Effects of loess-paleosol interbedding on soil moisture transport and soil microstructure
-
摘要:
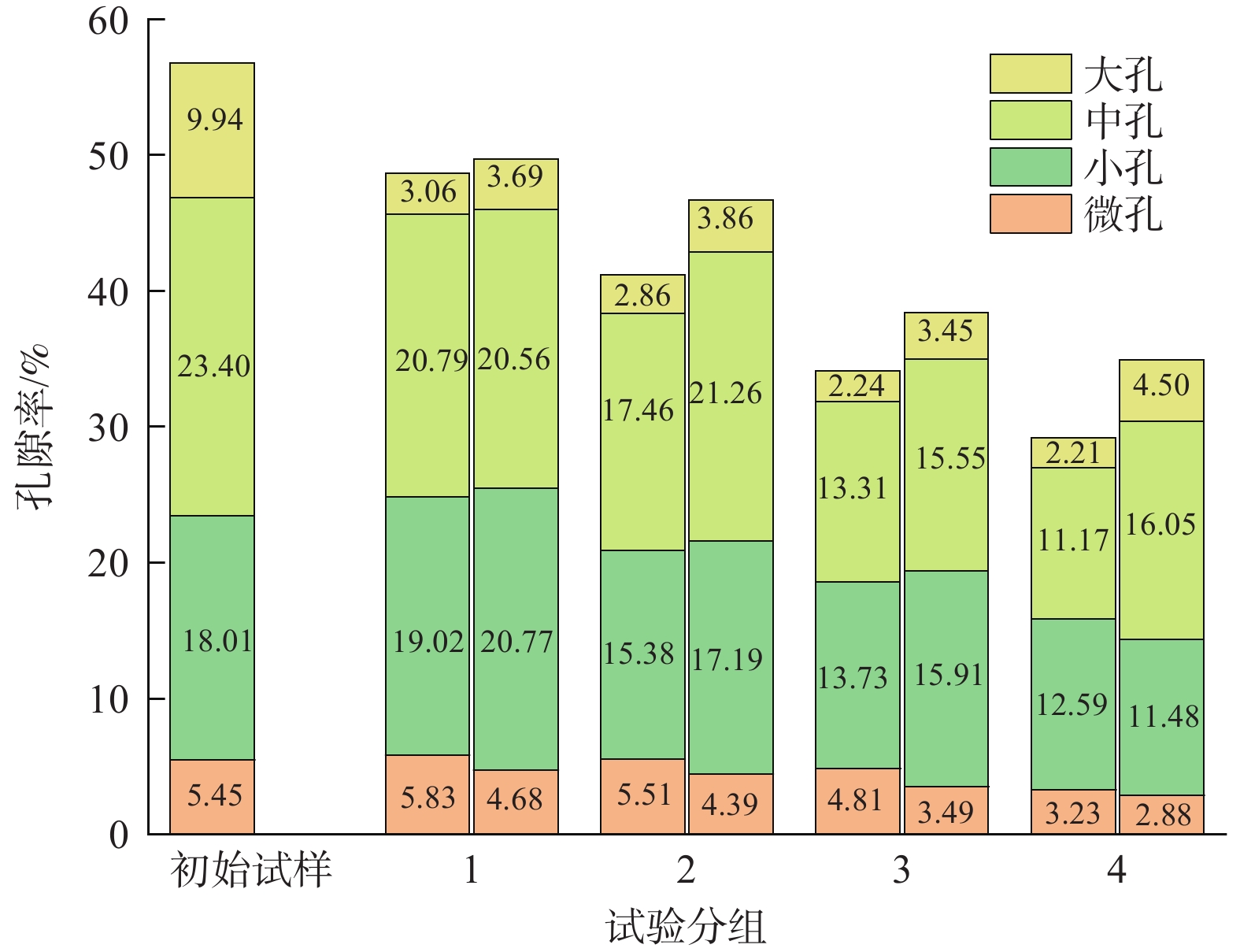
黄土地区地质灾害问题的发生大多与水在黄土中的入渗有关,而马兰黄土-古土壤互层结构对土壤水分入渗规律的影响显著。为揭示古土壤阻滞作用下黄土水分运移规律及其对黄土体微结构的影响,为黄土地区工程实践提供理论基础,该研究以陕西省泾阳县南塬的黄土为研究对象,采用土柱模型进行水分入渗试验,研究黄土-古土壤互层条件下土壤水分运移规律。在此基础上,通过微结构测试、分形维数和概率熵等指标的计算,分析黄土-古土壤互层条件下土壤水分运移对黄土微结构的影响。结果表明:古土壤层的透水性弱,湿润锋抵达黄土与古土壤界面处产生瞬态滞水,且随着入渗强度增加滞水时间增加;古土壤层影响下黄土与古土壤界面处的滞水会导致孔隙结构相互连通,孔隙空间平均增加4.13%,孔隙方向概率熵平均减少0.029,分形维数平均减小0.076,即古土壤层的阻水作用使得界面处黄土的孔隙空间增大,孔隙排列有序,孔隙形态规则。研究结果为黄土地区的工程建设和生态环境保护提供科学支撑。
Abstract:Geological disaster occurrences in loess regions are intrinsically linked to water infiltration in loess, with the Malan loess-paleosol interlayer structure significantly influencing the infiltration patterns of soil moisture. This research was carried out to reveal the moisture migration characteristics in loess-paleosol interlayers, and to investigate the influence of the moisture migration on the microstructure of loess, providing a theoretical basis for engineering practice and scientific research in loess areas. In this study, we focused on the loess of the South Plateau in Jingyang County, Shaanxi Province, and conducted water infiltration tests using a soil column model to investigate the soil moisture transport dynamics under loess-paleosol interlayer conditions. Subsequently, we analyzed the impact of soil moisture transport on the loess microstructure under these conditions through microstructural testing, and calculation of fractal dimension and probability entropy. The findings revealed that the permeability of the paleosol layer was low, causing transient water stagnation when the wetting front reached the loess-paleosol interface. The stagnant water at the interface of loess and paleosol under the influence of the paleosol layer will lead to the interconnection of pore structure, and the pore space will increase by 4.13% on average, and the analysis of the indexes of fractal dimension and probability entropy shows that the probability entropy of the pore direction decreases by 0.029 on average, and the fractal dimension decreases by 0.076 on average, i.e., the water-blocking effect of the paleosol layer makes the pore space of the loess at the interface increase, the pores are arranged in an orderly manner, and the pore morphology is regular. The results of the study provide scientific support for the engineering construction and eco-environmental protection in loess areas.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- paleosol /
- soil column test /
- water infiltration /
- microstructure
-

-
表 1 室内土柱渗水试验方案
Table 1. Scenarios of seepage test using soil columns
试验
编号土柱类型 入渗速率
/(mL·min−1)渗水
时长/h入渗强度
/(mm·d−1)1 L1 1 8.0 18 L1—S1 2 L1 2 4.0 36 L1—S1 3 L1 3 2.8 55 L1—S1 4 L1 5 1.7 92 L1—S1 表 2 渗透前后黄土试样的孔隙方向概率熵
Table 2. Probability entropy of pore direction of loess specimens before and after infiltration
试验样品 初始试样 1 2 3 4 L1 L1—S1 L1 L1—S1 L1 L1—S1 L1 L1—S1 概率熵 0.785 0.899 0.878 0.918 0.861 0.909 0.883 0.954 0.944 表 3 渗透前后黄土试样的孔隙分形维数
Table 3. Pore fractal dimension of loess specimens before and after infiltration
试验样品 拟合方程 孔隙分形维数 初始试样 lgA = 0.843lgL − 0.128 1.686 1 L1 lgA = 0.814lgL − 0.098 1.628 L1—S1 lgA = 0.807lgL − 0.069 1.614 2 L1 lgA = 0.894lgL − 0.526 1.788 L1—S1 lgA = 0.810lgL − 0.047 1.620 3 L1 lgA = 0.860lgL − 0.133 1.720 L1—S1 lgA = 0.820lgL − 0.343 1.640 4 L1 lgA = 0.901lgL − 0.314 1.802 L1—S1 lgA = 0.880lgL − 0.125 1.760 -
[1] SHAO Xianxian,ZHANG Huyuan,TAN Yu. Collapse behavior and microstructural alteration of remolded loess under graded wetting tests[J]. Eng Geol,2018,233:11 − 22. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.025
[2] LUO Hao,WU Faquan,CHANG Jinyuan,et al. Microstructural constraints on geotechnical properties of Malan Loess:A case study from Zhaojiaan landslide in Shaanxi Province,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,236:60 − 69. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.002
[3] LI Yanrong,SHI Wenhui,AYDIN A,et al. Loess genesis and worldwide distribution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2020,201:102947. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102947
[4] 魏亚妮,范文,麻广林. 黄土高原马兰黄土微结构特征及湿陷机理[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2022,44(4):581 − 592. [WEI Yani,FAN Wen,MA Guanglin. Characteristics of microstructure and collapsible mechanism of Malan Loess in Loess Plateau,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2022,44(4):581 − 592. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WEI Yani, FAN Wen, MA Guanglin. Characteristics of microstructure and collapsible mechanism of Malan Loess in Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(4): 581 − 592. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] LI Peiyue,KOU Xiaomei,WANG Yong,et al. Building a more sustainable Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2024,35(1):283 − 287. doi: 10.1007/s12583-024-1970-3
[6] 许领,戴福初. 泾阳南塬黄土滑坡特征参数统计分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(5):28 − 32. [XU Ling,DAI Fuchu. Statistical analysis of the characteristic parameters of loess landslides at the South Jingyang Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(5):28 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Ling, DAI Fuchu. Statistical analysis of the characteristic parameters of loess landslides at the South Jingyang Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2008, 35(5): 28 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 亓星,许强,李斌,等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡地表水入渗机制初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(3):418 − 424. [QI Xing,XU Qiang,LI Bin,et al. Preliminary study on mechanism of surface water infiltration at Heifangtai loess landslides in Gansu[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(3):418 − 424. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
QI Xing, XU Qiang, LI Bin, et al. Preliminary study on mechanism of surface water infiltration at Heifangtai loess landslides in Gansu[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(3): 418 − 424. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] CHEN Yinfu,LI Peiyue,WANG Yuanhang,et al. Unraveling the mystery of water-induced loess disintegration:A comprehensive review of experimental research[J]. Sustainability,2024,16(6):2463. doi: 10.3390/su16062463
[9] MUNADI,SOLEKHUDIN I,ZULIJANTO A. A numerical study of steady infiltration from a single irrigation channel with an impermeable soil layer[J]. Eng Lett,2020,28(3):643 − 650.
[10] ZACHARA J,BRANTLEY S,CHOROVER J,et al. Internal domains of natural porous media revealed:Critical locations for transport,storage,and chemical reaction[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(6):2811 − 2829.
[11] LUO Zuosen,LI Jianlin,JIANG Qiao,et al. Effect of the water-rock interaction on the creep mechanical properties of the sandstone rock[J]. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering,2018,62(2):451 − 461.
[12] 赵志强,戴福初,闵弘,等. 原状黄土-古土壤中水分入渗过程研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(9):2611 − 2621. [ZHAO Zhiqiang,DAI Fuchu,MIN Hong,et al. Research on infiltration process in undisturbed loess-paleosol sequence[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(9):2611 − 2621. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Zhiqiang, DAI Fuchu, MIN Hong, et al. Research on infiltration process in undisturbed loess-paleosol sequence[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(9): 2611 − 2621. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] TROCHON B,BUSTILLO V,CANER L,et al. Main water pathways in cultivated clayey calcisols in molassic hills in southwestern France:Toward spatialization of soil waterlogging[J]. Vadose Zone Journal,2023,22(5):e20272. doi: 10.1002/vzj2.20272
[14] JAIN A,MITTAL S,SHUKLA S K. Liquefaction proneness of stratified sand-silt layers based on cyclic triaxial tests[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2023,15(7):1826 − 1845. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.09.015
[15] 曹春山,吴树仁,潘懋,等. 古土壤力学特性及其对黄土滑坡的意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(5):127 − 132. [CAO Chunshan,WU Shuren,PAN Mao,et al. Mechanics characteristics of paleosol and its implication to loess landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(5):127 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CAO Chunshan, WU Shuren, PAN Mao, et al. Mechanics characteristics of paleosol and its implication to loess landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(5): 127 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 胡庆国,袁宁,刘登生,等. 多层结构土质边坡降雨入渗过程及稳定性影响分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2018,31(2):67 − 74. [HU Qingguo,YUAN Ning,LIU Dengsheng,et al. Analysis of rainfall infiltration process and stability of soil slope with multilayer structure[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2018,31(2):67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HU Qingguo, YUAN Ning, LIU Dengsheng, et al. Analysis of rainfall infiltration process and stability of soil slope with multilayer structure[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(2): 67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] AL-MUKHTAR M,KHATTAB S,ALCOVER J F. Microstructure and geotechnical properties of lime-treated expansive clayey soil[J]. Engineering Geology,2012,139/140:17 − 27. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.04.004
[18] RABOT E,WIESMEIER M,SCHLÜTER S,et al. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions:A review[J]. Geoderma,2018,314:122 − 137. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.11.009
[19] SCHLÜTER S,SAMMARTINO S,KOESTEL J. Exploring the relationship between soil structure and soil functions via pore-scale imaging[J]. Geoderma,2020,370:114370. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114370
[20] XIE Wanli,LI Ping,ZHANG Maosheng,et al. Collapse behavior and microstructural evolution of loess soils from the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2018,15(8):1642 − 1657. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-5006-2
[21] MCHIRGUI W,MILLET O,AMIRI O. Theoretical study and simulation of moisture transport in unsaturated porous media by periodic homogenization[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2015,39(4):409 − 435. doi: 10.1002/nag.2315
[22] 李培月,何晓东,周长静,等. 苏里格地区致密砂岩矿物组成与微观结构及其对水力压裂的潜在影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):1 − 11. [LI Peiyue,HE Xiaodong,ZHOU Changjing,et al. Mineral compositions and microstructural characteristics of the tight sandstone reservoir in the Sulige Area and their potential influence on hydraulic fracturing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Peiyue, HE Xiaodong, ZHOU Changjing, et al. Mineral compositions and microstructural characteristics of the tight sandstone reservoir in the Sulige Area and their potential influence on hydraulic fracturing[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(3): 1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] YANG Chunliu,WU Jianhua,LI Peiyue,et al. Evaluation of soil-water characteristic curves for different textural soils using fractal analysis[J]. Water,2023,15(4):772. doi: 10.3390/w15040772
[24] XU Panpan,ZHANG Qiying,QIAN Hui,et al. Microstructure and permeability evolution of remolded loess with different dry densities under saturated seepage[J]. Engineering Geology,2021,282:105875. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105875
[25] 王静,周刘光,钟春玲,等. 冻融作用下粉砂土微观结构变化对宏观力学参数的影响研究[J]. 公路,2017,62(10):22 − 30. [WANG Jing,ZHOU Liuguang,ZHONG Chunling,et al. Impact of silty sand soil microstructure change on macro-mechanical parameters under freezing and thawing[J]. Highway,2017,62(10):22 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Jing, ZHOU Liuguang, ZHONG Chunling, et al. Impact of silty sand soil microstructure change on macro-mechanical parameters under freezing and thawing[J]. Highway, 2017, 62(10): 22 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陈正汉,郭楠. 非饱和土与特殊土力学及工程应用研究的新进展[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(1):1 − 54. [CHEN Zhenghan,GUO Nan. New developments of mechanics and application for unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(1):1 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
CHEN Zhenghan, GUO Nan. New developments of mechanics and application for unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 1 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 杨春柳. 基于分形理论的非饱和黄土渗透特性研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2023. [YANG Chunliu. Permeability Characteristics of Unsaturated Loess Based on Fractal Theory[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
YANG Chunliu. Permeability Characteristics of Unsaturated Loess Based on Fractal Theory[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 王永焱,滕志宏. 中国黄土的地层划分[J]. 地质论评,1983,29(3):201 − 208. [WANG Yongyan,TENG Zhihong. Stratigraphical division of the loess in China[J]. Geological Review,1983,29(3):201 − 208. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
WANG Yongyan, TENG Zhihong. Stratigraphical division of the loess in China[J]. Geological Review, 1983, 29(3): 201 − 208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 李萍,李同录,王阿丹,等. 黄土中水分迁移规律现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(5):1331 − 1339. [LI Ping,LI Tonglu,WANG Adan,et al. In-situ test research on regularities of water migration in loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(5):1331 − 1339. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Ping, LI Tonglu, WANG Adan, et al. In-situ test research on regularities of water migration in loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(5): 1331 − 1339. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 徐盼盼. 重塑黄土渗透性变化的水-土作用机制研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2021. [XU Panpan. Study on water-soil interaction mechanism of permeability change of remolded loess[D]. Xi’an:Chang’an University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
XU Panpan. Study on water-soil interaction mechanism of permeability change of remolded loess[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 洪勃,唐亚明,冯卫,等. 吕梁山区马兰黄土抗剪强度参数的区域变化规律及其影响因素试验研究[J]. 西北地质,2023,56(2):272 − 281. [HONG Bo,TANG Yaming,FENG Wei,et al. Regional variation and influencing factors of shear strength parameters of Malan loess in Lüliang area[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(2):272 − 281. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HONG Bo, TANG Yaming, FENG Wei, et al. Regional variation and influencing factors of shear strength parameters of Malan loess in Lüliang area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 272 − 281. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] WU Jianhua,YANG Ningning,LI Peiyue,et al. Influence of moisture content and dry density on the compressibility of disturbed loess:a case study in Yan’an city,China[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(7):6212. doi: 10.3390/su15076212
[33] 李华,李同录,江睿君,等. 基于滤纸法的非饱和渗透性曲线测试[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(3):895 − 904. [LI Hua,LI Tonglu,JIANG Ruijun,et al. Measurement of unsaturated permeability curve using filter paper method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(3):895 − 904. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
LI Hua, LI Tonglu, JIANG Ruijun, et al. Measurement of unsaturated permeability curve using filter paper method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(3): 895 − 904. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 赵景波,王长燕,刘护军,等. 陕西洛川黄土剖面上部土层水分入渗规律与含水条件研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(1):124 − 129. [ZHAO Jingbo,WANG Changyan,LIU Hujun,et al. A study of water infiltration and water-bearing condition of the L1—S4 layers in Luochuan,Shaanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(1):124 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Jingbo, WANG Changyan, LIU Hujun, et al. A study of water infiltration and water-bearing condition of the L1—S4 layers in Luochuan, Shaanxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(1): 124 − 129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 张龙,陈正汉,孙树国,等. 非饱和重塑Q2和Q3黄土的渗水特性研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报,2016,14(2):1 − 5. [ZHANG Long,CHEN Zhenghan,SUN Shuguo,et al. Permeability of unsaturated remolded Q2 and Q3 loess[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2016,14(2):1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHANG Long, CHEN Zhenghan, SUN Shuguo, et al. Permeability of unsaturated remolded Q2 and Q3 loess[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2016, 14(2): 1 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[36] 赵枝艳,张常亮,沈伟,等. 黄土-古土壤饱和渗透性与孔隙分布特征关系研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(1):47 − 56. [ZHAO Zhiyan,ZHANG Changliang,SHEN Wei,et al. Research on the relationship between saturated permeability and pore distribution characteristics of loess-paleosol[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(1):47 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHAO Zhiyan, ZHANG Changliang, SHEN Wei, et al. Research on the relationship between saturated permeability and pore distribution characteristics of loess-paleosol[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(1): 47 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 邵龙潭,王助贫,关立军,等. 非饱和土中水流入渗和气体排出过程的求解[J]. 水科学进展,2000,11(1):8 − 13. [SHAO Longtan,WANG Zhupin,GUAN Lijun,et al. Numerical simulation of the process of pore water infiltration and pore gas flow in unsaturated soil[J]. Advances in Water Science,2000,11(1):8 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
SHAO Longtan, WANG Zhupin, GUAN Lijun, et al. Numerical simulation of the process of pore water infiltration and pore gas flow in unsaturated soil[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2000, 11(1): 8 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 韩同春,苏钰钦,张宇. 双层结构边坡降雨入渗与坡面径流耦合分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,2020,52(6):145 − 152. [HAN Tongchun,SU Yuqin,ZHANG Yu. Coupling analysis of rainfall infiltration and slope runoff in two-layered slope[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020,52(6):145 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HAN Tongchun, SU Yuqin, ZHANG Yu. Coupling analysis of rainfall infiltration and slope runoff in two-layered slope[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(6): 145 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 雷祥义. 中国黄土的孔隙类型与湿陷性[J]. 中国科学 (B辑 化学 生物学 农学 医学 地学),1987,17(12):1309 − 1318. [LEI Xiangyi. Pore types and collapsibility of loess in China[J]. Science in China(Ser B),1987,17(12):1309 − 1318. (in Chinese)]
LEI Xiangyi. Pore types and collapsibility of loess in China[J]. Science in China(Ser B), 1987, 17(12): 1309 − 1318. (in Chinese)
[40] 郑佳,庄建琦,孔嘉旭,等. 基于CT扫描的黄土孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):211 − 222. [ZHENG Jia,ZHUANG Jianqi,KONG Jiaxu,et al. Study of loess pore structure characteristics based on CT scanning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):211 − 222. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
ZHENG Jia, ZHUANG Jianqi, KONG Jiaxu, et al. Study of loess pore structure characteristics based on CT scanning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 211 − 222. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 任晓虎,许强,赵宽耀,等. 反复入渗对重塑黄土渗透特性的影响[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2):130 − 138. [REN Xiaohu,XU Qiang,ZHAO Kuanyao,et al. Effect of repeated infiltration on permeability characteristics of remolded loess[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(2):130 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
REN Xiaohu, XU Qiang, ZHAO Kuanyao, et al. Effect of repeated infiltration on permeability characteristics of remolded loess[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 130 − 138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[42] 施斌. 粘性土击实过程中微观结构的定量评价[J]. 岩土工程学报,1996,18(4):60 − 65. [SHI Bin. Quantitative evaluation of microstructure of cohesive soil during compaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,1996,18(4):60 − 65. (in Chinese)]
SHI Bin. Quantitative evaluation of microstructure of cohesive soil during compaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 18(4): 60 − 65. (in Chinese)
[43] CHEN Huie,JIANG Yaling,NIU Cencen,et al. Dynamic characteristics of saturated loess under different confining pressures:A microscopic analysis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(2):931 − 944. doi: 10.1007/s10064-017-1101-9
[44] 霍润科,王龙飞,李曙光,等. 受酸腐蚀砂岩的损伤特性和分析模型[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(1):1 − 9. [HUO Runke,WANG Longfei,LI Shuguang,et al. Characteristics and analytical model of acid-corroded sandstone[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)]
HUO Runke, WANG Longfei, LI Shuguang, et al. Characteristics and analytical model of acid-corroded sandstone[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: