Numerical analysis of rainfall type landslide in Jichang town considering strain-softening
-
摘要:
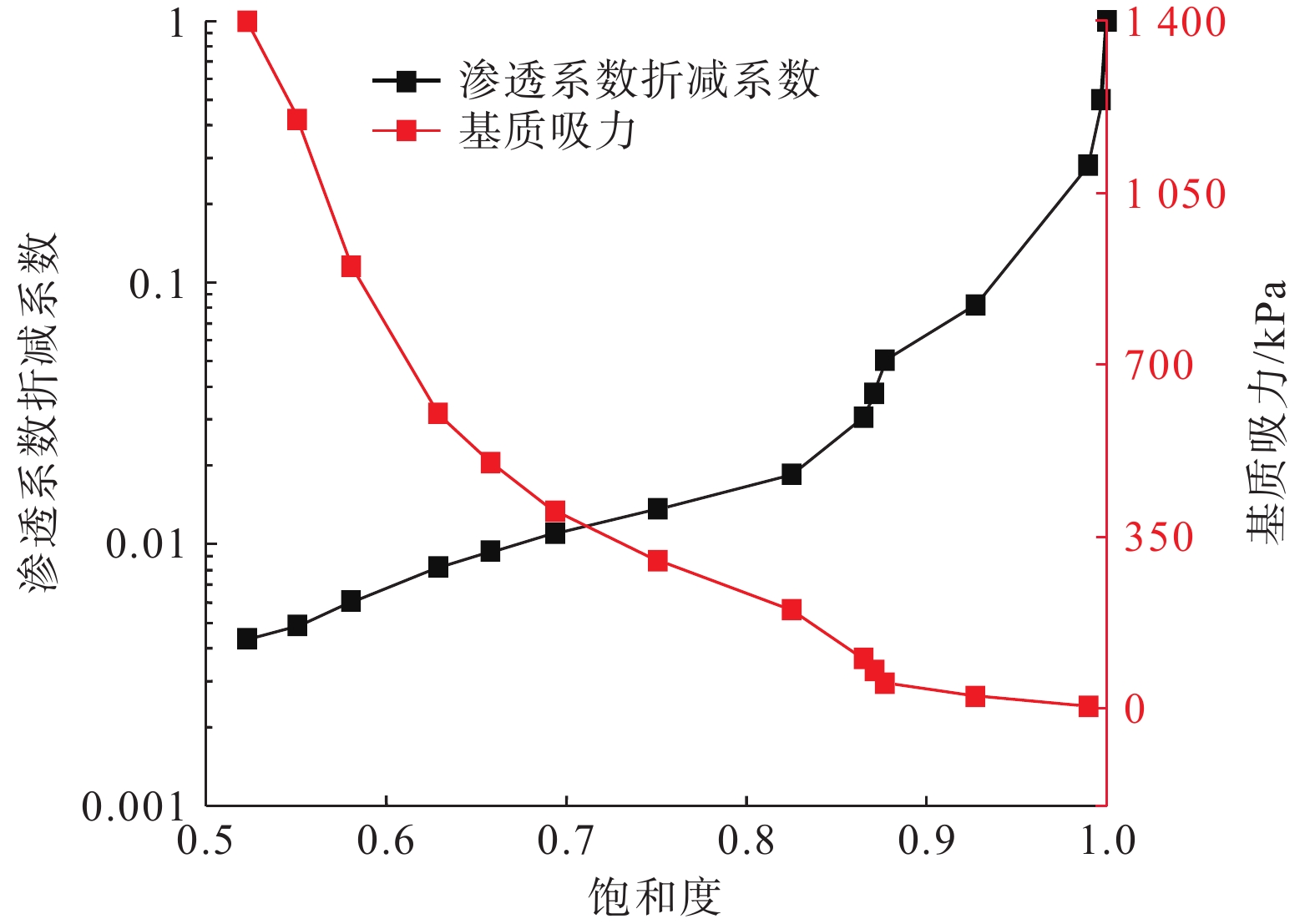
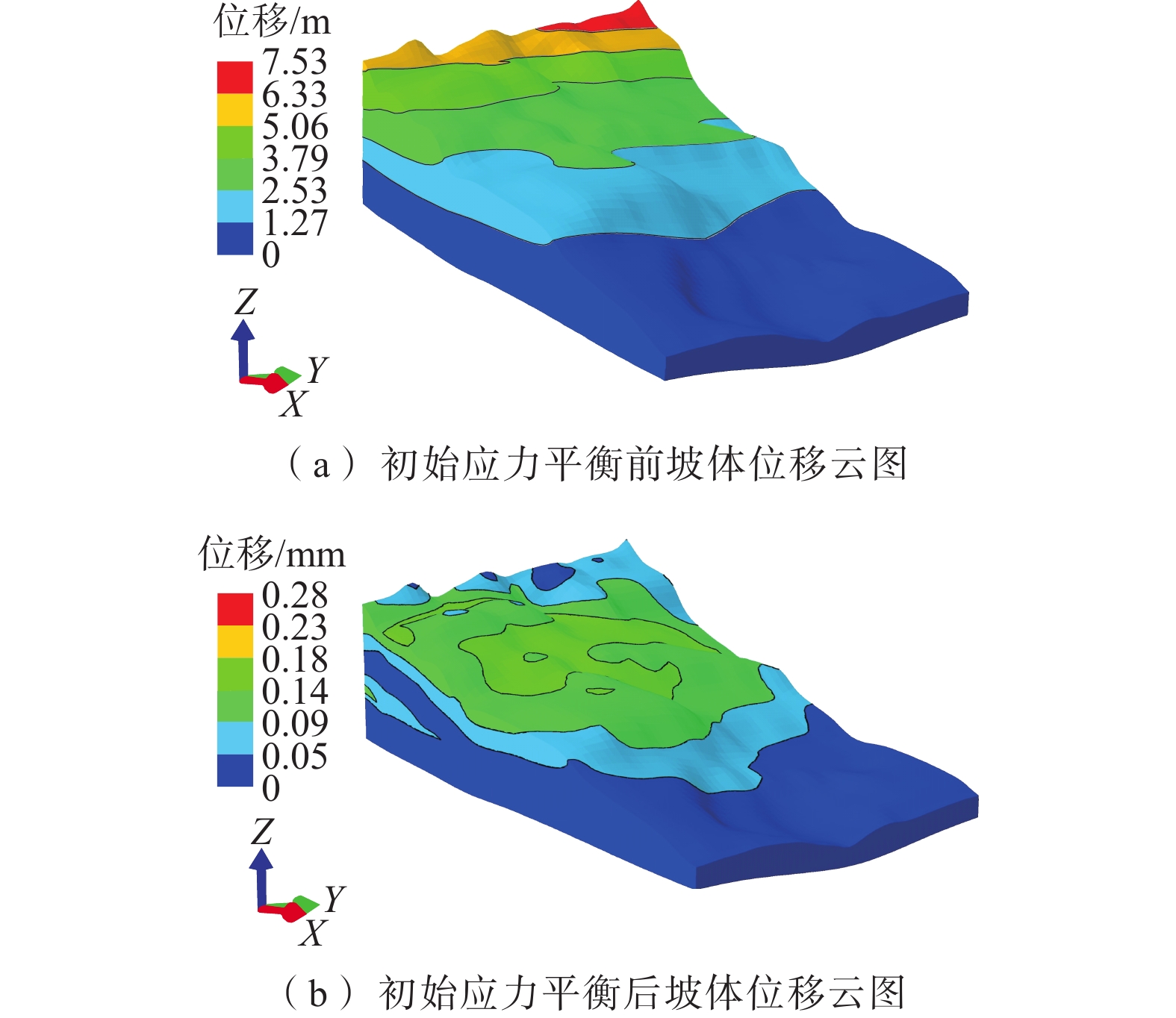
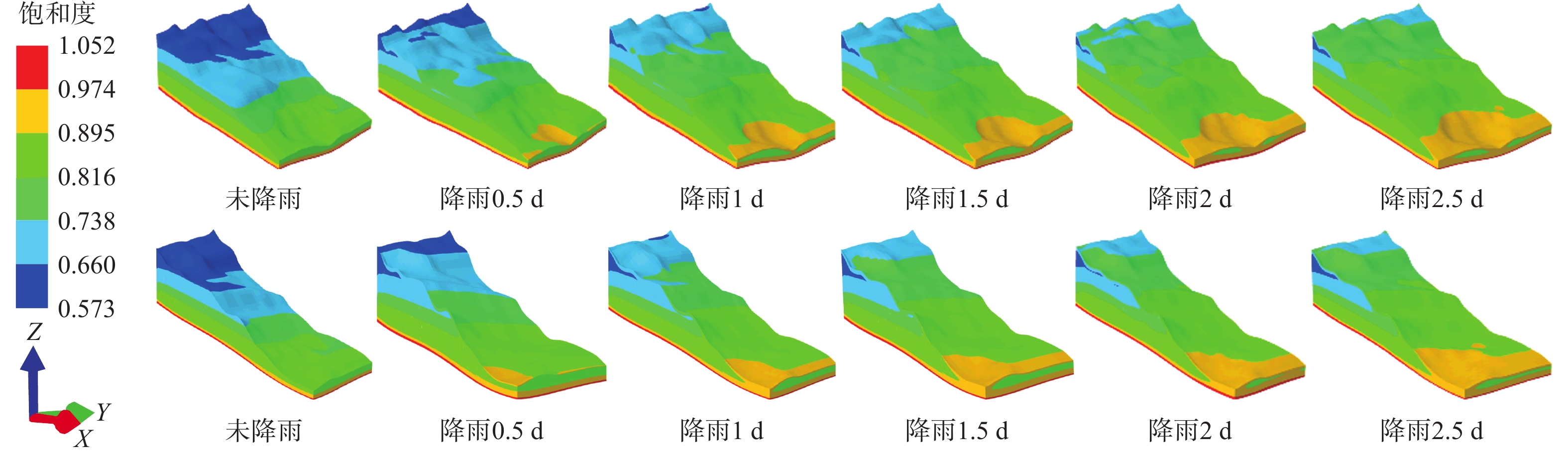
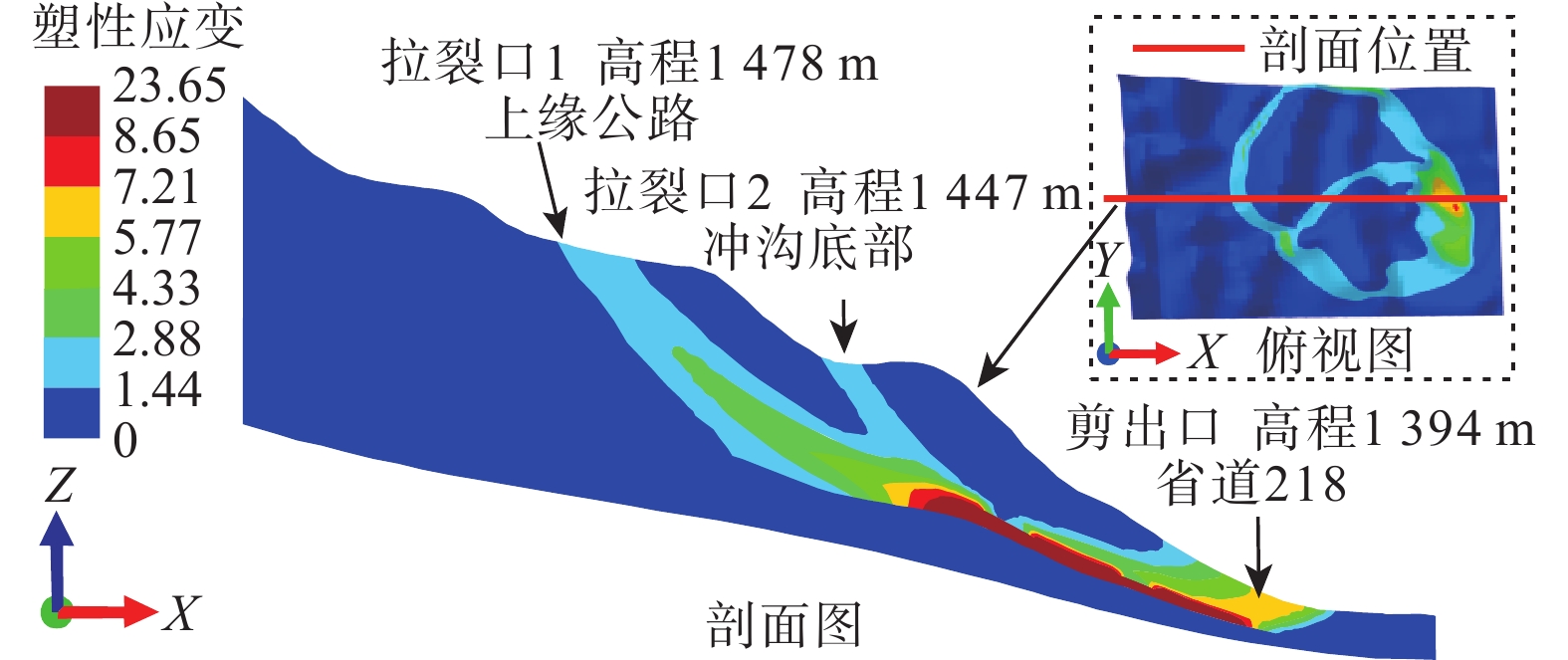
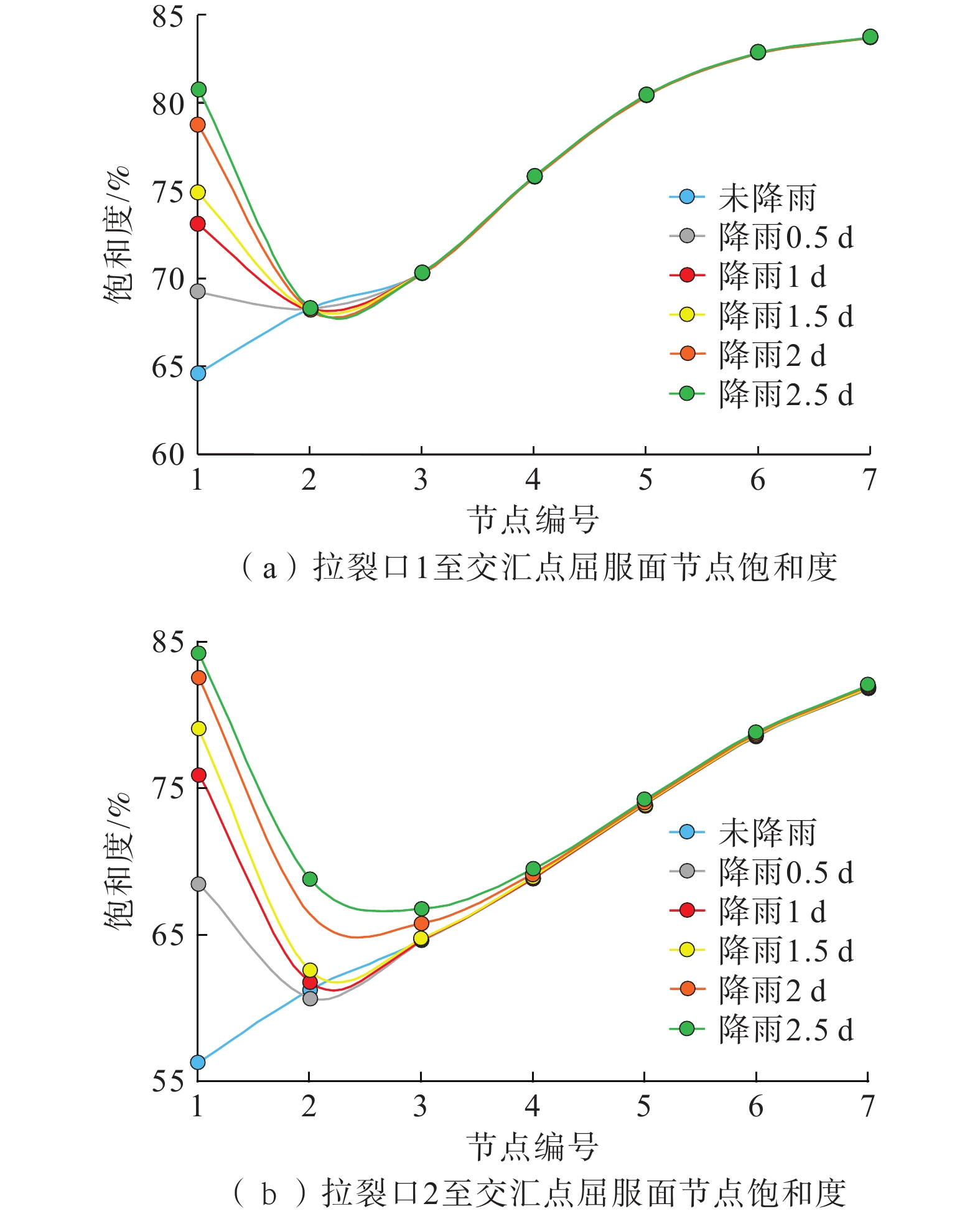
降雨入渗改变斜坡渗流场的同时也降低了土体强度,极易诱发滑坡。滑坡过程中,滑带土体常呈现应变软化现象。以应变软化模型为基础的双参数强度折减法的研究,目前处于起步阶段,以往研究及分析滑坡稳定性时均忽略了渗流场的影响。六盘水地区红棕色土保水性强,有明显的应变软化特征,该地曾发生多次大中型滑坡。根据红棕色土特点研究致灾机理,有利于滑坡的防治。针对六盘水鸡场镇周家坡滑坡建立三维地质模型,基于非饱和土流固耦合理论建立了坡体流场与应力场相互作用的数学模型,利用有限元和考虑土体应变软化的双参数强度折减法,对滑坡进行雨水渗流和稳定性模拟。结果表明:在降雨后雨水多在表层土中沿坡面切向和横向流入下缘和冲沟,并非全部垂直入渗。相对上缘其他区域,冲沟底部饱和度上升明显,强度下降最大。随降雨时间的延长,坡体内形成沿冲沟的塑性贯通区,使得滑坡稳定性大幅下降。降雨过程中对比经典折减法和考虑应变软化的双折减法所得稳定系数由偏小转为偏大,但差距均在4%以内。由此可见,红棕色土应变软化对滑坡稳定性负面影响不显著,且随降雨而减弱,建议对此类滑坡的防治重点在降低冲沟土体渗透性。研究结果可为同类滑坡的防治提供一定的理论依据。
Abstract:Rainfall infiltration not only changes the seepage field of the slope, but also reduces the soil strength, which is easy to induce landslide. The soil in the slip zone often shows strain softening during the landslide process. However, the research of the two-parameter strength reduction method based on the strain softening model is still in its infancy, and the influence of seepage field has been ignored when analyzing the stability of landslides in the previous studies. The red-brown soil in the Liupanshui area has strong water retention and obvious strain softening characteristics, and many large and medium-sized landslides have occurred in this area. Understanding the disaster-causing mechanism according to the characteristics of red-brown soil is conducive to the prevention and control of landslides. A three-dimensional geological model was established for the Zhoujiapo landslide in Jichang town, Liupanshui city. Based on the fluid-structure interaction theory of unsaturated soil, a mathematical model of the interaction between the flow field and the stress field of slope was established. The rainwater seepage and the stability of the landslide were simulated by using the finite element and the two-parameter strength reduction method considering the strain softening of the soil. The results show that after rainfall, the rainwater mostly flows into the lower edge and gully along the slope in the surface soil in the tangential and transverse directions rather than all vertical infiltration. The saturation at the bottom of the gully increases significantly and the intensity decreases the most compared to other areas at the upper edge. With time extension of rainfall, a plastic penetration zone along the gully is formed in the slope, which greatly reduces the stability of the landslide. Compared with the classical reduction method, the stability coefficient obtained by the double reduction method considering strain softening in the rainfall process changes from small to large, but the difference was within 4%. It can be seen that the negative impact of red-brown soil strain softening on landslide stability is not significant and weakens with rainfall. The prevention and control of such landslides should focus on reducing the permeability of gully soil. This study provides a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of similar landslides.
-
Key words:
- seepage of unsaturated soils /
- strain softening /
- double reduction /
- landslide; stability
-

-
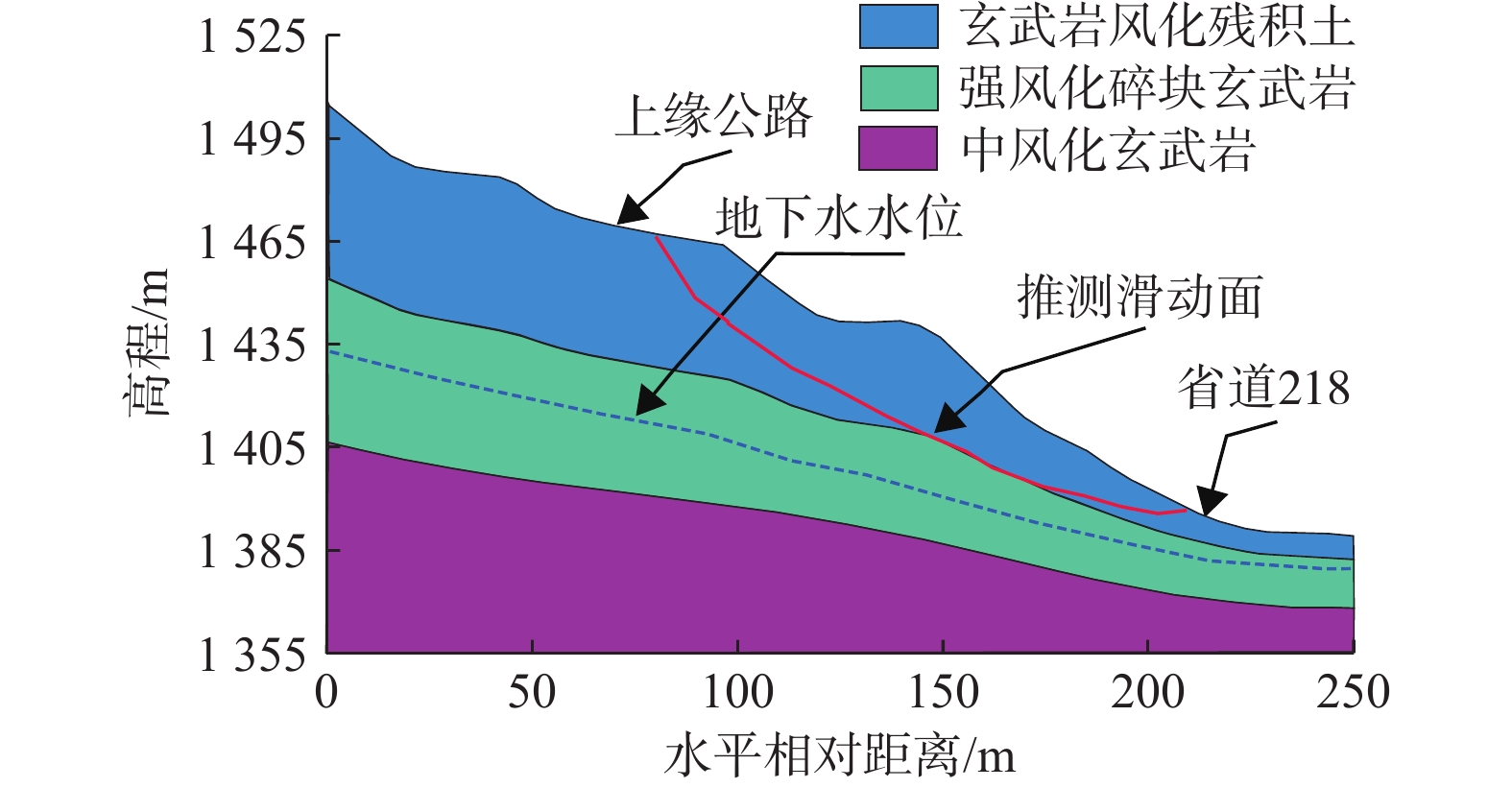
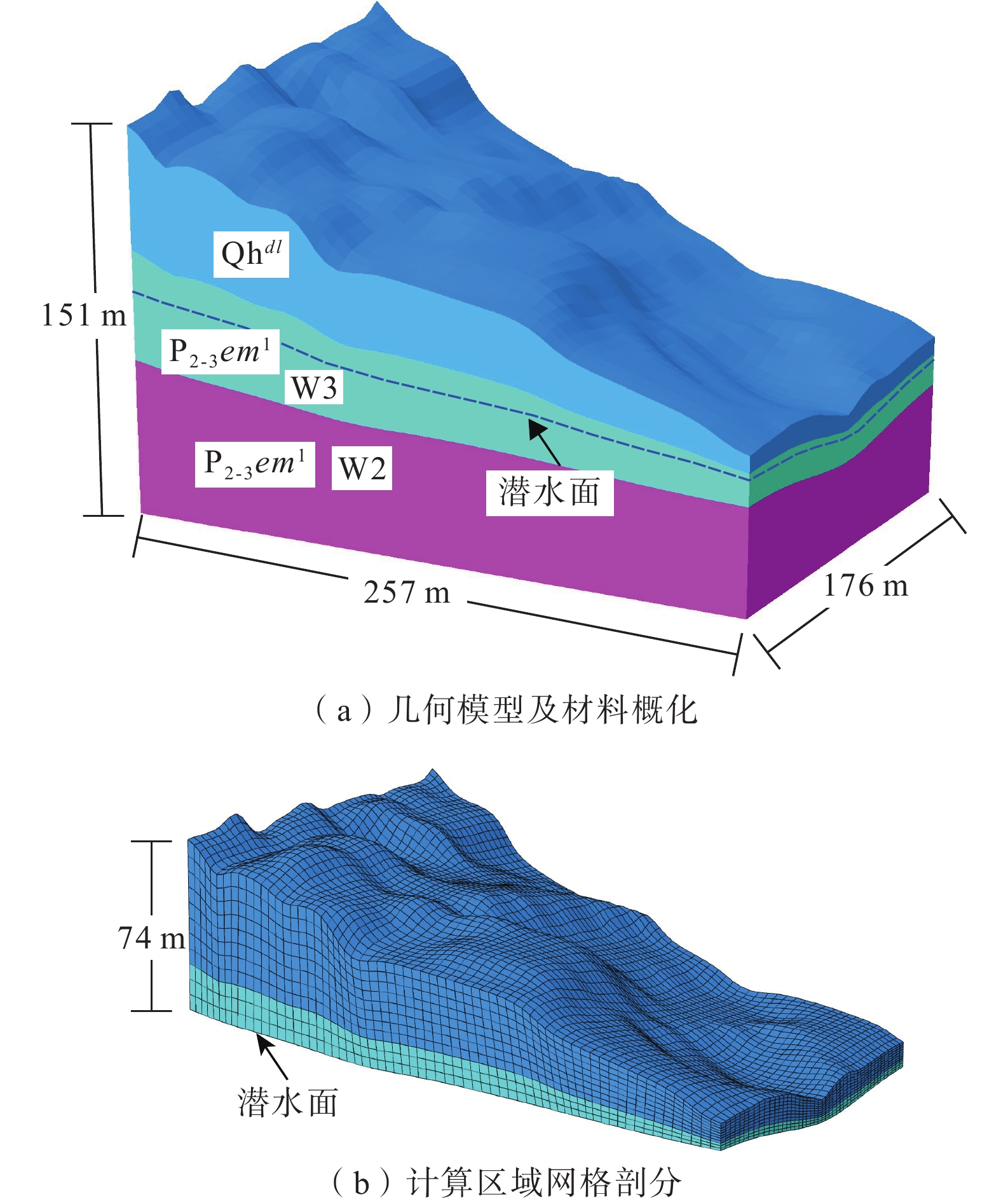
表 1 地层岩土物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of formation rock and soil
地层物理
力学参数玄武岩残
积土强风化碎块
玄武岩-残积土中风化
玄武岩干重度/(kN·m−3) 13.1 24.6 27.1 压缩模量/MPa 5.21 57.20 3120 泊松比 0.35 0.30 0.25 峰值黏聚力/kPa 8.41 189 1460 峰值内摩擦角/(°) 20.16 38.40 40.36 残余黏聚力/kPa 3.82 — — 残余内摩擦角/(°) 14.6 — — 吸力内摩擦角/(°) 14 — — 饱和渗透系数/(m·s−1) 8.35E-6 2.8E-6 3E-7 孔隙比 1.33 0.68 0.25 表 2 不同折减法滑坡稳定系数
Table 2. Stability coefficients of landslide with different reduction methods
模拟工况 经典强度折减法FS 考虑应变软化的双折减法 FSc FSφ 综合稳定系数FS 稳定渗流 1.32 1.41 1.202 1.311 降雨0.5天 1.27 1.35 1.176 1.268 降雨1天 1.24 1.31 1.158 1.239 降雨1.5天 1.22 1.28 1.145 1.218 降雨2天 1.16 1.22 1.116 1.172 降雨2.5天 1.09 1.16 1.086 1.126 -
[1] 孟生勇,江兴元,杨义,等. 降雨诱发堆积体滑坡水土响应与稳定性时空演化试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(1):104 − 112. [MENG Shengyong,JIANG Xingyuan,YANG Yi,et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(1):104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
MENG Shengyong, JIANG Xingyuan, YANG Yi, et al. An experimental study of spatial-temporal evolution of water-soil response and stability of a rainfall-induced accumulation landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(1): 104 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 宋德光, 吴瑞安, 马德芹, 等. 四川泸定昔格达组滑坡灾害运动过程模拟分析[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(12):2185 − 2197. [SONG Deguang, WU Ruian, MA Deqin, et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation, Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(12):2185 − 2197.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
SONG Deguang, WU Ruian, MA Deqin, et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation, Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(12): 2185 − 2197.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] ZHANG Xia,LI Peng,LI Zhanbin,et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the July 25,2013,Tianshui Group-occurring geohazards[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(5):219. doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6542-8
[4] 张晨阳,张泰丽,张明,等. 东南沿海地区玄武岩残积土雨水运移特征及滑坡失稳数值模拟[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):42 − 50. [ZHANG Chenyang,ZHANG Taili,ZHANG Ming,et al. Rainfall infiltration characteristics and numerical simulation of slope instability in the basalt residual soil in the coastal area of Southeast China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Chenyang, ZHANG Taili, ZHANG Ming, et al. Rainfall infiltration characteristics and numerical simulation of slope instability in the basalt residual soil in the coastal area of Southeast China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 42 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 熊超, 孙红月. 基于多因素-多尺度分析的阶跃型滑坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2023,53(4):1175 − 1184. [XIONG Chao, SUN Hongyue. Step-Like Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Multi-Factor and Multi-Scale Analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2023,53(4):1175 − 1184.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
XIONG Chao, SUN Hongyue. Step-Like Landslide Displacement Prediction Based on Multi-Factor and Multi-Scale Analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1175 − 1184.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated Soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1980,44(5):892 − 898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
[7] 曹渊,王铁良,王文科,等. 饱和-非饱和渗流三维数学模型及数值方法[J]. 固体力学学报,2013,33(增刊1):79 − 83. [CAO Yuan,WANG Tieliang,WANG Wenke,et al. 3-d theoretical model and numerical method of saturated-unsaturated seepage[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics,2013,33(Sup 1):79 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CAO Yuan, WANG Tieliang, WANG Wenke, et al. 3-d theoretical model and numerical method of saturated-unsaturated seepage[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2013, 33(Sup 1): 79 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 石爱红,李国庆,丁德民,等. 考虑非饱和土基质吸力的丁家坡滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):141 − 151. [SHI Aihong,LI Guoqing,DING Demin,et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHI Aihong, LI Guoqing, DING Demin, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Dingjiapo landslide considering the matric suction of unsaturated soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 141 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李华,史文兵,朱要强,等. 贵州省水城县 “7•23” 灾难性滑坡形成机制研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2020,29(6):188 − 198. [LI Hua,SHI Wenbing,ZHU Yaoqiang,et al. Study on the formation mechanism of “7•23” catastrophic landslide in Shuicheng County,Guizhou Province,China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(6):188 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Hua, SHI Wenbing, ZHU Yaoqiang, et al. Study on the formation mechanism of “7•23” catastrophic landslide in Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province, China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2020, 29(6): 188 − 198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 吴益平,卢里尔,薛阳. 基于临界状态的边坡渐进破坏力学模型分析及应用[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(5):1 − 7. [WU Yiping,LU Lier,XUE Yang. Application of landslide progressive failure mechanical model based on the critical stress state[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(5):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WU Yiping, LU Lier, XUE Yang. Application of landslide progressive failure mechanical model based on the critical stress state[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈亚烽,陈国庆,严明,等. 基于一阶线性应变软化理论的边坡稳定性研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):180 − 188. [CHEN Yafeng,CHEN Guoqing,YAN Ming,et al. Study on slope stability considering first-order linear strain-softening theory[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):180 − 188. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Yafeng, CHEN Guoqing, YAN Ming, et al. Study on slope stability considering first-order linear strain-softening theory[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 180 − 188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 刘建强,许强,郑光,等. 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水化学特征反映的水-岩(土)作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):132 − 140. [LIU Jianqiang,XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LIU Jianqiang, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Water-rock/soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 闫玉平,肖世国. 考虑滑带强度参数分区取值的堆积层滑坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):44 − 49. [YAN Yuping,XIAO Shiguo. Stability analysis method for bedrock-talus landslides considering strength parameter partition of slip shear band[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YAN Yuping, XIAO Shiguo. Stability analysis method for bedrock-talus landslides considering strength parameter partition of slip shear band[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(2): 44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] SKEMPTON A W. Residual strength of clays in landslides,folded strata and the laboratory[J]. Géotechnique,1985,35(1):3 − 18.
[15] 何成,唐辉明,申培武,等. 应变软化边坡渐进破坏模式及稳定性可靠度[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(2):697 − 707. [HE Cheng,TANG Huiming,SHEN Peiwu,et al. Progressive failure mode and stability reliability of strain-softening slope[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(2):697 − 707. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Cheng, TANG Huiming, SHEN Peiwu, et al. Progressive failure mode and stability reliability of strain-softening slope[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(2): 697 − 707. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 何忠明,吴维,付宏渊,等. 基于应变软化模型的软岩高边坡过程稳定性研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,44(3):1203 − 1208. [HE Zhongming,WU Wei,FU Hongyuan,et al. Process stability of soft rock high slope based on strain softening model[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2013,44(3):1203 − 1208. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HE Zhongming, WU Wei, FU Hongyuan, et al. Process stability of soft rock high slope based on strain softening model[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(3): 1203 − 1208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 黄盛锋,陈志波,郑道哲. 基于灰色关联度法和强度折减法的边坡稳定性影响因素敏感性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):35 − 40. [HUANG Shengfeng,CHEN Zhibo,ZHENG Daozhe. Sensitivity analysis of factors influencing slope stability based on grey correlation and strength reduction method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):35 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUANG Shengfeng, CHEN Zhibo, ZHENG Daozhe. Sensitivity analysis of factors influencing slope stability based on grey correlation and strength reduction method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(3): 35 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈国庆,黄润秋,周辉,等. 边坡渐进破坏的动态强度折减法研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(4):1140 − 1146. [CHEN Guoqing,HUANG Runqiu,ZHOU Hui,et al. Research on progressive failure for slope using dynamic strength reduction method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(4):1140 − 1146. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Guoqing, HUANG Runqiu, ZHOU Hui, et al. Research on progressive failure for slope using dynamic strength reduction method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(4): 1140 − 1146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 侯世伟,张永峰,张皓,等. 基于局部软化阶梯双折减法的土坡稳定性研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2022,42(4):705 − 713. [HOU Shiwei,ZHANG Yongfeng,ZHANG Hao,et al. Research on progressive failure of slope based on softening law and step double reduction method[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2022,42(4):705 − 713. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HOU Shiwei, ZHANG Yongfeng, ZHANG Hao, et al. Research on progressive failure of slope based on softening law and step double reduction method[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2022, 42(4): 705 − 713. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 薛海斌,党发宁,尹小涛,等. 边坡强度参数非等比例相关联折减法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2015,34(增刊2):4005 − 4012. [XUE Haibin,DANG Faning,YIN Xiaotao,et al. Research on method of slope strength parameters non-proportional associated reduction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2015,34(Sup 2):4005 − 4012. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XUE Haibin, DANG Faning, YIN Xiaotao, et al. Research on method of slope strength parameters non-proportional associated reduction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(Sup 2): 4005 − 4012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 彭双麒,许强,郑光,等. 碎屑流堆积物粒度分布与运动特性的关系——以贵州纳雍普洒村崩塌为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):122 − 129. [PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Relationship between particle size distribution and movement characteristics of rock avalanche deposits: a case study of the Pusa village rock avalanche in Nayong of Guizhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):122 − 129.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
PENG Shuangqi, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Relationship between particle size distribution and movement characteristics of rock avalanche deposits: a case study of the Pusa village rock avalanche in Nayong of Guizhou[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(4): 122 − 129.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 党杰,董吉,何松标,等. 机载LiDAR与地面三维激光扫描在贵州水城独家寨崩塌地质灾害风险调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):106 − 113. [DANG Jie, DONG Ji, HE Songbiao, et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):106 − 113.(in Chinese with English abstract)]
DANG Jie, DONG Ji, HE Songbiao, et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 106 − 113.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 曾攀. 有限元分析及应用[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2004. [ZENG Pan. Finite element analysis and applications[M]. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press,2004. (in Chinese)]
ZENG Pan. Finite element analysis and applications[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. (in Chinese)
[24] BIOT M A. General theory of three-dimensional consolidation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,1941,12(2):155 − 164. doi: 10.1063/1.1712886
[25] 陈卫忠,伍国军,贾善坡. 2010. ABAQUS在隧道及地下工程中的应用[M]. 北京:中国水利水电出版社,232 – 235. [CHEN Weizhong,WU Guojun,JIA Shanpo. Application of ABAQUS in Tunnel and Underground Engineering[M]. Beijing:China Water Resources and Hydropower Press,2010:232 – 235. (in Chinese)]
CHEN Weizhong, WU Guojun, JIA Shanpo. Application of ABAQUS in Tunnel and Underground Engineering[M]. Beijing: China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, 2010: 232 – 235. (in Chinese)
[26] FREDLUND D G,MORGENSTERN N R. Stress state variables for unsaturated soils[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1977,103(5):447 − 466. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000423
[27] 陈亮胜,韦秉旭,廖欢,等. 膨胀土边坡非饱和渗流及渐进性破坏耦合分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):132 − 140. [CHEN Liangsheng,WEI Bingxu,LIAO Huan,et al. A coupling analysis of unsaturated seepage and progressive failure of an expansive soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Liangsheng, WEI Bingxu, LIAO Huan, et al. A coupling analysis of unsaturated seepage and progressive failure of an expansive soil slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(4): 132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] CARTER J P,YEUNG S K. Analysis of cylindrical cavity expansion in a strain weakening material[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,1985,1(3):161 − 180. doi: 10.1016/0266-352X(85)90021-7
[29] ZIENKIEWICZ O C,HUMPHESON C,LEWIS R W. Associated and non-associated visco-plasticity and plasticity in soil mechanics[J]. Géotechnique,1975,25(4):671 − 689.
[30] ISAKOV A,MORYACHKOV Y. Estimation of slope stability using two-parameter criterion of stability[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2014,14(3):6014004. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000326
[31] 赵炼恒,曹景源,唐高朋,等. 基于双强度折减策略的边坡稳定性分析方法探讨[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(10):2977 − 2984. [ZHAO Lianheng,CAO Jingyuan,TANG Gaopeng,et al. Discussion on slope stability analysis with double strength reduction technique[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(10):2977 − 2984. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Lianheng, CAO Jingyuan, TANG Gaopeng, et al. Discussion on slope stability analysis with double strength reduction technique[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(10): 2977 − 2984. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 郑永来,吴卓睿. 基于最短折减路径法的边坡安全系数研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):28 − 34. [ZHENG Yonglai,WU Zhuorui. Estimation of slope safety factor based on trajectory reduction method[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):28 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHENG Yonglai, WU Zhuorui. Estimation of slope safety factor based on trajectory reduction method[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 28 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 王参松. 贵州玄武岩残积土工程力学特性试验研究[D]. 武汉:武汉科技大学,2012. [WANG Cansong. Testing study on engineering mechanical properties of basalt residual soil in Guizhou[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University of Science and Technology,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Cansong. Testing study on engineering mechanical properties of basalt residual soil in Guizhou[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 田小波,刘鑫. 贵州玄武岩残积土现场渗透试验研究[J]. 土工基础,2012,26(4):123 − 125. [TIAN Xiaobo,LIU Xin. In-situ permeability tests in Guizhou basalt residual soils[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation,2012,26(4):123 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
TIAN Xiaobo, LIU Xin. In-situ permeability tests in Guizhou basalt residual soils[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation, 2012, 26(4): 123 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] ALONSO E,GENS A,LLORET A,et al. Effect of rain infiltration on the stability of slopes[J]. Unsaturated Soils,1995(1):241 − 249.
[36] 余沛,柴寿喜,魏厚振,等. 不同干密度下玄武岩残积土土水特征曲线分析[J]. 工程勘察,2012,40(7):1 − 5. [YU Pei,CHAI Shouxi,WEI Houzhen,et al. Analysis on soil-water characteristic curve of basalt residual soil considering influence of the different dry densities[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2012,40(7):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YU Pei, CHAI Shouxi, WEI Houzhen, et al. Analysis on soil-water characteristic curve of basalt residual soil considering influence of the different dry densities[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2012, 40(7): 1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 李晋鹏,汪磊,王俊,等. 考虑抗剪强度衰减特性的膨胀土边坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):29 − 36. [LI Jinpeng,WANG Lei,WANG Jun,et al. Stability analysis of expansive soil slopes considering shear strength decay characteristics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):29 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Jinpeng, WANG Lei, WANG Jun, et al. Stability analysis of expansive soil slopes considering shear strength decay characteristics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 29 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: