A comprehensive study of the maintaining mechanisms for hydrological cycle and ecological evolution and function in the northwest inland river basins of China
-
摘要:
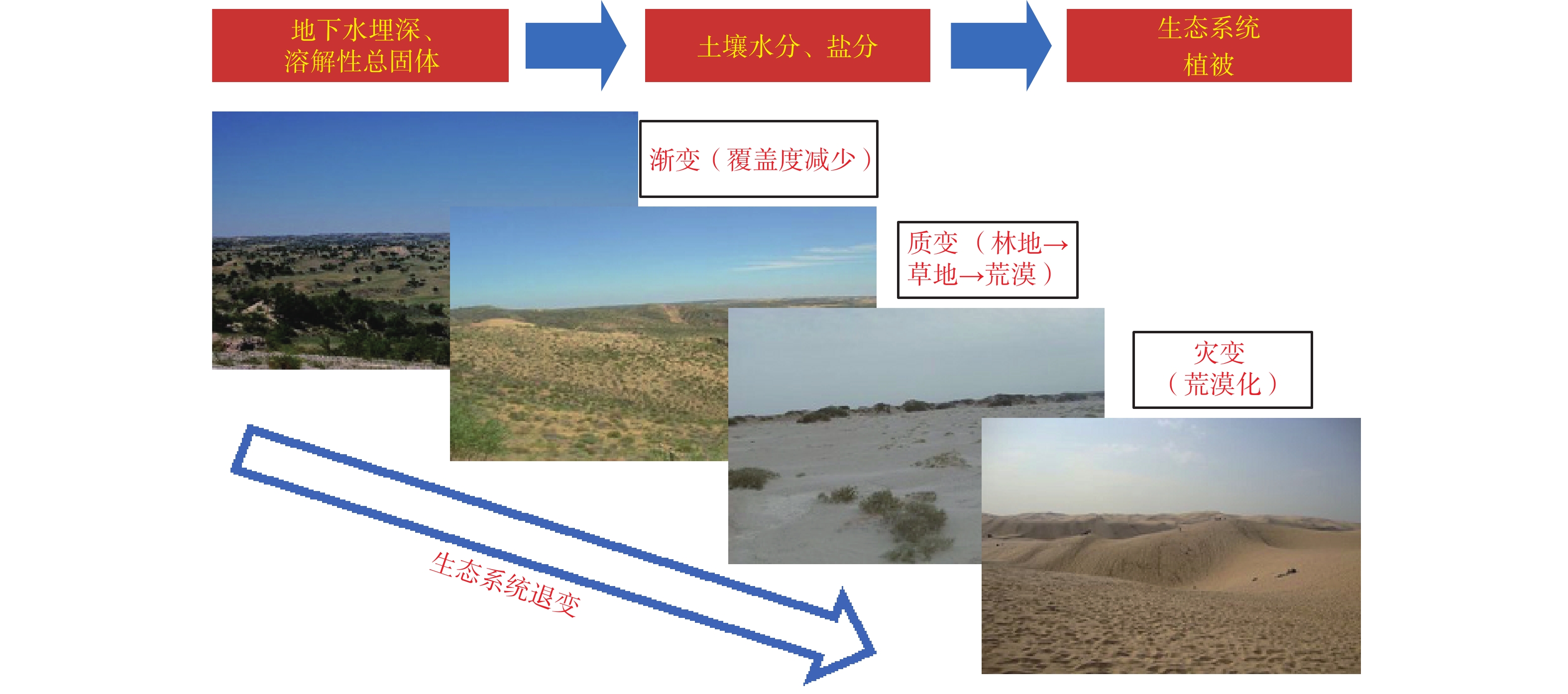
在气候变化、生态保护以及水资源调控影响下,西北内陆河流域水循环和生态环境状态发生了显著改变,迫切需要解答气候变化对植被恢复和产水量的影响,调水和压采等措施下地下水水位动态、管控指标及其对生态环境的维持机制。为此,文章阐述了内陆河流域气候-植被-土壤-水文相互作用机理以及上中下游演变状况。针对上游产水区,提出了山区气候变化下植被和水文动态演变模拟和预测方法,得出石羊河上游山区气候暖湿趋势和植被水分利用效率的提高,可降低植被恢复对增加蒸腾量、减少产水量的影响程度;但如未来继续升温,水分利用效率提高的正效应将被植被恢复增加的水分消耗抵消,从而减小径流量。针对中下游绿洲-荒漠过渡区,通过分析荒漠植被-土壤(水盐)-地下水作用机理,提出了西北干旱区生态地下水水位埋深和生态需水量确定方法及阈值,得出荒漠植被适宜和极限生态地下水水位埋深的平均值分别为2.9 m和5.5 m,对应埋深下的单位面积荒漠植被生长季平均蒸腾耗水量为0.08~0.10 m3/m2。针对尾闾湖区,建立生态输水量与尾闾湖地下水水位、生态指标之间关系,提出了石羊河流域尾闾湖生态输水优化方案,得出青土湖生态输水量应提高至0.45×108 m3/a。在流域层面,采用水资源-社会经济-生态环境协调的系统分析手段,提出了石羊河流域满足地下水均衡、供需平衡和生态功能的多水源调控方案,即“保田增林”或“以田换林”方案。
Abstract:In recent decades, the hydrological cycle, ecology and environment of the inland river basins in northwest China have been significantly changed due to climate change and implementations of the ecological protection and water division projects. It is necessary to investigate how climate change affects vegetation restoration and runoff generation, and how groundwater table variation and its controlling index maintain ecology and environment under the inter-basin water diversion and reduction of groundwater withdrawal. In this study, we illustrate the mechanism of climate-vegetation-soil-hydrology interactions and their evolutions in the upper, middle and lower reaches of the catchments. For the upper reaches, we propose a method of simulation and prediction of mountain vegetation and hydrological changes under climate warming and wetting. When the method is applied in the Shiyang River basin, the results demonstrate that increase of efficient water use can reduce vegetation recover induced evaporation (thus runoff reduction). In the oasis-desert transition areas of the middle and lower reaches, we analyze desert vegetation-soil (moisture and salt)-groundwater interactions, and propose methods to determine critical values of the ecological groundwater depth and water requirement. For the terminal lake, we establish the relationships among ecological water division, groundwater table and ecological index. These relationships are used to optimize the schemes of ecological water division. In the whole inter-basin, we apply a system analysis approach of water resources-economic and social development-ecological and environment processes to obtain the schemes of the multi-water source allocations in the Shiyang River basin. These schemes can maintain groundwater withdrawal and recharge balance, water requirement and supply balance and ecological functions.
-

-
[1] 耿雷华,黄永基,郦建强,等. 西北内陆河流域水资源特点初析[J]. 水科学进展,2002,13(4):496 − 501. [GENG Leihua,HUANG Yongji,LI Jianqiang,et al. Analysis on water resources characters of endorheic drainage in Northwest China[J]. Advances in Water Science,2002,13(4):496 − 501. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2002.04.018
[2] 高前兆,仵彦卿. 河西内陆河流域的水循环分析[J]. 水科学进展,2004,15(3):391 − 396. [GAO Qianzhao,WU Yanqing. Analysis of water cycle in inland river basins in Hexi Region[J]. Advances in Water Science,2004,15(3):391 − 396. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2004.03.023
[3] 祁晓凡,李文鹏,崔虎群,等. 黑河流域中游盆地地表水与地下水转化机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):29 − 43. [QI Xiaofan,LI Wenpeng,CUI Huqun,et al. Study on the conversion mechanism of surface water and groundwater in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):29 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李文鹏,邵新民,祁晓凡,等. 黑河中游盆地南部山区地下水对平原区侧向径流补给量的估算[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(3):1 − 10. [LI Wenpeng,SHAO Xinmin,QI Xiaofan,et al. Estimation of groundwater lateral flow in the southern mountainous area of the middle Heihe River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(3):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 程国栋,肖洪浪,徐中民,等. 中国西北内陆河水问题及其应对策略—以黑河流域为例[J]. 冰川冻土,2012,28(3):406 − 413. [CHENG Guodong,XIAO Hongliang,XU Zhongmin,et al. Water issue and its countermeasure in the inland river basins of Northwest China:A case study in Heihe River Basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2012,28(3):406 − 413. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] GAO X,YE B S,ZHANG S Q,et al. Glacier runoff variation and its influence on river runoff during 1961—2006 in the Tarim River Basin,China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2010,53(6):880 − 891. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-0073-4
[7] QIN J,LIU Y X,CHANG Y P,et al. Regional runoff variation and its response to climate change and human activities in Northwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(20):1 − 14.
[8] 贾文雄,赵珍,俎佳星,等. 祁连山不同植被类型的物候变化及其对气候的响应[J]. 生态学报,2016,36(23):7826 − 7840. [JIA Wenxiong,ZHAO Zhen,ZU Jiaxing,et al. Phenological variation in different vegetation types and their response to climate change in the Qilian Mountains,China,1982—2014[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2016,36(23):7826 − 7840. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李娟,龚纯伟. 祁连山国家公园植被覆盖变化地形分异效应[J]. 水土保持通报,2021,41(3):228 − 237. [LI Juan,GONG Chunwei. Effects of terrain factors on vegetation cover change in National Park of Qilian mountains[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,41(3):228 − 237. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2021.03.031
[10] 孙自永,王俊友,葛孟琰,等. 基于水稳定同位素的地下水型陆地植被识别:研究进展、面临挑战及未来研究展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(1):11 − 20. [SUN Ziyong,WANG Junyou,GE Mengyan,et al. Isotopic approaches to identify groundwater dependent terrestrial vegetation:Progress,challenges,and prospects for future research[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(1):11 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘恒,钟华平,顾颖. 西北干旱内陆河区水资源利用与绿洲演变规律研究—以石羊河流域下游民勤盆地为例[J]. 水科学进展,2001,12(3):378 − 384. [LIU Heng,ZHONG Huaping,GU Ying. Water resources development and oasis evolution in inland river basin of arid zone of northwest China:A case study in Minqin basin of Shiyang river[J]. Advances in Water Science,2001,12(3):378 − 384. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2001.03.017
[12] HUANG F,OCHOA C G,CHEN X,et al. Modeling oasis dynamics driven by ecological water diversion and implications for oasis restoration in arid endorheic basins[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2021,593:125774. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125774
[13] ZHANG Q,YANG J H,WANG W,et al. Climatic warming and humidification in the arid region of Northwest China:multi-scale characteristics and impacts on ecological vegetation[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research,2021,35(1):113 − 127. doi: 10.1007/s13351-021-0105-3
[14] 丁永建,张世强. 西北内陆河山区流域内循环过程与机理研究:现状与挑战[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):719 − 727. [DING Yongjian,ZHANG Shiqiang. Study on water internal recycle process and mechanism in typical mountain areas of inland basins,northwest China:progress and challenge[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):719 − 727. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0719
[15] 王玉洁,秦大河. 气候变化及人类活动对西北干旱区水资源影响研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展,2017,13(5):483 − 493. [WANG Yujie,QIN Dahe. Influence of climate change and human activity on water resources in arid region of northwest China:An overview[J]. Climate Change Research,2017,13(5):483 − 493. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] HE Z B,ZHAO W Z,HU L H,et al. Effect of forest on annual water yield in the mountains of an arid inland river basin:A case study in the Pailugou catchment on northwestern China’s Qilian Mountains[J]. Hydrological Processes,2012,26(4):613 − 621. doi: 10.1002/hyp.8162
[17] 何志斌,杜军,陈龙飞,等. 干旱区山地森林生态水文研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,2016,31(10):1078 − 1089. [HE Zhibin,DU Jun,CHEN Longfei,et al. Review on montane forest eco-hydrology in arid area[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2016,31(10):1078 − 1089. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2016.10.1078
[18] GAO B,YANG D W,QIN Y,et al. Change in frozen soils and its effect on regional hydrology in the upper Heihe Basin,the northeast Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. The Cryosphere Discussions,2017:1 − 55. doi: 10.5194/tc-2017-171
[19] 陈腊娇,朱阿兴,秦承志,等. 流域生态水文模型研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展,2011,30(5):535 − 544. [CHEN Lajiao,ZHU Axing,QIN Chengzhi,et al. Review of eco-hydrological models of watershed scale[J]. Progress in Geography,2011,30(5):535 − 544. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.05.003
[20] 冯起,尹振良,席海洋. 流域生态水文模型研究和问题[J]. 第四纪研究,2014,34(5):1082 − 1093. [FENG Qi,YIN Zhenliang,XI Haiyang. Review and issues of eco-hydrological models of watershed scale[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2014,34(5):1082 − 1093. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.05.17
[21] 周天军,邹立维,陈晓龙. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6)评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展,2019,15(5):445 − 456. [ZHOU Tianjun,ZOU Liwei,CHEN Xiaolong. Commentary on the coupled model intercomparison project phase 6(CMIP6)[J]. Climate Change Research,2019,15(5):445 − 456. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] GERTEN D,SCHAPHOFF S,HABERLANDT U,et al. Terrestrial vegetation and water balance—hydrological evaluation of a dynamic global vegetation model[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2004,286(1/2/3/4):249 − 270.
[23] PRENTICE I C, COWLING S A. Dynamic global vegetation models[C]//Encyclopedia of Biodiversity. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013: 670-689.
[24] SCHAPHOFF S,VON BLOH W,RAMMIG A,et al. LPJmL4–a dynamic global vegetation model with managed land–Part 1:Model description[J]. Geoscientific Model Development,2018,11(4):1343 − 1375. doi: 10.5194/gmd-11-1343-2018
[25] SITCH S,SMITH B,PRENTICE I C,et al. Evaluation of ecosystem dynamics,plant geography and terrestrial carbon cycling in the LPJ dynamic global vegetation model[J]. Global Change Biology,2003,9(2):161 − 185. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00569.x
[26] LI Q L,ISHIDAIRA H. Development of a biosphere hydrological model considering vegetation dynamics and its evaluation at basin scale under climate change[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2012,412/413:3 − 13. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.08.046
[27] PAPPAS C,FATICHI S,RIMKUS S,et al. The role of local-scale heterogeneities in terrestrial ecosystem modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2015,120(2):341 − 360.
[28] WANIA R,ROSS I,PRENTICE I C. Implementation and evaluation of a new methane model within a dynamic global vegetation model:LPJ-WHyMe v1.3. 1[J]. Geoscientific Model Development,2010,3(2):565 − 584. doi: 10.5194/gmd-3-565-2010
[29] 黄日超. 内陆河流域上游植被-水文动态对气候变化的响应-以石羊河流域为例[D]. 南京: 河海大学, 2021
HUANG Richao. Response of vegetation and hydrological dynamics to climate change in the upper of inland river basin: A case study of Shiyang River Basin[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 李佳芳. 石羊河上游—祁连山冷龙岭西营河流域同位素径流分割研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2017
LI Jiafang. Isotope runoff segmentation of the xiyin river basin in the Lenglongling of the Qilian mountains[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 党学亚,卢娜,顾小凡,等. 柴达木盆地生态植被的地下水阈值[J]. 水文地质工程地,2019,46(3):1 − 8. [DANG Xueya,LU Na,GU Xiaofan,et al. Groundwater threshold of ecological vegetation in Qaidam Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] COOPER D J,SANDERSON J S,STANNARD D I,et al. Effects of long-term water table drawdown on evapotranspiration and vegetation in an arid region phreatophyte community[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2006,325(1/2/3/4):21 − 34.
[33] 李小玉,宋冬梅,肖笃宁. 石羊河下游民勤绿洲地下水矿化度的时空变异[J]. 地理学报,2005,60(2):319 − 327. [LI Xiaoyu,SONG Dongmei,XIAO Duning. The variability of groundwater mineralization in Minqin oasis[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2005,60(2):319 − 327. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2005.02.015
[34] SONG L,ZHU J,LI M,et al. Sources of water used by Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica trees based on stable isotope measurements in a semiarid sandy region of Northeast China[J]. Agricultural Water Management,2016,164:281 − 290. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2015.10.018
[35] LAIO F,TAMEA S,RIDOLFI L,et al. Ecohydrology of groundwater-dependent ecosystems:1. Stochastic water table dynamics[J]. Water Resources Research,2009,45(5):W05419.
[36] 张阳阳,陈喜,高满,等. 基于元数据分析的西北干旱区生态地下水位埋深及其影响因素[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2020,18(5):57 − 65. [ZHANG Yangyang,CHEN Xi,GAO Man,et al. Meta-analysis of ecological depth to groundwater table and its influencing factors in aird region of northwest China[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2020,18(5):57 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 刘秀强,陈喜,刘琴,等. 西北干旱区尾闾湖过渡带陆面蒸发和潜水对土壤水影响的同位素分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(6):52 − 59. [LIU Xiuqiang,CHEN Xi,LIU Qin,et al. Variation of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in soil water and soil water evaporation depth around Terminal Lake in arid region of Northwest China[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2021,35(6):52 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.157
[38] 刘秀强,陈喜,张阳阳,等. 青土湖土壤剖面盐分特征及其定量表述研究[J]. 干旱区研究,2020,37(5):1174 − 1182. [LIU Xiuqiang,CHEN Xi,ZHANG Yangyang,et al. Study on salt distribution characteristics and mathematical expression of the soil profile in Qingtu Lake[J]. Arid Zone Research,2020,37(5):1174 − 1182. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2020.05.10
[39] 陈永金,陈亚宁,薛燕. 干旱区植物耗水量的研究与进展[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2004,18(6):152 − 158. [CHEN Yongjin,CHEN Yaning,XUE Yan. The progress and perspective of study on water consumption of vegetation in arid region[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources & Environment,2004,18(6):152 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2004.06.030
[40] 石磊,盛后财,满秀玲,等. 不同尺度林木蒸腾耗水测算方法述评[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,40(4):149 − 156. [SHI Lei,SHENG Houcai,MAN Xiuling,et al. A review of the calculation method of water consumption by tree transpiration in different scales[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition),2016,40(4):149 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 高冠龙,冯起,刘贤德,等. 三种经验模型模拟荒漠河岸柽柳叶片气孔导度[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(10):3486 − 3494. [GAO Guanlong,FENG Qi,LIU Xiande,et al. Simulating the leaf stomatal conductance of the desert riparian Tamarix ramosissima Ledeb based on three empirical models[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(10):3486 − 3494. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 张阳阳,陈喜,高满,等. 内陆干旱区典型旱生植物蒸腾耗水量模拟研究[J]. 生态学报,2021,41(19):7751 − 7762. [ZHANG Yangyang,CHEN Xi,GAO Man,et al. Simulation of transpiration for typical xeromorphic plants in inland arid region of Northwestern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(19):7751 − 7762. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[43] TARDIEU F,SIMONNEAU T,PARENT B. Modelling the coordination of the controls of stomatal aperture,transpiration,leaf growth,and abscisic acid:update and extension of the Tardieu-Davies model[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(8):2227 − 2237. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv039
[44] 许静,吴鑫悦,李文龙. 区域尺度生态保护红线分区研究:以我国西北地区为例[J]. 草业科学,2021,38(7):1218 − 1230. [XU Jing,WU Xinyue,LI Wenlong. Ecological conservation redline zoning at the regional scale:A case study of northwest China[J]. Pratacultural Science,2021,38(7):1218 − 1230. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0587
[45] 陈怀顺,赵晓英. 西北地区不同类型区生态恢复的途径与措施[J]. 草业科学,2000,17(5):65 − 68. [CHEN Huaishun,ZHAO Xiaoying. The approach and measures for ecological restoration in northwest China[J]. Pratacultural Science,2000,17(5):65 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0629.2000.05.015
[46] 陈乐. 石羊河流域面向生态的水资源优化配置研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2014
CHEN Le. Research on water resources optimalallocation of Shiyang River Basin in ecological[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[47] 王金哲,张光辉,崔浩浩,等. 适宜西北内陆区地下水功能区划的体系指标属性与应用[J]. 水利学报,2020,51(7):796 − 804. [WANG Jinzhe,ZHANG Guanghui,CUI Haohao,et al. System index attribute and application of groundwater function zoning in northwest inland area of China[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2020,51(7):796 − 804. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20200206
-




 下载:
下载: