Application of machine learning to aquifer analyses:Locating hydrogeological boundaries with water table monitoring data
-
摘要:
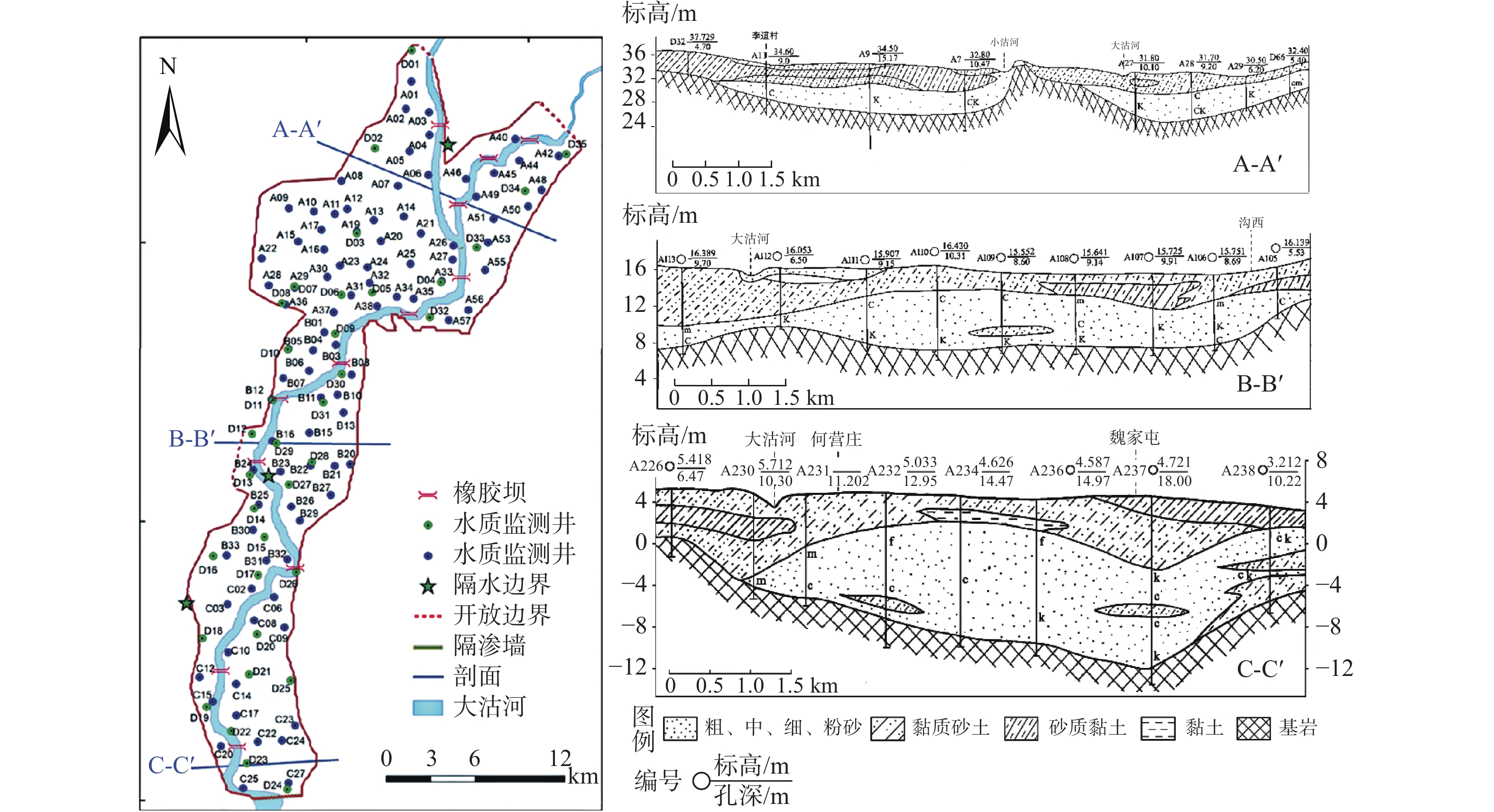
随着我国地下水监测工作的高速发展,高频率高密度水位监测数据的出现催生了对其进行深入信息挖掘的需求。在传统地下水模型研究中,地下水水位监测值常位于模型构建过程的下游,当水位监测的时空密度逐渐增大时,新增信息无法有效传导至模型的规划阶段并指导概念模型的修订。文章提出了一种地下水系统补排边界的识别方法,在不建立地下水数值模型的前提下,以监测井空间位置为节点,按照德劳内原则建立三角网格。在此网格系统中,首先定义一个水力梯度变换函数gradF,以求取网格中任意位置的水力梯度;借鉴机器学习领域的优化算法,使用水力梯度场驱动含水层中随机分布质点的运行轨迹,并以此推断和识别区域内地下水补给和排泄边界。在环境地学计算平台EnviFusion-CGS中实现,并构建了详细工作流程。以山东省青岛市大沽河中下游含水层为示范区,对含水系统的补给区和排泄区的空间分布及其动态变化进行了分析,取得了良好效果。本研究为构建和修订已有含水层概念模型提供了新思路。
Abstract:Groundwater level fluctuations in China are being monitored with unprecedented frequency and density, which drives the need for mining such types of data. In a typical aquifer analysis project, groundwater level data is generally applied after the completion of the aquifer conceptual framework. When the temporal and spatial density of groundwater level data gradually increases, the information gain needs to be effectively transformed into conceptual knowledge of the model. In this study, we propose a method to identify hydrological boundaries based on the groundwater level monitoring data. In this method we discretize space into a triangular mesh using monitoring wells as the initial nodes, and a transformation function gradF is defined to calculate the hydraulic gradient at any given location on the mesh. The hydraulic gradient field is subsequently use to drive an array of randomly scattered particles to obtain the streamline representation of the flow field, which will in turn serve as the basis for deducing and refining the recharge and discharge boundaries of a hydrogeological domain. This method is implemented into the geo-environmental scientific computation platform (EnviFusion-CGS), and a detailed work flow is developed to facilitate the development of the aquifer conceptual model. This method is applied to the hydrogeological investigation of the Dagu aquifer located in Qingdao of Shandong Province, where the spatial distributions and dynamic fluctuations of the hydrogeological boundaries are identified.
-
Key words:
- high density /
- groundwater level monitoring /
- conceptual model /
- groundwater /
- recharge boundary /
- discharge boundary
-

-
[1] 严宇红, 周政辉. 国家地下水监测工程站网布设成果综述[J]. 水文,2017,37(5):74 − 78. [YAN Yuhong, ZHOU Zhenghui. Introduction to network layout of national groundwater monitoring project[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2017,37(5):74 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2017.05.014
[2] 田志仁, 李名升, 夏新, 等. 我国地下水环境监测现状和工作建议[J]. 环境监控与预警,2020,12(6):1 − 6. [TIAN Zhiren, LI Mingsheng, XIA Xin, et al. Current situation and suggestions of groundwater monitoring work in China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning,2020,12(6):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2020.06.001
[3] RAJABI M M, ATAIE-ASHTIANI B, SIMMONS C T. Model-data interaction in groundwater studies: Review of methods, applications and future directions[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2018,567:457 − 477. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.053
[4] 薛禹群, 吴吉春. 地下水数值模拟在我国—回顾与展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1997,24(4):21 − 24. [XUE Yuqun, WU Jichun. Numerical simulation of groundwater in retrospect and prospect in China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1997,24(4):21 − 24. (in Chinese)
[5] 薛禹群. 中国地下水数值模拟的现状与展望[J]. 高校地质学报,2010,16(1):1 − 6. [XUE Yuqun. Present situation and prospect of groundwater numerical simulation in China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2010,16(1):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.01.001
[6] 中国地质调查局. 水文地质手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
China Geological Survey. Handbook of hydrogeology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012. (in Chinese)
[7] 易立新, 徐鹤. 地下水数值模拟[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009.
YI Lixin, XU He. Numerical simulation of groundwater[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[8] 李家兴. 基于深度学习的含水层参数反演研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
LI Jiaxing. Research on inverse problem of aquifer parameters based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李竞生, 姚磊华. 含水层参数识别方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003.
LI Jingsheng, YAO Leihua. Identification method of aquifer parameter[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003. (in Chinese)
[10] 何清, 李宁, 罗文娟, 等. 大数据下的机器学习算法综述[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2014,27(4):327 − 336. [HE Qing, LI Ning, LUO Wenjuan, et al. A survey of machine learning algorithms for big data[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence,2014,27(4):327 − 336. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2014.04.007
[11] 刘光亚. 水文地质数值模拟的拟合问题[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1992(4):2 − 4. [LIU Guangya. The fitting problem of hydrogeological numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1992(4):2 − 4. (in Chinese)
[12] 张双圣, 强静, 刘汉湖, 等. 基于贝叶斯公式的地下水污染源识别[J]. 中国环境科学,2019,39(4):1568 − 1578. [ZHANG Shuangsheng, QIANG Jing, LIU Hanhu, et al. Identification of groundwater pollution sources based on Bayes' theorem[J]. China Environmental Science,2019,39(4):1568 − 1578. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.04.027
[13] NESTEROV Y. Introductory lectures on convex optimization: a basic course (applied optimization)[M]. Boston: Springer Science & Business Media, 2004: 51−110.
[14] 焦李成, 杨淑媛, 刘芳, 等. 神经网络七十年: 回顾与展望[J]. 计算机学报,2016,39(8):1697 − 1716. [JIAO Licheng, YANG Shuyuan, LIU Fang, et al. Seventy years beyond neural networks: retrospect and prospect[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers,2016,39(8):1697 − 1716. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 褚蕾蕾, 陈绥阳, 周梦. 计算智能的数学基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.
CHU Leilei, CHEN Suiyang, ZHOU Meng. Mathematical basis of Computational Intelligence [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
[16] 陈海虹, 黄彪, 刘峰, 等. 机器学习原理及应用[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 2017.
CHEN Haihong, HUANG Biao, LIU Feng, et al. Principle and application of machine learning[M]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Press, 2017. (in Chinese)
[17] WANG J, TAO Q. Machine learning: the state of the art[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems,2008,23(6):49 − 55. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2008.107
[18] BOTTOU L, CURTIS F E, NOCEDAL J. Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning[J]. SIAM Review,2018,60(2):223 − 311. doi: 10.1137/16M1080173
[19] POLYAK B T. Introduction to optimization[M]. New York: Optimization Software, 1987.
[20] CAUCHY A L. Méthode générale pour la résolution des systemes d'équations simultanées[J]. Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences,1847:536 − 538.
[21] ROBBINS H, MONRO S. A stochastic approximation method[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1951,22(3):400 − 407. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729586
[22] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature,1986,323(6088):533 − 536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0
[23] 史加荣, 王丹, 尚凡华, 等. 随机梯度下降算法研究进展[J]. 自动化学报,2021,47(9):2103-2119. [SHI Jiarong, WANG Dan, SHANG Fanhua, et al. Research advances on stochastic gradient descent algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica,2021,47(9):2103-2119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] ATTOUCH H, BOLTE J, SVAITER B F. Convergence of descent methods for semi-algebraic and tame problems: proximal algorithms, forward-backward splitting, and regularized Gauss-Seidel methods[J]. Mathematical Programming,2013,137(1/2):91 − 129.
[25] 王惊晓, 高乾坤, 汪群山. 一种具有最优收敛速度的正则化境面下降算法[J]. 计算机工程,2014,40(6):148 − 153. [WANG Jingxiao, GAO Qiankun, WANG Qunshan. A regularization mirror descent algorithm with optimal convergence rate[J]. Computer Engineering,2014,40(6):148 − 153. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2014.06.032
[26] 刘梓懿. 多步梯度法的收敛性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2020.
LIU Ziyi. On the convergence rate of the multi-step methods[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] GHADIMI E, SHAMES I, JOHANSSON M. Multi-step gradient methods for networked optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2013,61(21):5417 − 5429. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2278149
[28] 孔康, 汪群山, 梁万路. L1正则化机器学习问题求解分析[J]. 计算机工程,2011,37(17):175 − 177. [KONG Kang, WANG Qunshan, LIANG Wanlu. Solution analysis of L1 regularized machine learning problem[J]. Computer Engineering,2011,37(17):175 − 177. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2011.17.059
[29] TSENG P, YUN S. Incrementally updated gradient methods for constrained and regularized optimization[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications,2014,160(3):832 − 853. doi: 10.1007/s10957-013-0409-2
[30] YU N. Gradient methods for minimizing composite functions[J]. Mathematical Programming,2013,140(1):125 − 161. doi: 10.1007/s10107-012-0629-5
[31] DAVID W P. User’s guide for MODPATH/MODPATH-PLOT, Version 3: A particle tracking post-processing package for MODFLOW, the U. S. Geological Survey finite-difference ground-water flow model[R]. Reston: Geological Survey, 1994.
[32] RUNGE C D T. Über die numerische Auflösung von Differentialgleichungen[J]. Mathematische Annalen, Springer,1895,46(2):167 − 178.
[33] KUTTA M. Beitrag zur näherungsweisen Integration totaler Differentialgleichungen[J]. Zeitschrift für Mathematik und Physik,1901,46:435 − 453.
[34] 廖凯华. 大沽河流域土壤水资源评价及农业节水灌溉模式研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2009.
LIAO Kaihua. Study on evaluation of soil water resources and water saving irrigation modes in Dagu river basin[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 尹子悦. 大沽河流域地下水时空演变特征及数值模拟[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2019.
YIN Ziyue. Spatial-temporal variations of groundwater and its numerical simulation in the Dagu river basin[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 贾立华. 大沽河地下水库脆弱性评价[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2003.
JIA Lihua. Vulnerability assessment to the Dagu river groundwater reservoir[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 林国庆, 郑西来, 李海明. 下水库人工补给的模型研究—以大沽河地下水库为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2005,35(5):745 − 750. [LIN Guoqing, ZHENG Xilai, LI Haiming. Simulation of artificial recharge for a groundwater reservoir: a case study of the daguhe groundwater reservoir[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao,2005,35(5):745 − 750. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 张旭洋, 林青, 黄修东, 等. 大沽河流域土壤水-地下水流耦合模拟及补给量估算[J]. 土壤学报,2019,56(1):101 − 113. [ZHANG Xuyang, LIN Qing, HUANG Xiudong, et al. Numerical simulation coupling soil water/groundwater and estimation of groundwater recharge in dagu river basin[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2019,56(1):101 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 尹明泉, 王治良, 王通国, 等. 青岛市大沽河水源地地下水资源潜力分析[J]. 山东国土资源,2005,21(4):30 − 34. [YIN Mingquan, WANG Zhiliang, WANG Tongguo, et al. Potentiality analysis on underground water resource in daguhe water source area in Qingdao City[J]. Land and Resources in Shandong Province,2005,21(4):30 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2005.04.014
[40] 杨丽娟. 大沽河平原区地下水资源评价[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
YANG Lijuan. Evaluation of groundwater resources in dagu river[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: