The influence of permafrost degradation on the change of suprapermafrost water : A case study in the source areaof the Yellow River
-
摘要:
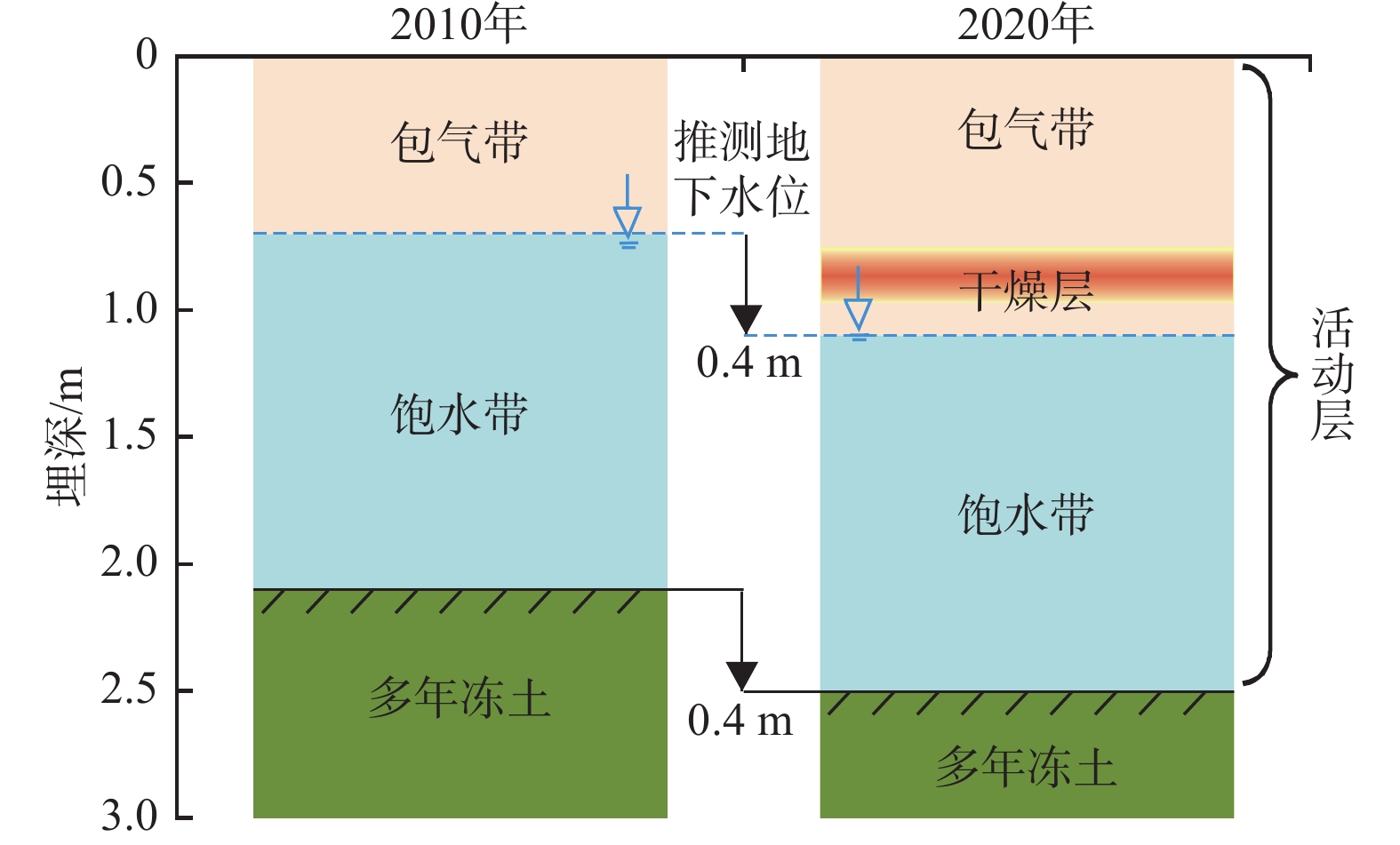
冻结层上水是支撑寒区生态系统的重要水源和维持寒区水热循环过程的重要纽带,科学认识冻土退化对冻结层上水的影响作用,对气候变化加剧下高寒地区水资源及生态保护具有重要意义。针对黄河源区多年冻土退化的水文效应,基于典型监测点冻土地温、含水率监测数据和黄河沿水文站断面径流变化数据,分析黄河源区多年冻土退化特征,探讨冻结层上水水位埋深和补给过程对多年冻土退化的响应。结果表明:2010—2020年监测点0~2.4 m剖面上平均升温0.42 °C,多年冻土上界面埋深由2.1 m降至2.5 m,平均下降速率4 cm/a;以2018年为时间节点,冻结层上水埋深由0.9 m以浅降至0.9~1.8 m之间;冻土退化引起活动层融化期(5—10月)的径流过程提前、径流极值比降低、1月份径流过程线更加凸出。地温是控制冻结层上水变化的核心要素,在暖湿化的气候变化条件下,多年冻土退化将改变冻结层上水的动态特征及其与地表水之间的水力联系,进一步影响黄河源区的水文生态过程。
Abstract:The supra-permafrost water is a vital water source to support the ecosystem and an important link in maintaining the hydrothermal cycle in the permafrost area. Under the intensification of climate change, scientific understanding of the effect of permafrost degradation on the supra-permafrost water is of great significance to water resources and ecological protection. Focusing on the hydrological effects of permafrost degradation in the source areas of the Yellow River, this study analyzed the degradation characteristics of permafrost, and revealed the response of the depth of groundwater level and recharge process of the supra-permafrost water to the permafrost degradation, on the basis of the temperature and moisture content of frozen soil at typical monitoring points and the runoff change at the Huangheyan Hydrologic Station. The results show that the average temperature increased 0.42 °C at the 0−2.4 m profile of the monitoring point from 2010 to 2020. The depth of the upper interface of the permafrost reduced from 2.1m to 2.5 m, with an average decrease rate of 4cm/a. After 2018, the depth of supra-permafrost water level reduced from less than 0.9 m to 0.9−1.8 m. The permafros degradation led to the runoff process in the melting period of active layer (May−October) being advanced, the ratio of extreme value being reduced, and the runoff hydrograph in January being more prominent. Ground temperature is the dominant factor in controlling the changes of depth of the supra-permafrost water. Under the condition of warm and humid climate change, Permafrost degradation would change the dynamic characteristics of the water above the frozen layer and its hydraulic relationship with surface water, affecting the hydrological and ecological processes in the source area of the Yellow River.
-
Key words:
- permafrost degradation /
- suprapermafrost water /
- soil water /
- runoff /
- source area of the Yellow River /
- climate change
-

-
表 1 不同深度监测层位每年融化(地温>0 °C)天数变化
Table 1. Annual change of melting days (ground temperature>0 °C) from the different monitoring layers
年份 融化天数/d 埋深0.5 m 埋深0.9 m 埋深1.8 m 埋深2.4 m 2010 139 113 31 0 2011 132 106 34 0 2012 140 107 42 0 2013 150 109 40 0 2014 142 108 38 0 2015 141 119 55 0 2016 138 113 60 0 2017 146 116 62 0 2018 148 116 67 12 2019 151 124 69 23 2020 147 118 63 29 -
[1] 程国栋,金会军. 青藏高原多年冻土区地下水及其变化[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(1):1 − 11. [CHENG Guodong,JIN Huijun. Groundwater in the permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and it changes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(1):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHENG Guodong, JIN Huijun . Groundwater in the permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and it changes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013 ,40 (1 ):1 −11 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[2] 曹文炳,万力,周训,等. 黄河源区冻结层上水地质环境影响研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2003,30(6):6 − 10. [CAO Wenbing,WAN Li,ZHOU Xun,et al. A study of the geological environmental of suprapermafrost water in the headwater area of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2003,30(6):6 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.06.002
CAO Wenbing, WAN Li, ZHOU Xun, et al . A study of the geological environmental of suprapermafrost water in the headwater area of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2003 ,30 (6 ):6 −10 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[3] 常娟,王根绪,李春杰,等. 青藏高原连续多年冻土区的冻结层上水季节动态及其对活动层土壤冻融过程的响应特征[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2015,45(4):481-493. [CHANG Juan,WANG Genxu,LI Chunjie,et al. Seasonal dynamics of suprapermafrost groundwater and its response to the freeing-thawing processes of soil in the permafrost region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae),2015,45(4):481-493. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CHANG Juan, WANG Genxu, LI Chunjie, et al. Seasonal dynamics of suprapermafrost groundwater and its response to the freeing-thawing processes of soil in the permafrost region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 2015, 45(4): 481-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] OLIVA M,PEREIRA P,ANTONIADES D. The environmental consequences of permafrost degradation in a changing climate[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,616/617:435 − 437. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.285
[5] CZERNIAWSKA J,CHLACHULA J. Climate-change induced permafrost degradation in Yakutia,East Siberia[J]. Arctic,2020,73(4):509 − 528. doi: 10.14430/arctic71674
[6] CAO Wei,SHENG Yu,WU Jichun,et al. Soil hydrological process and migration mode influenced by the freeze-thaw process in the activity layer of permafrost regions in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology,2021,184:103236. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2021.103236
[7] SHENG Yu,MA Shuai,CAO Wei,et al. Spatiotemporal changes of permafrost in the Headwater Area of the Yellow River under a changing climate[J]. Land Degradation & Development,2020,31(1):133 − 152.
[8] 代军臣,王根绪,宋春林,等. 三江源区径流退水过程演变规律[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2018,27(6):1342 − 1350. [DAI Junchen,WANG Genxu,SONG Chunlin,et al. Study on the law of runoff retreat in the three-river headwaters rgion[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2018,27(6):1342 − 1350. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201806018
DAI Junchen, WANG Genxu, SONG Chunlin, et al . Study on the law of runoff retreat in the three-river headwaters rgion[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2018 ,27 (6 ):1342 −1350 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[9] MA Qiang,JIN Huijun,BENSE V F,et al. Impacts of degrading permafrost on streamflow in the source area of Yellow River on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research,2019,10(4):225 − 239. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2020.02.001
[10] SONG Chunlin,WANG Genxu,MAO Tianxu,et al. Linkage between permafrost distribution and river runoff changes across the Arctic and the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2020,63(2):292 − 302. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9383-6
[11] 罗斯琼,李红梅,马迪,等. 三江源冻土-植被相互作用及气候效应研究现状及展望[J]. 高原气象,2022,41(2):255 − 267. [LUO Siqiong,LI Hongmei,MA Di,et al. Review and prospects of frozen soil-vegetation interaction and climate effects in the three rivers source region[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2022,41(2):255 − 267. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LUO Siqiong, LI Hongmei, MA Di, et al . Review and prospects of frozen soil-vegetation interaction and climate effects in the three rivers source region[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2022 ,41 (2 ):255 −267 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[12] 叶仁政,常娟. 中国冻土地下水研究现状与进展综述[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(1):183 − 196. [YE Renzheng,CHANG Juan. Study of groundwater in permafrost regions of China:status and process[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019,41(1):183 − 196. (in Chinese with English abstract)
YE Renzheng, CHANG Juan . Study of groundwater in permafrost regions of China: status and process[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019 ,41 (1 ):183 −196 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[13] 曹伟,盛煜,吴吉春,等. 黄河源区不同类型冻土土壤水分入渗特性[J]. 生态学报,2021,41(2):655 − 664. [CAO Wei,SHENG Yu,WU Jichun,et al. Soil moisture infiltration characteristics of different types of frozen soil in the Source Area of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(2):655 − 664. (in Chinese with English abstract)
CAO Wei, SHENG Yu, WU Jichun, et al . Soil moisture infiltration characteristics of different types of frozen soil in the Source Area of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021 ,41 (2 ):655 −664 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[14] HUANG Huan, CHEN Changfu, MO Xiaojie, et al. Mechanisms of salt rejection at the ice-liquid interface during the freezing of pore fluids in the seasonal frozen soil area[J]. China Geology,2021,4(3):449 − 457.
[15] FRAMPTON A,PAINTER S L,DESTOUNI G. Permafrost degradation and subsurface-flow changes caused by surface warming trends[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2013,21(1):271 − 280. doi: 10.1007/s10040-012-0938-z
[16] 李玉平,韩添丁,沈永平,等. 天山南坡清水河与阿拉沟流域径流变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 冰川冻土,2018,40(1):127 − 135. [LI Yuping,HAN Tianding,SHEN Yongping,et al. Characteristics of runoff variation and its response to climate change of Qingshuihe River and Alagou River watersheds in southern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2018,40(1):127 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Yuping, HAN Tianding, SHEN Yongping, et al . Characteristics of runoff variation and its response to climate change of Qingshuihe River and Alagou River watersheds in southern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2018 ,40 (1 ):127 −135 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[17] 刘金平,任艳群,张万昌,等. 雅鲁藏布江流域气候和下垫面变化对径流的影响研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2022,44(1):275 − 287. [LIU Jinping,REN Yanqun,ZHANG Wanchang,et al. Study on the influence of climate and underlying surface change on runoff in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2022,44(1):275 − 287. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Jinping, REN Yanqun, ZHANG Wanchang, et al . Study on the influence of climate and underlying surface change on runoff in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2022 ,44 (1 ):275 −287 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[18] 蒋佑承,刘蛟,商滢. 气候变化对多年冻土区径流组成的影响分析——以长江源区为例[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2021(3):63 − 68. [JIANG Youcheng,LIU Jiao,SHANG Ying. Research on the influence of climate change on the different runoff components in the permafrost area:A case study of the source area of the Yangtze River[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2021(3):63 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
JIANG Youcheng, LIU Jiao, SHANG Ying . Research on the influence of climate change on the different runoff components in the permafrost area: A case study of the source area of the Yangtze River[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower,2021 (3 ):63 −68 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[19] ZHU Yu,LIU Shiyin,YI Ying,et al. Spatio-temporal variations in terrestrial water storage and its controlling factors in the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Hydrology Research,2021,52(1):323 − 338. doi: 10.2166/nh.2020.039
[20] 张国庆,王蒙蒙,周陶,等. 青藏高原湖泊面积、水位与水量变化遥感监测研究进展[J]. 遥感学报,2022,26(1):115 − 125. [ZHANG Guoqing,WANG Mengmeng,ZHOU Tao,et al. Progress in remote sensing monitoring of lake area,water level,and volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2022,26(1):115 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Guoqing, WANG Mengmeng, ZHOU Tao, et al . Progress in remote sensing monitoring of lake area, water level, and volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2022 ,26 (1 ):115 −125 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[21] 刘宝康,李林,杜玉娥,等. 青藏高原可可西里卓乃湖溃堤成因及其影响分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2016,38(2):305 − 311. [LIU Baokang,LI Lin,DU Yu’e,et al. Causes of the outburst of Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil,Tibetan Plateau,and its impact on surrounding environment[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2016,38(2):305 − 311. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LIU Baokang, LI Lin, DU Yu’e, et al . Causes of the outburst of Zonag Lake in Hoh Xil, Tibetan Plateau, and its impact on surrounding environment[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2016 ,38 (2 ):305 −311 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[22] 张建云,刘九夫,金君良,等. 青藏高原水资源演变与趋势分析[J]. 中国科学院院刊,2019,34(11):1264 − 1273. [ZHANG Jianyun,LIU Jiufu,JIN Junliang,et al. Evolution and trend of water resources in qinghai-tibet plateau[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2019,34(11):1264 − 1273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Jianyun, LIU Jiufu, JIN Junliang, et al . Evolution and trend of water resources in qinghai-tibet plateau[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2019 ,34 (11 ):1264 −1273 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[23] XU Ran,HU Hongchang,TIAN Fuqiang,et al. Projected climate change impacts on future streamflow of the Yarlung Tsangpo-Brahmaputra River[J]. Global and Planetary Change,2019,175:144 − 159. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.01.012
[24] 白雁翎,王芳,刘扬. 大通河上游径流演变及驱动因素定量分析[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2021,19(1):103 − 110. [BAI Yanling,WANG Fang,LIU Yang. Quantitative analysis of runoff evolution and driving factors in the upper reaches of Datong River[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2021,19(1):103 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
BAI Yanling, WANG Fang, LIU Yang . Quantitative analysis of runoff evolution and driving factors in the upper reaches of Datong River[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2021 ,19 (1 ):103 −110 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[25] YU Guoqiang, WANG Qian, ZHU Lifeng, et al. Regulation of vegetation pattern on the hydrodynamic processes of erosion on hillslope in Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2023,11(1):4 − 19.
[26] 宋蕾. 青藏高原黄河源区冻土水文效应模拟研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学,2021. [SONG Lei. Simulation study on hydrological effect of frozen soil in the source area of the Yellow River in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SONG Lei. Simulation study on hydrological effect of frozen soil in the source area of the Yellow River in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] JIN Huijun,HE Ruixia,CHENG Guodong,et al. Changes in frozen ground in the Source Area of the Yellow River on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau,China,and their eco-environmental impacts[J]. Environmental Research Letters,2009,4(4):045206. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/4/4/045206
[28] 张山清,普宗朝,李景林,等. 1961—2010年新疆季节性最大冻土深度对冬季负积温的响应[J]. 冰川冻土,2013,35(6):1419 − 1427. [ZHANG Shanqing,PU Zongchao,LI Jinglin,et al. Response of the maximum depth of seasonal freezing to the cumulated negative temperature in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2013,35(6):1419 − 1427. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Shanqing, PU Zongchao, LI Jinglin, et al . Response of the maximum depth of seasonal freezing to the cumulated negative temperature in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2013 ,35 (6 ):1419 −1427 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[29] 孙永寿,刘弢,李燕. 黄河源区降水径流一致性及影响因素分析[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(10):51 − 55. [SUN Yongshou,LIU Tao,LI Yan. Analysis on the consistency of precipitation and runoff in the source area of the Yellow River and its influencing factors[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(10):51 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2021.10.010
SUN Yongshou, LIU Tao, LI Yan . Analysis on the consistency of precipitation and runoff in the source area of the Yellow River and its influencing factors[J]. Yellow River,2021 ,43 (10 ):51 −55 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[30] LU Zhixiang,FENG Qi,ZOU Songbing,et al. The heterogeneity of hydrometeorological changes during the period of 1961—2016 in the source region of the Yellow River,China[J]. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2020,12(2):104 − 118.
[31] 李万志,刘玮,张调风,等. 气候和人类活动对黄河源区径流量变化的贡献率研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2018,40(5):985 − 992. [LI Wanzhi,LIU Wei,ZHANG Tiaofeng,et al. The contribution rate of climate and human activities on runoff change in the source regions of Yellow River[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2018,40(5):985 − 992. (in Chinese with English abstract)
LI Wanzhi, LIU Wei, ZHANG Tiaofeng, et al . The contribution rate of climate and human activities on runoff change in the source regions of Yellow River[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2018 ,40 (5 ):985 −992 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[32] 段中华,乔有明,全小龙,等. 黄河源区湿地、草地土壤理化性质和碳氮组成及其稳定同位素特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报,2015,29(4):247 − 252. [DUAN Zhonghua,QIAO Youming,QUAN Xiaolong,et al. Analysis of nitrogen and carbon composition and stable isotope characteristics and physicochemical properties of wetland and grassland soil in source region of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2015,29(4):247 − 252. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DUAN Zhonghua, QIAO Youming, QUAN Xiaolong, et al . Analysis of nitrogen and carbon composition and stable isotope characteristics and physicochemical properties of wetland and grassland soil in source region of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2015 ,29 (4 ):247 −252 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[33] 王生廷,盛煜,曹伟,等. 基于地貌分类的黄河源区多年冻土层地下冰储量估算[J]. 水科学进展,2017,28(6):801 − 810. [WANG Shengting,SHENG Yu,CAO Wei,et al. Estimation of permafrost ice reserves in the source area of the Yellow River using landform classification[J]. Advances in Water Science,2017,28(6):801 − 810. (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG Shengting, SHENG Yu, CAO Wei, et al . Estimation of permafrost ice reserves in the source area of the Yellow River using landform classification[J]. Advances in Water Science,2017 ,28 (6 ):801 −810 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[34] ZHU Liang,YANG Mingnan,LIU Jingtao,et al. Evolution of the freeze-thaw cycles in the source region of the Yellow River under the influence of climate change and its hydrological effects[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2022,10(4):322 − 334.
[35] ZHU Liang,LIU Jingtao,YANG Mingnan,et al. Evolutionary trend of water cycle in Beichuan River Basin of China under the influence of vegetation restoration[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2021,9(3):202 − 211.
[36] 张光辉,费宇红,申建梅,等. 降水补给地下水过程中包气带变化对入渗的影响[J]. 水利学报,2007,38(5):611 − 617. [ZHANG Guanghui,FEI Yuhong,SHEN Jianmei,et al. Influence of unsaturated zone thickness on precipitation infiltration for recharge of groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2007,38(5):611 − 617. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHANG Guanghui, FEI Yuhong, SHEN Jianmei, et al . Influence of unsaturated zone thickness on precipitation infiltration for recharge of groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2007 ,38 (5 ):611 −617 . (in Chinese with English abstract)[37] 孙才奇,李川川,陈艺鑫,等. 天山冰缘环境活动层冻融过程定位观测研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2013,35(2):272 − 279. [SUN Caiqi,LI Chuanchuan,CHEN Yixin,et al. A long term monitoring of frost heaving in periglacial environment in the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2013,35(2):272 − 279. (in Chinese with English abstract)
SUN Caiqi, LI Chuanchuan, CHEN Yixin, et al . A long term monitoring of frost heaving in periglacial environment in the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2013 ,35 (2 ):272 −279 . (in Chinese with English abstract) -




 下载:
下载: