foundations,2001,41(2):53 − 76.
[4] ZHANG F, CUI Y J, ZENG L L, et al. Anisotropic features of natural Teguline clay[J]. Engineering Geology,2019,261:105275.
[5] ROUAINIA M, MUIR WOOD D. A kinematic hardening constitutive model for natural clays with loss of structure[J]. Géotechnique,2000,50(2):153 − 164.
[6] 曾玲玲, 陈晓平. 软土在不同应力路径下的力学特性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(5):1264 − 1270. [ZENG Lingling, CHEN Xiaoping. Analysis of mechanical characteristics of soft soil under different stress paths[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(5):1264 − 1270. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.012
[7] 刘恩龙, 沈珠江. 不同应力路径下结构性土的力学特性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(10):2058 − 2064. [LIU Enlong, SHEN Zhujiang. Mechanical behavior of structured soils under different stress paths[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(10):2058 − 2064. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.10.017
[8] 刘嘉英, 周伟, 马刚, 等. 颗粒材料三维应力路径下的接触组构特性[J]. 力学学报,2019,51(1):26 − 35. [LIU Jiaying, ZHOU Wei, MA Gang, et al. Contact fabric characteristics of granular materials under three dimensional stress paths[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2019,51(1):26 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-338
[9] 王清, 孔元元, 张旭东, 等. 结构性土体固结压力的力学效应[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(5):987 − 994. [WANG Qing, KONG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Xudong, et al. Mechanical effect of pre-consolidation pressure of structural behavior soil[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016,51(5):987 − 994. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.023
[10] 王清, 王凤艳, 肖树芳. 土微观结构特征的定量研究及其在工程中的应用[J]. 成都理工学院学报,2001,28(2):148 − 153. [WANG Qing, WANG Fengyan, XIAO Shufang. A quantitative study of the microstructure characteristics of soil and its application to the engineering[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,2001,28(2):148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] SUN Q, ZHENG J X. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional inherent fabric in cross-anisotropic granular soils[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2019,116:103197.
[12] 顾迪, 严学新, 张云, 等. 上海黏土压缩回弹变形的微观机理[J]. 水文地质工程地,2020,47(4):123 − 131. [GU Di, YAN Xuexin, ZHANG Yun, et al. Micro-mechanism of compression and rebound of clay in Shanghai[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):123 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] BAYESTEH H, MIRGHASEMI A A. Numerical simulation of porosity and tortuosity effect on the permeability in clay: Microstructural approach[J]. Soils and Foundations,2015,55(5):1158 − 1170.
[14] SEYEDI HOSSEININIA E. Discrete element modeling of inherently anisotropic granular assemblies with polygonal particles[J]. Particuology,2012,10(5):542 − 552.
[15] DAI B B, YANG J, ZHOU C Y, et al. DEM investigation on the effect of sample preparation on the shear behavior of granular soil[J]. Particuology,2016,25:111 − 121.
[16] WANG R, CAO W, ZHANG J M. Dependency of dilatancy ratio on fabric anisotropy in granular materials[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2019,145(10):04019076.
[17] 宋晶, 王清, 夏玉斌, 等. 真空预压处理高黏粒吹填土的物理化学指标[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(5):1476 − 1480. [SONG Jing, WANG Qing, XIA Yubing, et al. Physical and chemical indicators of dredger fill with high clay by vacuum preloading[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2011,41(5):1476 − 1480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 朱楠, 刘春原, 王文静, 等. 衡水湖地区湿地湖泊相黏土工程地质特性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(1):125 − 132. [ZHU Nan, LIU Chunyuan, WANG Wenjing, et al. Investigation of engineering geological characteristics of the marshy and lacustrine clays in the Hengshui Lake area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(1):125 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] MARSCHALL T A, TEITEL S. Athermal shearing of frictionless cross-shaped particles of varying aspect ratio[J]. Granular Matter,2019,22(1):1 − 13.
[20] 袁斌, 霍宇翔, 巨能攀, 等. 颗粒棱度指标的改进及其对剪切特性的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):167 − 173. [YUAN Bing, HUO Yuxiang, JU Nengpan, et al. Improvement of grain edge index and its effect on shear characteristics[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):167 − 173. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] GONG J, NIE Z H, ZHU Y G, et al. Exploring the effects of particle shape and content of fines on the shear behavior of sand-fines mixtures via the DEM[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2019,106:161 − 176.
-



 下载:
下载: