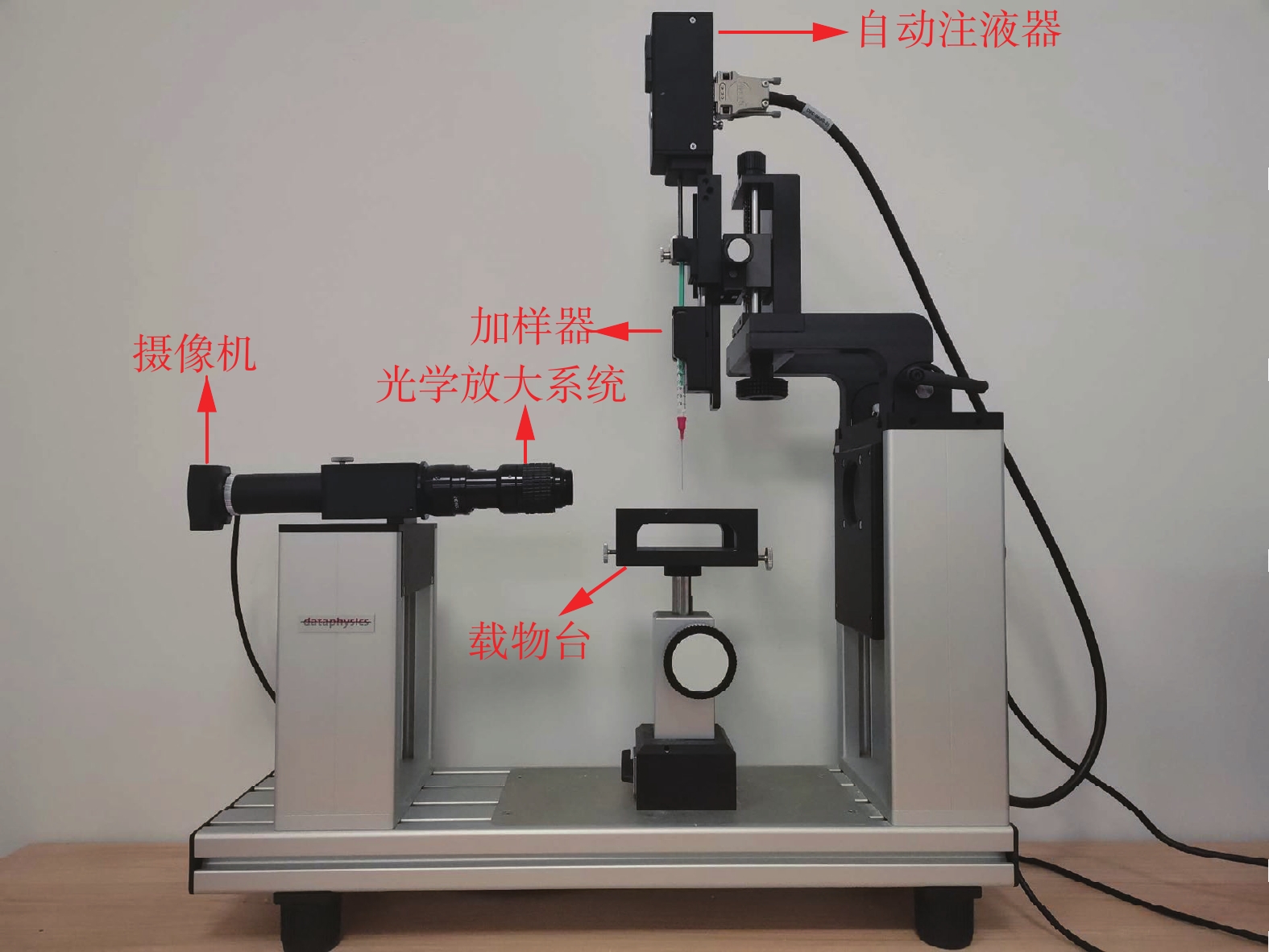
Water entrance-and-release capacity and contact angle of improved granite residual soil
-
摘要:
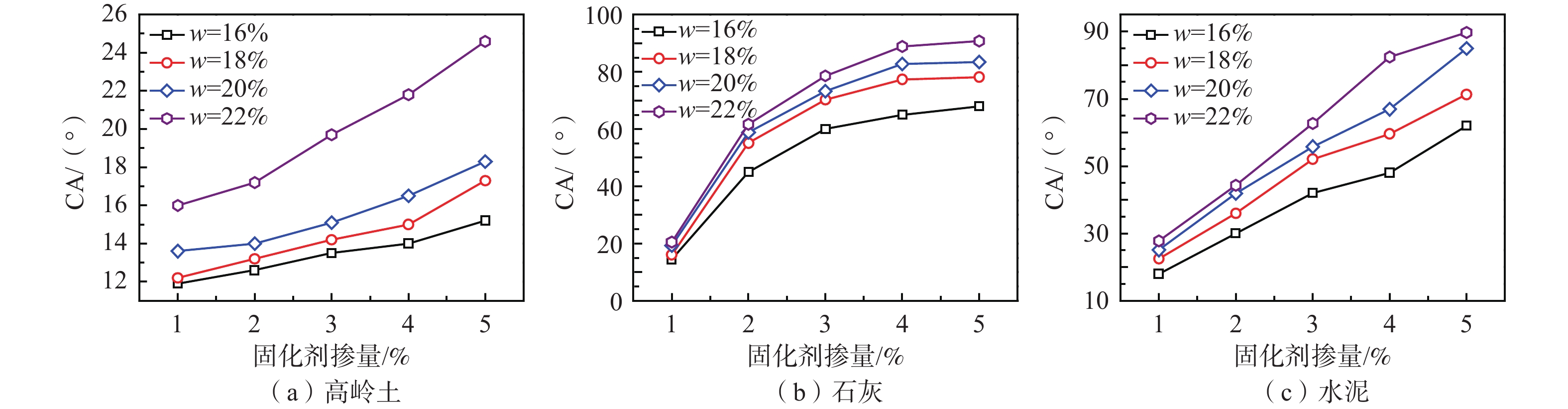
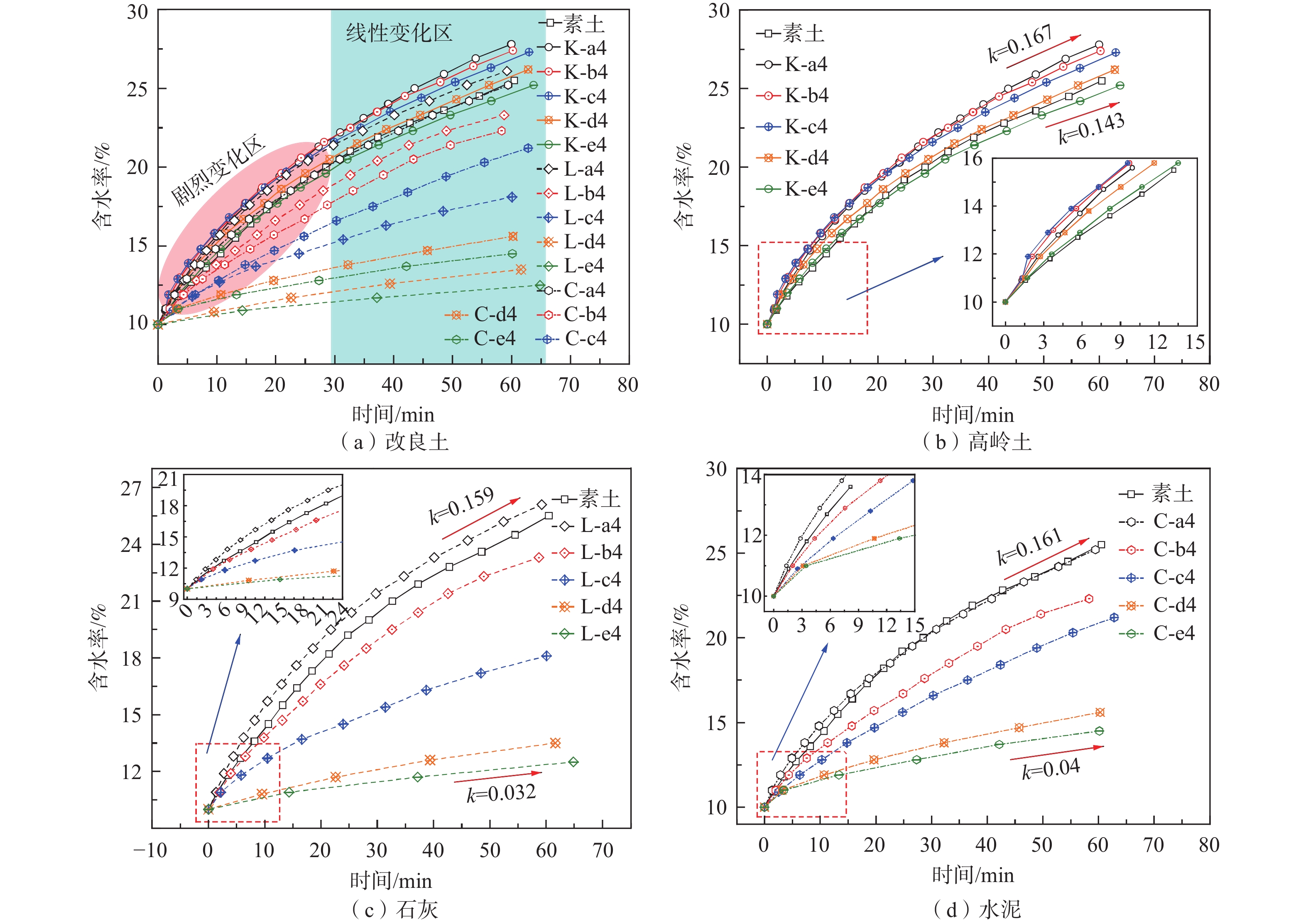
花岗岩残积土的进失水能力与其软化崩解的特殊力学特性息息相关,现有的改良土研究都着重于土体宏观力学与微观结构的变化,忽视了固化剂对土颗粒表面性质的影响。为了探索固化剂改良后的花岗岩残积土进失水能力及三相接触角的变化规律,开展了水滴入渗试验、接触角测量试验、进水试验和失水试验,并结合扫描电镜和红外光谱方法,定性及定量分析了花岗岩残积土在不同固化剂作用下微观结构和化学成分的变化规律对花岗岩残积土进失水能力的影响机制。结果表明:(1)不同含量的改良剂能不同程度地影响花岗岩残积土表层斥水性能;随着固化剂掺量的提高,土体的表面斥水性增强,三相接触角变大,进失水能力减弱;固化剂改良土体的效果依次为石灰、水泥、高岭土,且改良土体的进失水能力变化与土体表面斥水性和三相接触角的变化有明显的相关性。(2)改良花岗岩残积土进失水能力的变化由土体内部结构的改变以及表面性质的改变共同导致。(3)水泥和石灰主要依靠离子的交换团聚作用、土壤固化剂对土颗粒的包裹作用、硬凝反应以及碳酸化作用减弱土颗粒外部的双电层及其表面自由能,使土体斥水性和初始接触角变大;而高岭土主要依靠自身对水分子的吸附作用,对土体的斥水性和接触角影响不大。结果可为固化剂改变土体表面性质导致的接触角变化规律提供一定科学依据,也为不同渗透需求的实际工程选取改良剂提供一定参考。
Abstract:Water entrance-and-release capacity of granite residual soil is closely related to the special mechanical properties of softening and disintegration. Existing research on the improved soil focuses on the macro-mechanical properites and variation of micro-structure of soil, and ignores the influence of curing agent on the soil surface properties. To explore the water entrance-and-release capacity of granite residual soil improved by curing agent and the variation of three-phase antenna, the water drop infiltration test, contact angle measurement test, water inlet test and water entrance-and-release test were carried out. Combined with scanning electron microscopy and infrared spectroscopy, the influence mechanism of microstructure and chemical composition of granite residual soil under different curing agents on entrance-and-release of granite residual soil was analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. The results show that (1) different contents of curing agent can affect the surface water repellency of granite residual soil to different degrees. With the increasing curing agent content, the surface water repellency of soil increases, the three-phase antenna becomes larger, and the water release capacity weakens. (2) The improvement effect of lime is stronger than that of cement and kaolin, and the change of water entrance-and-release capacity of modified soil is obviously correlated to the change of water repulsion and three-phase antenna. The change of water entrance-and-release capacity of improved granite residual soil is caused by the changes of soil internal structure and surface property. (3) Cement and lime mainly rely on ion exchange agglomeration, soil curing agent's wrapping effect on soil particles, hard coagulation reaction and carbonation to weaken the double electric layer and surface free energy on the surface of soil particles, so that the soil water repulsion and initial contact angle become larger. Kaolin mainly depends on its adsorption of water molecules, but it has little effect on the water repellency and contact angle of soil. The results can provide a scientific basis for the variation of contact angle caused by the change of soil surface properties by curing agent, and also provide a reference for the selection of improvement in practical engineering with different permeability requirements.
-

-
表 1 花岗岩残积土基本物性指标
Table 1. Basic properties of granite residual soil
参数 取土深度
/m含水率
/%天然密度
/(g·cm−3)液限
/%塑限
/%塑性指数 黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)数值 1.0 14.25 1.64 35.2 21.7 13.5 15 33.1 表 2 土的斥水性分级
Table 2. Water repellency grade of soils
WDPT /s WDPT< 5 5 ≤ WDPT< 60 60 ≤ WDPT< 600 600 ≤ WDPT< 3600 WDPT≥ 3600 斥水等级 亲水性 轻微斥水性 强斥水性 严重斥水性 超斥水性 表 3 试样分类及编号
Table 3. Sample classification and numbering
固化剂
掺量/%含水率/% 固化剂
掺量/%含水率/% 固化剂
掺量/%含水率/% 16±0.3 18±0.3 20±0.3 22±0.3 16±0.3 18±0.3 20±0.3 22±0.3 16±0.3 18±0.3 20±0.3 22±0.3 1 C-a1 C-a2 C-a3 C-a4 1 L-a1 L-a2 L-a3 L-a4 1 K-a1 K-a2 K-a3 K-a4 2 C-b1 C-b2 C-b3 C-b4 2 L-b1 L-b2 L-b3 L-b4 2 K-b1 K-b2 K-b3 K-b4 3 C-c1 C-c2 C-c3 C-c4 3 L-c1 L-c2 L-c3 L-c4 3 K-c1 K-c2 K-c3 K-c4 4 C-d1 C-d2 C-d3 C-d4 4 L-d1 L-d2 L-d3 L-d4 4 K-d1 K-d2 K-d3 K-d4 5 C-e1 C-e2 C-e3 C-e4 5 L-e1 L-e2 L-e3 L-e4 5 K-e1 K-e2 K-e3 K-e4 注:C代表水泥;L代表石灰;K代表高岭土。 -
[1] 陈正汉. 非饱和土与特殊土力学的基本理论研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014,36(2):201 − 272. [CHEN Zhenghan. On basic theories of unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014,36(2):201 − 272. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201402001
CHEN Zhenghan. On basic theories of unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(2): 201-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201402001
[2] 孙银磊, 汤连生, 刘洁. 非饱和土微观结构与粒间吸力的研究进展[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(4):1095 − 1122. [SUN Yinlei, TANG Liansheng, LIU Jie. Advances in research on microstructure and intergranular suction of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(4):1095 − 1122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Yinlei, TANG Liansheng, LIU Jie. Advances in research on microstructure and intergranular suction of unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(4): 1095-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 简文彬, 胡海瑞, 罗阳华, 等. 干湿循环下花岗岩残积土强度衰减试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(3):592 − 597. [JIAN Wenbin, HU Hairui, LUO Yanghua, et al. Experimental study on deterioration of granitic residual soil strength in wetting-drying cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(3):592 − 597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIAN Wenbin, HU Hairui, LUO Yanghua, et al. Experimental study on deterioration of granitic residual soil strength in wetting-drying cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(3): 592-597. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王清, 唐大雄, 张庆云, 等. 中国东部花岗岩残积土物质成分和结构特征的研究[J]. 长春地质学院学报,1991,21(1):73 − 81. [WANG Qing, TANG Daxiong, ZHANG Qingyun, et al. A study on the structure and composition of granite residual soil in the eastern China[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science,1991,21(1):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Qing, TANG Daxiong, ZHANG Qingyun, et al. A study on the structure and composition of granite residual soil in the eastern China[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 1991, 21(1): 73-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] LI C S, KONG L W, SHU R J, et al. Disintegration characteristics in granite residual soil and their relationship with the collapsing gully in South China[J]. Open Geosciences,2020,12(1):1116 − 1126. doi: 10.1515/geo-2020-0178
[6] KONG L W, SAYEM H M, TIAN H H. Influence of drying–wetting cycles on soil-water characteristic curve of undisturbed granite residual soils and microstructure mechanism by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-spin relaxation time (T2) relaxometry[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2018,55(2):208 − 216. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2016-0614
[7] 尹松, 白林杰, 李新明, 等. 压实花岗岩残积土的崩解特性试验研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2021,38(9):121 − 127. [YIN Song, BAI Linjie, LI Xinming, et al. Experimental study on disintegration characteristics of compacted granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2021,38(9):121 − 127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200536
YIN Song, BAI Linjie, LI Xinming, et al. Experimental study on disintegration characteristics of compacted granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(9): 121-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20200536
[8] 王章琼, 高云, 沈雷, 等. 石灰改性红砂岩残积土工程性质试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(2):416 − 421. [WANG Zhangqiong, GAO Yun, SHEN Lei, et al. Engineering properties of lime-modifiedred sandstone residual soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(2):416 − 421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Zhangqiong, GAO Yun, SHEN Lei, et al. Engineering properties of lime-modifiedred sandstone residual soil[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(2): 416-421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 张桂荣, 罗紫婧, 邵勇, 等. 水泥、粉煤灰改良细砂土的工程特性与改良机理[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2019,17(5):128 − 132. [ZHANG Guirong, LUO Zijing, SHAO Yong, et al. Engineering characteristics and improvement mechanism of cement and fly ash improved fine sand[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2019,17(5):128 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Guirong, LUO Zijing, SHAO Yong, et al. Engineering characteristics and improvement mechanism of cement and fly ash improved fine sand[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2019, 17(5): 128-132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 费伦林, 郭利杨, 张琦, 等. 石灰与水泥改性花岗岩残积土耐久性的对比评价[J]. 交通技术,2017,6(5):185 − 191. [FEI Lunlin, GUO Liyang, ZHANG Qi, et al. Comparative evaluation of durability of granite residual soil modified by lime and cement[J]. Open Journal of Transportation Technologies,2017,6(5):185 − 191. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/OJTT.2017.65025
FEI Lunlin, GUO Liyang, ZHANG Qi, et al. Comparative evaluation of durability of granite residual soil modified by lime and cement[J]. Open Journal of Transportation Technologies, 2017, 6(5): 185-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/OJTT.2017.65025
[11] YONG R N, OUHADI V R. Experimental study on instability of bases on natural and lime/cement-stabilized clayey soils[J]. Applied Clay Science,2007,35(3/4):238 − 249.
[12] 刘清秉, 项伟, 崔德山, 等. 离子土固化剂改良膨胀土的机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2011,33(4):648 − 654. [LIU Qingbing, XIANG Wei, CUI Deshan, et al. Mechanism of expansive soil improved by ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2011,33(4):648 − 654. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Qingbing, XIANG Wei, CUI Deshan, et al. Mechanism of expansive soil improved by ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(4): 648-654. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘清秉, 项伟, 崔德山. 离子土固化剂对膨胀土结合水影响机制研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(10):1887 − 1895. [LIU Qingbing, XIANG Wei, CUI Deshan. Effect of ionic soil stabilizer on bound water of expansive soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(10):1887 − 1895. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Qingbing, XIANG Wei, CUI Deshan. Effect of ionic soil stabilizer on bound water of expansive soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(10): 1887-1895. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王严, 胡卸文, 杨瀛, 等. 火烧迹地土壤斥水性和渗透性变化特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):40 − 45. [WANG Yan, HU Xiewen, YANG Ying, et al. Research on the change in soil water repellency and permeability in burned areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):40 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Yan, HU Xiewen, YANG Ying, et al. Research on the change in soil water repellency and permeability in burned areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(6): 40-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 张光辉, 刘国彬. 黄土丘陵区小流域土壤表面特性变化规律研究[J]. 地理科学,2001,21(2):118 − 122. [ZHANG Guanghui, LIU Guobin. Spatial and temporal variability of soil surface properties in Danangou Catchment in loess hill and hilly region[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2001,21(2):118 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.02.005
ZHANG Guanghui, LIU Guobin. Spatial and temporal variability of soil surface properties in DanangouCatchment in loess hill and hilly region[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2001, 21(2): 118-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2001.02.005
[16] 李毅, 商艳玲, 李振华, 等. 土壤斥水性研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(1):68 − 75. [LI Yi, SHANG Yanling, LI Zhenhua, et al. Advance of study on soil water repellency[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2012,43(1):68 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.01.014
LI Yi, SHANG Yanling, LI Zhenhua, et al. Advance of study on soil water repellency[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(1): 68-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.01.014
[17] 陈俊英, 张智韬, 汪志农, 等. 土壤斥水性影响因素及改良措施的研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2010, 41(7): 84 − 89
CHEN Junying, ZHANG Zhitao, WANG Zhinong et al. Influencing factors and amelioration of soil water repellency[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2010, 41(7): 84 − 89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈宇龙, 孙欢. 非饱和亲水性和疏水性砂的剪切行为[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2019,59(12):961 − 966. [CHEN Yulong, SUN Huan. Shear behavior of hydrophilic and hydrophobic unsaturated sands[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2019,59(12):961 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHEN Yulong, SUN Huan. Shear behavior of hydrophilic and hydrophobic unsaturated sands[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2019, 59(12): 961-966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨松, 吴玉琴, 周明凯. 斥水红黏土的增湿强度特性研究[J]. 土壤,2021,53(1):183 − 189. [YANG Song, WU Yuqin, ZHOU Mingkai. Study on wetting strength characteristics of water repellency red clay[J]. Soils,2021,53(1):183 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Song, WU Yuqin, ZHOU Mingkai. Study on wetting strength characteristics of water repellency red clay[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(1): 183-189. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张虎元, 彭宇, 王学文, 等. 抗疏力固化剂改性黄土进失水能力研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(增刊 1):19 − 26. [ZHANG Huyuan, PENG Yu, WANG Xuewen, et al. Water entrance-and-release ability of loess soil modified by consolid system[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(Sup 1):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Huyuan, PENG Yu, WANG Xuewen, et al. Water entrance-and-release ability of loess soil modified by consolid system[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(Sup1): 19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 杨松, 龚爱民, 吴珺华, 等. 接触角对非饱和土中基质吸力的影响[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(3):674 − 678. [YANG Song, GONG Aimin, WU Junhua, et al. Effect of contact angle on matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(3):674 − 678. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Song, GONG Aimin, WU Junhua, et al. Effect of contact angle on matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(3): 674-678. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 汤连生, 王思敬. 湿吸力及非饱和土的有效应力原理探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报,2000,22(1):83 − 88. [TANG Liansheng, WANG Sijing. Absorbed suction and principle of effective stress in unsaturated soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2000,22(1):83 − 88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.01.015
TANG Liansheng, WANG Sijing. Absorbed suction and principle of effective stress in unsaturated soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(1): 83-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2000.01.015
[23] 周建, 邓以亮, 曹洋, 等. 杭州饱和软土固结过程微观结构试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2014,45(6):1998 − 2005. [ZHOU Jian, DENG Yiliang, CAO Yang, et al. Experimental study of microstructure of Hangzhou saturated soft soil during consolidation process[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2014,45(6):1998 − 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Jian, DENG Yiliang, CAO Yang, et al. Experimental study of microstructure of Hangzhou saturated soft soil during consolidation process[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(6): 1998-2005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] LIU C, TANG C S, SHI B, et al. Automatic quantification of crack patterns by image processing[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2013,57:77 − 80.
[25] 吴玉琴, 杨蕊, 代启亮, 等. 无黏性土增湿-脱湿过程中接触角的特性[J]. 水土保持通报,2021,41(1):167 − 172. [WU Yuqin, YANG Rui, DAI Qiliang, et al. Contact angle characteristics of cohesionless soil during humidification and dehumidification[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,41(1):167 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WU Yuqin, YANG Rui, DAI Qiliang, et al. Contact angle characteristics of cohesionless soil during humidification and dehumidification[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 41(1): 167-172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张齐齐, 王家鼎, 刘博榕, 等. 水泥改良土微观结构定量研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(3):92 − 96. [ZHANG Qiqi, WANG Jiading, LIU Borong, et al. Quantitative research on microstructure of modified soil with cement[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(3):92 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Qiqi, WANG Jiading, LIU Borong, et al. Quantitative research on microstructure of modified soil with cement[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(3): 92-96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 杨志强, 郭见扬. 石灰处理土的物理力学性质及其微观机理的研究[J]. 岩土力学,1991,12(3):11 − 23. [YANG Zhiqiang, GUO Jianyang. The physio-mechanical properties and micro-mechanism in lime-soil system[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,1991,12(3):11 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Zhiqiang, GUO Jianyang. The physio-mechanical properties and micro-mechanism in lime-soil system[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1991, 12(3): 11-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 郭永春, 屈智辉, 许福周, 等. 利用原子力显微镜探针刺入测试黏土颗粒水化膜厚度的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):105 − 112. [GUO Yongchun, QU Zhihui, XU Fuzhou, et al. An experimental study of the measuring hydration film thickness of clay particles with atomic force microscope probe[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):105 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
GUO Yongchun, QU Zhihui, XU Fuzhou, et al. An experimental study of the measuring hydration film thickness of clay particles with atomic force microscope probe[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 105-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: