An improved soil abrasion testing method for shield tunnelling based on LCPC
-
摘要:
法国桥梁道路实验室磨蚀性(Labroatoire Central de Ponts et Chaussées,LCPC)试验是测试土体磨蚀性的一种常用方法,但现有LCPC试验在评估盾构隧道土体磨蚀性时存在土体颗粒有效破碎率高、测试过程中颗粒级配变化较大等问题。鉴于此,采用圆形测试钢片替代原有矩形测试钢片,并进行对比试验。结果表明:改进后的圆形测试钢片比原有矩形测试钢片导致的土样颗粒有效破碎率大幅降低,提高了土样在LCPC试验过程中颗粒级配的稳定性;改进后的圆形测试钢片在测试过程中的磨损以磨粒磨损为主,有效剔除了冲击磨损,更符合盾构隧道工程特点;在以磨粒磨损为主时,2种测试条件下的磨损指数(LCPC abrasivity coefficient,LAC)值换算关系为LAC矩=0.93LAC圆,其中LAC矩为矩形钢片测试条件下的LAC值,LAC圆为圆形钢片测试条件下的LAC值;改进后的试验方法准确评估了北京地铁19号线右安门外站—牛街站区间和大兴国际机场线3#风井—草桥站区间的圆砾卵石地层的磨蚀性。本研究对于提高LCPC试验方法评价盾构隧道土体磨蚀性的准确性提供了重要途径。
Abstract:The Labroatoire Central de Ponts et Chaussées (LCPC) test is a commonly used method to test the abrasivity of soil, however, the existing LCPC tests have some shortcomings in evaluating the abrasivity of shield tunnel soil, such as the high effective breakage rate of soil particles and large changes in particle size distribution during testing. In view of this, a circular steel sheet is used to replace the original rectangular steel sheet, and a comparative test is carried out. The test results show that the improved circular steel sheet significantly reduces the effective breakage rate of soil samples compared with the rectangular steel sheet, and improves the stability of particle size distribution in the LCPC test. The wear of the circle steel sheet in the test process is mainly abrasive wear, which effectively eliminates the impact wear and is more in line with the characteristics of shield tunnel engineering. The analysis shows that the conversion relationship between the two LCPC abrasivity coefficients is LAC矩=0.93LAC圆 when abrasive wear is the main wear. The improved testing method accurately evaluates the abrasivity of the pebble layer crossed by the shield tunnel sections Youanmen-Niujie of Beijing Subway Line 19 and 3# Fengjing-Caoqiao of the Beijing Daxing International Airport Line. This study improves the accuracy of the LCPC test method in evaluating the soil abrasion of shield tunnel.
-
Key words:
- LCPC abrasivity test /
- shield tunnel /
- soil abrasivity /
- particle breakage /
- cutting tool wear
-

-
表 1 LAC值与磨蚀性强度判断标准[15 − 17,29,30]
Table 1. LAC value and standard for judging abrasive[15 − 17,29,30]
LAC值 磨蚀性强度 >2000 超高的磨蚀性 1250~2000 高磨蚀性 500~1250 较高的磨蚀性 250~500 一般的磨蚀性 50~250 微小的磨蚀性 0~50 没有磨蚀性 表 2 LCPC试验过程中土体颗粒级配变化及LAC值
Table 2. Change of soil particle size and LAC value during LCPC test
测试时间
/minLAC值
/(g·t−1)土样
质量/g不同粒径土颗粒质量/g <0.075 mm 0.075~
<0.25 mm0.25~
<0.5 mm0.5~
<1 mm1~
<2 mm2~
<4 mm4~
<5 mm5~
<6.5 mm6.5~
<8 mm8~
10 mm0 0 500 12 17 34 65 47 29 14 25 31 226 0.5 111.97 499 33 32 40 55 43 31 24 41 69 131 1 193.60 499 47 37 49 51 46 34 30 49 70 86 2 336.29 498 61 42 52 58 42 43 31 39 56 74 3 453.87 497 69 43 61 64 50 40 35 35 45 55 5 633.93 496 77 45 72 74 39 47 31 24 42 45 表 3 测试钢片形状及质量参数
Table 3. Test steel sheet shape and quality parameters
种类 尺寸/mm 表面积/mm2 体积/mm3 质量/g 矩形钢片 长50,宽25,厚5 3183.7 12168.3 47.0±0.3 圆形钢片 直径50,厚5 4643.7 19293.3 73.7±0.3 表 4 试验方案及结果
Table 4. Test scheme and results
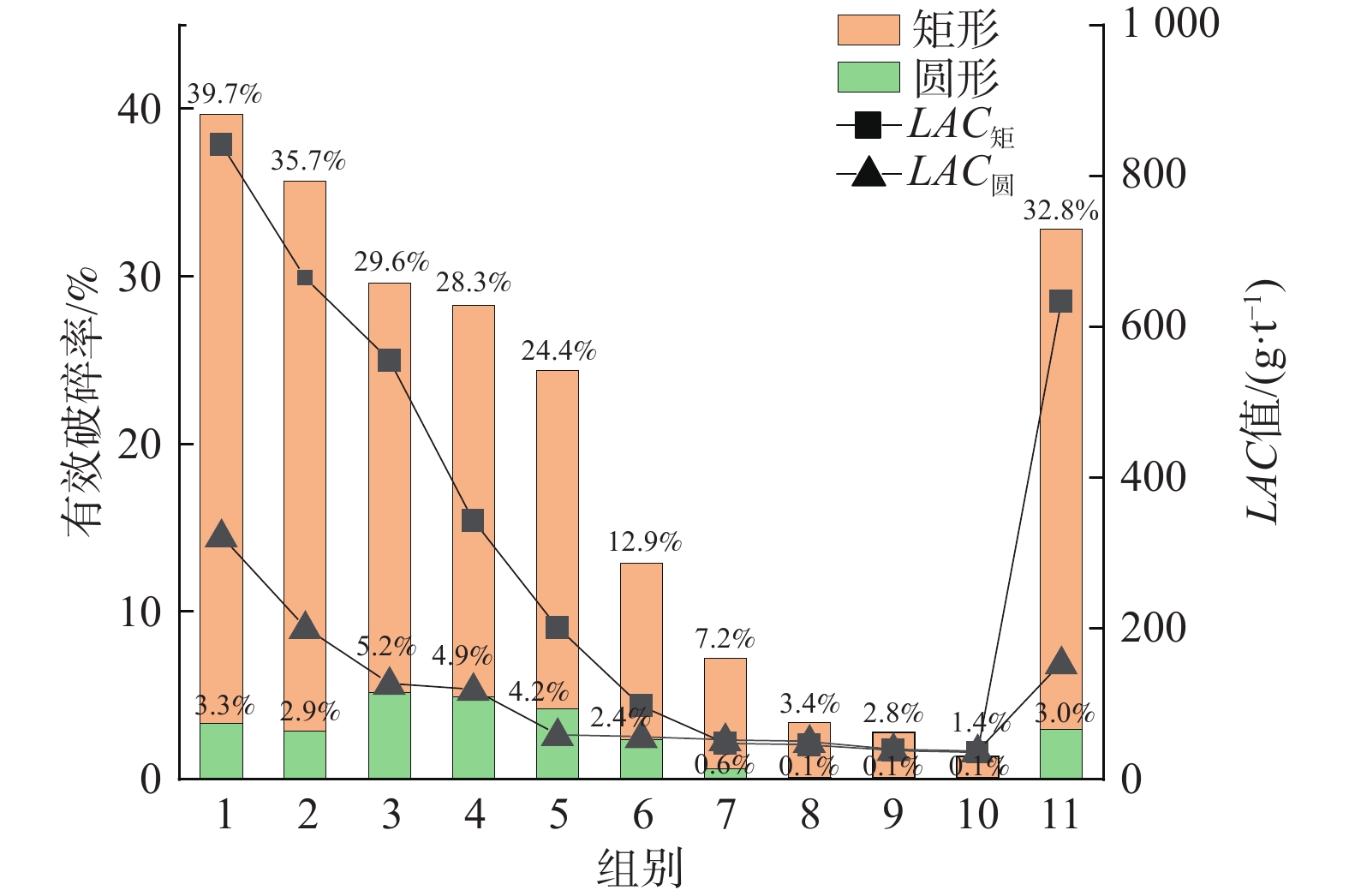
组别 不同粒径土颗粒质量/g LAC值/(g·t−1) 有效破碎率/% <0.075 mm 0.075~
<0.25 mm0.25~
<0.5 mm0.5~
<1 mm1~
<2 mm2~
<4 mm4~
<5 mm5~
<6.5 mm6.5~
<8 mm8~
10 mmLAC矩 LAC圆 k 矩形 圆形 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 500 841.71 322.89 2.61 39.7 3.3 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 500 0 665.37 201.11 3.31 35.7 2.9 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 500 0 0 555.33 127.53 4.36 29.6 5.2 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 500 0 0 0 343.10 119.40 2.87 28.3 4.9 5 0 0 0 0 0 500 0 0 0 0 201.53 59.30 3.40 24.4 4.2 6 0 0 0 0 500 0 0 0 0 0 97.53 56.47 1.73 12.9 2.4 7 0 0 0 500 0 0 0 0 0 0 47.79 52.53 0.91 7.2 0.6 8 20 20 60 400 0 0 0 0 0 0 45.61 50.46 0.90 3.4 0.1 9 25 25 100 350 0 0 0 0 0 0 38.22 39.70 0.96 2.8 0.1 10 30 50 120 300 0 0 0 0 0 0 35.84 38.13 0.94 1.4 0.1 11 12 17 34 65 47 29 14 25 31 226 633.93 154.47 4.10 32.8 3.0 注:LAC矩为矩形钢片测试条件下的LAC值;LAC圆为圆形钢片测试条件下的LAC值;k为LAC矩与LAC圆的比值。 -
[1] 周建军,宋佳鹏,谭忠盛. 砂卵石地层地铁盾构盘形滚刀磨蚀性研究[J]. 土木工程学报,2017,50(增刊1):31 − 35. [ZHOU Jianjun,SONG Jiapeng,TAN Zhongsheng. Study on abrasive properties of shielded hob in subway shield of sandy gravel formation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2017,50(Sup 1):31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHOU Jianjun, SONG Jiapeng, TAN Zhongsheng. Study on abrasive properties of shielded hob in subway shield of sandy gravel formation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 50(Sup 1): 31 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 付钊,柯宁静,卢康明,等. 深埋小净距多线平行盾构掘进相互作用分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):44 − 54. [FU Zhao,KE Ningjing,LU Kangming,et al. An analysis of interaction of deep buried close approaching multi-line parallel shield tunneling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):44 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
FU Zhao, KE Ningjing, LU Kangming, et al . An analysis of interaction of deep buried close approaching multi-line parallel shield tunneling[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (2 ):44 −54 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 胡焕校,杨万松,孙端阳. 长沙板岩地层地铁盾构施工渣土改良试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):100 − 107. [HU Huanxiao,YANG Wansong,SUN Duanyang. Soil conditioning test for EPB shield tunneling in slate stratum in the Changsha region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):
100 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 杨志勇,王霆,江玉生. 无水砂卵石地层土压平衡盾构主动换刀技术研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2016,53(1):147 − 152. [YANG Zhiyong,WANG Ting,JIANG Yusheng. Active cutter replacement techniques for EPB shield tunnelling in a waterless sandy cobble stratum[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2016,53(1):147 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2016.01.022
YANG Zhiyong, WANG Ting, JIANG Yusheng . Active cutter replacement techniques for EPB shield tunnelling in a waterless sandy cobble stratum[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2016 ,53 (1 ):147 −152 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[5] 杨育. 厦门轨道交通3号线跨海段盾构滚刀磨损预测[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2018,38(增刊1):182 − 187. [YANG Yu. Prediction of disc cutter wear of shield used in sea-crossing section on Xiamen rail transit line No. 3[J]. Tunnel Construction,2018,38(Sup 1):182 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YANG Yu. Prediction of disc cutter wear of shield used in sea-crossing section on Xiamen rail transit line No. 3[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2018, 38(Sup 1): 182 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 蔡昱,祝和意,杨小玉,等. 引汉济渭秦岭隧洞高磨蚀性硬岩TBM滚刀磨损试验研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2018,38(9):1579 − 1584. [CAI Yu,ZHU Heyi,YANG Xiaoyu,et al. Experimental study of disc cutter abrasion of TBM used in Qinling tunnel of Hanjiang River-Weihe River water conveyance project with high abrasive hard rock[J]. Tunnel Construction,2018,38(9):1579 − 1584. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAI Yu, ZHU Heyi, YANG Xiaoyu, et al . Experimental study of disc cutter abrasion of TBM used in Qinling tunnel of Hanjiang River-Weihe River water conveyance project with high abrasive hard rock[J]. Tunnel Construction,2018 ,38 (9 ):1579 −1584 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[7] 潘涛. 软土地区双线区间盾构隧道施工对周边地表以及建筑物沉降的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(1):101 − 108. [PAN Tao. Influences of double-track shield tunnel construction on settlements of adjacent ground and buildings in a soft soil area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(1):101 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
PAN Tao . Influences of double-track shield tunnel construction on settlements of adjacent ground and buildings in a soft soil area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022 ,49 (1 ):101 −108 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[8] 苏永华,王栋. 基于离散元法的砂石混合体直剪试验结果分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(6):97 − 104. [SU Yonghua,WANG Dong. An analysis of direct shear test results of sand-gravel mixture based on the discrete element method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(6):97 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SU Yonghua, WANG Dong . An analysis of direct shear test results of sand-gravel mixture based on the discrete element method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021 ,48 (6 ):97 −104 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] 张晓平,唐少辉,吴坚,等. 苏通GIL综合管廊工程泥水盾构穿越致密复合砂层磨蚀性预测分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(5):1364 − 1373. [ZHANG Xiaoping,TANG Shaohui,WU Jian,et al. Prediction and analysis of abrasiveness of dense sandy stratum by slurry shield at Sutong GIL utility tunnel engineering[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(5):1364 − 1373. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Xiaoping, TANG Shaohui, WU Jian, et al . Prediction and analysis of abrasiveness of dense sandy stratum by slurry shield at Sutong GIL utility tunnel engineering[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017 ,25 (5 ):1364 −1373 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[10] NILSEN B,DAHL F,HOLZHAUSER J,et al. SAT:NTNU’s new soil abrasion test[J]. Tunnels and Tunnelling International,2006,38(5):43 − 45.
[11] JAKOBSEN P D,BRULAND A,DAHL F. Review and assessment of the NTNU/SINTEF Soil Abrasion Test (SAT™) for determination of abrasiveness of soil and soft ground[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2013,37:107 − 114. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.04.003
[12] JAKOBSEN P D,LANGMAACK L,DAHL F,et al. Development of the Soft Ground Abrasion Tester (SGAT) to predict TBM tool wear,torque and thrust[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2013,38:398 − 408. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2013.07.021
[13] ROSTAMI J,GHASEMI A,GHARAHBAGH E A,et al. Study of dominant factors affecting cerchar abrasivity index[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2014,47(5):1905 − 1919. doi: 10.1007/s00603-013-0487-3
[14] ROSTAMI J,GHARAHBAGH E A,PALOMINO A M,et al. Development of soil abrasivity testing for soft ground tunneling using shield machines[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2012,28:245 − 256. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2011.11.007
[15] ABU BAKAR M Z,MAJEED Y,ROSTAMI J. Influence of moisture content on the LCPC test results and its implications on tool wear in mechanized tunneling[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2018,81:165 − 175. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.07.021
[16] HAMZABAN M T,JAKOBSEN P D,SHAKERI H,et al. Water content,effective stress,and rotation speed impact on the abrasivity of granular soils in LCPC test results[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,87:41 − 55. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.02.003
[17] ABU BAKAR M Z,MAJEED Y,RASHID M A,et al. Wear mechanisms of LCPC rock abrasivity test impellers of materials equivalent to TBM cutter head face tools[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2021,116:104122. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.104122
[18] 李潮. 砂卵石地层土压平衡盾构关键参数计算模型研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京),2013. [LI Chao. Study on the calculation models of key parameters of the EPB shield machine in sandy cobble ground [D]. Beijing:China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing),2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Chao. Study on the calculation models of key parameters of the EPB shield machine in sandy cobble ground [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] HAMZABAN M T,TAVANA N H,JAKOBSEN P D,et al. The effect of the plastic behavior of clay particles on LCPC abrasive coefficient[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,92:103054. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2019.103054
[20] BARZEGARI G,UROMEIHY A,ZHAO Jian. A newly developed soil abrasion testing method for tunnelling using shield machines[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology,2013,46(1):63 − 74. doi: 10.1144/qjegh2012-039
[21] WEI Yingjie,YANG Yuyou,TAO Mingjiang. Effects of gravel content and particle size on abrasivity of sandy gravel mixtures[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,243:26 − 35. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.06.009
[22] GHARAHBAGH E A,QIU Tong,ROSTAMI J. Evaluation of granular soil abrasivity for wear on cutting tools in excavation and tunneling equipment[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,2013,139(10):1718 − 1726. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000897
[23] ALAVI G E,ROSTAMI J,TALEBI K. Experimental study of the effect of conditioning on abrasive wear and torque requirement of full face tunneling machines[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2014,41:127 − 136.
[24] GHARAHBAGH E A,ROSTAMI J,PALOMINO A M. New soil abrasion testing method for soft ground tunneling applications[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2011,26(5):604 − 613. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2011.04.003
[25] BARZEGARI G,UROMEIHY A,ZHAO Jian. Parametric study of soil abrasivity for predicting wear issue in TBM tunneling projects[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2015,48:43 − 57. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2014.10.010
[26] HASHEMNEJAD A,GHAFOORI M,AZALI S T. Utilizing water,mineralogy and sedimentary properties to predict LCPC abrasivity coefficient[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2016,75(2):841 − 851. doi: 10.1007/s10064-015-0779-9
[27] HAMZABAN M T,MOHAMMADI N R S,JAKOBSEN P D. The effect of the particle size distribution curve on the abrasivity of non-cohesive soils in LCPC test[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2020,105:103573. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103573
[28] KAHRAMAN S,FENER M,KÄSLING H,et al. The influences of textural parameters of grains on the LCPC abrasivity of coarse-grained igneous rocks[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2016,58:216 − 223. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2016.05.011
[29] SUN Zhengyang,YANG Zhiyong,JIANG Yusheng,et al. Influence of particle size distribution,test time,and moisture content on sandy stratum LCPC abrasivity test results[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(1):611 − 625. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01927-3
[30] YANG Zhiyong,YANG Xing,DING Yanjie,et al. Characteristics of conditioned sand for EPB shield and its influence on cutterhead torque[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2022,17(12):5813 − 5828. doi: 10.1007/s11440-022-01666-7
[31] HARDIN B O. Crushing of soil particles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1985,111(10):1177 − 1192. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:10(1177)
-




 下载:
下载: